Types of weight loss surgery encompass a spectrum of procedures, each with its own unique mechanisms, benefits, and drawbacks. Understanding these different approaches is crucial for individuals considering this option. This guide delves into the various surgical interventions available, from restrictive to malabsorptive, and combined techniques. We’ll explore the historical context, surgical mechanisms, potential complications, and success rates of each type, helping you make an informed decision about your weight loss journey.
This exploration will not only cover the different surgical procedures but also delve into crucial pre- and post-operative considerations, including patient selection criteria, pre-operative evaluations, nutritional factors, and post-operative care. Furthermore, we’ll examine long-term outcomes, potential risks, and illustrative case studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of weight loss surgery.
Introduction to Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, is a complex and potentially life-altering procedure for individuals with severe obesity. It’s not a quick fix; rather, it’s a tool that, when combined with lifestyle changes, can significantly improve health and well-being. Understanding the different types of surgery, their mechanisms, and potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial for making an informed decision.This approach aims to address the root causes of obesity and its associated health risks, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and sleep apnea.
The surgery, coupled with comprehensive medical support and long-term commitment to healthy habits, can lead to substantial and lasting weight loss.
Different weight loss surgeries have varying approaches, each with potential benefits and drawbacks. Beyond the surgical procedures, strengthening your core muscles plays a crucial role in long-term success. A strong core, as detailed in this helpful article on benefits of core muscles , can improve stability and support, aiding in recovery and potentially making the transition to a healthier lifestyle easier after surgery.
Ultimately, understanding the different types of weight loss surgery, alongside a focus on core strength, is key to informed decision-making.
Overview of Weight Loss Surgery Options
Bariatric procedures vary in their mechanisms, targeting different aspects of the digestive system to achieve weight loss. The primary goals of these procedures are to reduce food intake, limit nutrient absorption, or a combination of both. These strategies are tailored to the individual’s needs and health status.
Historical Context of Weight Loss Surgery
The development of weight loss surgery has a rich history, evolving from early experimental procedures to sophisticated and refined techniques used today. The initial attempts focused on creating restrictive pouches in the stomach. Over time, surgical innovations have resulted in procedures that effectively address both restriction and malabsorption, leading to more effective and safer outcomes.
Types of Surgical Interventions
A variety of surgical interventions are available for weight loss. These techniques can be categorized based on their mechanisms of action, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Comparison of Weight Loss Surgery Approaches
| Type of Surgery | Mechanism | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | Reduces stomach size, promoting satiety and restricting food intake. | Generally less invasive than bypass procedures, lower risk of dumping syndrome, quicker recovery. | May not be as effective for extreme obesity, potential for long-term nutritional deficiencies if not managed properly. |
| Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass | Creates a small stomach pouch and reroutes the small intestine, limiting food absorption. | Significant weight loss potential, effective for type 2 diabetes management. | Higher risk of complications, potential for nutrient deficiencies, more complex procedure, longer recovery period. |
| Adjustable Gastric Banding | A band is placed around the stomach, restricting food intake by adjusting the tightness. | Less invasive compared to bypass procedures, easier to adjust. | Less effective for significant weight loss, requires lifelong adjustments, higher risk of slippage or erosion of the band. |
| Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) | A combination of restrictive and malabsorptive approaches, creating a very small stomach pouch and rerouting the small intestine to bypass most of the stomach and duodenum. | Excellent weight loss results, highly effective for diabetes management. | Highest risk of complications, potential for severe nutritional deficiencies, and requires long-term nutritional support. |
Types of Restrictive Procedures
Restrictive weight loss surgeries focus on reducing the stomach’s capacity, thus limiting the amount of food a person can consume. These procedures aim to induce a feeling of fullness sooner and promote gradual weight loss. Understanding the different restrictive techniques is crucial for patients considering bariatric surgery, as each approach has unique advantages and disadvantages.Restrictive procedures work by physically altering the stomach’s size and shape, preventing overeating.
