Fat vs water soluble vitamins are crucial for our health, playing distinct roles in the body. Understanding their differences in absorption, storage, and function is key to maintaining optimal well-being. This exploration delves into the unique characteristics of each type, examining their absorption mechanisms, storage capacities, and dietary sources. We’ll also explore potential interactions and…
Tag: nutrition
Are Brussels Sprouts Good for You?
Are brussel sprouts good for you – Are Brussels sprouts good for you? This exploration delves into the nutritional powerhouse that is the Brussels sprout, examining its vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and potential health benefits. We’ll cover everything from the sprout’s impressive nutritional profile to various culinary uses, potential drawbacks, and comparisons to other cruciferous vegetables….
How to Follow a Gastroparesis Diet A Guide
How to follow a gastroparesis diet is crucial for managing this digestive condition. Gastroparesis slows the emptying of food from your stomach, impacting everything from digestion to nutrient absorption. This detailed guide offers practical strategies for navigating a gastroparesis diet, from understanding the principles to crafting personalized meal plans. The following sections will cover essential…
Is Beef Jerky Healthy? A Deep Dive
Is beef jerky healthy? This question sparks a fascinating exploration into the nutritional landscape of this popular snack. We’ll delve into the nutritional profile, scrutinize processing methods, and weigh the potential health benefits against the risks. From the protein content to the sodium load, we’ll cover everything you need to know to make an informed…
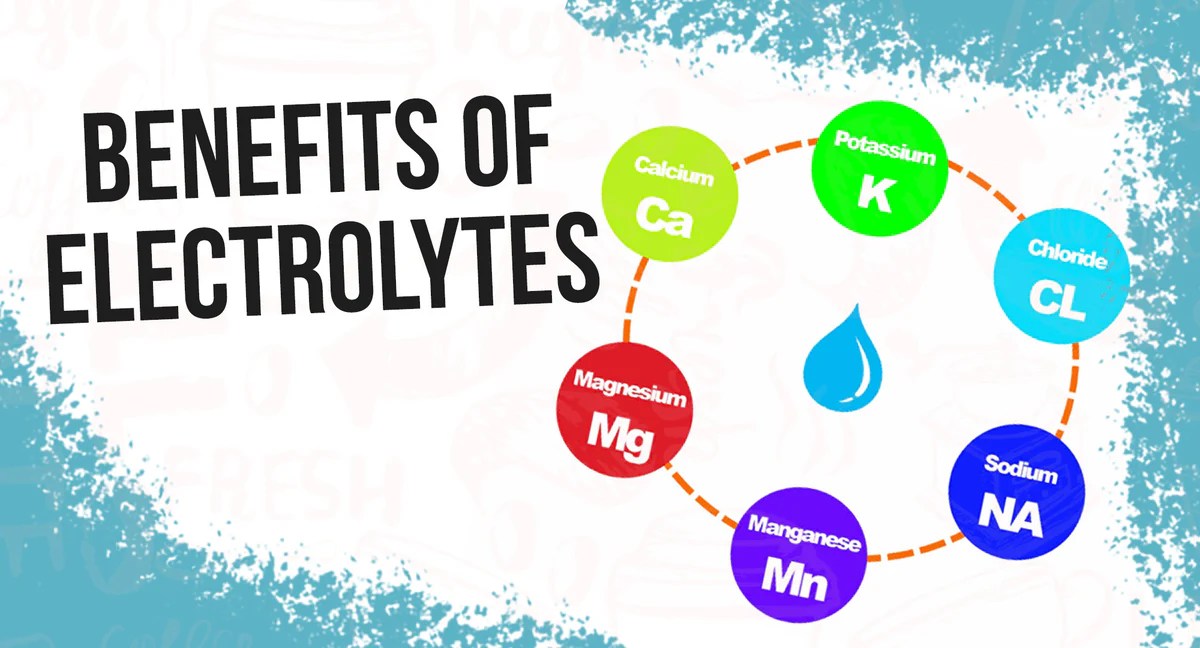
What Happens When Your Body Is Low on Electrolytes
What happens when your body is low on electrolytes sets the stage for a fascinating exploration into the vital role these minerals play in our well-being. Electrolytes, essential minerals like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, are crucial for a multitude of bodily functions. From nerve impulses to muscle contractions, and from hydration to blood pressure…
Two Dates a Day for Health Benefits A Deep Dive
Two dates a day for health benefits: This post explores the potential advantages of incorporating two dates daily into your diet. From understanding the nutritional powerhouse that dates are, to learning how to incorporate them into various meals and snacks, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll examine different date types, preparation methods, potential…
Watercress Benefits A Nutrition Profile
Watercress benefits and nutrition profile sets the stage for an exploration of this vibrant leafy green. From its historical uses to its modern-day health advantages, we’ll delve into the nutritional value, potential health benefits, and various ways to enjoy this versatile ingredient. Discover the surprising wealth of nutrients packed within each bite. This comprehensive guide…
Vitamins to Avoid with Blood Pressure
Vitamins to avoid with blood pressure are crucial for managing hypertension. Certain vitamins, while generally beneficial, can sometimes elevate blood pressure in susceptible individuals. Understanding which vitamins might be problematic, and how to navigate these nuances safely, is key to maintaining cardiovascular health. A balanced diet, coupled with informed decisions about vitamin intake, is essential…
Can You Overdose on Vitamins? A Deep Dive
Can you overdose on vitamins? This crucial question delves into the potential dangers of excessive vitamin intake. Vitamins are essential for bodily functions, but like any substance, too much can be detrimental. Understanding the potential for overdose, the mechanisms behind toxicity, and the symptoms involved is key to making informed choices about your health and…
What to Eat After Food Poisoning A Guide
What to eat after food poisoning? This guide provides a comprehensive overview of safe foods to consume after experiencing food poisoning. It delves into the types of food poisoning, immediate actions to take, and dietary considerations. We’ll explore foods to eat and avoid, covering everything from hydration to recovery, and even preventative measures to avoid…