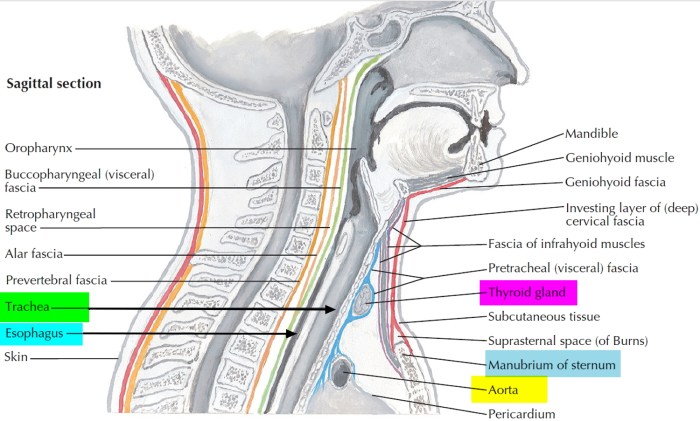
Trachea function and conditions and diagram provides a comprehensive overview of the windpipe, its crucial role in respiration, and the various conditions that can affect it. We’ll explore its intricate structure, examining how air travels through it, its impact on the overall respiratory system, and the diseases that can impact this vital part of our…
Tag: health
Can Coconut Oil Cause Yeast Infections?
Can coconut oil cause yeast infections? This question is frequently asked, and the answer isn’t as straightforward as some might claim. Coconut oil, with its purported health benefits, has sparked interest as a potential remedy for various ailments, including yeast infections. However, the scientific evidence surrounding its efficacy and potential side effects needs careful consideration….
Ask an Expert HIV Support Groups
Ask an expert HIV support groups sets the stage for a deep dive into the crucial world of support for those living with HIV. We’ll explore the different types of groups, from online forums to in-person meetings, and examine the vital role of members and facilitators. This journey delves into finding the right support, addressing…
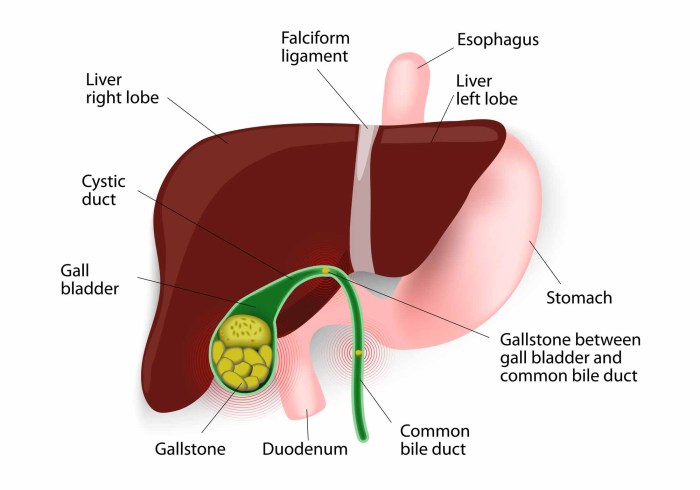
Gallbladder Disease Causes and Risk Factors
Gallbladder disease causes and risk factors are multifaceted, encompassing lifestyle choices, genetics, and underlying medical conditions. Understanding these elements is crucial for proactive health management. This exploration delves into the interplay of diet, obesity, family history, and other influences that contribute to gallbladder issues. We’ll examine the role of various factors in increasing your risk…
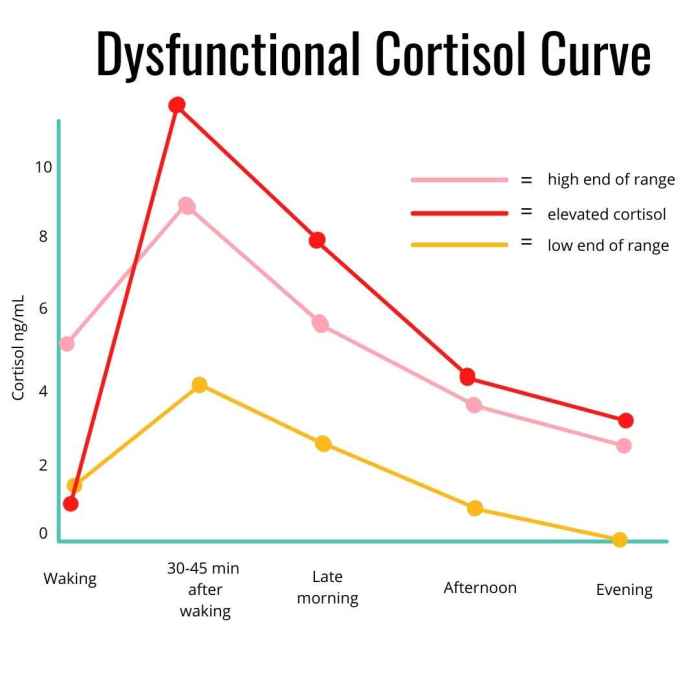
How to Lower Cortisol Your Guide
How to lower cortisol is a crucial question for anyone experiencing stress or its negative health effects. This comprehensive guide dives deep into understanding the complexities of cortisol, identifying potential causes of elevated levels, and exploring natural and lifestyle adjustments for effective management. We’ll cover everything from understanding cortisol’s role in the body to specific…
Do Fevers Cause Brain Damage? Exploring the Risks
Do fevers cause brain damage? This question is a crucial one for parents and healthcare professionals alike. While fevers are a natural part of the immune response, understanding the potential risks and protective factors is key to ensuring a healthy outcome. This blog post delves into the complex relationship between fever and brain damage, exploring…
Is White Bread Bad for You? A Deep Dive
Is white bread bad for you? This question delves into the nutritional profile, potential health risks, and even the cultural context surrounding this seemingly simple food. We’ll explore the nutritional breakdown, examining carbohydrates, protein, and vitamins, and comparing it to whole-wheat alternatives. We’ll also discuss the glycemic index, potential weight gain concerns, and digestive health…
What is a Carcinogen Understanding the Dangers
What is a carcinogen? It’s a substance that can cause cancer. This exploration delves into the science behind these harmful compounds, from their various classifications to the long-term health effects they can trigger. We’ll uncover the mechanisms by which carcinogens damage DNA, examine the sources of exposure, and discuss strategies for prevention and mitigation. Understanding…
Coughing Up Mucus COVID Understanding the Symptoms
Coughing up mucus COVID is a significant concern for those affected. This detailed exploration delves into the characteristics of this symptom, examining the various consistencies, colors, and volumes of mucus produced throughout the illness. We’ll compare it to other respiratory ailments, offering a clear picture of what to expect. Understanding the different stages and how…
Best Time of Day for Vitamin D
Best time of day to take vitamin D is a crucial question for maximizing its benefits. Factors like sunlight exposure, dietary habits, and individual health conditions all play a role in how well your body absorbs vitamin D. This exploration delves into the science behind optimal vitamin D intake, from understanding circadian rhythms to the…