The smaller stomach size triggers a feeling of fullness with smaller portions, ultimately reducing calorie intake. The reduced food capacity leads to a decreased intake of calories and fosters a healthy weight loss trajectory.
Gastric Banding
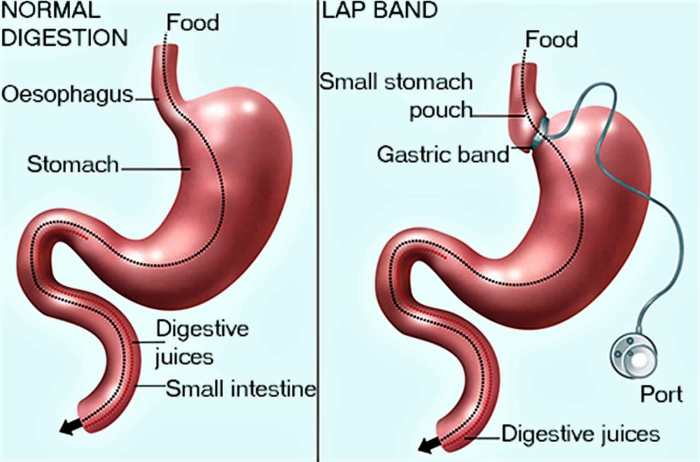
Gastric banding involves placing a band around the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch. This adjustable band regulates the passage of food into the rest of the stomach. The band is typically filled with saline solution to adjust the size of the pouch.The procedure’s primary advantage is its adjustable nature, allowing for fine-tuning of the restriction.
This approach is considered less invasive compared to other restrictive procedures. However, it requires frequent follow-up visits for band adjustments, and the band itself can occasionally slip or erode. Furthermore, long-term results can vary, and the success rate depends on patient adherence to dietary and lifestyle modifications.
Sleeve Gastrectomy
Sleeve gastrectomy involves removing a large portion of the stomach, shaping it into a tube-like structure. This procedure permanently reduces the stomach’s size, limiting the amount of food that can be accommodated. The surgery is performed laparoscopically, minimizing incisions and recovery time.The procedure offers a more substantial and permanent restriction compared to banding. However, it’s a more complex procedure with potential complications like leaks or strictures.
Long-term follow-up is also important to address potential nutritional deficiencies.
Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG)
The vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG) procedure involves surgically removing a large portion of the stomach, creating a smaller, tubular stomach. The key mechanism behind this procedure is the reduction in stomach volume, which prompts a feeling of fullness with smaller portions of food. This reduced stomach capacity results in lower caloric intake, leading to weight loss.Advantages of VSG include a relatively lower risk of complications compared to other restrictive procedures and a significant weight loss potential.
However, patients undergoing VSG may experience some nutritional deficiencies if not carefully monitored. There is also a possibility of the sleeve developing a stricture, which can lead to further complications.
Comparison of Restrictive Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Potential Complications | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric Banding | Adjustable band around the stomach; creates a small pouch. | Band slippage, erosion, need for adjustments, potential for pouch dilation. | Moderate (dependent on patient adherence) |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy | Large portion of stomach removed, creating a tube-like structure. | Leaks, strictures, nutritional deficiencies, potential for dumping syndrome. | High (with appropriate follow-up) |
| Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy (VSG) | Significant portion of stomach removed, creating a smaller, tubular stomach. | Leaks, strictures, nutritional deficiencies, possible dumping syndrome. | High (with appropriate follow-up) |
Types of Malabsorptive Procedures
Malabsorptive weight loss surgeries are designed to reduce the amount of calories the body absorbs from food. These procedures work by altering the digestive tract, making it harder for the intestines to absorb nutrients. While often more complex than restrictive procedures, they can lead to significant weight loss and, in some cases, remission of obesity-related diseases. Understanding the mechanisms and potential consequences of these procedures is crucial for informed decision-making.
