Does milk make you taller? This age-old question sparks curiosity and debate. We’ll delve into the intricate relationship between milk consumption and height, exploring the science behind growth and development, the nutritional value of various milk types, and the evidence from scientific studies. This exploration promises to shed light on whether that glass of milk…
How Long Does Metoprolol Take to Work?
How long does it take for metoprolol to work? This crucial question often arises for patients prescribed this beta-blocker. Understanding the factors influencing its onset, from dosage to individual physiology, is key to managing expectations and ensuring effective treatment. This exploration delves into the intricacies of metoprolol’s action, examining the timeframes involved in achieving its…
Opill OTC Available for Retail A Deep Dive
Opill OTC available for retail is a significant development with implications for consumer access and healthcare. This post explores the legal frameworks, pharmacy practices, consumer demand, supply chain management, and marketing strategies surrounding the retail availability of these medications. We’ll examine the differences in regulations across various regions and how these factors impact the retail…
How Long Does Valium Take to Work?
How long does it take Valium to work? This question is crucial for anyone considering or currently taking this medication. Valium, or diazepam, is a powerful benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizures. Understanding the factors influencing its onset of action is key to managing expectations and ensuring optimal results. Different factors like…
Adenosis Enlarged Breast Lobules A Comprehensive Guide
Adenosis enlarged breast lobules is a condition characterized by the abnormal growth of the milk-producing glands within the breasts. Understanding the intricacies of this condition, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management, is crucial for both patients and healthcare professionals. This guide delves into the various aspects of adenosis enlarged breast lobules, providing a clear…
How to Uncover a Doctors Medical Malpractice History
