What causes heat rash? This common skin condition, often mistaken for other skin problems, is more than just a summer nuisance. Understanding the underlying factors behind heat rash is key to preventing and effectively managing this uncomfortable issue. From the role of humidity to the impact of clothing, we’ll explore the environmental and personal factors that contribute to its development.
This comprehensive guide delves into the different types of heat rash, examining their symptoms, causes, and effective management strategies. We’ll explore how various factors, such as clothing choices and physical activity, can influence your risk. Whether you’re an active individual, a parent concerned about your child, or someone simply looking for a deeper understanding of skin health, this article will offer practical insights and actionable advice.
Let’s get started!
Defining Heat Rash
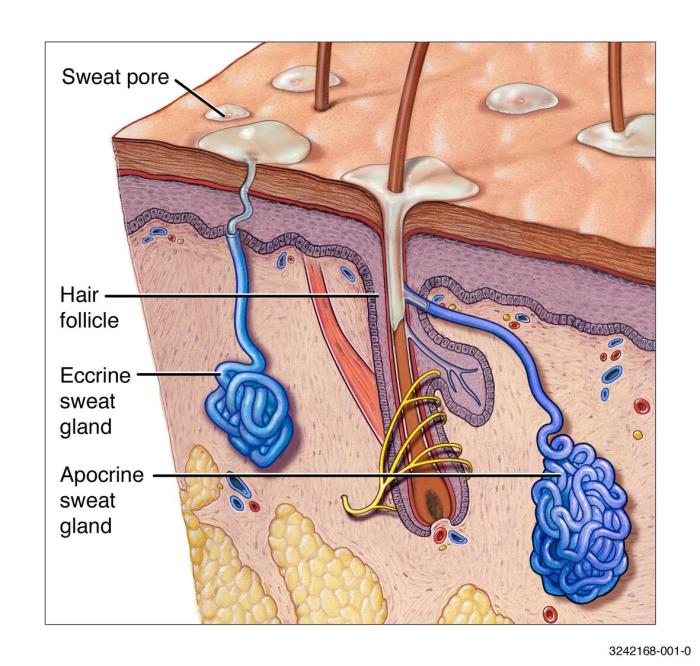
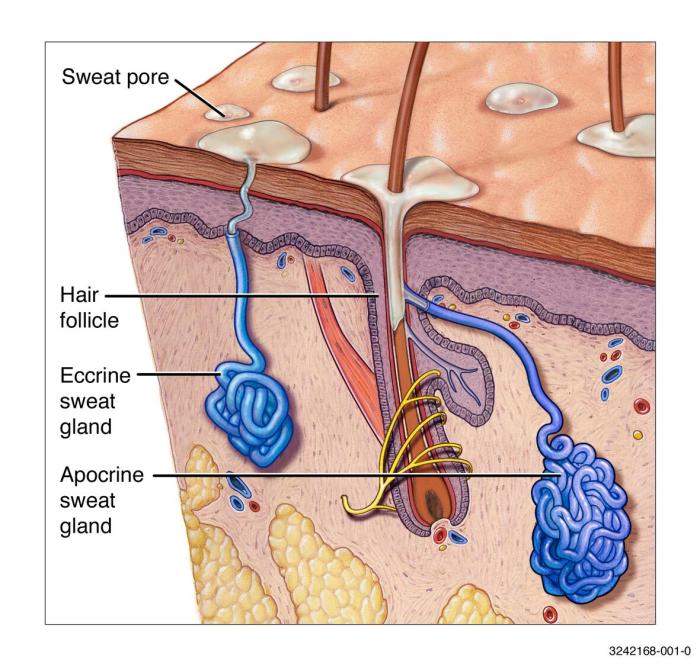
Heat rash, medically known as miliaria, is a common skin condition triggered by excessive sweating in hot and humid environments. It’s characterized by small, red bumps or blisters that appear on the skin, often in areas with a lot of sweat glands. Understanding the different types and causes of heat rash is crucial for effective management and prevention.The body’s natural cooling mechanism involves sweating.
When sweat ducts become blocked, sweat gets trapped beneath the skin, leading to inflammation and the characteristic symptoms of heat rash. This blockage can be due to various factors, including tight clothing, humidity, and even certain medications. Early recognition and appropriate treatment are essential for minimizing discomfort and preventing complications.
