Solu Medrol for MS provides a potent anti-inflammatory approach to managing multiple sclerosis (MS). This guide delves into the intricacies of its use, from acute exacerbations to long-term management. Understanding the mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and patient considerations is crucial for effective treatment strategies. The article explores the role of inflammation in MS…
Tag: medication
Alcohol & Arthritis Drugs Is It Forbidden?
Is alcohol forbidden when taking arthritis drugs? This crucial question impacts many people living with arthritis, demanding careful consideration of potential interactions. Different arthritis medications interact with alcohol in various ways, and understanding these interactions is vital for safe and effective treatment. This post will delve into the potential risks and benefits, providing valuable insights…
Topamax Topiramate for Weight Loss A Comprehensive Guide
Topamax topiramate for weight loss is a controversial topic, and understanding its potential benefits and risks is crucial. This guide delves into the science behind Topamax’s effect on weight, examining clinical trials, patient experiences, and medical professional recommendations. We’ll explore the mechanisms of action, dosage, potential side effects, and compare Topamax to other weight loss…
How Long Does Valium Take to Work?
How long does it take Valium to work? This question is crucial for anyone considering or currently taking this medication. Valium, or diazepam, is a powerful benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizures. Understanding the factors influencing its onset of action is key to managing expectations and ensuring optimal results. Different factors like…
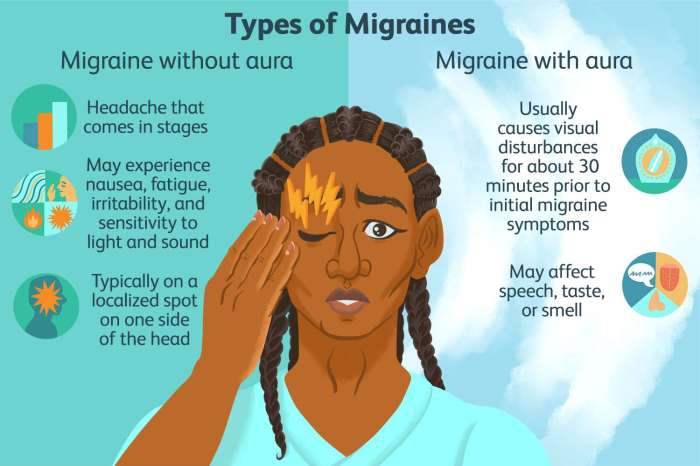
Episodic Migraine Prevention Medications A Guide
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a crucial aspect of managing these debilitating headaches. This guide delves into the various types of preventative treatments, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and important considerations for patient selection. We’ll explore everything from CGRP inhibitors to beta-blockers, providing a comprehensive overview to help you understand the best…
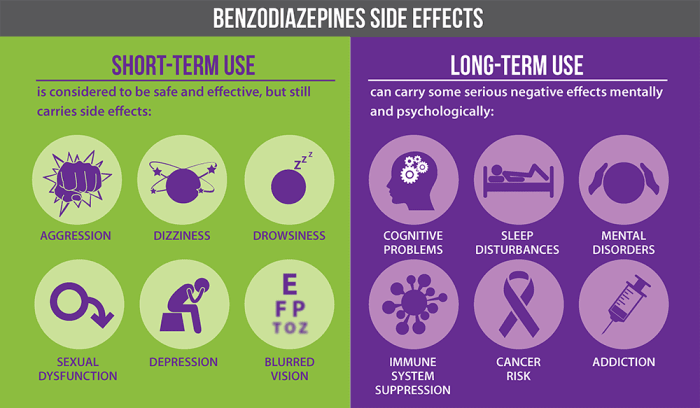
Benzodiazepines Uses, Types, and Risks
Uses types and risks of benzodiazepines – Benzodiazepines: Uses, Types, and Risks sets the stage for a detailed exploration of these medications. This in-depth look will cover everything from their chemical makeup and mechanism of action to their various applications, potential dangers, and long-term considerations. We’ll analyze different types, examining their potency, duration, and common…
DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis A Comprehensive Guide
DMARDs for rheumatoid arthritis are a crucial part of managing this chronic autoimmune disease. These disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs work to slow or halt the progression of the disease, improving quality of life for those affected. This guide explores the various types of DMARDs, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and treatment strategies, empowering…
Side Effects of Statins A Comprehensive Guide
Side effects of statins can range from mild discomfort to serious health concerns. This comprehensive guide delves into the potential side effects of statins, exploring everything from common issues like muscle pain to less frequent but potentially severe complications. We’ll cover the science behind these effects, discuss factors that influence their occurrence, and provide practical…
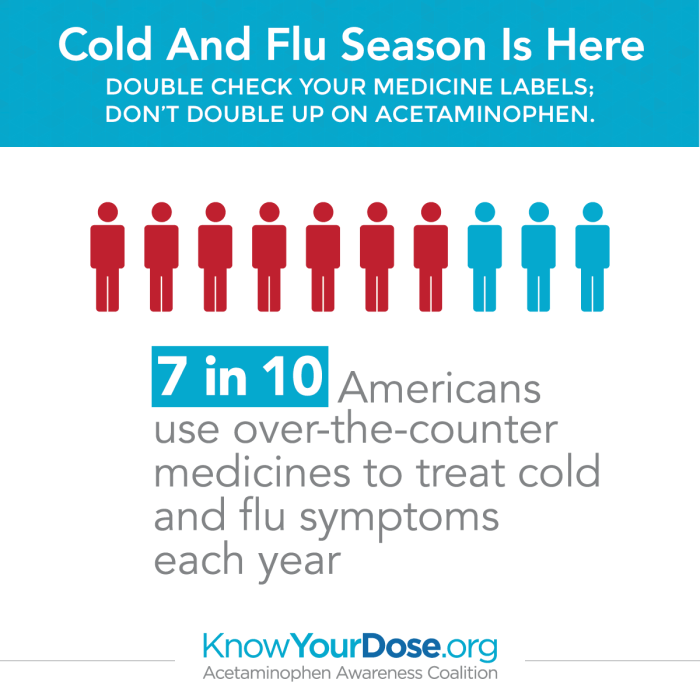
Overdosing on Cold and Flu Medications A Guide
Overdosing on cold and flu medications is a serious issue that can have severe consequences. Many people take these medications without fully understanding the risks involved. This guide explores the dangers of exceeding recommended dosages, detailing the various types of cold and flu medications prone to overdose, potential symptoms, and steps to take in case…
Can You Drink Alcohol While Taking Viagra?
Can you drink alcohol while taking Viagra? This question is important for anyone considering combining these substances. Understanding the potential interactions between alcohol and Viagra is crucial for responsible use and to ensure your well-being. This article delves into the possible interactions, the importance of medical advice, safety precautions, alternative options, and dosage information, providing…