Ligyrophobia fear of loud noises – Ligyrophobia, fear of loud noises, can significantly impact a person’s life, from everyday interactions to their overall well-being. This fear isn’t just about a dislike for boisterous sounds; it’s a complex phobia that triggers intense physical and emotional responses. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and coping mechanisms is crucial for…
Tag: anxiety
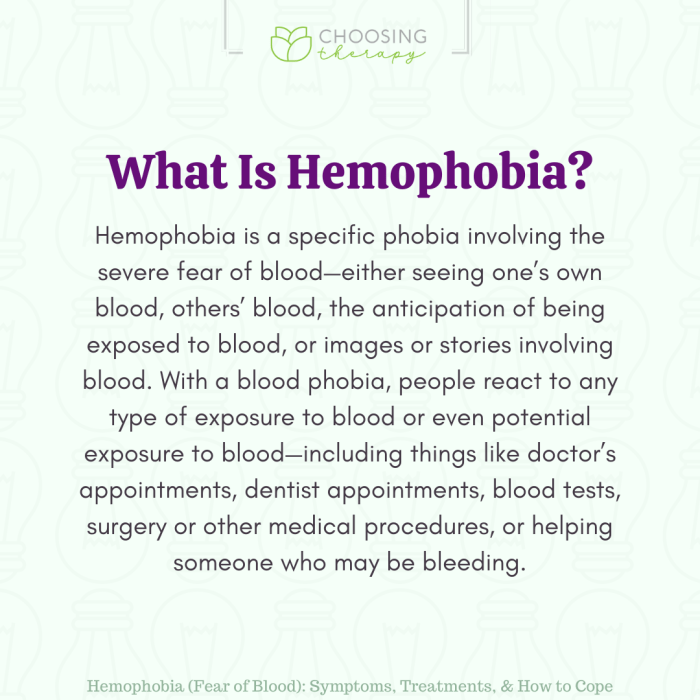
Hemophobia Fear of Blood Understanding and Coping
Hemophobia fear of blood – Hemophobia, fear of blood, is a specific phobia that can significantly impact a person’s life. This detailed exploration delves into the nuances of this condition, from its defining characteristics and symptoms to potential causes, effective treatments, and practical coping mechanisms. We’ll also examine the cultural and societal perspectives surrounding blood,…
How Long Does Valium Take to Work?
How long does it take Valium to work? This question is crucial for anyone considering or currently taking this medication. Valium, or diazepam, is a powerful benzodiazepine used to treat anxiety, muscle spasms, and seizures. Understanding the factors influencing its onset of action is key to managing expectations and ensuring optimal results. Different factors like…
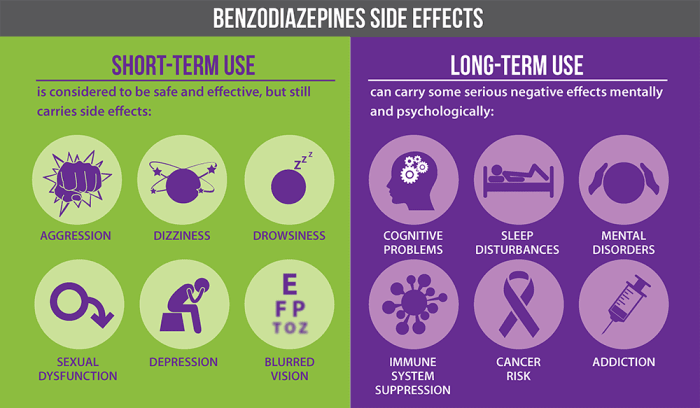
Benzodiazepines Uses, Types, and Risks
Uses types and risks of benzodiazepines – Benzodiazepines: Uses, Types, and Risks sets the stage for a detailed exploration of these medications. This in-depth look will cover everything from their chemical makeup and mechanism of action to their various applications, potential dangers, and long-term considerations. We’ll analyze different types, examining their potency, duration, and common…
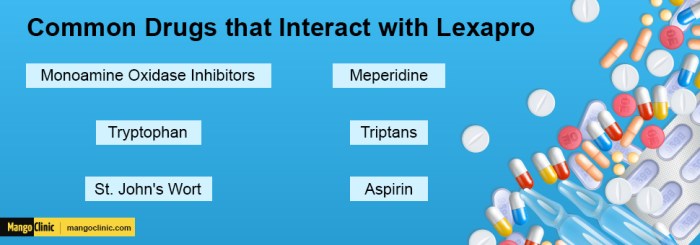
Prozac Fluoxetine vs Lexapro Escitalopram A Deep Dive
Prozac fluoxetine vs lexapro escitalopram: A comparison of these two popular antidepressants, both Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), is crucial for individuals seeking effective treatment. This in-depth look examines their mechanisms of action, common side effects, dosage ranges, and potential interactions. Understanding the nuances between these drugs empowers informed decision-making with a healthcare professional. This…
What Does Low Serotonin Feel Like? Unveiling the Impact
What does low serotonin feel like? This exploration dives deep into the often-misunderstood world of low serotonin levels, revealing the multifaceted impact they can have on your well-being. We’ll examine the emotional, physical, cognitive, social, and even behavioral changes that can accompany these lower-than-normal serotonin levels. From subtle mood fluctuations to more pronounced symptoms, understanding…
How Long Do Anxiety Attacks Last? Understanding Duration
How long do anxiety attacks last? This question plagues many experiencing these intense episodes. The answer isn’t straightforward, as attack duration varies significantly based on numerous factors. Understanding these factors, from the initial trigger to the role of individual responses, is key to navigating and managing anxiety. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of…
How Long Does Klonopin Take to Work?
How long does klonopin take to work? Understanding the factors influencing Klonopin’s effectiveness is crucial for managing anxiety or other conditions. This journey explores the various factors impacting its onset, from dosage and administration method to individual patient responses and potential side effects. We’ll delve into the science behind Klonopin’s action and discuss how individual…
Anxiety Stress and Diarrhea Understanding the Link
Anxiety stress and diarrhea are often intertwined, with the connection running deeper than many realize. This blog post delves into the physiological mechanisms linking anxiety and stress to digestive issues like diarrhea. We’ll explore the role of the autonomic nervous system, the impact on the gut microbiome, and common symptoms. Understanding this complex interplay is…
Ashwagandha Benefits, Side Effects, and More
Ashwagandha benefits side effects and more – Delving into ashwagandha benefits, side effects, and more, this introduction immerses readers in a comprehensive exploration of this ancient adaptogen. From its historical use to modern research, we’ll uncover the potential benefits and potential risks associated with ashwagandha. We’ll also examine dosage recommendations, precautions, and interactions with other…