Types of Heat Rash
Heat rash manifests in various forms, each with distinct characteristics. These variations stem from the depth of sweat duct blockage. Miliaria crystallina, miliaria rubra, and miliaria profunda are the most common types.
Heat rash, a common skin irritation, often develops due to blocked sweat ducts. It’s frequently triggered by hot and humid weather, but certain medical conditions, like arthritis on one side of the body, arthritis on one side of the body , can sometimes make you more susceptible. The resulting inflammation can potentially disrupt the normal functioning of sweat glands, increasing the risk of heat rash.
So, while hot weather is a major culprit, other factors can contribute to its appearance.
Miliaria Crystallina
Miliaria crystallina, often the most superficial form, is characterized by small, clear blisters that resemble tiny, water-filled bumps on the skin. These blisters are typically less than 2 millimeters in diameter. They usually appear on areas like the chest, back, and face. The blisters are often itchy and mildly uncomfortable. They tend to resolve on their own within a few days without treatment.
Miliaria Rubra
Miliaria rubra, also known as prickly heat, is a more inflamed form of heat rash. It’s characterized by small, red papules or vesicles, which are raised bumps that may contain fluid. These lesions are often itchy and can appear on the skin’s surface, particularly on the upper body and neck. The inflammation and redness are more pronounced than in miliaria crystallina.
Miliaria Profunda
Miliaria profunda is the deepest form of heat rash, impacting the deeper sweat ducts. It presents as large, firm, and slightly raised bumps that are typically a deeper red or even purplish color. These lesions are less itchy than the other types but can be more painful. They often appear on the upper back, chest, and sometimes the arms.
Because it involves deeper layers, it can take longer to resolve.
Comparison of Heat Rash Types
| Type | Symptoms | Causes | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Miliaria Crystallina | Small, clear blisters; slightly itchy | Blocked sweat ducts; heat and humidity | Cool baths/compresses; loose-fitting clothing; avoiding overheating |
| Miliaria Rubra | Small, red bumps; itchy | Blocked sweat ducts; heat and humidity; friction | Cool baths/compresses; loose-fitting clothing; avoiding overheating; over-the-counter anti-itch creams |
| Miliaria Profunda | Large, firm, raised bumps; deeper red/purple; less itchy, potentially painful | Blocked sweat ducts; heat and humidity; prolonged exposure | Cool baths/compresses; loose-fitting clothing; avoiding overheating; potentially oral medications for severe cases |
Synonyms for Heat Rash
This list provides alternative terms for heat rash, including colloquial names used in everyday language.
- Prickly heat: This is a common colloquial term for miliaria rubra, emphasizing the prickly sensation associated with the condition.
- Heat rash: This is a widely understood and accepted general term for the condition.
- Sweat rash: This term highlights the connection between sweating and the rash’s development.
- Miliaria: This is the medical term encompassing all forms of heat rash.
- Heat bumps: This colloquial term describes the raised appearance of the skin lesions.
Causes of Heat Rash: What Causes Heat Rash
Heat rash, a common skin condition, often arises from overheating and excessive sweating. Understanding the environmental factors that contribute to its development is crucial for prevention. This deeper dive into the causes of heat rash will highlight the critical role of temperature, humidity, clothing, and physical activity in triggering this uncomfortable skin reaction.Environmental factors play a significant role in heat rash development.
High temperatures and humidity create an environment where the body struggles to cool down effectively. This leads to excessive sweating, which, if not properly managed, can cause the sweat ducts to become blocked.
Environmental Factors
High temperatures and humidity significantly impact the body’s ability to regulate its temperature. When the surrounding air is excessively hot and humid, the body’s natural cooling mechanisms, such as sweating, become less effective. The air’s high moisture content prevents sweat from evaporating quickly, trapping heat against the skin. This leads to overheating and the potential for heat rash.
For instance, a humid day with a temperature of 90°F can be much more uncomfortable and contribute to heat rash than a dry day at the same temperature.
Role of Clothing
Clothing choices can significantly affect the development of heat rash. Tight-fitting, dark-colored, and synthetic fabrics trap heat and moisture against the skin, hindering evaporation. This can lead to overheating and blocked sweat ducts, increasing the risk of heat rash. Loose-fitting, light-colored, and breathable fabrics, on the other hand, allow air to circulate, facilitating evaporation and preventing overheating.
