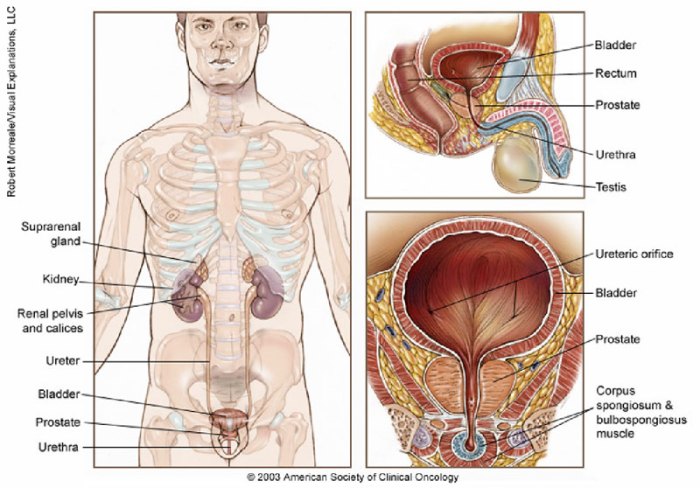
Prostate cancer survival rate is a crucial factor for patients and their families. This guide delves into the factors impacting survival, from early detection to treatment options and research advancements. We’ll explore five-year and ten-year survival rates across different stages of prostate cancer, highlighting the significance of early diagnosis and the effectiveness of various treatment approaches. Understanding these statistics empowers informed decisions and offers a realistic perspective on the challenges and potential outcomes.
This comprehensive look at prostate cancer survival rates examines the influence of crucial factors like age, health, and lifestyle choices on patient outcomes. We’ll present a detailed analysis of survival rates categorized by treatment type, stage, and demographic factors. The goal is to provide a clear and concise understanding of the factors that affect survival, allowing individuals to make informed decisions and stay informed about this significant health concern.
Overview of Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
Prostate cancer is a common malignancy, and its survival rates vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these rates, along with the factors influencing them, is crucial for patients and healthcare professionals alike. This section provides a comprehensive overview of prostate cancer survival rates, including stage-specific data, treatment options, and influential factors.Prostate cancer, while often treatable, can present in different stages of severity, impacting the likelihood of successful treatment.
The progression and treatment of the disease are directly correlated with the stage of diagnosis. Early detection and prompt intervention can significantly improve survival chances.
While prostate cancer survival rates are generally quite high with early detection and treatment, it’s also important to consider alternative approaches. For example, exploring natural treatment options for pancreatitis pain, like those detailed in this helpful guide, natural treatment for pancreatitis pain , might offer complementary relief. Ultimately, a proactive approach, combining conventional medicine with alternative methods, could potentially enhance overall well-being in the long run for prostate cancer patients.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates by Stage
Prostate cancer survival rates are influenced by the stage of the disease at diagnosis. Generally, the earlier the cancer is detected, the higher the survival rate. The five-year and ten-year survival rates are commonly used metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments and the overall prognosis.
Five-Year and Ten-Year Survival Rates
Data on five-year and ten-year survival rates for various stages of prostate cancer are available from reputable medical sources. These rates provide a general indication of the likelihood of a patient surviving for a specified period after diagnosis. It’s important to remember these are averages; individual outcomes can vary.For example, localized prostate cancer (confined to the prostate gland) typically has high five-year survival rates exceeding 95%, while more advanced stages, such as metastatic prostate cancer (spread to other parts of the body), show lower survival rates.
Specific figures will vary based on the specific stage and treatment approach.
Factors Influencing Prostate Cancer Survival Rates
Several factors influence prostate cancer survival rates. These include the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the patient’s overall health, the chosen treatment approach, and adherence to the treatment plan. Age, genetic predisposition, and lifestyle choices also play a role.
Treatment Options and Their Impact on Survival
Different treatment options are available for prostate cancer, each with varying impacts on survival rates. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences.* Active Surveillance: This approach involves monitoring the cancer closely without immediate treatment. It’s suitable for patients with slow-growing cancers and is often associated with higher long-term survival rates when appropriate for the specific case.
