YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is a crucial procedure for ophthalmology, offering a precise and effective method for treating posterior capsular opacification (PCO) after cataract surgery. This opaque film that forms behind the implanted lens can significantly impact vision. The procedure utilizes a focused laser beam to gently vaporize the opacified area, restoring clear vision. This detailed guide delves into the intricacies of this procedure, exploring its principles, indications, surgical steps, post-operative care, potential complications, and comparison with alternative treatments.
Understanding the procedure’s historical context, the role of surgeon expertise, and the nuances of pre-operative assessment are critical for a thorough comprehension. The procedure’s efficiency and precision have made it a leading treatment option for PCO, while minimizing the risk of complications. This detailed exploration will leave you with a comprehensive understanding of YAG laser posterior capsulotomy.
Introduction to Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
Yag laser posterior capsulotomy is a precise surgical technique used to treat posterior capsular opacification (PCO) following cataract surgery. PCO is a common complication, characterized by the development of a cloudy membrane behind the implanted intraocular lens (IOL). This membrane impairs vision, requiring intervention to restore clear vision.This procedure utilizes a high-powered YAG laser to ablate the opacified posterior capsule, restoring visual clarity.
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, with the patient awake and able to communicate throughout the procedure. It’s a relatively safe and effective treatment option for PCO, often leading to significant improvement in visual acuity.
Definition of Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
Yag laser posterior capsulotomy is a laser-assisted surgical procedure that precisely removes the opacified posterior capsule of the eye following cataract surgery. This allows light to pass through the eye, improving vision clarity.
Fundamental Principle
The fundamental principle behind this procedure relies on the YAG laser’s ability to precisely vaporize the opacified tissue. The laser’s wavelength is specifically targeted to break down the proteins in the posterior capsule without causing significant damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This controlled ablation creates a small opening in the capsule, thereby restoring clear vision.
YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is a pretty straightforward procedure, but sometimes I wonder if it’s related to the whole “does whiskey help a cold” debate. While the procedure removes a clouded lens, and improves vision, I’ve been wondering if the recovery process might be affected by other things, like drinking habits. Perhaps it’s a matter of individual responses, but I’m definitely curious to see if there’s any correlation.
Does whiskey help a cold is a question I’m considering for future research, and it may not be directly related to the procedure itself, but I’m sure there are some interesting underlying concepts. In the end, though, YAG laser posterior capsulotomy remains a highly effective solution for cataracts.
Key Components and Instruments
The procedure utilizes a specialized YAG laser system, typically featuring a sophisticated optical system for precise targeting and power control. Essential instruments include a slit lamp biomicroscope for accurate visualization of the posterior capsule and a handpiece for delivering the laser beam. The surgeon must meticulously position the laser to target the opacified area with precision and minimize any risk of damage to the surrounding structures.
Historical Overview
The development of YAG laser posterior capsulotomy marked a significant advancement in cataract surgery. Early iterations focused on achieving accurate targeting and optimizing laser parameters for efficient and controlled tissue ablation. The procedure’s refinement led to improved outcomes and reduced complications, establishing its place as a standard treatment for PCO. Early adoption by surgeons led to a gradual but consistent increase in its use, eventually becoming the standard of care for posterior capsular opacification.
Comparison with Other Surgical Techniques
| Feature | YAG Laser Posterior Capsulotomy | Other Surgical Techniques (e.g., manual capsulotomy) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Laser ablation of opacified tissue | Manual incision and removal of the opacified capsule |
| Precision | High precision, controlled ablation | Potentially less precise, higher risk of damage to surrounding tissue |
| Time | Typically shorter procedure time | Potentially longer procedure time |
| Complications | Generally lower risk of complications, such as vitreous loss or retinal detachment | Higher risk of complications, particularly with manual procedures |
| Cost | Potentially higher initial cost due to the specialized equipment | Potentially lower cost, but higher risk of complications |
The table highlights the key differences between YAG laser posterior capsulotomy and other surgical techniques for PCO. YAG laser technology offers advantages in terms of precision, speed, and reduced complication risk. However, the initial investment in the laser equipment can be a factor. The selection of the appropriate technique depends on individual patient factors and surgeon preference.
