High blood pressure and erectile dysfunction are often linked, and understanding this connection is crucial for proactive health management. This exploration delves into the physiological mechanisms behind this association, examining the prevalence of both conditions and the factors that contribute to their development. We’ll also cover diagnosis, management strategies, potential complications, and ultimately, preventative measures….
What is Nociceptive Pain A Deep Dive
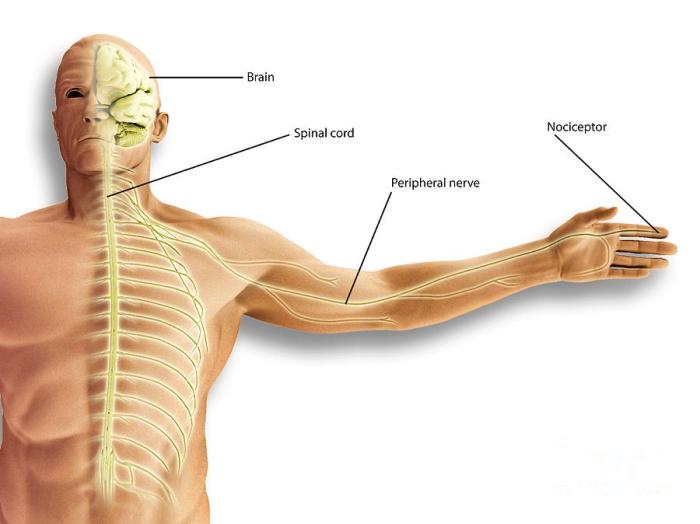
What is nociceptive pain? It’s pain originating from actual or potential tissue damage. This isn’t just a fleeting discomfort; it’s a complex physiological response triggered by various stimuli. From a simple burn to a persistent muscle strain, understanding the mechanisms behind nociceptive pain is crucial for effective pain management. This exploration delves into the science…
Could Prednisone Cause Mood Swings?
Could prednisone cause mood swings? This question delves into the potential link between the powerful corticosteroid prednisone and fluctuations in mood. Understanding how this medication impacts the body’s neurochemistry is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This exploration investigates the mechanisms behind prednisone’s effect on various neurotransmitters, leading to potential mood changes. Prednisone, often…
Propofol for Surgery How Do They Wake You Up?
Propofol for surgery how do they wake you up – Propofol for surgery: how do they wake you up? This question delves into the fascinating world of anesthesia, exploring the intricate process of inducing and maintaining a state of unconsciousness for surgical procedures. We’ll examine the science behind propofol, from its mechanism of action to…
Lead Poisoning Signs, Symptoms, and Complications
Lead poisoning signs symptoms and complications – Lead poisoning signs, symptoms, and complications are a serious concern, impacting both children and adults. This article delves into the various sources of lead exposure, highlighting the pathways through which lead enters the body. We’ll explore the distinct symptoms in children and adults, potential complications, and the crucial…
Celexa vs Zoloft Similarities and Differences
Celexa vs Zoloft similarities and differences is a crucial topic for those considering these medications for mental health conditions. Both are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other related disorders. Understanding their similarities and differences is essential for informed decision-making alongside a healthcare professional. This comprehensive comparison…
Is It Bad to Sleep Right After Eating? A Deep Dive
Is it bad to sleep right after eating? This question is a common concern for many, and the answer isn’t a simple yes or no. Digestion is a complex process, and the timing of sleep after a meal can significantly impact its efficiency and overall health. This exploration delves into the science behind digestion, potential…
Observation or Inpatient Hospital A Deep Dive
Observation or inpatient hospital sets the stage for understanding the nuances of medical care. This exploration delves into the critical differences between observation and inpatient stays, examining the various factors that influence a patient’s admission, from the reasons behind choosing observation to the complex medical procedures performed. We’ll also look at the patient experience, staff…
EGCG Supplement Benefits and Safety A Deep Dive
EGCG supplement benefits and safety are a complex topic. This exploration delves into the chemical makeup, potential health advantages, safety considerations, and factors specific to different groups. We’ll cover everything from the various forms of EGCG supplements to their potential interactions with other substances, and even examine historical uses. Getting informed is key to making…
How to Get Rid of Scars A Comprehensive Guide
How to get rid of scars? This comprehensive guide dives deep into understanding scars, from their various types and causes to effective home remedies, topical treatments, and even medical procedures. We’ll explore everything from preventing scarring to long-term management strategies, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this journey towards healthier, smoother skin. We’ll look…