Mechanisms of Malabsorptive Surgeries
Malabsorptive procedures achieve weight loss by decreasing the surface area available for nutrient absorption in the small intestine. This reduction in absorption leads to fewer calories being taken from ingested food. The procedures typically involve creating a smaller stomach pouch and bypassing or shortening sections of the small intestine. The body then receives fewer calories and fewer nutrients from food, promoting weight loss.
The resulting nutrient deficiencies can be significant and require careful monitoring and supplementation.
Different weight loss surgeries tackle the issue from various angles, but maintaining a healthy pH balance is often overlooked. While procedures like gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomies are effective, consider exploring natural remedies to restore ph balance, like incorporating more alkaline foods into your diet. These methods can help optimize your body’s environment for weight loss, and combined with surgical interventions, can potentially enhance long-term results.
Ultimately, the best approach to weight loss surgery involves careful consideration of individual needs and circumstances.
Specific Techniques in Malabsorptive Procedures
Several different malabsorptive procedures exist, each with its unique technique and potential outcomes.
Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS)
BPD/DS is a complex procedure that involves a combination of restrictive and malabsorptive elements. A small stomach pouch is created, and a significant portion of the small intestine is bypassed. This bypass reduces the amount of bile and pancreatic enzymes mixing with food, further hindering nutrient absorption. The procedure aims to create a significant reduction in calorie absorption.
The surgical technique involves separating the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine) from the rest of the small intestine. The duodenum is then reconnected to the jejunum (the middle part of the small intestine), creating a very short, bypassed portion of the small intestine. This limits the time food spends in the intestines, further reducing absorption.
Sleeve Gastrectomy with Duodenal-Ileal Bypass
This procedure combines the restrictive element of a sleeve gastrectomy with a malabsorptive component. In this approach, a sleeve gastrectomy reduces stomach size, while a duodenal-ileal bypass diverts food away from a significant portion of the small intestine, thereby reducing absorption. The specific technique involves creating a sleeve-shaped stomach, bypassing the duodenum and jejunum, and reconnecting the remaining intestine to the ileum (the last part of the small intestine).
This combination approach targets both reducing stomach capacity and decreasing nutrient absorption.
Table of Malabsorptive Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Potential Complications | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS) | Combines restrictive and malabsorptive elements. Creates a small stomach pouch and bypasses a significant portion of the small intestine. | Nutrient deficiencies, diarrhea, dumping syndrome, vitamin deficiencies, possible complications associated with a complex surgery. | Generally high, but requires meticulous post-operative care. |
| Sleeve Gastrectomy with Duodenal-Ileal Bypass | Combines sleeve gastrectomy with duodenal-ileal bypass, reducing stomach capacity and limiting nutrient absorption. | Similar complications to BPD/DS, including nutrient deficiencies, potential for malabsorption-related problems. | Success rates vary, depending on surgical technique and patient factors. |
Types of Combined Procedures: Types Of Weight Loss Surgery
Combining different weight loss surgical techniques can offer a more tailored approach to bariatric surgery, potentially leading to better outcomes for individuals with specific needs. These combined procedures aim to maximize weight loss while minimizing the potential risks associated with individual procedures. Understanding the mechanisms and variations in these combined procedures is crucial for informed decision-making.
Mechanisms Behind Combined Surgeries
Combined bariatric procedures typically leverage the strengths of two or more techniques. For instance, a restrictive procedure might be combined with a malabsorptive one to achieve both reduced food intake and reduced nutrient absorption. This synergistic effect aims to accelerate and improve weight loss outcomes. The specific mechanisms vary depending on the combination chosen, but generally aim to reduce caloric intake, limit nutrient absorption, and modify gut hormone release to enhance the overall metabolic response to weight loss.