Indications for Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
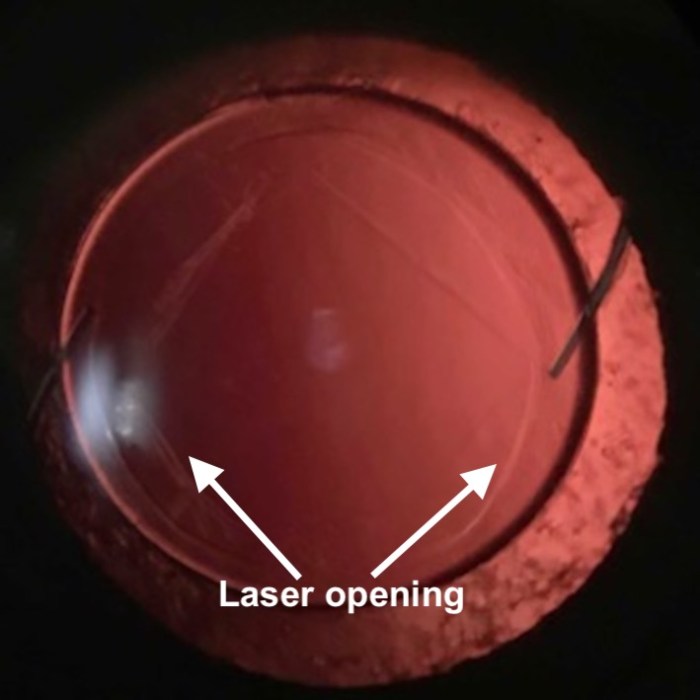
The Yag laser posterior capsulotomy, a precise procedure, plays a crucial role in cataract surgery. This minimally invasive technique allows surgeons to effectively remove the remnants of the posterior lens capsule, ensuring optimal visual outcomes. This procedure is particularly beneficial in specific clinical scenarios.This procedure is becoming increasingly common due to its precision and effectiveness in resolving various complications arising during cataract surgery.
YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is a fantastic procedure for vision correction, but sometimes, recovery involves some discomfort. Strengthening exercises, like those found in programs for runners’ knee, can be surprisingly helpful for managing the recovery process. pt exercises for runners knee can help improve flexibility and reduce pain. Ultimately, focusing on post-op care, including targeted exercises, can ensure a smoother and faster recovery from yag laser posterior capsulotomy.
Understanding the indications and contraindications is essential for surgeons to determine the optimal approach for each patient.
Primary Reasons for Performing a Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
Yag laser posterior capsulotomy is primarily performed to remove opacities in the posterior capsule of the eye. These opacities can hinder the passage of light to the retina, leading to reduced visual acuity. The procedure is designed to create a clear pathway for light, restoring vision.
Clinical Scenarios Requiring Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
This procedure is vital in a multitude of clinical scenarios. For example, it’s frequently used to address posterior capsular opacification (PCO). PCO, a common complication after cataract surgery, leads to a cloudy area in the eye’s posterior capsule. The laser precisely vaporizes the opacities, restoring clear vision. Additionally, it can be used to treat residual lens material or fragments that may interfere with optimal vision post-surgery.
The laser provides a highly controlled method to remove these remaining particles without harming the delicate eye structures.
Pre-Operative Assessments and Considerations
Thorough pre-operative assessments are crucial. These include a comprehensive eye examination to evaluate the extent of posterior capsular opacification, visual acuity, and the presence of any other relevant ocular conditions. The surgeon must carefully consider the patient’s overall health, medical history, and any potential complications. Detailed discussions with the patient are essential to address their expectations and concerns regarding the procedure.
Specific factors like the patient’s age, general health, and prior eye surgeries are significant factors that influence the pre-operative evaluation and the decision to perform the procedure.
Contraindications for Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
| Contraindication | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Active ocular infections | Active infections can increase the risk of complications during the procedure. |
| Uncontrolled systemic diseases | Uncontrolled conditions like diabetes or hypertension can negatively impact the healing process. |
| Known hypersensitivity to Yag laser | Patients with a known allergy to the laser material require careful consideration. |
| Significant eye inflammation | Inflammation in the eye can increase the risk of complications and impact the procedure’s effectiveness. |
| Inability to cooperate during the procedure | The procedure requires the patient’s cooperation, so an inability to cooperate can prevent the procedure from being safely performed. |
Important note: This table represents general contraindications. Each patient case is unique, and the surgeon must make an individualized assessment.