Surgery
Prostatectomy, the surgical removal of the prostate gland, is a common treatment option for localized prostate cancer. It can lead to high survival rates, particularly in early stages, but may also have potential side effects.
Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy targets prostate cancer cells with high-energy radiation. It’s an effective treatment for localized prostate cancer and is frequently used in combination with other therapies.
Hormone Therapy
This treatment method aims to reduce the production of hormones that fuel prostate cancer growth. It’s often used in advanced prostate cancer cases, and its effectiveness in improving survival rates varies.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs are used to kill cancer cells. They are often used in combination with other treatments, particularly for advanced prostate cancer, to improve survival rates.
Treatment Options and Survival Rates
| Stage | Treatment | 5-Year Survival Rate | 10-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localized | Active Surveillance | >95% | >90% |
| Localized | Surgery | >95% | >90% |
| Localized | Radiation Therapy | >90% | >85% |
| Regional | Combination Therapy | 70-85% | 60-75% |
| Metastatic | Hormone Therapy | 40-60% | 20-40% |
Note: Survival rates are estimates and can vary based on individual patient characteristics and treatment response. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Factors Affecting Prostate Cancer Survival
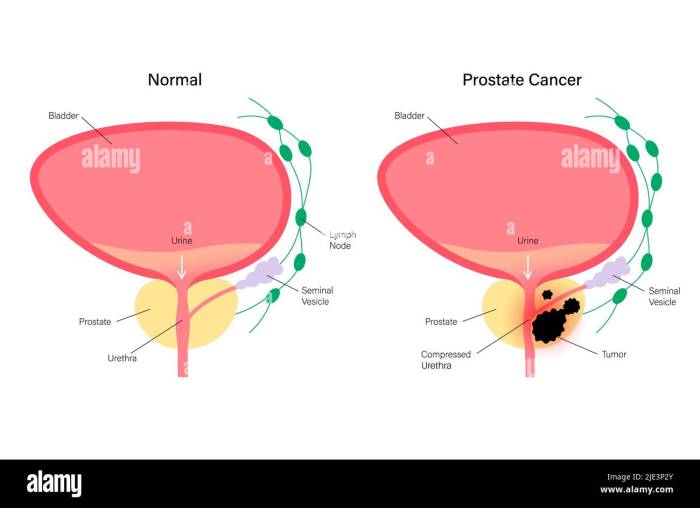
Understanding prostate cancer survival isn’t a simple calculation. Many factors influence the journey of a patient diagnosed with this disease. From the crucial role of early detection to the impact of lifestyle choices, a comprehensive understanding is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. This exploration delves into the key determinants of prostate cancer survival.Prostate cancer survival rates are significantly influenced by a multitude of interconnected factors.
These factors span from readily modifiable lifestyle choices to the inherent biological characteristics of the cancer itself, along with the individual’s overall health. Early detection, for instance, plays a pivotal role in increasing the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival.
Significance of Early Detection
Early detection is paramount in improving prostate cancer survival. The earlier prostate cancer is diagnosed, the more likely it is to be confined to the prostate gland. At this stage, treatment options are often less invasive and have a higher chance of cure. This localized form of the disease has a far better prognosis than advanced-stage cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Prostate cancer survival rates are definitely on the rise, thanks in part to better treatments. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role, and that includes dietary choices like considering the nutritional benefits of different types of omega-3 fatty acids. For example, exploring the differences between algae oil and fish oil could be beneficial in optimizing your overall health, which ultimately could influence prostate cancer survival rates.
Learn more about algae oil vs fish oil here and how it might fit into your health strategy.
The impact of early diagnosis is demonstrably positive, as it allows for intervention at a critical point, potentially preventing the disease from progressing.
Role of Age, Overall Health, and Lifestyle Choices
Age, overall health, and lifestyle choices all play a significant role in prostate cancer survival. Older individuals and those with pre-existing health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes, might face different challenges in their treatment and recovery. A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, can positively influence survival outcomes. Furthermore, reducing exposure to carcinogens and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial factors.
For example, studies have shown a link between a diet high in processed foods and an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
Impact of Cancer Type
The specific type of prostate cancer—whether it’s an aggressive or slow-growing form—has a direct impact on survival rates. