Acne and oily skin can be a real challenge, affecting self-esteem and confidence. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, types, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, home remedies, skincare routines, and even how your skin reacts to products. We’ll explore everything from hormonal imbalances and genetics to dietary choices, environmental factors, and stress levels. We’ll cover various…
Tag: skincare
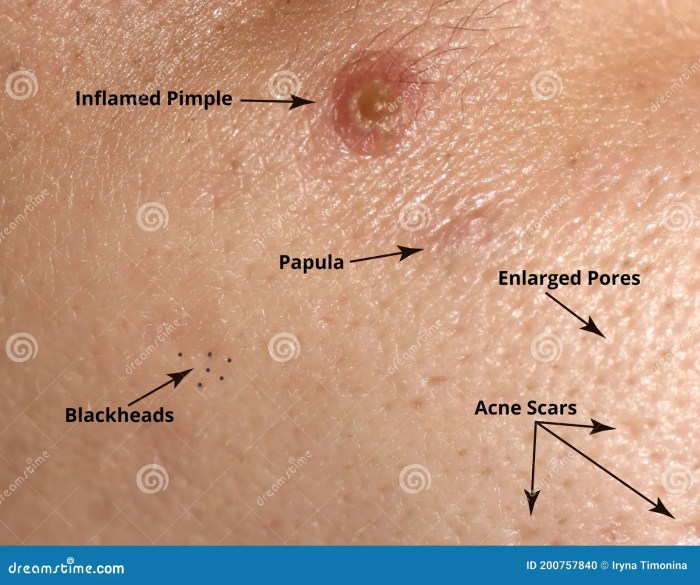
Papule Definition of an Acne Papule A Comprehensive Guide
Papule definition of an acne papule delves into the specifics of this skin condition. Understanding what constitutes an acne papule is key to effective management and treatment. This in-depth exploration covers everything from defining the papule itself to examining its causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Acne papules are small, solid bumps on the skin. They’re…
The Benefits of Emu Oil A Deep Dive
The benefits of emu oil are multifaceted, extending from skincare to potential health applications. Derived from the emu, a large flightless bird native to Australia, this natural oil has garnered significant interest for its purported moisturizing and healing properties. From reducing scars to soothing inflammation, emu oil’s versatility is truly remarkable. This exploration delves into…
The Benefits of Sea Buckthorn A Comprehensive Guide
The benefits of sea buckthorn are truly remarkable. This versatile fruit, known for its rich nutritional profile and diverse applications, has been used for centuries in various cultures. From boosting your immune system to promoting radiant skin, sea buckthorn offers a multitude of potential health advantages. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of…
Is Water Good or Bad for Dry Skin?
Is water good or bad for dry skin? This seemingly simple question delves into a complex relationship between hydration and skin health. Understanding how different types of water interact with various skin types and conditions is crucial for effective skincare. From the hydration benefits of drinking water to the potential drawbacks of harsh water in…
How to Pick a Face Soap Your Guide
How to pick a soap to wash your face is a crucial step in skincare. Different skin types, soap ingredients, and even the formulation itself all play a vital role in achieving healthy, radiant skin. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know, from understanding your skin type to selecting the right…
What is an Esthetician? Unveiling the Profession
What is an esthetician? This profession blends artistry and science, focusing on the beauty and health of the skin. They’re more than just skin deep, possessing a profound understanding of skincare, treatments, and client care. From facials and waxing to product recommendations and consultations, estheticians play a crucial role in promoting healthy skin and boosting…
How to Prevent Acne A Comprehensive Guide
How to prevent acne? This guide dives deep into understanding acne, from its various types and causes to effective prevention strategies. We’ll explore dietary choices, skincare routines, lifestyle habits, and even medical treatments. Get ready to conquer your acne woes and unlock clear, healthy skin! Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions, can be frustrating…
Can I Close My Large Pores? A Deep Dive
Can I close my large pores? This question sparks curiosity and a desire for clearer, smoother skin. Understanding the causes, from genetics to skincare habits, is key to effectively addressing this common concern. We’ll explore various methods, from simple home remedies to professional treatments, and even delve into the science behind pore size and appearance….
Eczema on Face Treatment A Comprehensive Guide
Eczema on face treatment is a crucial aspect of managing this common skin condition. This guide delves into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options, from simple home remedies to professional medical interventions. We’ll explore everything from understanding different types of facial eczema to managing flare-ups and preventing recurrence. Facial eczema can be frustrating and…