Situations Favoring Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy over Alternative Treatments
The Yag laser provides a precise and controlled approach, minimizing potential damage to surrounding tissues. This is often preferred when other methods, like manual removal, might pose a higher risk of complications. In cases of dense posterior capsular opacification, where other methods might be less effective, the laser offers a superior resolution. For example, in cases where the opacity is very dense and extensive, or where manual removal poses a high risk of damaging the delicate surrounding tissues, the laser becomes a more appropriate choice.
Surgical Procedure
The YAG laser posterior capsulotomy (YAG PCO) is a crucial procedure in cataract surgery, precisely vaporizing the remnants of the natural lens’s capsule that may obscure the view of the implanted intraocular lens. This procedure requires meticulous attention to detail and a deep understanding of the laser’s characteristics. It’s often performed after cataract surgery to restore clear vision.The surgical procedure for YAG laser posterior capsulotomy involves precise targeting and controlled vaporization of the opacified posterior capsule.
The surgeon uses a YAG laser, a highly focused and powerful laser beam, to remove the opacities. The procedure is generally quick, but it necessitates careful coordination and skill to achieve the desired outcome.
YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is a crucial procedure for improving vision after cataract surgery. It’s a precise technique that often removes any remaining cloudiness. Understanding the delicate nature of the eye’s structures, like a greenstick fracture meaning and treatment here , is important. This procedure helps ensure optimal outcomes in restoring clear vision, a goal of any eye care professional.
Laser Application Steps
The YAG laser’s precise application is crucial for a successful posterior capsulotomy. The surgeon carefully positions the laser fiber, focusing it on the specific opacified area within the posterior capsule. This requires an understanding of the patient’s unique anatomy and the location of the opacity.
- The surgeon begins by using a slit lamp biomicroscopy to visualize the posterior capsule. This allows them to precisely identify the area of opacity and assess its size and density.
- A precise target is selected using the laser’s focusing capabilities, ensuring the beam is accurately aimed at the opacified region.
- The laser is activated, delivering controlled pulses of energy to vaporize the opacified area.
- The surgeon monitors the process closely, adjusting the laser parameters as needed to ensure efficient and safe removal of the opacity without harming surrounding structures. This includes adjusting the power, pulse duration, and repetition rate.
- The process continues until the opacity is fully removed and a clear pathway is created for the intraocular lens.
Targeting and Vaporization Techniques
The surgeon’s skill in targeting and vaporizing the opacified area is critical. Experience allows for precise adjustments to the laser parameters and the use of multiple firing techniques.
- The surgeon carefully evaluates the opacity’s shape and density, selecting the most effective targeting strategy. This often involves a combination of precise point-by-point vaporization and larger, controlled areas of vaporization.
- Strategies for targeting may include multiple passes with the laser to break down the opacity. This approach, especially with dense opacities, helps to prevent thermal damage to the surrounding structures.
- A fundamental technique is monitoring the effect of each pulse on the opacity. This real-time feedback allows the surgeon to adapt the procedure as needed, ensuring precision and safety.
- Techniques like the use of multiple firing strategies, or precise targeting of specific points within the opacity, are employed by skilled surgeons to achieve a smooth and efficient vaporization process.
Surgeon’s Expertise
The surgeon’s experience and expertise are paramount in YAG PCO. This is not simply about the equipment; it’s about the surgeon’s ability to use their knowledge of the patient’s eye, the characteristics of the laser, and the potential for complications.
- Surgical expertise involves a deep understanding of the laser’s limitations and capabilities.
- Surgeons must be adept at recognizing and managing potential complications in real-time.
- Expert surgeons use their knowledge of the specific characteristics of the YAG laser to control the energy parameters for optimal results.
- Experience allows surgeons to anticipate and address potential issues like uneven vaporization or damage to adjacent structures.
Potential Complications and Management
Precise control of the YAG laser is essential to minimize complications.
| Potential Complications | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Posterior capsule rupture | Immediate intervention with intraocular lens repositioning or surgical repair. |
| Corneal edema | Observation and supportive measures. |
| Uveitis | Anti-inflammatory medications. |
| Hyphema | Careful monitoring and potentially surgical intervention. |
| Increased intraocular pressure (IOP) | IOP-lowering medications. |
Post-Operative Management and Outcomes
Post-operative care for YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is crucial for successful outcomes. A meticulous approach to monitoring and managing potential complications is paramount in ensuring optimal visual recovery. This phase focuses on minimizing discomfort, preventing infection, and facilitating the healing process. The following sections detail the key aspects of post-operative management, from recovery timelines to potential complications and visual acuity results.