Specific Techniques Involved
Various techniques are employed in combined bariatric procedures. One common combination involves a restrictive procedure, such as a sleeve gastrectomy, combined with a duodenal switch. This approach restricts food intake through the sleeve gastrectomy and minimizes nutrient absorption through the duodenal switch. Another example is the combination of a gastric bypass with a small bowel resection, aiming to reduce food intake and nutrient absorption through both methods.
These procedures involve meticulous surgical manipulation of the stomach, small intestine, and sometimes the large intestine. The surgical techniques employed will vary depending on the specific combination of procedures chosen.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks
Combined procedures offer potential benefits such as improved weight loss and metabolic outcomes compared to individual procedures. They can address specific patient needs that might not be adequately addressed by a single procedure. However, combined procedures also carry a higher risk of complications, including nutritional deficiencies, bleeding, and infections. Furthermore, the increased complexity of the surgery may lead to longer recovery times and a higher risk of complications.
The potential benefits must be carefully weighed against the increased risk profile of each combined approach.
Comparison of Combined Surgical Procedures, Types of weight loss surgery
Different combined surgical procedures have varying degrees of restrictiveness and malabsorptive effects. For example, a sleeve gastrectomy with a duodenal switch is more malabsorptive than a sleeve gastrectomy with a gastric band. Understanding the specific mechanisms of each procedure is crucial for tailoring the approach to the individual patient’s needs and risk factors. The choice of procedure should be based on careful evaluation of the patient’s medical history, body mass index (BMI), and overall health status.
Table of Combined Procedures
| Procedure | Description | Potential Complications | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sleeve Gastrectomy with Duodenal Switch | Combines the restrictive sleeve gastrectomy with the malabsorptive duodenal switch. | Nutritional deficiencies, dumping syndrome, internal hernia, bleeding, infection, and strictures. | Generally high, often exceeding 80% effective in significant weight loss. |
| Gastric Bypass with Small Bowel Resection | Combines the gastric bypass procedure with a resection of a portion of the small intestine to further reduce nutrient absorption. | Increased risk of nutritional deficiencies, leakages, internal hernias, and strictures. | Success rates are generally high, but with potential for complications due to the combined complexity. |
| Adjustable Gastric Band with Sleeve Gastrectomy | Combines the adjustable gastric band, which is adjustable, with a sleeve gastrectomy. | Risk of band slippage, erosion, or infection. Potential for complications associated with the sleeve gastrectomy. | Success rates are generally good, but can vary based on individual patient response and adherence to post-operative care. |
Patient Selection and Pre-operative Considerations
Choosing the right patient for weight loss surgery is crucial for a successful outcome. It’s not just about the numbers on a scale; it’s about assessing the individual’s overall health, psychological readiness, and commitment to lifestyle changes. Careful pre-operative evaluation and preparation are essential to minimize risks and maximize the benefits of this life-altering procedure.Pre-operative evaluation and preparation are designed to ensure that patients are as healthy as possible before undergoing surgery.
This involves identifying potential complications and addressing them through medical interventions, lifestyle adjustments, and psychological support. A multidisciplinary approach is vital to ensure a smooth and successful transition for the patient.
Patient Selection Criteria
Patient selection criteria are multifaceted and designed to identify individuals who are most likely to benefit from weight loss surgery and who can successfully adhere to the necessary lifestyle changes. These criteria typically include a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or higher with obesity-related health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea.
Additionally, psychological factors such as a realistic understanding of the surgery’s limitations and a commitment to long-term lifestyle changes are also considered. The patient’s motivation, understanding of the procedure’s risks and benefits, and support system play critical roles in the selection process. Patients with significant underlying medical conditions may not be suitable candidates, and the decision must be made on a case-by-case basis.
Pre-operative Evaluations and Assessments
Comprehensive pre-operative evaluations are essential to assess the patient’s overall health status and identify any potential complications. These evaluations typically include a thorough physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. Detailed medical history review, including any past surgical procedures, medications, and allergies, is also vital. This process helps determine the patient’s suitability for surgery and identify any pre-existing conditions that may require intervention or management prior to the procedure.