Heat rash, those annoying little red bumps, is often caused by trapped sweat. Sometimes, though, it can be a bit tricky to tell if you’ve got heat rash or something else, like itchy bumps on elbows. If you’re experiencing itchy bumps on elbows, it’s a good idea to check out this resource on itchy bumps on elbows for some possible causes.
Ultimately, proper identification of the cause of heat rash, like excessive sweating or tight clothing, is key to finding relief.
The choice of clothing is especially critical in hot and humid environments.
Physical Activity and Heat Rash, What causes heat rash
Physical activity increases the body’s metabolic rate and heat production. This increased heat production combined with the strain on the body’s cooling mechanisms can contribute to sweating and overheating, making individuals more susceptible to heat rash, especially in hot and humid conditions. Activities like strenuous exercise, playing sports, or working outdoors during extreme heat can trigger heat rash.
Susceptibility to Heat Rash
Certain populations are more susceptible to heat rash due to factors like age, underlying health conditions, and medications. Infants and young children, older adults, and individuals with chronic health conditions or taking certain medications that affect sweating may have a higher risk of developing heat rash in hot conditions. Individuals with obesity may also be more susceptible due to increased body heat generation.
Impact of Clothing Materials on Heat Rash Risk
The table below illustrates how different clothing materials affect body temperature and heat rash risk. It highlights the importance of choosing breathable fabrics in hot and humid environments.
| Clothing Material | Breathability | Body Temperature Impact | Heat Rash Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | High | Moderate cooling | Low |
| Polyester | Low | Heat retention | High |
| Linen | High | Excellent cooling | Low |
| Silk | Moderate | Moderate cooling | Low to Moderate |
| Wool | Low | Heat retention | High |
Symptoms and Recognition
Recognizing heat rash is crucial for prompt and effective treatment. Understanding the common symptoms, their visual characteristics, and how they differ from other skin conditions allows for accurate diagnosis and appropriate action. Early detection can prevent the rash from worsening and causing discomfort.Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, typically presents as small, red bumps or blisters on the skin.
These eruptions are often accompanied by an itchy or prickly sensation. The symptoms and severity can vary depending on the individual and the environmental conditions.
Common Symptoms
Heat rash often manifests as a collection of small, red bumps, sometimes appearing as blisters filled with clear fluid. These bumps are frequently itchy and may feel prickly or burning. The skin around the bumps might also be slightly swollen or inflamed. In severe cases, the rash can become more widespread and persistent.
Visual Characteristics of Heat Rash
Heat rash typically appears as clusters of small, raised bumps or papules, ranging in size from pinpricks to small peas. The skin around these bumps might appear reddened or inflamed. The rash’s appearance can vary based on the severity of the condition and the location on the body. For example, on the neck and chest, the bumps might be more prominent, while on the groin area, they may appear as tiny, red bumps or blisters.
Differentiation from Other Skin Conditions
Distinguishing heat rash from other skin conditions is important for proper management. While heat rash is typically characterized by small, red bumps, some other skin conditions can also cause similar symptoms. It’s important to note that accurate diagnosis requires a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Symptoms Suggesting a More Serious Condition
While heat rash is usually a benign condition, certain symptoms could indicate an underlying issue. The presence of fever, pus-filled blisters, or significant swelling alongside the rash should prompt immediate medical attention. A rapid spread of the rash or persistent pain also warrants a doctor’s evaluation. These signs could potentially indicate a more serious infection or underlying medical problem.
Differentiating Factors Between Heat Rash and Other Skin Rashes
| Characteristic | Heat Rash | Other Skin Rashes (e.g., Allergic Reactions, Infections) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Small, red bumps or blisters, often in clusters. | Can vary greatly, from flat red patches to large, raised welts or blisters. |
| Distribution | Often concentrated in areas with high moisture or friction. | May appear anywhere on the body, depending on the cause. |
| Itching | Often itchy and prickly. | Can be itchy, but also accompanied by burning, stinging, or pain. |
| Associated Symptoms | Usually no fever or other systemic symptoms. | May be accompanied by fever, chills, body aches, or other systemic symptoms, depending on the cause. |
Risk Factors and Prevention
Heat rash, a common skin condition, often develops when the body’s temperature regulation system struggles to keep up with the heat. Understanding the factors that contribute to its occurrence and implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of discomfort and complications. Proactive steps like staying hydrated and maintaining a cool environment are crucial for preventing heat rash.Heat rash, also known as prickly heat, typically occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, preventing sweat from escaping the skin.