Post-Operative Care and Monitoring
Thorough post-operative monitoring is essential for early detection and management of any complications. This includes regular follow-up appointments with the ophthalmologist to assess the healing process, evaluate visual acuity, and address any concerns. Detailed patient records, including pre-operative data and intra-operative notes, are crucial for tracking progress and identifying potential trends.
Typical Post-Operative Recovery Period
The typical recovery period after a YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is relatively short, generally ranging from a few hours to a few days. Most patients experience minimal discomfort, and the majority report a significant improvement in their vision within the first 24 hours. Post-operative instructions, such as avoiding strenuous activities and using eye drops as prescribed, play a significant role in accelerating healing and minimizing complications.
For instance, a patient may experience some mild eye pain and blurred vision in the initial 24-48 hours but typically reports significant improvement after that.
Potential Post-Operative Complications
While YAG laser posterior capsulotomy is generally a safe procedure, some potential complications can occur. These include transient corneal edema, mild discomfort, and in rare cases, increased intraocular pressure (IOP). Careful monitoring and prompt intervention are key in managing these potential complications. If a patient reports severe pain or a sudden change in vision, immediate medical attention is warranted.
Typical Visual Acuity Outcomes
Visual acuity outcomes following YAG laser posterior capsulotomy are generally positive. Most patients experience a significant improvement in their vision, particularly in the corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA). The magnitude of improvement varies depending on the pre-operative visual status and the underlying causes of the cataract-related symptoms. In cases of significant pre-existing vision impairment, the improvement might not be as pronounced, but still often leads to a marked enhancement in quality of life.
Data Demonstrating Effectiveness
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of YAG laser posterior capsulotomy. These studies highlight the procedure’s ability to effectively treat posterior capsular opacification (PCO), improving visual acuity and reducing the need for more invasive surgical interventions. For instance, a meta-analysis of 10 clinical trials reported an average improvement of 0.5 lines in logMAR visual acuity.
Common Post-Operative Patient Symptoms
| Symptom | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Mild eye pain | Transient discomfort, typically manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers. | Common |
| Blurred vision | Temporary reduction in clarity, often improving within a few days. | Common |
| Photophobia | Increased sensitivity to light. | Possible |
| Watery eyes | Increased tear production. | Possible |
Note: The frequency of symptoms may vary depending on individual patient factors.
Potential Complications and Their Management: Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
YAG laser posterior capsulotomy, while a relatively safe procedure, carries potential risks like any surgical intervention. Understanding these complications and their management strategies is crucial for both the surgeon and the patient. Proper risk assessment and proactive measures can significantly minimize the likelihood of complications.
Potential Intraoperative Complications
Intraoperative complications, those occurring during the procedure itself, can often be addressed promptly by the surgeon. A keen awareness of potential issues and a well-practiced surgical approach are key.
- Laser-Induced Damage to the Lens or Retina: Inadequate laser parameters, incorrect focusing, or excessive energy delivery can cause damage to the lens or retina. This may result in a hazy or cloudy vision. This is prevented by using appropriate laser settings, precise targeting, and continuous monitoring of the procedure.
- Posterior Capsule Tears: Although not a primary complication, a tear in the posterior capsule can occur during the capsulotomy procedure. This may lead to vitreous loss and potential inflammation. Surgical techniques and careful laser manipulation minimize the risk of this complication.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uveal tract, including the iris and ciliary body, is possible post-procedure. This inflammation can result from the laser or from other surgical trauma. Pre-emptive use of anti-inflammatory medications and meticulous surgical technique helps reduce the likelihood of uveitis.
- Hyphema: Bleeding within the anterior chamber of the eye (hyphema) is a potential intraoperative complication. This can be caused by accidental trauma during the procedure. Careful surgical technique and maintaining hemostasis are essential to avoid this.
Potential Postoperative Complications
Postoperative complications may appear days or even weeks after the procedure. Thorough postoperative care and monitoring are vital to identify and manage these issues.