Cardiovascular, pulmonary, and other relevant systems are assessed to evaluate the patient’s ability to withstand the surgery.
Psychological and Nutritional Factors
Psychological factors are significant in the success of weight loss surgery. Patients need to be psychologically prepared for the lifestyle changes and challenges that come with the procedure. This includes understanding the surgery’s limitations, committing to long-term lifestyle changes, and developing a realistic expectation of the weight loss outcomes. Support systems, including family and friends, can be crucial in this process.
Nutritional counseling is essential to help patients develop healthy eating habits and understand the importance of balanced nutrition. A multidisciplinary team, including psychologists and registered dietitians, is often involved in providing guidance and support.
Pre-surgical Preparation
Proper pre-surgical preparation is vital to ensure a smooth and successful procedure. This preparation involves a structured approach to address the patient’s medical needs and lifestyle factors. It is designed to optimize the patient’s overall health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Dietary Modifications: A structured dietary plan, often implemented by registered dietitians, is crucial. This involves gradually transitioning to a healthier diet, minimizing processed foods, and focusing on nutrient-rich whole foods. This phase helps optimize the patient’s nutritional status and prepares their digestive system for the surgical changes.
- Weight Management Strategies: Pre-surgical weight loss, when possible and safe, is often recommended. This can be achieved through a combination of dietary changes and increased physical activity. This helps minimize the surgical risks and improves the overall outcomes.
- Medications and Supplements: Patients need to inform their medical team about all medications, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, and supplements. This information helps the team manage any potential interactions and adjust the patient’s medications as needed. It is important to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen to avoid any complications.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking significantly increases the risk of complications after weight loss surgery. Smoking cessation programs are typically encouraged and supported to help patients quit smoking before the procedure. This can significantly improve the recovery process and overall outcomes.
- Blood Work and Medical Evaluations: Regular blood tests and medical evaluations help monitor the patient’s health and identify any potential issues that require intervention before surgery. This ensures that the patient is as healthy as possible before undergoing the procedure.
- Psychological Evaluation and Support: A psychological evaluation can help assess the patient’s psychological readiness for surgery. This can involve addressing concerns and anxieties about the procedure, developing coping mechanisms, and ensuring a strong support system is in place. A mental health professional can assist the patient in navigating this crucial phase.
- Education and Counseling: Comprehensive education about the surgery, including potential risks and benefits, and lifestyle changes, is essential. Patients should receive counseling and support to address concerns and provide realistic expectations. Understanding the procedure and long-term commitment is key to success.
Post-operative Care and Recovery
Weight loss surgery is a significant undertaking, and the journey doesn’t end with the procedure itself. Successful outcomes depend heavily on meticulous post-operative care, which encompasses a range of factors, from nutritional adjustments to managing potential complications. This phase requires diligent attention and adherence to prescribed guidelines for a safe and effective recovery.
Importance of Post-operative Care
Post-operative care is crucial for optimal recovery and long-term success after weight loss surgery. It involves comprehensive monitoring, dietary guidance, and management of potential complications. Proper care minimizes risks, accelerates healing, and helps patients maintain the weight loss achieved through the surgery. It also educates patients on lifestyle changes necessary for sustainable weight management.
Typical Recovery Process and Timelines
Recovery timelines vary depending on the specific procedure, individual factors, and the patient’s adherence to post-operative instructions. Generally, the initial few days are focused on healing and managing any pain or discomfort. The recovery period may extend to several weeks, during which patients experience gradual improvements in mobility and energy levels. Dietary adjustments and physical activity are gradually introduced under the guidance of healthcare professionals.
For example, a patient might start with clear liquids and progress to soft foods, gradually increasing the variety and volume of their diet. Physical activity is often introduced slowly, focusing on low-impact exercises.
