What is quadruple bypass heart surgery? This procedure involves rerouting blood flow around blocked coronary arteries in the heart. It’s a significant surgical intervention, often chosen when other treatments aren’t sufficient. Understanding the details, from the reasons for the surgery to the potential long-term effects, is crucial for anyone considering or learning about this complex medical process.
This detailed look at quadruple bypass heart surgery explores the surgical process, patient selection criteria, potential risks and complications, and the vital post-operative recovery journey. We’ll also examine alternative treatments and the long-term considerations for patients who undergo this procedure.
Introduction to Quadruple Bypass Heart Surgery: What Is Quadruple Bypass Heart Surgery
Quadruple bypass heart surgery is a complex cardiovascular procedure where multiple blocked coronary arteries are treated by creating new passages for blood flow. This intricate operation aims to restore blood supply to the heart muscle, alleviating chest pain and preventing potentially life-threatening complications. Understanding the reasons behind this procedure, the historical context, and how it compares to other bypass types is crucial for comprehending its significance in modern cardiology.
Quadruple bypass heart surgery is a serious procedure where doctors reroute blood flow around blocked arteries in the heart. Understanding the underlying causes of heart issues, like cardiac sarcoidosis, is crucial. For instance, learning more about cardiac sarcoidosis, which can cause heart problems, can help you better understand the risks and recovery processes of quadruple bypass surgery, which can be complicated.
Knowing what to expect is key for patients considering this major procedure. cardiac sarcoidosis what you should know Ultimately, thorough preparation is vital for a positive outcome following quadruple bypass surgery.
Definition and Purpose
Quadruple bypass surgery involves grafting blood vessels from other parts of the body to bypass four blocked coronary arteries. This reroutes blood flow around the blocked sections, restoring oxygen and nutrient delivery to the heart muscle. The primary purpose is to improve blood flow to the heart, reducing angina (chest pain), preventing heart attack (myocardial infarction), and improving overall heart function.
Common Reasons for Quadruple Bypass
This procedure is typically performed when a patient has significant blockages in four major coronary arteries. These blockages often result from atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. Symptoms such as persistent chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue may indicate the need for this procedure. The severity and location of the blockages, as well as the patient’s overall health, are carefully evaluated to determine the appropriateness of quadruple bypass.
In some cases, a quadruple bypass may be necessary to prevent a severe heart attack or to improve the quality of life for patients with significant coronary artery disease.
Historical Context
The development of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery, including quadruple bypass, marked a significant advancement in cardiovascular care. Early procedures involved rudimentary techniques and often had high complication rates. Over time, surgical techniques and anesthetic practices have significantly improved, resulting in higher success rates and lower risks. The introduction of minimally invasive techniques further refined the procedure, reducing recovery time and patient discomfort.
The historical evolution of this surgical approach has been crucial in addressing the growing prevalence of coronary artery disease.
Comparison with Other Bypass Surgeries
| Type of Bypass | Number of Blocked Arteries Addressed | Complexity | Recovery Time | Risk of Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Bypass | 1 | Least Complex | Relatively Short | Generally Low |
| Double Bypass | 2 | Moderate Complexity | Moderate | Moderate |
| Triple Bypass | 3 | High Complexity | Longer | Higher |
| Quadruple Bypass | 4 | Highest Complexity | Longest | Highest |
This table highlights the increasing complexity and recovery time associated with each type of bypass surgery. The number of blocked arteries addressed directly correlates with the surgical complexity and potential risks. Factors like patient health, extent of blockage, and surgeon expertise play a critical role in determining the appropriate type of bypass surgery.
Surgical Procedure and Techniques
A quadruple bypass surgery, a complex cardiovascular procedure, involves rerouting blood flow around blocked coronary arteries. The precise steps and approaches depend on the individual patient’s unique anatomy and the extent of blockage. This intricate process requires careful planning and execution to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Surgical Approaches
The primary surgical approaches for quadruple bypass surgery are traditional open-heart surgery and minimally invasive techniques. The choice between these methods is based on patient factors, surgeon expertise, and the severity of the blockage. Minimally invasive techniques often involve smaller incisions, potentially leading to less postoperative pain and a faster recovery. However, the surgeon’s skill and the complexity of the blockage are key considerations in selecting the appropriate approach.