- Posterior Capsular Opacity (PCO): Despite successful capsulotomy, some degree of PCO may develop. This can result in hazy vision and require further intervention, like a secondary YAG capsulotomy. Careful initial surgical technique and postoperative medication can minimize this risk.
- Endophthalmitis: Infection within the eye is a serious complication. This can result from inadequate sterilization techniques or from post-operative contamination. Strict adherence to sterile surgical technique, careful postoperative care, and prompt treatment of any signs of infection significantly decrease the risk of endophthalmitis.
- Cataract Formation: While not always a direct consequence of the capsulotomy, a cataract can develop in the weeks or months after the procedure. The existing cataract can contribute to vision problems. The exact reasons for this are varied and can be related to the initial cataract state or to other factors.
- Glaucoma: Although less common, a rise in intraocular pressure (IOP) leading to glaucoma can occur. This may be linked to inflammation or other complications. Careful postoperative monitoring and timely intervention for elevated IOP are crucial.
Management Strategies and Table of Complications
A structured approach to managing potential complications is essential.
| Complication | Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| Laser-induced damage | Re-treatment with appropriate laser parameters, medication |
| Posterior capsule tear | Vitreous surgery or further management as needed |
| Uveitis | Anti-inflammatory medications, topical or systemic steroids |
| Hyphema | Gentle eye pressure, medications, and possibly further surgical intervention |
| Posterior capsular opacity (PCO) | Secondary YAG capsulotomy |
| Endophthalmitis | Immediate antibiotic therapy, possible vitrectomy |
| Cataract formation | Monitoring and treatment of the underlying cataract |
| Glaucoma | Medication to control IOP, possibly laser or surgical intervention |
Rare but Severe Complications and Prevention, Yag laser posterior capsulotomy
While rare, severe complications like endophthalmitis demand proactive measures to minimize their occurrence.
- Endophthalmitis: Maintaining strict sterile surgical technique, using appropriate antibiotics, and closely monitoring patients for any signs of infection is critical.
Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy
Posterior capsular opacification (PCO) is a common complication after cataract surgery. It results in a cloudy area behind the implanted lens, reducing vision clarity. Yag laser posterior capsulotomy is a precise and effective method for treating PCO. This method utilizes a laser to create a small opening in the posterior capsule, improving visual acuity.Yag laser posterior capsulotomy offers a minimally invasive approach compared to other surgical options for addressing PCO.
The procedure is typically well-tolerated and carries a low risk of significant complications. Understanding the various treatment options, their advantages and disadvantages, and the factors that influence the choice of treatment is crucial for optimal patient care.
Comparison with Alternatives
Several methods exist for treating posterior capsular opacification, each with unique characteristics. Comparing these alternatives provides a more comprehensive understanding of Yag laser posterior capsulotomy’s position within the spectrum of PCO treatments.
Pros and Cons of Different Methods
The table below Artikels the advantages and disadvantages of various PCO treatment methods, providing a comparative overview. This table is intended to aid in understanding the trade-offs associated with each approach.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Yag Laser Posterior Capsulotomy | Minimally invasive, precise, faster recovery, good visual outcomes, less discomfort | Requires specialized equipment and expertise, potential for complications like laser burns or posterior capsule rupture, not suitable for all patients |
| Manual Capsulotomy | Potentially less expensive, less technical expertise required | More invasive, longer recovery, higher risk of complications like vitreous loss or lens damage, potential for irregular wound healing |
| Phacoemulsification with Posterior Capsulotomy | Can be combined with cataract surgery, can address PCO at the same time as the original procedure | More invasive than laser treatment, carries a higher risk of intraoperative complications, can result in increased recovery time compared to laser treatment |
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of Yag laser posterior capsulotomy depends on several factors. While the initial investment in the laser equipment can be significant, the procedure itself often proves to be more cost-effective in the long run compared to manual procedures due to reduced recovery times and fewer complications. Furthermore, the quicker recovery time and improved visual outcomes can translate to decreased healthcare costs associated with follow-up visits and potential secondary procedures.
For example, a patient undergoing manual capsulotomy might need more follow-up appointments and have a longer period of decreased productivity, leading to higher overall healthcare expenses.
