Why do scabs itch? This seemingly simple question delves into a fascinating interplay of biology, wound healing, and potential underlying conditions. From the inflammatory response that kicks off wound repair to the nerve endings that signal the itch, there’s a complex process at play. Understanding this process can lead to better management and prevention strategies….
Tag: skin conditions
Skin Boils Picture Gallery Visual Guide
Skin boils picture gallery sets the stage for a comprehensive visual guide to understanding these common skin conditions. This resource will provide clear images and descriptions of skin boils at various stages, helping you identify them accurately. We’ll explore different types, potential causes, and even treatment options. Learn how to distinguish skin boils from similar…
Pagets Disease of the Breast A Comprehensive Guide
Pagets disease of the breast – Paget’s disease of the breast is a rare skin condition that often presents as a rash or eczema-like lesion on the nipple or areola. Understanding this condition, from its characteristics to treatment options, is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of…
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Home Remedies A Guide
Hidradenitis suppurativa home remedies offer a potential path toward managing this chronic skin condition. This guide explores various approaches, from natural ingredients to lifestyle changes, to provide a comprehensive overview. We’ll delve into potential benefits and drawbacks, along with essential considerations before trying any home remedy. Understanding the nuances of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is crucial…
Four Skin Conditions That Make Your Feet Itch
Four skin conditions that make your feet itch can be incredibly frustrating. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms is key to finding relief. This guide explores athlete’s foot, eczema, psoriasis, and other fungal infections, providing detailed information about each condition, including symptoms, causes, treatments, and preventative measures. We’ll also discuss home remedies and when to…
Sebaceous Hyperplasia Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Sebaceous hyperplasia causes symptoms and treatments are explored in detail. This comprehensive guide dives into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for sebaceous hyperplasia, a common skin condition. We’ll examine the underlying reasons for its development, the visible signs it presents, and the different approaches to managing it. Understanding this condition empowers individuals to…
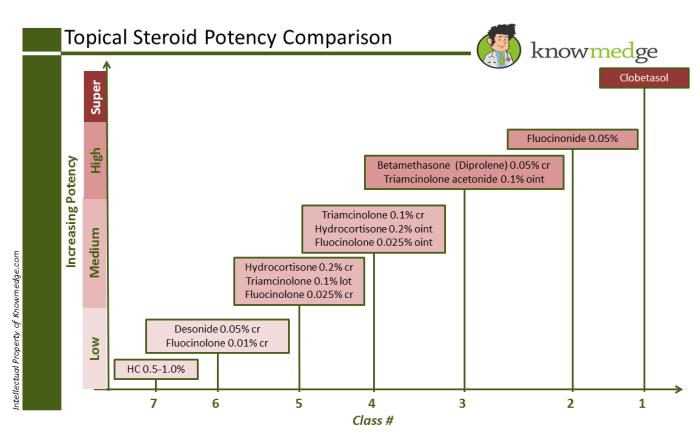
Steroids Topical Steroid Strengths A Deep Dive
Steroids topical steroid strengths are crucial for treating various skin conditions. This guide delves into the different potencies, their applications, and potential side effects. Understanding the strengths and appropriate usage is vital for effective treatment and minimizing adverse reactions. We’ll explore the diverse range of skin conditions treatable with topical steroids, examining the factors determining…
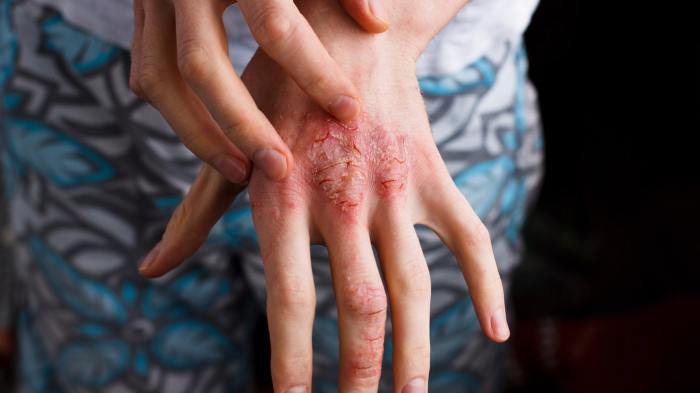
Treating Psoriasis on Hands and Feet A Comprehensive Guide
Treating psoriasis on your hands and feet can be a challenging journey, but understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. This guide delves into the intricacies of hand and foot psoriasis, providing a comprehensive overview of its causes, symptoms, and a range of treatment approaches, from topical medications…
Common Foot Skin Problems A Deep Dive
Common foot skin problems affect many people, from athletes to the elderly. This comprehensive guide explores the various types, causes, symptoms, and effective prevention and treatment strategies. Understanding these issues is key to maintaining healthy feet and preventing discomfort and potential complications. We’ll cover everything from identifying different types of foot skin conditions to the…
Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema A Deep Dive
Atopic dermatitis vs eczema – are they the same thing? This exploration delves into the similarities and differences between these skin conditions, highlighting their often-overlapping nature. We’ll uncover the historical understanding, examine the underlying causes, and explore the nuances of diagnosis and management. Understanding these distinctions is key to providing the best possible care for…