Steps Involved in a Quadruple Bypass
The surgical procedure typically follows these steps:
- Anesthesia and Positioning: The patient is placed under general anesthesia, and the chest is opened through a sternotomy, a surgical incision down the center of the breastbone.
- Identifying and Preparing the Vessels: The surgeon identifies the blocked coronary arteries and selects healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body (e.g., leg veins, internal mammary arteries). These vessels are carefully prepared to ensure a proper fit for grafting.
- Creating the Bypass Grafts: The chosen vessels are carefully dissected and connected to the blocked arteries, creating bypass pathways for blood to flow around the blockages.
- Connecting the Grafts: The surgeon uses specialized sutures and techniques to securely attach the grafts to the coronary arteries and the donor vessels, ensuring a strong and reliable connection.
- Closing the Incision: Once all bypass grafts are in place, the surgical site is meticulously closed with sutures. The heart and chest are rejoined.
- Monitoring and Recovery: Post-surgery, the patient is closely monitored in an intensive care unit (ICU) to ensure stable recovery. Vital signs, heart function, and any complications are closely watched.
Specialized Tools and Equipment
Advanced tools and equipment are essential for precision and safety during a quadruple bypass procedure. These include:
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass Machine: This machine takes over the function of the heart and lungs, allowing the surgeon to operate on a still heart.
- Surgical Instruments: Specific instruments, such as micro-surgical scissors and fine forceps, are used to manipulate and connect the blood vessels with extreme precision.
- Monitoring Equipment: Continuous monitoring of vital signs, heart function, and blood flow is crucial during the procedure and afterward.
Traditional vs. Minimally Invasive Techniques
Traditional open-heart surgery involves a larger incision, while minimally invasive techniques employ smaller incisions and specialized tools.
- Traditional Open-Heart Surgery: Offers greater access for complex procedures but may lead to longer recovery times and greater postoperative pain.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Employ smaller incisions and may lead to less postoperative pain and faster recovery times, though not always suitable for all cases.
Arteries Targeted in a Quadruple Bypass
| Artery | Description |
|---|---|
| Left Anterior Descending (LAD) | Supplies blood to the front and bottom of the heart. |
| Right Coronary (RCA) | Supplies blood to the right side of the heart. |
| Left Circumflex (LCX) | Supplies blood to the left side of the heart. |
| Other Targeted Arteries | Depending on the individual patient’s anatomy, other arteries may be targeted for bypass grafting. |
Patient Selection and Preparation

Choosing the right candidates for quadruple bypass surgery is crucial for a successful outcome. This meticulous process involves evaluating the patient’s overall health, the severity of their condition, and their ability to withstand the procedure. The selection process is a collaborative effort between the patient, cardiologist, and surgical team.
Criteria for Patient Selection
Careful assessment is performed to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from the procedure and who can tolerate the potential risks. Factors considered include the extent and location of coronary artery disease, overall health status, and the presence of any other significant medical conditions. Patients with stable angina or severe, disabling symptoms of heart disease are prime candidates.
The surgeon’s evaluation considers the patient’s functional capacity, age, and overall well-being. The aim is to select patients with a reasonable chance of a positive outcome while minimizing the risks associated with the procedure.
Pre-operative Assessments and Tests
Thorough pre-operative assessments are essential to evaluate the patient’s current health status and identify any potential complications. These assessments involve a comprehensive physical examination, including blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECGs), and imaging studies. Imaging studies, such as cardiac catheterization and coronary angiography, are frequently used to pinpoint the specific areas of blockage in the coronary arteries. These tests help determine the severity and location of the blockages, enabling the surgical team to plan the most effective procedure.
The tests also evaluate the overall health of the heart and blood vessels.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary and lifestyle modifications are critical for improving the patient’s overall health and reducing the risk of complications. A healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol is recommended to help manage blood lipid levels and reduce the risk of further plaque buildup. Smoking cessation is highly recommended, as smoking significantly damages blood vessels and increases the risk of heart problems.
Patients are also encouraged to engage in regular exercise to improve their cardiovascular health. Lifestyle changes like managing stress levels and maintaining a healthy weight can contribute significantly to the success of the procedure.
Medications and Procedures for Pre-operative Preparation
Specific medications and procedures are often necessary to prepare the patient for surgery. Medications are used to control blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other medical conditions. Blood thinners may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots. The patient may also undergo specific procedures to further evaluate their condition, such as stress tests or echocardiograms. All these pre-operative preparations help ensure that the patient is in the best possible condition for the surgery.
Potential Risks and Complications
Quadruple bypass surgery, like any major surgical procedure, carries inherent risks. These risks can include but are not limited to: bleeding, infection, blood clots, stroke, heart attack, and damage to surrounding tissues. These complications are relatively infrequent, but the possibility exists. Furthermore, the patient’s pre-existing health conditions can contribute to complications. Factors such as age, the extent of the disease, and the patient’s overall health significantly influence the potential risks.
The surgical team carefully assesses these factors to determine the optimal course of action for each patient.
Quadruple bypass heart surgery involves rerouting blood flow around four blocked coronary arteries. It’s a significant procedure, but understanding the emotional toll on patients, like those experiencing selective mutism in adults , is equally crucial. Ultimately, the focus remains on restoring healthy blood flow and overall heart health after the surgery.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery

The journey after quadruple bypass surgery is a crucial phase in the patient’s recovery. Post-operative care focuses on managing pain, promoting healing, and preventing complications. A multidisciplinary team, including nurses, doctors, physical therapists, and dietitians, plays a vital role in guiding patients through this process. Early intervention and adherence to prescribed protocols are essential for a successful recovery.A smooth post-operative recovery hinges on diligent adherence to medical advice.
Patients must be proactive in communicating their symptoms and concerns to the healthcare team. This proactive approach allows for prompt identification and management of any potential issues, maximizing the chances of a safe and swift return to a healthy lifestyle.
Post-Operative Care Process Summary
Post-operative care involves a comprehensive approach to monitoring and managing patients’ health after the surgery. This encompasses close observation of vital signs, pain management, and the initiation of physical therapy exercises. Regular assessments ensure the patient’s recovery is progressing as expected and any complications are addressed promptly. The nursing staff plays a crucial role in this process, providing ongoing support and education to patients and their families.
Typical Recovery Timeline
The recovery timeline for quadruple bypass surgery varies depending on individual factors, such as overall health, age, and the complexity of the procedure. While a complete return to normal activities takes several weeks or months, patients typically experience significant improvements in their condition within the first few days and weeks after the surgery. Early mobilization, as directed by the physical therapist, plays a significant role in accelerating the recovery process.
Examples of improvements include reduced pain, improved mobility, and increased stamina. Patients should understand that their recovery is a gradual process and that setbacks may occur. Patience and perseverance are crucial in achieving a full recovery.
Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain management is paramount during the post-operative period. A combination of medication, such as analgesics and pain pumps, and non-pharmacological methods, such as heat therapy and relaxation techniques, is often employed. The goal is to minimize pain and discomfort while preventing the development of complications. Pain management plans are tailored to individual needs and are regularly adjusted based on patient feedback and response to treatment.
Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in restoring function and promoting healing. A physical therapist will design a customized exercise program to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Early mobilization, as directed by the therapist, helps prevent complications such as blood clots and pneumonia. These exercises are gradually increased in intensity and duration as the patient progresses through their recovery.
Exercises are tailored to individual needs and limitations, and patients are encouraged to actively participate in their rehabilitation program.
Common Post-Operative Complications
Several potential complications can arise following quadruple bypass surgery. These complications, though relatively rare, can significantly impact the recovery process and necessitate prompt medical intervention. Identifying and addressing complications early is crucial for optimal outcomes.
Potential Complications and Treatment Strategies
| Potential Complications | Treatment Strategies |
|---|---|
| Infection | Antibiotics, wound care, and close monitoring. |
| Blood Clots (Deep Vein Thrombosis – DVT) | Anticoagulant medications, compression stockings, and elevation of the affected limb. |
| Arrhythmias | Medications, pacemakers, or other interventions as determined by the cardiologist. |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Antiarrhythmic medications, anticoagulants, or electrical cardioversion. |
| Heart Failure | Medications to improve heart function, possibly additional procedures. |
| Bleeding | Blood transfusions, pressure dressings, and/or surgical intervention. |
| Wound Dehiscence | Surgical repair of the wound. |
Long-Term Outcomes and Considerations
Quadruple bypass surgery, while offering a significant chance for improved heart health, isn’t a one-and-done solution. Long-term success hinges on several factors, including adherence to lifestyle changes and ongoing medical monitoring. Understanding the potential impacts, both positive and negative, is crucial for patients and their families to make informed decisions about their health journeys.
Long-Term Effects of Quadruple Bypass Surgery
The effects of quadruple bypass surgery extend far beyond the immediate recovery period. Patients may experience improvements in their overall well-being, but also face potential challenges that require careful management. Physical stamina often increases, allowing for more active participation in daily life, but some patients may experience lingering fatigue or discomfort. It’s important to note that individual experiences can vary greatly.
Impact on Lifestyle and Daily Activities
Quadruple bypass surgery often necessitates lifestyle modifications to maintain long-term health and prevent the recurrence of heart problems. This might involve adopting a heart-healthy diet, increasing physical activity levels gradually, and managing stress effectively. The goal is to create a sustainable lifestyle that promotes overall well-being and supports the success of the surgery. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats, and avoidance of smoking.
The recovery period can vary, and some individuals may experience temporary limitations in their daily activities, but many patients eventually return to their previous levels of activity, albeit with certain limitations and adjustments.
Success Rates Compared to Other Treatments
Success rates for quadruple bypass surgery are generally high, but they should be compared to other treatment options, like medication or minimally invasive procedures. The success rate is contingent on patient adherence to lifestyle modifications, appropriate medical follow-up, and overall health conditions. While bypass surgery is effective, it’s essential to weigh the benefits and risks relative to alternative approaches, especially for patients with less severe conditions.
Comparative data should be evaluated based on factors such as patient demographics, specific health conditions, and surgeon expertise. Success rates vary depending on the patient’s overall health and adherence to post-operative instructions.
Potential for Recurrence of Heart Problems
While quadruple bypass surgery significantly improves heart health, the possibility of future heart problems remains. The likelihood of recurrence depends on factors such as the underlying cause of the initial heart disease, patient compliance with post-operative recommendations, and ongoing health conditions. Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in reducing the risk of recurrence. Regular checkups and adherence to medications are essential.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Health
Implementing significant lifestyle changes is essential for the long-term success of quadruple bypass surgery. This includes adopting a heart-healthy diet, incorporating regular exercise into daily routines, and managing stress effectively. A healthy diet is vital for maintaining optimal blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and weight, which are critical for preventing future cardiovascular problems. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, strengthens the heart muscle, and improves overall cardiovascular health.
Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce blood pressure and improve overall well-being.
Comparison of Long-Term Follow-Up Care
| Type of Follow-Up Care | Frequency | Focus | Typical Activities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine Checkups | Annually or as needed | Monitoring overall health, detecting potential complications, and adjusting medications. | Physical examination, blood tests, ECG, and discussions about lifestyle. |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs | Typically 6-12 weeks after surgery | Developing and maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercise, diet, and stress management. | Structured exercise programs, nutritional counseling, and education sessions. |
| Specialized Cardiology Consultations | As needed | Addressing specific cardiac concerns or complications. | Follow-up with cardiologists to address emerging issues or to receive guidance on lifestyle adjustments. |
This table Artikels the key components of long-term follow-up care after quadruple bypass surgery. Each type of follow-up plays a unique role in promoting optimal recovery and preventing future issues.
