Can arthritis shorten your lifespan? This question delves into the complex relationship between arthritis and overall health. Different types of arthritis, like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, impact daily life in various ways, from mobility to overall well-being. Understanding the potential effects on physical function, mental health, and nutrition is crucial in comprehending how arthritis might…
Tag: rheumatoid arthritis
DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Comprehensive Guide
DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis are a crucial part of managing this chronic autoimmune disease. These disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs work to slow or halt the progression of the disease, improving quality of life for those affected. This guide explores the various types of DMARDs, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and treatment strategies, empowering…
Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis A Deep Dive
Types of rheumatoid arthritis sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complexities of this chronic autoimmune disease. We’ll explore the various forms of rheumatoid arthritis, examining their unique characteristics, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types is crucial for effective management and a better quality of life. This…
Collagen for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Deep Dive
Collagen for rheumatoid arthritis: Understanding this potential treatment option requires a deep dive into the complexities of both conditions. Rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease, attacks the body’s own tissues, particularly the joints. This inflammation can lead to significant pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. The body’s natural collagen production, crucial for joint health, may be…
Rheumatoid Arthritis vs Arthritis A Deep Dive
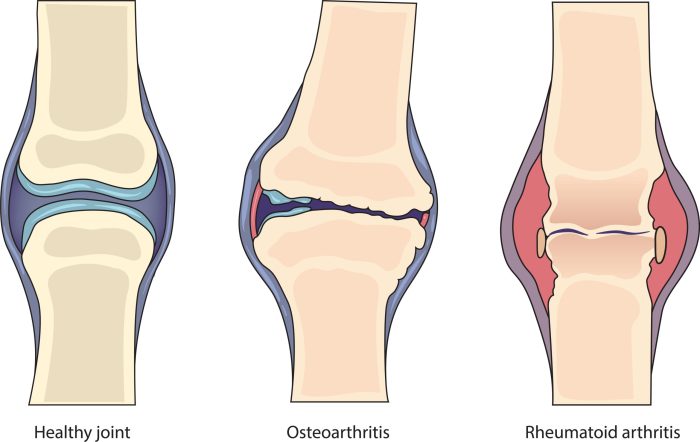
Rheumatoid arthritis vs arthritis: Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for effective management and treatment. This comprehensive overview explores the nuances of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), contrasting it with general arthritis, to provide a clearer picture of these often-confused ailments. We’ll delve into their causes, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options, offering a practical…
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment Not Working A Guide
Rheumatoid arthritis treatment not working can be incredibly frustrating. It’s a journey filled with emotional ups and downs, where hope clashes with disappointment. This guide delves into the complexities of ineffective treatment, offering practical strategies for navigating the challenges and exploring alternative pathways. Understanding the reasons why a treatment isn’t working is crucial. We’ll explore…
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Shingles Vaccine A Deep Dive
Rheumatoid arthritis and shingles vaccine sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complexities of navigating health decisions when facing both conditions. This exploration delves into the potential interactions, immunological considerations, and clinical trials surrounding these two health concerns. We’ll unpack the specifics of each condition, analyze possible interactions between…
Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Neck Understanding the Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis in the neck can significantly impact your quality of life, causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Understanding the specific ways RA affects the cervical spine, along with its symptoms and treatment options, is crucial for effective management. This guide delves into the complexities of rheumatoid arthritis in the neck, providing a comprehensive overview…
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis Flares A Deep Dive
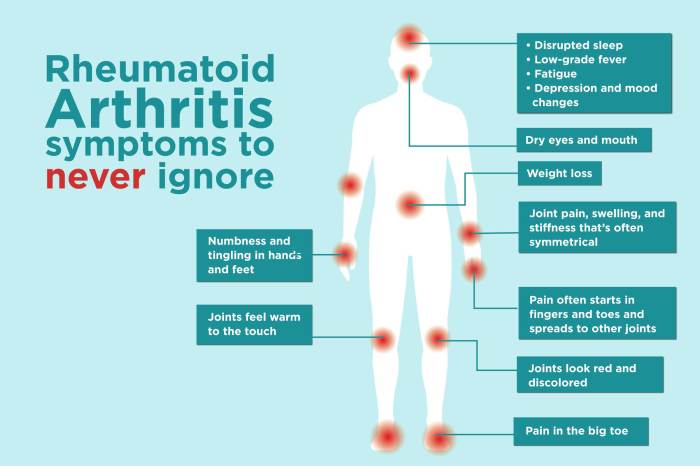
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis flares sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complexities of this chronic condition. We’ll explore the various symptoms, their progression, and triggers, shedding light on how flares impact daily life. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life. This comprehensive…
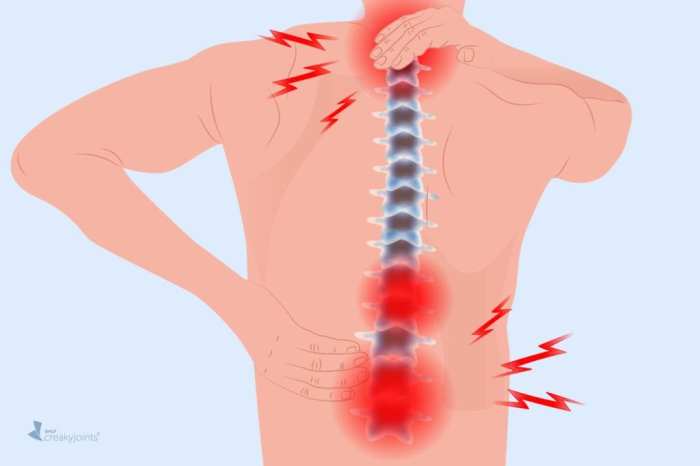
Rheumatoid Arthritis Back Pain Understanding the Impact
Rheumatoid arthritis back pain is a complex condition that significantly impacts a person’s life. It’s not just about aches and stiffness; it’s about understanding the underlying mechanisms, the various symptoms, and the available treatment options. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of RA back pain, providing a detailed overview of its causes, diagnosis, and…