Should I take vitamins during cancer treatment? This crucial question weighs heavily on many facing cancer and their families. The nutritional needs of cancer patients are complex, often significantly altered by the disease and its treatments. This exploration delves into the intricate relationship between vitamins, cancer treatment, and overall well-being, offering a comprehensive overview of…
Tag: supplements
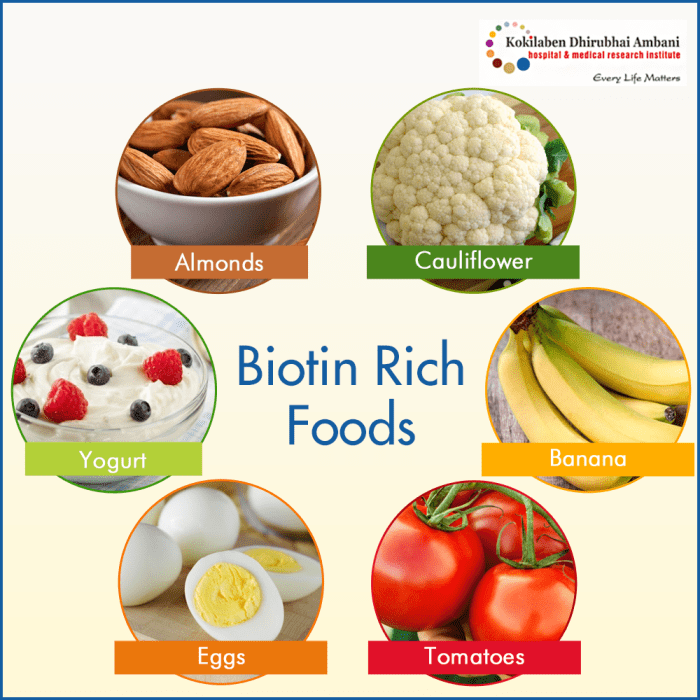
Biotin for Hair Growth A Deep Dive
Biotin for hair growth is a topic of considerable interest, and for good reason. This exploration delves into the fascinating world of biotin, examining its role in supporting not only healthy hair but also overall bodily functions. We’ll uncover the science behind biotin’s impact on hair follicle health, analyze supplementation strategies, and explore factors that…
Magnesium for Muscle Pain A Deep Dive
Magnesium for muscle pain is a crucial topic for understanding the role of this vital mineral in maintaining healthy muscles. Magnesium plays a significant part in muscle function, and deficiencies can lead to a range of issues, including persistent muscle aches and discomfort. This article explores the intricate connection between magnesium and muscle pain, examining…
Fish Oil Supplements AFib Risk A Deep Dive
Fish oil supplements AFib risk is a complex issue, with ongoing research attempting to unravel the potential connections between these dietary supplements and the development of Atrial Fibrillation (AFib). This blog post delves into the science behind fish oil’s purported cardiovascular benefits and examines the existing evidence linking fish oil intake to AFib risk. We’ll…
The Benefits of Carnosine A Deep Dive
The benefits of carnosine, a naturally occurring compound, are increasingly recognized for its potential impact on muscle function, cellular health, and even neurological well-being. This exploration delves into the science behind carnosine, examining its various roles and potential applications. We’ll uncover how carnosine impacts everything from athletic performance to the aging process. Carnosine, a dipeptide…
Using L-Arginine for Health A Comprehensive Guide
Using l arginine for health – Using L-arginine for health is a fascinating area of study, exploring how this amino acid can impact various aspects of well-being. From cardiovascular health to exercise performance, and even erectile function, L-arginine’s potential benefits are extensive. This guide delves into the science behind L-arginine, examining its role in the…
Breastfeeding Supplements What Works & Choosing Wisely
Supplements for breastfeeding what works and how to choose the right ones can be confusing. This guide dives deep into the world of breastfeeding supplements, exploring the potential benefits, risks, and crucial considerations for new mothers. We’ll uncover which supplements might truly support your journey and how to evaluate them safely and effectively. From understanding…
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Gallbladder Issues
Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues offer a range of potential solutions, from dietary changes to herbal remedies. Understanding how these approaches work and their potential benefits, along with potential risks, is key to making informed choices. This exploration delves into various natural strategies for gallbladder support, emphasizing the importance of consulting with a…
Too Much Vitamin D A Deep Dive
Too much vitamin D, while crucial for bone health, can be detrimental if not managed properly. This comprehensive guide delves into the dangers of excessive vitamin D intake, exploring the defining factors, potential sources, and the serious implications for various demographics. We’ll uncover the symptoms, risk factors, and crucial strategies for prevention and management. Understanding…
The Benefits of Rutin Supplements A Deep Dive
The benefits of rutin supplements are gaining traction in health circles. This comprehensive exploration delves into the potential advantages of incorporating rutin into your daily regimen. We’ll examine its sources, forms, dosages, and potential health benefits, while also addressing potential risks and side effects. Rutin, a naturally occurring flavonoid, is found in various fruits and…