Potential Risks and Complications
Quadruple bypass surgery, while offering life-saving benefits for those with severe coronary artery disease, carries potential risks and complications. Understanding these risks allows patients and their families to make informed decisions alongside their healthcare team. A thorough understanding of these potential issues is crucial for effective management and achieving the best possible outcomes.The likelihood of complications varies greatly depending on individual factors such as age, overall health, pre-existing conditions, and the surgical technique employed.
Careful patient selection, meticulous surgical planning, and a robust post-operative care regimen are essential to minimize the risk of complications.
Surgical Site Complications
Surgical procedures, even those as precise as quadruple bypass surgery, can sometimes lead to complications at the surgical site. These complications can range from minor issues to more serious problems. Proper wound care and meticulous surgical technique play a crucial role in preventing and managing these complications.
- Wound Infection: Infections at the incision site can occur, requiring antibiotic treatment and potentially extending the recovery period. The frequency of wound infection after cardiac surgery is estimated to be between 1-5% of cases. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic therapy are essential to manage this complication. Careful surgical technique, including meticulous skin preparation and sterile technique, plays a significant role in preventing wound infections.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery can lead to anemia and require blood transfusions. This risk is managed by carefully monitoring blood loss during the operation and having readily available blood products. In cases of excessive bleeding, surgical intervention may be necessary to control the bleeding source. For example, in a recent case, a patient experienced significant bleeding post-surgery.
Quadruple bypass surgery is a serious procedure where four blocked arteries in the heart are replaced. This complex heart surgery is often a last resort for those experiencing severe chest pain. Sometimes, conditions like psoriatic arthritis and pernicious anemia can impact overall health, potentially increasing the risk of heart disease, which might lead to the need for such a procedure.
Understanding the factors that influence cardiovascular health is key for anyone considering or undergoing quadruple bypass heart surgery. Psoriatic arthritis and pernicious anemia are examples of conditions that can influence the need for this type of heart surgery. Ultimately, the decision to proceed with quadruple bypass surgery is a personal one, made after careful consideration of individual health factors.
The surgical team promptly addressed the bleeding by identifying and clamping the source vessel. This swift intervention prevented further complications.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are potential complications, especially in the post-operative period. These blood clots can cause significant discomfort and potentially life-threatening complications. Preventive measures like early mobilization and anticoagulant therapy are crucial in reducing the risk of blood clots. In a patient who developed a PE post-surgery, prompt diagnosis and treatment with anticoagulants and supportive measures were critical to recovery.
Cardiovascular Complications, What is quadruple bypass heart surgery
Cardiovascular complications are a significant concern in patients undergoing quadruple bypass surgery. The heart is a complex organ, and any disruption during the procedure can have repercussions.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): AFib, an irregular heartbeat, can develop post-surgery. This condition can increase the risk of stroke and other cardiac complications. Management typically involves medication to control the heart rhythm. In a recent case, a patient experienced AFib after the surgery. The medical team effectively managed the arrhythmia with anti-arrhythmic medications, preventing further complications.
- Cardiac Tamponade: Rarely, bleeding can accumulate around the heart, causing pressure on the heart and reducing its ability to function. Immediate intervention, often surgical, is necessary to drain the fluid and restore normal heart function. Careful monitoring for signs of cardiac tamponade is essential in the immediate post-operative period.
Other Potential Complications
Other potential complications can occur, though less frequently.
- Neurological Complications: Transient neurological issues, such as confusion or weakness, can arise. These typically resolve with time, but prompt assessment and management are necessary. A recent case involved a patient who experienced temporary confusion post-surgery. The team meticulously monitored the patient and implemented supportive care until the neurological symptoms subsided.
- Renal Dysfunction: Kidney function can be affected in some cases. This can be related to the stress of the surgery or the use of certain medications. Careful monitoring of kidney function is critical to ensure early detection and appropriate management.