This can lead to inflamed, small red bumps or blisters, particularly in areas with heavy perspiration. By addressing the risk factors and practicing preventative measures, you can significantly decrease your likelihood of experiencing this uncomfortable skin condition.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing heat rash. These factors include prolonged exposure to high temperatures, especially when combined with high humidity. Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as heart or respiratory problems, might be more vulnerable. Additionally, those who are overweight or obese may be at a higher risk, as their bodies often produce more sweat.
Infants and young children are also more susceptible to heat rash due to their developing temperature regulation systems.
Preventive Measures
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of heat rash. Staying hydrated is paramount, as it helps the body regulate its temperature effectively. Maintaining a cool environment, whether through air conditioning, fans, or seeking shade, is equally important. Adequate hydration, along with a cool environment, are key to preventing heat rash.
Importance of Hydration and Cool Environment
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial during hot weather. Dehydration can compromise the body’s ability to regulate temperature, making it more susceptible to heat rash. Consuming plenty of water, electrolyte drinks, and other hydrating beverages is essential. Similarly, maintaining a cool environment through air conditioning or staying in shaded areas can prevent overheating and sweat blockage. The combination of hydration and a cool environment is essential for maintaining proper body temperature and preventing heat rash.
Recommended Clothing Choices
Choosing appropriate clothing can significantly reduce the risk of heat rash. Lightweight, breathable fabrics like cotton and linen are ideal for hot weather, as they allow for better airflow and moisture evaporation. Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors; therefore, opting for light-colored clothing is recommended. Avoid tight-fitting clothing, as it can restrict airflow and trap heat against the skin.
Choosing breathable, light-colored, and loose-fitting clothing is essential to prevent heat rash.
Table of Preventive Measures and Effectiveness
| Preventive Measure | Effectiveness Rating | Explanation ||—|—|—|| Staying hydrated | High | Drinking plenty of fluids helps the body regulate temperature, preventing sweat blockage. || Maintaining a cool environment | High | Air conditioning, fans, or shaded areas minimize overheating and sweat buildup. || Wearing breathable clothing | Moderate | Lightweight, breathable fabrics like cotton and linen allow for better airflow and moisture evaporation.
|| Avoiding strenuous activity during peak heat hours | High | Reducing physical exertion during the hottest parts of the day helps prevent overheating. || Using a cooling mist or spray | Low to Moderate | Can provide temporary relief, but doesn’t replace hydration and cool environments. |
Adjusting Activity Levels
Adjusting activity levels during hot weather is essential for preventing heat rash. Reduce strenuous physical activity during the hottest parts of the day, especially when the humidity is high. Shifting outdoor activities to cooler times of the day can help minimize the risk of overheating and subsequent heat rash. Strategic scheduling of outdoor activities is vital for preventing heat rash during peak heat hours.
Treatment and Management

Heat rash, while often uncomfortable, usually resolves on its own within a few days with proper care. Prompt and appropriate treatment focuses on relieving the symptoms and preventing further skin irritation. Understanding the best course of action can significantly reduce discomfort and speed up recovery.
Typical Treatment Approach
The primary treatment for heat rash centers around cooling and allowing the skin to breathe. This involves minimizing the factors that contribute to its development, such as heat and humidity, and promoting skin comfort. A crucial aspect is avoiding harsh scrubbing or scratching, as this can worsen the condition.
Soothing the Affected Skin
Several methods can soothe the irritated skin and promote healing. Cool compresses, applied gently and intermittently, can provide immediate relief. Avoiding hot showers or baths is essential, as these can further inflame the skin. Using a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer can help hydrate the skin and prevent further dryness. Avoiding harsh soaps and detergents is also crucial.
A cool, damp cloth can be gently applied to the affected area, and frequent light air circulation will help cool and soothe the skin.
