Side effects of statins can range from mild discomfort to serious health concerns. This comprehensive guide delves into the potential side effects of statins, exploring everything from common issues like muscle pain to less frequent but potentially severe complications. We’ll cover the science behind these effects, discuss factors that influence their occurrence, and provide practical…
Tag: health
What are these spots on my MRI?
What are these spots on my MRI? This question is understandably unsettling, and it’s completely valid to want clear answers about these markings. An MRI, a powerful diagnostic tool, uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Understanding the purpose of the scan, the types of scans, and…
How Long Do Short People Live? Unveiling the Truth
How long do short people live? This question delves into the complex relationship between height, health, and lifespan. While simple correlations might appear, a deeper exploration reveals the interwoven factors of genetics, environment, culture, and societal influences. The narrative explores a range of perspectives, from defining “short” across demographics and time periods to examining potential…
What is a Pathogen? A Deep Dive
What is a pathogen? This exploration delves into the fascinating world of disease-causing organisms, from the microscopic to the complex. We’ll unravel the mysteries behind these tiny invaders, examining their structures, functions, and the intricate ways they interact with their hosts. Understanding pathogens is crucial for comprehending human health and developing effective strategies to combat…
Asthmas Daily Impact Expert Insights
Ask an expert how does asthma impact daily life? This exploration delves into the multifaceted ways asthma affects everyday routines, from physical exertion and sleep to social interactions and mental well-being. We’ll examine how varying asthma severities influence daily life, and uncover practical strategies for managing symptoms and challenges. From the subtle impact on sleep…
Charmayne Andersons Asthma Journey A Personal Account
Charmayne anderson my personal journey with asthma – Charmayne Anderson’s My Personal Journey with Asthma takes readers on a deeply personal exploration of living with this chronic condition. From the initial diagnosis to the daily challenges and triumphs, Charmayne shares her experiences with honesty and vulnerability. This journey is not just about managing symptoms; it’s…
My Familys Asthma Journey A Personal Account
My family s journey with asthma – My family’s journey with asthma sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with personal experiences. We delve into the initial diagnosis, the challenges faced, and the ways we adapted our lives to manage this…
5 Components of Fitness Your Complete Guide
5 components of fitness sets the stage for a deep dive into the essential elements of a healthy lifestyle. This isn’t just about looking good; it’s about feeling amazing and achieving peak physical performance. From understanding the basics to crafting personalized workout routines, we’ll explore each component in detail, offering practical advice and insights. This…
Quiz Are You Eligible to Donate Blood?
Quiz are you eligible to donate blood – Quiz: Are you eligible to donate blood? This comprehensive guide dives into the fascinating world of blood donation, exploring the eligibility criteria, pre-donation screening, common reasons for ineligibility, and everything you need to know about preparing for and recovering from the process. Whether you’re curious about donating…
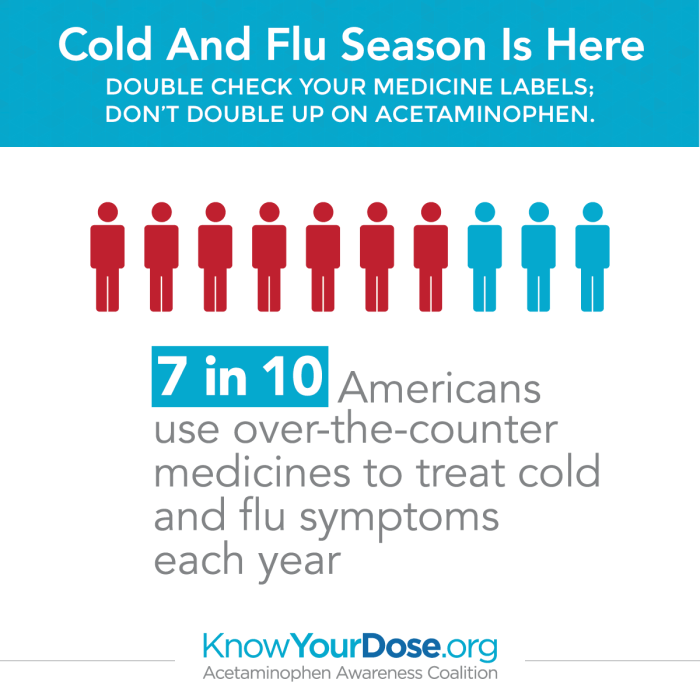
Overdosing on Cold and Flu Medications A Guide
Overdosing on cold and flu medications is a serious issue that can have severe consequences. Many people take these medications without fully understanding the risks involved. This guide explores the dangers of exceeding recommended dosages, detailing the various types of cold and flu medications prone to overdose, potential symptoms, and steps to take in case…