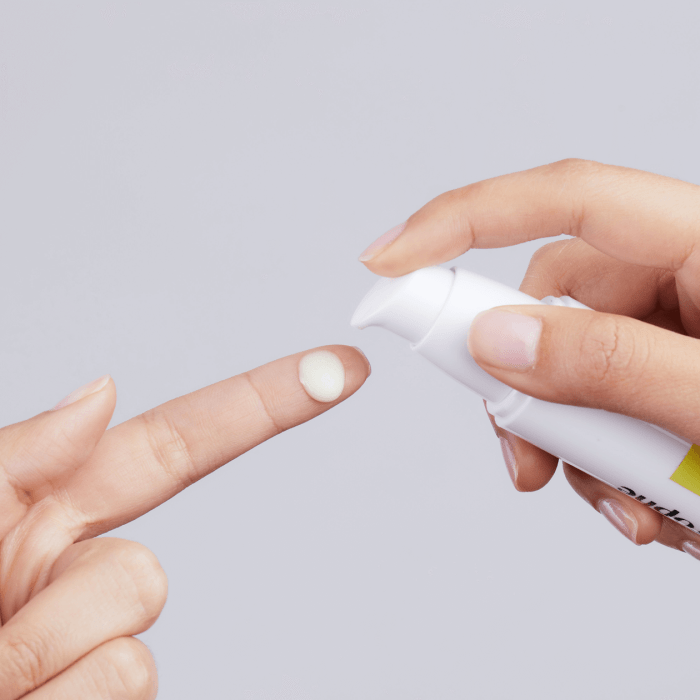
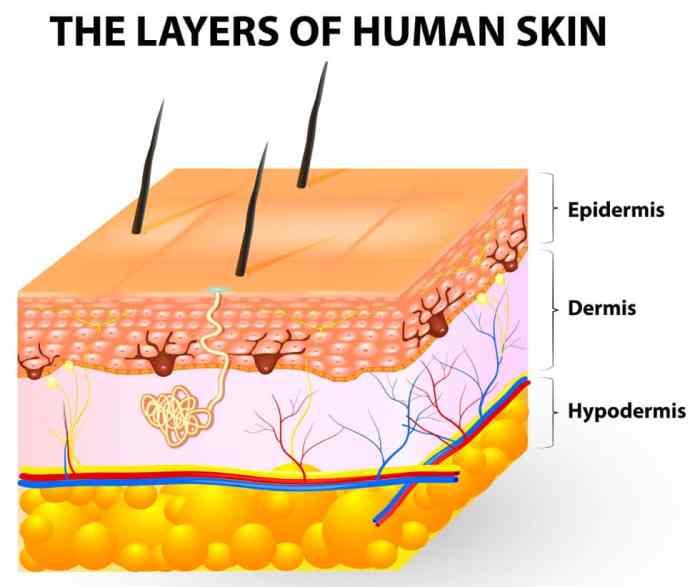
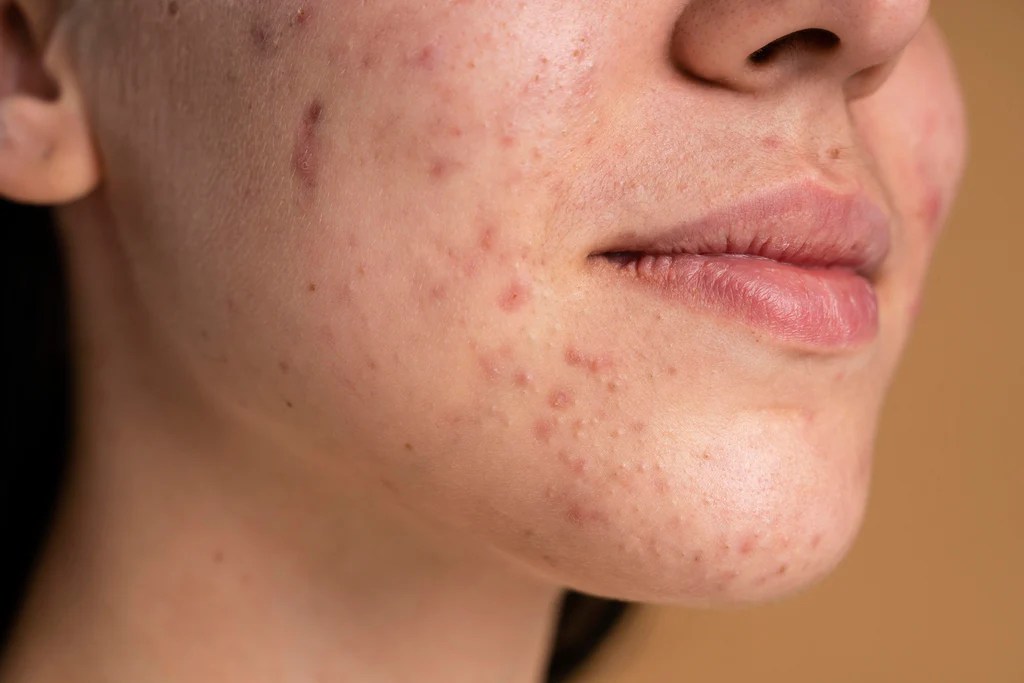
Tips for using benzoyl peroxide are crucial for effective acne treatment. This guide delves into everything you need to know about applying this common acne medication, from understanding its different strengths and forms to navigating potential side effects and combination therapies. We’ll cover proper application techniques, how to choose the right strength for your skin…
Tag: skin care
How to Get Rid of Peeling Skin A Comprehensive Guide
How to get rid of peeling skin? This comprehensive guide delves into the various causes, home remedies, medical treatments, and preventive measures for this common skin issue. From understanding the different types of peeling to exploring dietary considerations and tailored skincare routines, we’ll cover everything you need to know to restore healthy, smooth skin. We’ll…
How Often Should I Wash My Face? Your Guide
How often should I wash my face? This question plagues many, but the answer isn’t one-size-fits-all. Your skin type, daily activities, and even the environment play a crucial role in determining the ideal washing frequency. This guide delves into the factors affecting your face-washing routine, offering personalized insights for healthy skin. We’ll explore various skin…
What are Skin Tag Patches? A Comprehensive Guide
What are skin tag patches? They’re small, adhesive plasters designed to cover and potentially resolve skin tags. This comprehensive guide explores various types, application methods, ingredients, effectiveness, safety precautions, and comparisons to other removal methods. We’ll delve into the science behind these patches, offering a clear picture of their benefits and drawbacks. Learn everything you…
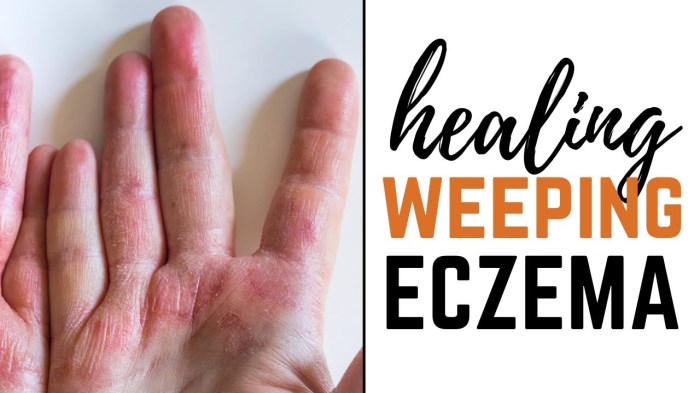
Weeping Eczema Overview and More
Weeping eczema overview and more delves into the complexities of this skin condition, offering a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and management. We’ll explore everything from the underlying triggers to effective treatments and preventive strategies. Prepare to gain valuable insights into this common yet often challenging skin issue. This comprehensive guide covers the full…