Avoiding Further Irritation
To prevent recurrence or worsening of the rash, maintaining a cool and dry environment is paramount. This means staying hydrated, dressing in loose-fitting, breathable clothing, and limiting strenuous activity during the hottest parts of the day. Staying cool and hydrated is key to avoiding further irritation and discomfort.
Importance of Avoiding Harsh Chemicals and Abrasive Materials
Harsh chemicals and abrasive materials can exacerbate the skin irritation associated with heat rash. Fragrant soaps, lotions, and powders can irritate sensitive skin, leading to more discomfort and prolonged healing. Choosing products specifically designed for sensitive skin can significantly reduce the risk of further irritation.
When Professional Medical Attention is Necessary
While heat rash typically resolves without medical intervention, certain situations warrant seeking professional help. If the rash is accompanied by fever, chills, or other systemic symptoms, or if the rash becomes excessively painful or swollen, consulting a dermatologist is recommended. If the rash shows signs of infection, such as pus or increasing redness, immediate medical attention is critical.
Seek medical advice if the rash doesn’t improve within a few days or if you experience severe discomfort.
Treatment Options Summary
| Treatment Option | Suitability | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Cool Compresses | Excellent for immediate relief | Apply gently and intermittently |
| Loose-fitting, Breathable Clothing | Crucial for preventing further heat buildup | Avoid tight or synthetic fabrics |
| Gentle Moisturizers | Hydrates and soothes skin | Choose fragrance-free varieties |
| Avoiding Hot Showers/Baths | Reduces skin irritation | Take cool showers/baths |
| Medical Consultation | Necessary for severe or persistent cases | Consult a dermatologist if symptoms worsen |
Heat Rash in Different Populations
Heat rash, a common skin condition, can manifest differently across various demographics. Understanding these variations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Factors like age, underlying medical conditions, and cultural practices can influence the presentation and severity of the rash.Recognizing the specific needs of different populations, particularly infants, children, older adults, and those with pre-existing medical conditions, is essential to provide appropriate care and prevent complications.
Tailoring preventive strategies and treatment plans to individual circumstances leads to better outcomes.
Heat rash, a common summer annoyance, is usually caused by trapped sweat and friction against the skin. Sometimes, though, other factors like a fever or even a headache on the right side headache on the right side might be contributing to the discomfort. Underlying health issues or reactions to certain fabrics can also play a role in heat rash development.
Unique Considerations for Infants and Children
Infants and young children are particularly vulnerable to heat rash due to their underdeveloped thermoregulation systems and higher surface area-to-volume ratios. Their skin is thinner and more delicate, making them more susceptible to irritation and discomfort. Infants may not be able to communicate their discomfort, leading to delayed diagnosis and potentially worsening the condition. Parents and caregivers should be vigilant for signs of heat rash, such as small, red bumps, and promptly seek medical attention if necessary.
Frequent diaper changes and loose, breathable clothing are critical preventative measures.
Considerations for Older Adults
Older adults often experience decreased sweating capacity and slower thermoregulation compared to younger individuals. This diminished ability to cool themselves increases their risk of developing heat rash, particularly in hot and humid environments. Chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes and heart disease, can further compromise thermoregulation and increase susceptibility. Maintaining hydration and using cooling strategies like fans and air conditioning is crucial for older adults to prevent heat rash.
Medical professionals should also address any underlying conditions that might exacerbate the risk.
Impact of Medical Conditions on Heat Rash Susceptibility
Certain medical conditions can significantly influence a person’s susceptibility to heat rash. Individuals with diabetes, obesity, or cardiovascular conditions often have compromised thermoregulation, making them more vulnerable. Medications, such as those that inhibit sweating, can also increase the risk. For example, individuals taking certain diuretics may lose excessive fluids, leading to dehydration and increasing their risk. Healthcare providers should assess patients with these conditions for potential increased susceptibility to heat rash.
Preventive Strategies for Different Demographics
| Demographic | Preventive Strategies |
|---|---|
| Infants and Children | Frequent diaper changes, loose-fitting breathable clothing, air conditioning or fans, avoidance of overheating situations, and frequent hydration checks. |
| Older Adults | Hydration, cooling strategies (fans, air conditioning), avoiding strenuous activity in extreme heat, and regular medical checkups. |
| Individuals with Medical Conditions | Regular hydration, managing underlying conditions, avoiding excessive exertion in heat, and consulting with healthcare providers about medication adjustments. |
| People with limited mobility | Frequent hydration, use of assistive devices for mobility to prevent overheating, and monitoring for symptoms of heat rash. |
The table above Artikels general preventive measures. Individualized strategies should be developed based on specific needs and circumstances.