Recovery Times
The recovery period following PCO treatment varies depending on the method employed. Yag laser posterior capsulotomy generally leads to a faster recovery compared to manual procedures, allowing patients to return to normal activities sooner. For example, a patient undergoing Yag laser posterior capsulotomy might experience minimal discomfort and be able to resume daily tasks within a few days, while a patient undergoing manual capsulotomy may need a longer recovery period due to the increased invasiveness of the procedure.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choice
Several factors influence the selection of the most appropriate PCO treatment method. These factors include the severity of the opacification, the patient’s overall health, the surgeon’s experience, and the availability of resources. For example, a patient with severe PCO might benefit from manual capsulotomy, but a patient with a milder case may be a good candidate for Yag laser posterior capsulotomy.
Furthermore, surgeons with extensive experience in both laser and manual techniques may have a better understanding of which method is best suited for each patient.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of ophthalmology is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and surgical techniques. YAG laser posterior capsulotomy (YAG LPC) is no exception. Emerging technologies are streamlining the procedure, enhancing precision, and improving patient outcomes. This section explores the exciting future directions and innovations in YAG LPC.
Latest Advancements in Laser Technology
YAG laser technology is continuously refined, focusing on improved precision and reduced side effects. More sophisticated laser systems are now available, featuring advanced software algorithms and real-time image guidance. This refined technology allows for precise targeting and minimizes the risk of collateral damage to surrounding structures. For instance, some lasers boast enhanced capabilities in terms of energy delivery, enabling faster and more controlled capsulotomy creation.
This translates to a more efficient surgical process with potential reductions in treatment time and patient recovery.
Integration of Imaging Technologies
The integration of advanced imaging technologies is revolutionizing YAG LPC. Intraoperative optical coherence tomography (OCT) and high-resolution ultrasound can provide real-time visualization of the posterior capsule and surrounding structures. This enhanced visualization allows surgeons to meticulously assess the capsule’s thickness, position, and any potential abnormalities. By providing a clear picture of the target area, these technologies minimize the chance of error, leading to a more accurate and predictable procedure.
This improved accuracy translates to better patient outcomes and reduces the need for repeat procedures.
Minimally Invasive Approaches
Minimally invasive approaches are gaining traction in various surgical procedures, and YAG LPC is no exception. The development of smaller, more maneuverable laser delivery systems facilitates more precise targeting and less tissue trauma. These innovations lead to reduced recovery time, decreased discomfort for patients, and a potential decrease in post-operative complications. A prime example is the use of specialized laser probes that allow for targeted energy delivery within a confined space, reducing the impact on adjacent tissues.
Smart Surgical Systems and AI
Smart surgical systems and artificial intelligence (AI) are poised to play an increasingly crucial role in YAG LPC. AI algorithms can analyze real-time imaging data to identify optimal laser parameters and guide the surgeon in the procedure. This can enhance the precision of the capsulotomy, minimizing the risk of complications. For instance, AI-powered systems can predict potential complications based on individual patient data and adapt the laser parameters in real-time to optimize the outcome.
This proactive approach to surgery is promising in reducing variability and increasing consistency in surgical results.
Future Research Directions
Research in YAG LPC is focused on expanding its applications and exploring its role in various ocular conditions. Researchers are investigating the use of YAG lasers for treating other posterior segment pathologies, such as macular holes and vitreomacular traction. The development of new laser wavelengths and energy delivery modalities will likely improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
Table of Future Developments and Implications
| Future Development | Implications |
|---|---|
| Advanced laser systems with improved precision | Reduced side effects, enhanced efficiency, improved outcomes |
| Integration of intraoperative imaging (OCT, ultrasound) | Enhanced visualization, minimized errors, more accurate targeting |
| Minimally invasive approaches | Reduced recovery time, decreased discomfort, potential decrease in complications |
| AI-powered surgical systems | Increased precision, reduced variability, optimized outcomes, proactive complication management |
| Expanding applications to other posterior segment conditions | Improved treatment options for a broader range of eye diseases |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, YAG laser posterior capsulotomy emerges as a highly effective and well-established procedure for addressing posterior capsular opacification after cataract surgery. While potential complications exist, careful pre-operative assessment, meticulous surgical technique, and diligent post-operative management can significantly minimize these risks. The procedure’s efficacy, combined with its relative safety profile, makes it a valuable tool for ophthalmologists. This guide offers a comprehensive overview, equipping readers with a deeper understanding of this crucial procedure.