Hypochlorous Acid Acne Body Odor A Deep Dive
Hypochlorous acid acne body odor is a topic gaining traction as a potential new treatment. This in-depth exploration examines the science behind HOCl, its potential benefits and risks for acne and body odor, and compares it to existing methods. We’ll delve into the chemical properties of HOCl, its mechanisms of action, and crucial safety considerations….
Sebaceous Hyperplasia Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Sebaceous hyperplasia causes symptoms and treatments are explored in detail. This comprehensive guide dives into the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for sebaceous hyperplasia, a common skin condition. We’ll examine the underlying reasons for its development, the visible signs it presents, and the different approaches to managing it. Understanding this condition empowers individuals to…
Best Sunscreen for Tattoos A Comprehensive Guide
What is the best sunscreen for tattoos? This in-depth guide explores the crucial considerations for protecting your ink from the sun’s harmful rays. We’ll delve into different sunscreen types, discuss crucial factors influencing your choice, and provide practical application techniques. From understanding the various ingredients in sunscreens to identifying potential issues and solutions, this guide…
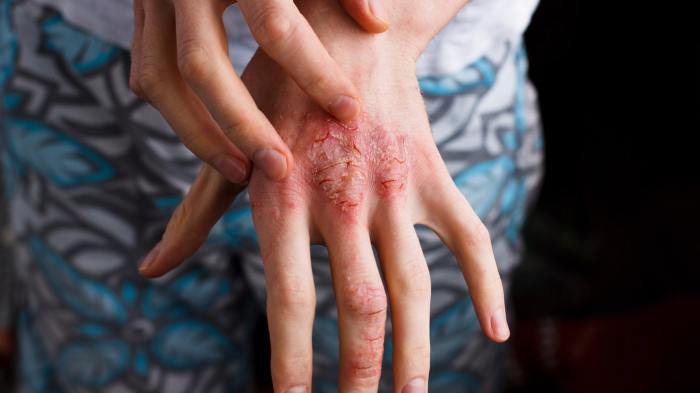
Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema A Deep Dive
Atopic dermatitis vs eczema – are they the same thing? This exploration delves into the similarities and differences between these skin conditions, highlighting their often-overlapping nature. We’ll uncover the historical understanding, examine the underlying causes, and explore the nuances of diagnosis and management. Understanding these distinctions is key to providing the best possible care for…
Do You Have Rosacea, Psoriasis, or Eczema?
Do you have rosacea psoriasis or eczema – Do you have rosacea, psoriasis, or eczema? This guide dives deep into the symptoms, differences, and diagnostic considerations for these common skin conditions. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of each, comparing their appearances, triggers, and typical patterns. Understanding these conditions is crucial for proper self-care and seeking…