Individualized Approaches to Heat Rash Management
Effective heat rash management necessitates an individualized approach. Factors such as the severity of the rash, the individual’s overall health, and the environmental conditions must be considered. Tailoring treatment to the specific needs of each patient is vital for optimal results.
Cultural Factors Influencing Heat Rash Prevention and Treatment
Cultural practices and beliefs can significantly influence how individuals perceive and manage heat rash. For example, some cultures may have traditional remedies for skin conditions that may or may not be effective or safe. It is crucial for healthcare providers to be aware of these cultural factors and to address them respectfully and appropriately when developing treatment plans.
Communication and education are vital in promoting effective heat rash prevention and treatment. Open communication between healthcare providers and patients about cultural practices is essential to ensure culturally sensitive care.
Illustrative Cases
Heat rash, while often a benign condition, can present in diverse ways. Understanding these variations through case studies is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This section delves into a specific case, highlighting the key symptoms, diagnostic process, and treatment strategies.Detailed analysis of individual cases, including relevant patient factors, allows for a deeper comprehension of heat rash’s presentation and implications.
This understanding is vital for healthcare professionals in providing personalized care and preventing complications.
Case Study: A Young Athlete
This case concerns a 16-year-old male high school athlete experiencing intense symptoms during a particularly hot and humid summer training camp. The patient, known for his intense training regimen, reported discomfort during his daily practices.
Case History:
- The athlete was participating in a rigorous training program involving multiple hours of practice each day.
- Environmental conditions were consistently hot and humid, with temperatures exceeding 30°C and high relative humidity.
- He experienced a sudden onset of skin eruptions, particularly on his neck, chest, and upper back. The rash was characterized by small, red bumps and patches.
- Symptoms intensified during and after training sessions.
- The patient reported no significant medical history or allergies.
- He was well-hydrated throughout the day, though sweat production was copious.
Symptoms and Recognition:
- Erythematous (reddened) papules and macules (small, flat, raised areas) appeared on the skin, primarily on the neck, chest, and back.
- The skin felt hot and itchy.
- Symptoms worsened with increased activity and were often relieved by rest and cooling.
- The patient reported no associated fever or other systemic symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Physical examination revealed the characteristic skin findings of heat rash, confirming the diagnosis.
- Treatment focused on cooling measures and symptomatic relief. This included frequent cool showers, loose-fitting clothing, and avoidance of strenuous activity during peak heat hours.
- Topical hydrocortisone cream was prescribed for itching relief, if needed.
- Emphasis was placed on maintaining adequate hydration by encouraging frequent fluid intake.
- The patient was advised on heat acclimatization strategies, such as gradually increasing training duration and intensity over time to better cope with the heat.
Diagnostic Flowchart for Heat Rash
A structured diagnostic approach is essential to accurately identify and manage heat rash. The flowchart below illustrates the steps involved in reaching a diagnosis:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Obtain a detailed patient history, including environmental exposures, activity levels, and symptom onset. |
| 2 | Perform a thorough physical examination, focusing on skin lesions and distribution. |
| 3 | Consider other differential diagnoses (e.g., allergic reactions, infections). |
| 4 | If skin findings are consistent with heat rash, confirm diagnosis through elimination of other possibilities. |
| 5 | Initiate appropriate treatment based on the severity and extent of the rash. |
Relationship to General Principles
This case highlights the importance of recognizing the interplay between environmental factors, physical exertion, and individual susceptibility in heat rash development. The athlete’s intense training in a hot environment created the ideal conditions for heat rash to manifest. Proper hydration and heat acclimatization are crucial preventative measures, as seen in the treatment strategy.
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the causes of heat rash is crucial for effective prevention and management. From the importance of staying hydrated and cool to the influence of clothing and activity levels, various factors contribute to heat rash development. By recognizing the specific symptoms and adopting preventative measures, individuals can minimize their risk and maintain comfort during warmer months.
Remember that personalized approaches are essential, especially when considering different demographics and potential underlying medical conditions. Stay informed, stay proactive, and stay cool!