Nutritional Recommendations and Dietary Restrictions
Proper nutrition is paramount during the post-operative phase. Patients are often initially restricted to a liquid diet, followed by a progression to soft, pureed, and eventually solid foods. The exact progression and restrictions depend on the type of surgery and individual needs. A registered dietitian plays a vital role in providing personalized nutritional guidance and meal planning.
A consistent intake of essential nutrients is crucial to maintain energy levels, support healing, and promote healthy weight management. This may involve specific nutritional supplements to ensure adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and proteins. Patients should closely follow the prescribed dietary plan to avoid complications and achieve optimal results.
Potential Complications and Their Management
While weight loss surgery is generally safe, potential complications can occur. These may include bleeding, infection, leaks in the digestive tract, nutritional deficiencies, and gallstones. Prompt diagnosis and management of these complications are crucial to prevent further health problems. Regular follow-up appointments, prompt reporting of any unusual symptoms, and adherence to prescribed medications are key to managing potential complications effectively.
For example, a patient experiencing persistent nausea or fever should immediately contact their surgeon.
Post-operative Follow-up Care Checklist
This checklist is designed to help patients remember essential post-operative follow-up care:
- Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon and dietitian.
- Report any unusual symptoms, such as pain, fever, or changes in bowel habits, immediately to your healthcare team.
- Adhere strictly to the prescribed dietary guidelines and nutritional supplements.
- Engage in recommended physical activity, gradually increasing intensity as tolerated.
- Practice good oral hygiene to prevent infections.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by making long-term changes in diet and exercise.
- Actively participate in support groups or counseling sessions to address emotional or psychological aspects of the recovery process.
Long-Term Outcomes and Potential Risks
Weight loss surgery can significantly improve health and quality of life, but long-term success hinges on careful planning and ongoing management. This phase encompasses the lasting effects of the procedure, potential complications, strategies for maintaining weight loss, and crucial nutritional considerations. Understanding these factors is essential for patients and healthcare providers to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Long-Term Weight Maintenance
Sustained weight loss after surgery often requires a lifestyle overhaul. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are paramount. Patients need to develop healthy habits that extend far beyond the initial recovery period. Long-term weight loss success stories highlight the importance of consistent adherence to these strategies.
Choosing the right weight loss surgery depends on individual factors, and sometimes considerations like birth control options come into play. For instance, if you’re looking for methods beyond hormonal options, exploring non hormonal birth control options can be important in the long run. Ultimately, understanding the various types of bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, is crucial for making an informed decision.
Potential Complications
Complications following weight loss surgery, while often manageable, can range from mild to severe. Careful monitoring and proactive management are crucial to minimizing these risks. A thorough understanding of the potential complications, including their frequency, is essential for both patients and medical professionals.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Malabsorptive procedures can lead to nutrient deficiencies due to reduced absorption. These deficiencies, such as vitamin B12, iron, or calcium, are often addressed with supplements and regular monitoring. Vitamin D deficiency is also possible. For instance, a patient might need regular vitamin B12 injections or dietary modifications to maintain adequate levels.
- Dumping Syndrome: This is a common complication, especially after restrictive procedures. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, cramping, and diarrhea after eating. Dietary adjustments, such as avoiding sugary or high-fat foods, can help manage these symptoms. For instance, a patient might need to eat smaller, more frequent meals to avoid discomfort.
- Gallstones: Changes in the digestive system can sometimes lead to gallstone formation. Regular check-ups and appropriate management strategies can help prevent or address these issues. For example, a patient might require cholecystectomy (gallbladder removal) if gallstones cause significant problems.
- Wound Healing Problems: Infections or complications related to surgical incisions can occur. Proper wound care and adherence to post-operative instructions are crucial for successful healing. For instance, careful monitoring and prompt treatment of any signs of infection are necessary.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Management
Addressing nutritional deficiencies is crucial for long-term health. A balanced diet, coupled with vitamin and mineral supplementation, can help prevent deficiencies. This necessitates regular blood tests and dietary counseling.
