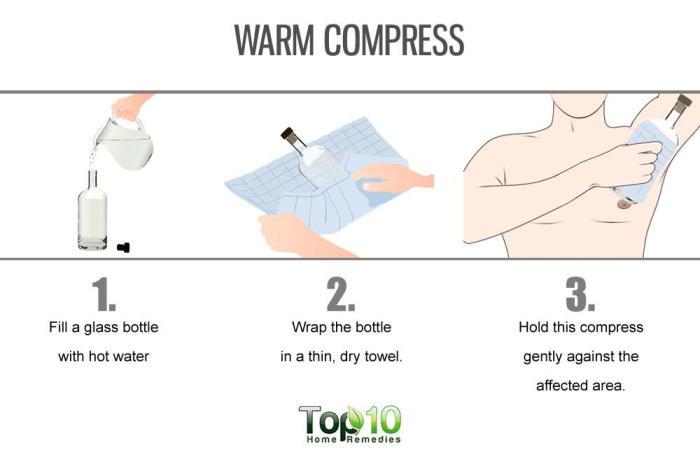
How to reverse atrial fibrillation naturally is a crucial question for many seeking alternative or complementary approaches to managing this condition. This guide delves into potential lifestyle modifications, dietary recommendations, herbal remedies, nutritional considerations, and mind-body practices that may help. We’ll explore various strategies, but remember that natural remedies are not a substitute for professional…
Tag: natural remedies
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Home Remedies A Guide
Hidradenitis suppurativa home remedies offer a potential path toward managing this chronic skin condition. This guide explores various approaches, from natural ingredients to lifestyle changes, to provide a comprehensive overview. We’ll delve into potential benefits and drawbacks, along with essential considerations before trying any home remedy. Understanding the nuances of Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is crucial…
The Benefits of Hawthorn A Comprehensive Guide
The benefits of hawthorn, a versatile plant with a rich history, are now being explored more deeply than ever. From its traditional use in various cultures to modern scientific research, hawthorn’s potential for promoting cardiovascular health and well-being is truly remarkable. This comprehensive guide delves into the different aspects of hawthorn, examining its nutritional profile,…
The Health Benefits of Boswellia A Deep Dive
The health benefits of boswellia, a resinous extract from the Boswellia tree, have captivated herbalists and health enthusiasts for centuries. This ancient remedy, often used in traditional medicine, boasts a range of potential applications, from easing arthritis pain to supporting digestive health. We’ll explore the science behind this intriguing plant, delving into its anti-inflammatory properties,…
Natural Remedies and Supplements for Gallbladder Issues
Natural remedies and supplements for gallbladder issues offer a range of potential solutions, from dietary changes to herbal remedies. Understanding how these approaches work and their potential benefits, along with potential risks, is key to making informed choices. This exploration delves into various natural strategies for gallbladder support, emphasizing the importance of consulting with a…
The Benefits of Emu Oil A Deep Dive
The benefits of emu oil are multifaceted, extending from skincare to potential health applications. Derived from the emu, a large flightless bird native to Australia, this natural oil has garnered significant interest for its purported moisturizing and healing properties. From reducing scars to soothing inflammation, emu oil’s versatility is truly remarkable. This exploration delves into…
Benefits of Essential Oils A Deep Dive
Benefits of essential oils are gaining popularity, and this comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of these natural extracts. From their ancient uses to modern scientific research, we’ll explore their origins, properties, potential benefits, and crucial safety considerations. Understanding the diverse ways essential oils can impact our well-being requires a nuanced approach, so let’s…
Can Lysine Help Heal Cold Sores?
Can lysine help to heal cold sores? This question sparks intrigue, delving into the potential of this amino acid to combat the pesky herpes simplex virus. We’ll explore the science behind lysine’s role, compare it to other treatments, and weigh the potential benefits and risks of supplementation. Understanding the evidence is key to making informed…
Ashwagandha Benefits, Side Effects, and More
Ashwagandha benefits side effects and more – Delving into ashwagandha benefits, side effects, and more, this introduction immerses readers in a comprehensive exploration of this ancient adaptogen. From its historical use to modern research, we’ll uncover the potential benefits and potential risks associated with ashwagandha. We’ll also examine dosage recommendations, precautions, and interactions with other…
Carrot Juice for Tan Myth or Magic?
Carrot juice for tan sets the stage for a fascinating exploration into the potential link between consuming carrots and achieving a sun-kissed complexion. We’ll delve into the science behind this age-old belief, examining the nutritional components of carrots and comparing them to sun-protective skin products. The journey promises to uncover the truth behind this popular…