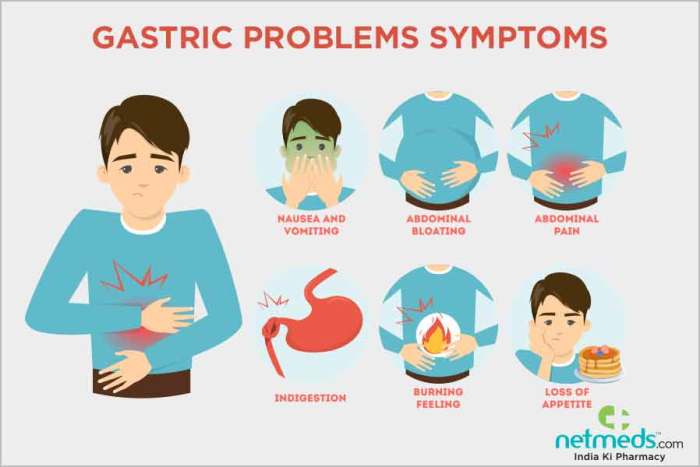
What is crohns colitis – What is Crohn’s Colitis? This chronic inflammatory condition affects the digestive tract, causing a range of symptoms and impacting daily life. Understanding the nuances of this complex disease, from its causes and stages to potential complications and treatment options, is crucial for those affected and those seeking to learn more….
Tag: digestive health
How to Follow a Gastroparesis Diet A Guide
How to follow a gastroparesis diet is crucial for managing this digestive condition. Gastroparesis slows the emptying of food from your stomach, impacting everything from digestion to nutrient absorption. This detailed guide offers practical strategies for navigating a gastroparesis diet, from understanding the principles to crafting personalized meal plans. The following sections will cover essential…
Tips for Relieving Intestinal Gas Through Movement A Guide
Tips for relieving intestinal gas through movement offers a practical approach to managing discomfort. This guide explores the connection between physical activity and digestive health, revealing how various movements can alleviate gas buildup. We’ll delve into specific exercises, posture, breathing techniques, and dietary considerations to create a personalized plan for gas relief. From gentle stretches…
Can Probiotics Help Acid Reflux?
Can probiotics help with acid reflux? This question sparks curiosity and debate among those seeking natural remedies for this common digestive ailment. Acid reflux, characterized by the burning sensation in the chest, often arises from stomach acid backing up into the esophagus. While conventional treatments exist, many people explore alternative approaches, including probiotics. This exploration…
What to Eat After Food Poisoning A Guide
What to eat after food poisoning? This guide provides a comprehensive overview of safe foods to consume after experiencing food poisoning. It delves into the types of food poisoning, immediate actions to take, and dietary considerations. We’ll explore foods to eat and avoid, covering everything from hydration to recovery, and even preventative measures to avoid…
Supplements for Acid Reflux Your Guide
Supplements for acid reflux can be a helpful tool in managing this common digestive issue. This comprehensive guide explores the world of supplements, from understanding the basics of acid reflux to exploring different types of supplements, their effectiveness, and safety concerns. We’ll also delve into supplement interactions, recommendations, and how to integrate them into your…
Rectal Ulcer Overview and More A Deep Dive
Rectal ulcer overview and more: Understanding rectal ulcers involves exploring their diverse types, common causes, and a range of potential symptoms. This comprehensive guide will delve into the complexities of these conditions, providing a detailed overview of diagnosis, treatment options, and preventative measures. From ischemic to inflammatory and infectious ulcers, we’ll uncover the factors contributing…
When to Take Apple Cider Vinegar Your Guide
When to take apple cider vinegar is a question that often arises for those exploring its potential health benefits. This guide delves into the optimal timing for consuming apple cider vinegar, considering various factors like digestive support, weight management, and blood sugar control. We’ll explore different types, potential benefits, and crucial considerations to help you…
Best Time to Take Collagen Your Absorption Guide
Best time to take collagen sets the stage for a deep dive into optimizing your collagen supplement routine. Understanding how your body absorbs collagen is key to maximizing its benefits. Factors like meal timing, blood sugar levels, digestive health, and even the specific form of collagen you choose all play a role in how effectively…
IBS vs Colon Cancer A Crucial Comparison
Kicking off with IBS vs colon cancer, this exploration delves into the often-confusing similarities and differences between these two conditions. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and colon cancer, while both affecting the digestive system, have distinct characteristics. Understanding these differences is vital for accurate diagnosis and effective management. This comprehensive guide will explore the symptoms, diagnostic…