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplements: Regular monitoring and supplementation of crucial vitamins and minerals are often necessary to maintain optimal health. This includes vitamins like vitamin D, B vitamins, and minerals like calcium and iron. For example, a patient might need to take a multivitamin daily, along with specific supplements as recommended by their doctor.
- Dietary Modifications: Adjustments to dietary intake are essential to ensure sufficient intake of key nutrients. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains. For instance, a patient might need to incorporate specific food groups, such as leafy greens, to increase their iron intake.
- Regular Monitoring: Blood tests are frequently conducted to monitor nutrient levels and identify any potential deficiencies early on. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are important. This helps in early detection and intervention.
Long-Term Weight Maintenance Strategies
Long-term weight maintenance requires consistent lifestyle changes. Support groups and behavioral therapy can play a crucial role in helping patients maintain their new lifestyle.
- Dietary Habits: Maintaining a balanced diet and portion control is critical. Consistent consumption of healthy foods and regular meal times help prevent weight gain. For example, a patient might track their food intake using a food diary or a calorie-counting app.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. This includes a combination of cardiovascular exercise and strength training. For example, a patient might engage in brisk walking, jogging, or cycling for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Behavioral Strategies: Addressing emotional eating and developing coping mechanisms for stress are crucial for long-term success. Support groups or counseling can provide valuable assistance. For instance, a patient might learn stress-reduction techniques to avoid emotional eating.
Illustrative Examples of Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss surgery, a life-altering procedure, can lead to significant and sustainable improvements in health for many individuals. However, the success of these procedures varies greatly depending on factors such as patient adherence to post-operative guidelines, lifestyle changes, and individual metabolic responses. Understanding real-life case studies provides valuable insights into the potential outcomes and challenges associated with these procedures.While no two patients are identical, these examples highlight common trends and illustrate the diversity of experiences with weight loss surgery.
The success stories underscore the transformative potential of these procedures, while acknowledging that a multi-faceted approach is crucial for long-term health improvement.
Case Studies of Successful Weight Loss Surgery
These case studies illustrate the potential for successful weight loss surgery. Each patient’s experience is unique, demonstrating the wide range of outcomes and the importance of personalized care.
| Case Study ID | Patient Characteristics | Procedure | Weight Loss (lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS-001 | Female, 35 years old, BMI 42, history of type 2 diabetes and hypertension | Sleeve Gastrectomy | 150 |
| CS-002 | Male, 48 years old, BMI 50, no pre-existing medical conditions | Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass | 185 |
| CS-003 | Female, 28 years old, BMI 38, pre-existing anxiety and depression | Adjustable Gastric Band | 100 |
| CS-004 | Male, 62 years old, BMI 45, pre-existing osteoarthritis and sleep apnea | Sleeve Gastrectomy | 120 |
Case Study CS-001, a 35-year-old female with pre-existing conditions, achieved significant weight loss (150 lbs) after undergoing a sleeve gastrectomy. This outcome demonstrates the positive impact of surgery on co-morbidities such as diabetes and hypertension. Similarly, CS-002, a 48-year-old male, experienced substantial weight loss (185 lbs) following a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, showcasing the effectiveness of this procedure in individuals without pre-existing conditions.
CS-003 highlights that weight loss surgery can be successful even in individuals with psychological factors such as anxiety and depression. Finally, CS-004 illustrates that surgery can be effective for patients with conditions like osteoarthritis and sleep apnea, demonstrating the potential for improved overall health.
Closure
In conclusion, navigating the world of weight loss surgery requires a thorough understanding of the diverse surgical options available. This comprehensive guide has illuminated the different types of procedures, their mechanisms, benefits, and drawbacks. We’ve also explored the crucial pre- and post-operative considerations, providing a framework for informed decision-making. Remember, this information is for educational purposes only, and consulting with a qualified medical professional is essential before making any decisions about weight loss surgery.