Preventive Measures
Effective preventive measures significantly reduce the risk of complications.
These measures include careful patient selection, thorough preoperative evaluation, meticulous surgical technique, and a robust post-operative care plan.
Summary Table
| Potential Complications | Frequency | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Wound Infection | 1-5% | Antibiotic therapy, wound care |
| Bleeding | Variable | Blood loss monitoring, surgical intervention if needed |
| Blood Clots (DVT/PE) | Variable | Early mobilization, anticoagulant therapy |
| Atrial Fibrillation | Variable | Medication to control heart rhythm |
| Cardiac Tamponade | Rare | Immediate surgical intervention |
| Neurological Complications | Variable | Monitoring, supportive care |
| Renal Dysfunction | Variable | Monitoring kidney function, medication adjustment |
Alternatives to Quadruple Bypass
A quadruple bypass, while a significant surgical intervention, isn’t always the optimal solution for patients with severe coronary artery disease. Several alternative treatments offer comparable, and sometimes superior, outcomes for specific patient profiles. Understanding these options allows for a more personalized approach to treatment, maximizing effectiveness and minimizing potential risks.
Alternative Treatment Options
Various procedures and therapies can address coronary artery disease without resorting to quadruple bypass surgery. These alternatives often involve less invasive approaches, potentially leading to quicker recovery times and reduced complications. The choice of alternative depends heavily on the individual patient’s specific condition, including the extent and location of the blockages, overall health, and preferences.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
PCI, often referred to as angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure that opens blocked coronary arteries. A catheter with a balloon tip is inserted into the artery, and the balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed passage. In many cases, a stent—a small mesh tube—is placed within the artery to maintain the opening. This procedure is highly effective in restoring blood flow and reducing angina symptoms.
Advantages include lower risk of major complications compared to bypass surgery, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays. However, some patients may require multiple PCI procedures or repeat interventions over time.
Coronary Artery Stenting
Similar to PCI, coronary artery stenting involves placing a stent within a narrowed coronary artery to keep it open. The key difference lies in the use of a stent, which provides structural support to the artery wall. This approach often leads to improved long-term outcomes compared to balloon angioplasty alone. Stents are often coated with medications to prevent the artery from narrowing again, a process known as drug-eluting stents.
Advantages include enhanced long-term patency and reduced restenosis risk. Disadvantages include the possibility of stent thrombosis (a blood clot forming within the stent) and the need for careful patient selection.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – Less Extensive
In cases where only a few arteries are significantly blocked, a less extensive CABG procedure may be a more appropriate choice than a quadruple bypass. This approach targets the specific blocked arteries, avoiding unnecessary incisions and tissue trauma. Advantages include lower risk of complications and a more streamlined recovery compared to quadruple bypass. Disadvantages include the need for careful evaluation of the extent of disease to ensure adequate coverage.
Comparison of Effectiveness and Safety
The effectiveness and safety of these alternative procedures vary depending on the specific case. PCI is generally considered a safe and effective option for many patients with single or limited blockages. Stenting often leads to better long-term results, but it may carry a higher risk of complications in certain patients. Less extensive CABG procedures are often a safer option than quadruple bypass for patients with limited disease.
Ultimately, the most suitable approach must be determined by a cardiovascular specialist after a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s condition.
Suitability Based on Individual Patient Conditions
Patient selection for any of these procedures is crucial. Factors such as the extent of coronary artery disease, overall health, and other medical conditions play a significant role in determining the most appropriate treatment option. For example, a patient with multiple, diffuse blockages might benefit more from a less extensive CABG procedure than PCI.
Table of Alternative Procedures
| Procedure | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| PCI | Minimally invasive, faster recovery, lower risk of major complications | Potential for restenosis, may require multiple procedures |
| Coronary Artery Stenting | Improved long-term patency, reduced restenosis risk | Higher risk of complications in certain patients, risk of stent thrombosis |
| Less Extensive CABG | Lower risk of complications, streamlined recovery, targeted approach | Need for careful evaluation of disease extent |
Illustrations and Visual Aids
Visual aids are crucial for understanding complex medical procedures like quadruple bypass surgery. They help to visualize the intricate anatomy involved, the surgical steps, and the long-term effects on the patient’s health. These illustrations make the process more accessible and easier to grasp, allowing patients and medical professionals to better comprehend the procedure and its implications.