How to uncover a doctors medical malpractice history – How to uncover a doctor’s medical malpractice history is a complex process, demanding careful research and understanding of legal boundaries. This exploration delves into the intricate world of medical malpractice, examining the crucial steps needed to investigate a doctor’s past actions. It’s vital to approach this…
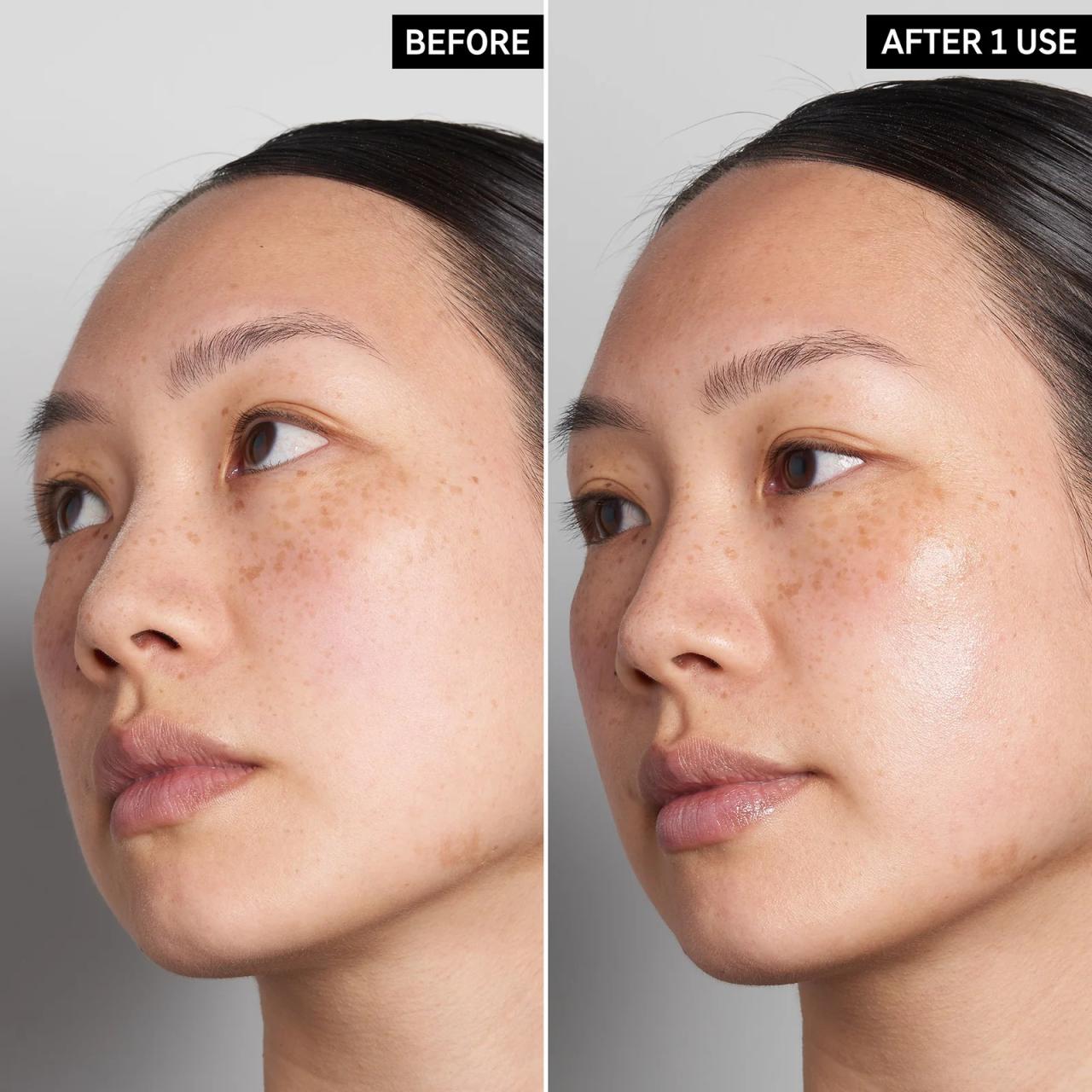
Hyaluronic Acid for Hair A Deep Dive
Hyaluronic acid for hair is a fascinating topic. This exploration delves into the science behind its potential benefits, examining different types and their applications in hair care. We’ll uncover the historical use of hyaluronic acid in beauty, debunk common myths, and discuss the mechanisms through which it might affect hair follicles. From hydration and elasticity…
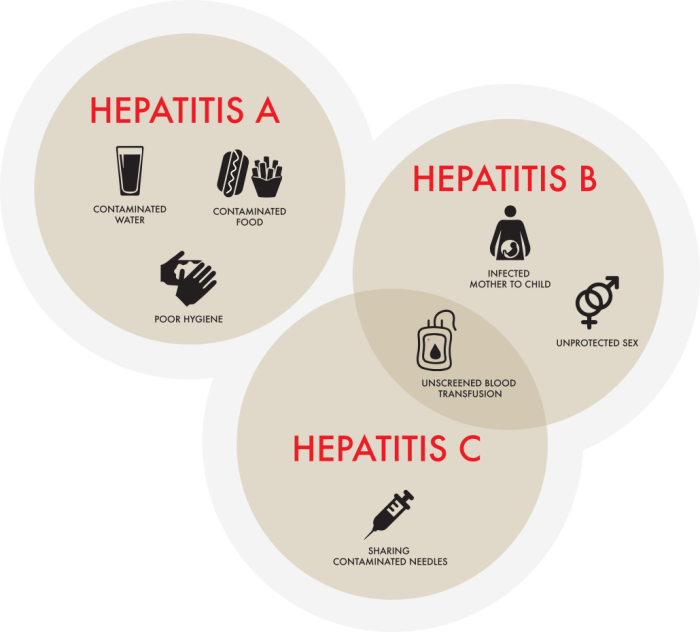
Which Hepatitis is the Worst? A Deep Dive
Which hepatitis is the worst? This question often arises, but there’s no single answer. The severity of hepatitis, a liver inflammation, varies significantly depending on the type (A, B, C, D, E) and individual factors. Understanding the different types, their transmission methods, and the potential long-term consequences is crucial for informed discussion. This exploration delves…
Pneumonia and COVID-19 A Deep Dive
Pneumonia and covid 19 – Pneumonia and COVID-19: This article delves into the complex interplay between these two respiratory illnesses. We’ll explore the shared symptoms, diagnostic challenges, and treatment strategies specific to patients experiencing both conditions. Understanding how pneumonia can complicate COVID-19 cases is crucial for healthcare professionals and those at risk. The co-occurrence of…
Can Macular Degeneration Cause Hallucinations?
Can macular degeneration cause hallucinations? This intriguing question delves into the complex relationship between the eyes, the brain, and vision. Macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss, affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. Different types of macular degeneration, like dry and wet, have varying impacts on…