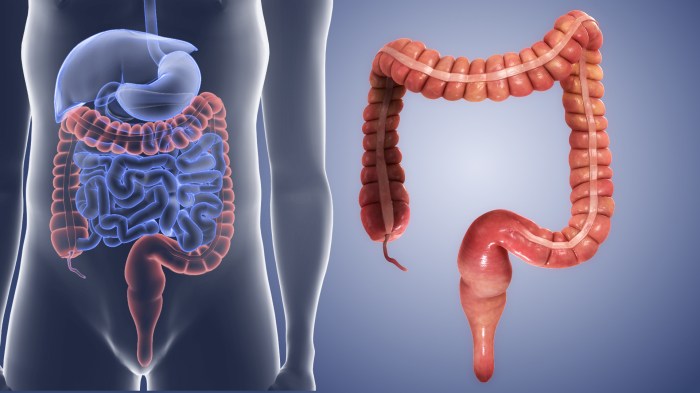
Treatment of colon cancer is a multifaceted journey, demanding a deep understanding of the disease’s stages, diverse treatment approaches, and individualized care plans. This exploration delves into the various strategies, from surgical interventions to innovative therapies, providing a comprehensive overview of the complexities involved. We’ll examine the different types of colon cancer, the diverse range…
What is Adipose Tissue A Deep Dive
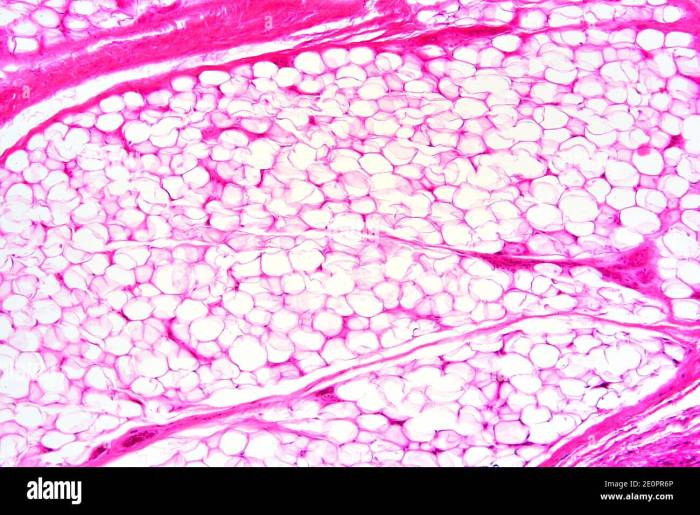
What is adipose tissue? It’s more than just fat; it’s a complex and crucial tissue in the human body, playing a vital role in energy storage, hormone regulation, and overall health. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of white, brown, and beige adipose tissue, uncovering their distinct characteristics, functions, and relationship to various health…
What Does Mouth Cancer Look Like? A Guide
What does mouth cancer look like? This introduction explores the often-overlooked visual characteristics of this serious condition. Understanding the early signs and symptoms is crucial for prompt detection and treatment. We’ll delve into the different types of oral cancer, their prevalence, and risk factors. Crucially, we’ll look at how to identify cancerous lesions, differentiating them…
Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool Olivia Munn
Breast cancer risk assessment tool Olivia Munn: This tool, inspired by Olivia Munn’s experiences and advocacy, offers a unique approach to understanding personal breast cancer risk. It delves into the various factors considered in these assessments, ranging from lifestyle choices to genetic predispositions. This assessment tool explores different types of risk assessments, from questionnaires to…
How to Reverse Atrial Fibrillation Naturally A Guide
How to reverse atrial fibrillation naturally is a crucial question for many seeking alternative or complementary approaches to managing this condition. This guide delves into potential lifestyle modifications, dietary recommendations, herbal remedies, nutritional considerations, and mind-body practices that may help. We’ll explore various strategies, but remember that natural remedies are not a substitute for professional…
The Health Benefits of Bifidobacterium A Deep Dive
The health benefits of bifobacterium – The health benefits of bifidobacterium are increasingly recognized for their positive impact on human well-being. This comprehensive exploration delves into the fascinating world of these beneficial bacteria, examining their role in digestive health, immune support, and potential impact on overall wellness. We’ll uncover how bifidobacteria work, their various species…
Asymptomatic Definition Importance and Controversy
Asymptomatic definition importance and controversy is a complex and crucial aspect of public health. Understanding how we define the absence of symptoms is essential for effective disease prevention and control strategies. This multifaceted issue involves diverse perspectives, ranging from medical definitions to public health implications, ethical considerations, and practical challenges in identification. Different medical and…
Donating Hair for Cancer Patients A Compassionate Act
Donating hair for people with cancer is a profoundly compassionate act that touches the lives of countless individuals. It’s a simple gesture that can offer remarkable emotional support and practical benefits to those undergoing the challenging journey of cancer treatment. This act of kindness involves a meticulous process, from understanding the different types of hair…
Things to Stop for a Longer Life
Things to stop if you want to live longer: This post delves into crucial lifestyle choices that can significantly impact your lifespan. We’ll explore the negative effects of unhealthy habits and offer actionable strategies to cultivate healthier practices. From diet and exercise to stress management and sleep hygiene, we’ll cover a comprehensive approach to a…
Magnesium for Muscle Pain A Deep Dive
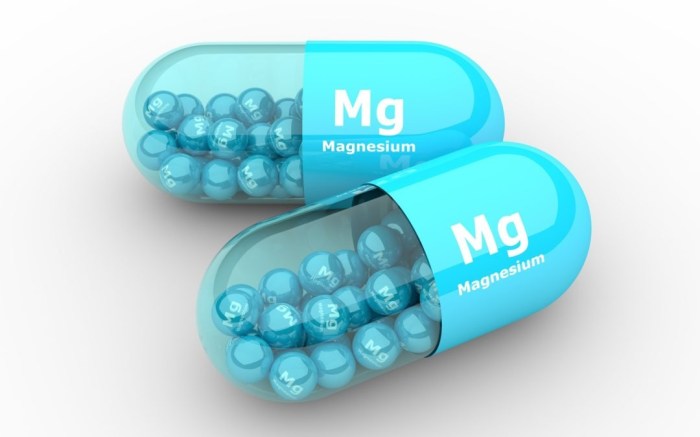
Magnesium for muscle pain is a crucial topic for understanding the role of this vital mineral in maintaining healthy muscles. Magnesium plays a significant part in muscle function, and deficiencies can lead to a range of issues, including persistent muscle aches and discomfort. This article explores the intricate connection between magnesium and muscle pain, examining…