Is coconut a tree nut? This question sparks curiosity and debate, especially among those with allergies or a keen interest in botany. Unraveling the truth requires a deep dive into botanical classifications, nutritional comparisons, and historical contexts. This exploration will demystify the differences between coconuts and true tree nuts. We’ll dissect the scientific characteristics that…
Tag: allergies
Sore Throat and Cough Understanding Causes and Relief
Sore throat and cough – a common ailment affecting people of all ages. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these symptoms, exploring everything from their various characteristics to potential causes and effective treatment options. We’ll examine how symptoms differ between adults and children, uncover common triggers, and compare them to similar conditions like…
Can Allergies Cause Body Aches?
Can allergies cause body aches? This question delves into the fascinating connection between allergic reactions and the often-misunderstood discomfort of body aches. Understanding the intricate mechanisms behind this link is key to recognizing and managing these symptoms effectively. From the initial triggers to the physiological responses, this exploration unravels the mysteries surrounding allergic body aches,…
Why Do I Have Itchy Eyes? Explained
Why do I have itchy eyes? This common problem can be frustrating, impacting daily life and comfort. From pesky allergies to more serious conditions, understanding the causes behind itchy eyes is key to finding relief. This guide delves into the various potential triggers, symptoms, and treatments, helping you pinpoint the source of your discomfort and…
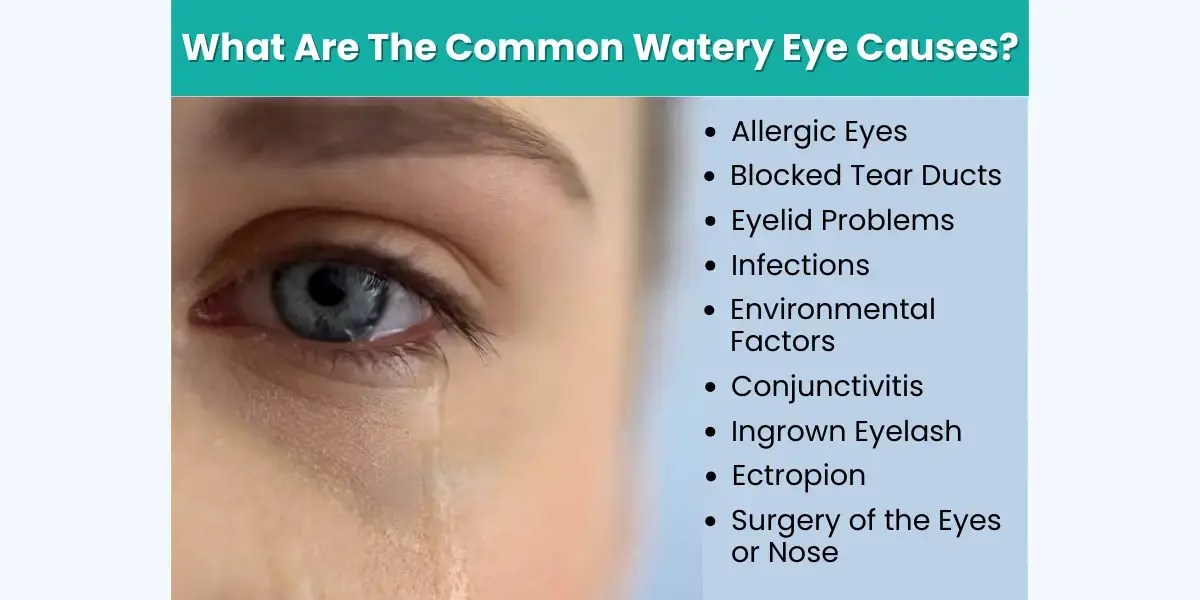
What Causes Watery Eyes? A Comprehensive Guide
What causes watery eyes? This insightful exploration delves into the myriad reasons behind those persistent, uncomfortable tears. From common allergies and infections to underlying medical conditions and environmental factors, we’ll uncover the root causes and provide a comprehensive understanding of this prevalent eye issue. This detailed guide will explore potential triggers, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment…
Can Allergies Cause Loss of Taste and Smell?
Can allergies cause loss of taste and smell? This intriguing question delves into the complex interplay between our immune system and sensory perception. Allergies, triggered by our bodies’ overreaction to harmless substances, can manifest in a wide range of symptoms, from the familiar runny nose to more subtle effects like changes in taste and smell….
Saline Spray Snoring Allergies A Deep Dive
Saline spray snoring allergies: This comprehensive guide explores the connection between nasal saline sprays, snoring, and allergies. We’ll examine how these sprays can potentially alleviate both snoring and allergy symptoms, and discuss the various factors influencing their effectiveness, from lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. From understanding the different mechanisms to comparing various spray types,…
Should I Take Claritin, Zyrtec, or Allegra?
Should i take claritin zyrtec or allegra – Should I take Claritin, Zyrtec, or Allegra? This question plagues many allergy sufferers. Each of these popular antihistamines tackles allergy symptoms differently, and understanding their nuances is key to choosing the right one for you. This guide delves into the specifics of each medication, considering factors like…
Nasal Congestion Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Nasal congestion symptoms causes and treatment – Nasal congestion symptoms, causes, and treatment: Understanding this common ailment is crucial for effective management. From the intricate workings of your nasal passages to the various triggers and remedies, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of stuffy noses. We’ll explore the anatomy, common symptoms, potential causes, and…
Do Allergy Shots Really Work? A Comprehensive Guide
Do allergy shots really work? This in-depth exploration delves into the effectiveness, potential side effects, and alternatives to allergy shots. We’ll examine the science behind how these treatments work, discuss factors that influence success, and weigh them against other allergy management options. Understanding the mechanisms of allergy shots, the types available, and their typical timelines…