Coronary Artery Diagram
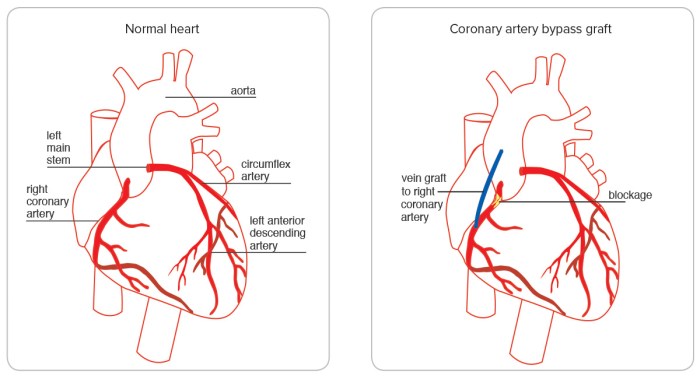
A diagram of the coronary arteries is essential for understanding the problem quadruple bypass surgery addresses. This illustration should clearly depict the coronary arteries originating from the aorta, their branching patterns, and their distribution throughout the heart muscle. The diagram should highlight the specific arteries affected by blockages in the case of a quadruple bypass, visually demonstrating the areas requiring surgical intervention.
The diagram should ideally be color-coded to differentiate between healthy and blocked arteries, enhancing clarity and comprehension.
Surgical Procedure Steps Diagram
Visualizing the surgical steps is vital for understanding the complexity of the procedure. A step-by-step diagram illustrating the quadruple bypass should show the surgeon’s approach to the blocked arteries, the process of grafting the bypass vessels, and the meticulous closure of the surgical incisions. The diagram should clearly label each step, ensuring that the viewer comprehends the sequence of actions taken by the surgical team.
High-quality images of the heart during different stages of the procedure would greatly enhance the understanding of the technique.
Heart Diagram Showing Quadruple Bypass
This illustration is crucial for visualizing the heart and the specific areas affected by the quadruple bypass. The diagram should highlight the four areas of blocked coronary arteries being bypassed. The illustration should clearly show the placement of the grafts, connecting the healthy vessels to the areas previously blocked. This visualization should enable the viewer to understand the overall impact of the surgery on the heart’s structure and function.
A color-coded representation of the healthy and affected arteries would be beneficial.
Post-Operative Recovery Process Illustration
A visual representation of the post-operative recovery process is essential for patients and their families. The illustration should show the patient’s progression from the immediate post-operative period to the gradual return to normal activities. The diagram should depict the various stages of recovery, such as monitoring in the intensive care unit, gradual mobilization, and the resumption of daily tasks.
It could also include visual cues about the patient’s vital signs, pain management, and medication schedules. The diagram should convey a sense of hope and the eventual return to a healthy lifestyle.
Long-Term Effects Illustration
A diagram illustrating the long-term effects of the procedure should show the positive impact on the patient’s quality of life. The illustration should depict the patient’s improved heart function and reduced risk of future cardiovascular events. It should include information on the patient’s ability to participate in physical activities and engage in daily life, highlighting the improvement in their overall well-being.
Examples of real-life cases of patients who have undergone quadruple bypass surgery and achieved successful long-term outcomes could be incorporated into the illustration.
Last Word
In conclusion, quadruple bypass heart surgery is a complex procedure with potential risks and benefits. It’s vital to carefully weigh the pros and cons with a healthcare professional. This detailed exploration should provide a clearer understanding of this important medical intervention, helping individuals and families make informed decisions about their health. Ultimately, choosing the right path to heart health is a personal journey, and open communication with medical experts is key.