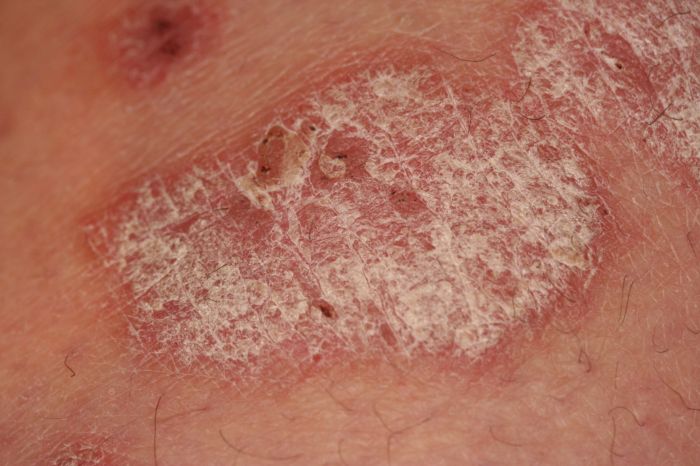
How to get rid of peeling skin? This comprehensive guide delves into the various causes, home remedies, medical treatments, and preventive measures for this common skin issue. From understanding the different types of peeling to exploring dietary considerations and tailored skincare routines, we’ll cover everything you need to know to restore healthy, smooth skin. We’ll…
Tag: psoriasis
Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Psoriasis A Guide
Anti inflammatory diet for psoriasis – Anti-inflammatory diet for psoriasis is a powerful approach to managing this chronic skin condition. It’s not just about avoiding certain foods, but about understanding how your diet directly impacts inflammation and your psoriasis symptoms. This comprehensive guide explores the principles, food choices, and practical strategies to create a personalized…
Conversation Issues Discussing Psoriasis A Deep Dive
Conversation issues discussing psoriasis are complex, encompassing a wide range of challenges faced by those living with the condition. This exploration delves into the nuances of communication, from understanding the emotional toll to navigating difficult conversations in various settings, including family, friendships, and the workplace. We’ll also examine the crucial role of support communities and…
Four Skin Conditions That Make Your Feet Itch
Four skin conditions that make your feet itch can be incredibly frustrating. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms is key to finding relief. This guide explores athlete’s foot, eczema, psoriasis, and other fungal infections, providing detailed information about each condition, including symptoms, causes, treatments, and preventative measures. We’ll also discuss home remedies and when to…
Skin Pain in Psoriasis A Deep Dive
Skin pain in psoriasis is a significant concern for many sufferers, impacting their daily lives and overall well-being. This detailed exploration delves into the various types of pain, their mechanisms, and the factors that exacerbate them. We’ll also examine the profound impact on daily routines, mental health, and social interactions. Further, we’ll discuss diagnosis, management…
Treating Psoriasis on Hands and Feet A Comprehensive Guide
Treating psoriasis on your hands and feet can be a challenging journey, but understanding the condition and exploring various treatment options is crucial for managing symptoms effectively. This guide delves into the intricacies of hand and foot psoriasis, providing a comprehensive overview of its causes, symptoms, and a range of treatment approaches, from topical medications…
Do You Have Rosacea, Psoriasis, or Eczema?
Do you have rosacea psoriasis or eczema – Do you have rosacea, psoriasis, or eczema? This guide dives deep into the symptoms, differences, and diagnostic considerations for these common skin conditions. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of each, comparing their appearances, triggers, and typical patterns. Understanding these conditions is crucial for proper self-care and seeking…
Cosmetic Treatments for Psoriasis A Comprehensive Guide
Cosmetic treatments with psoriasis are gaining increasing attention as individuals seek solutions to improve not only the medical aspects of the condition but also its impact on their appearance. This comprehensive guide delves into various approaches, from topical medications to advanced procedures, considering both the physical and psychological well-being of those affected by psoriasis. We’ll…
Ask an Expert Creative Psoriasis Management
Ask an expert creative ways to manage psoriasis: This comprehensive guide delves into a wide range of strategies, from understanding the nuances of psoriasis to exploring innovative lifestyle modifications and cutting-edge treatments. We’ll explore everything from the basics of psoriasis, its diverse types, and contributing factors, to the latest in topical therapies, phototherapy, and systemic…
Psoriasis and Your Life A Deep Dive
Psoriasis and your life intertwine in profound ways, impacting everything from daily routines to emotional well-being. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of living with psoriasis, offering insights into its effects, treatment options, and the importance of coping strategies. We’ll navigate the challenges and triumphs of managing this condition, emphasizing the journey of adaptation…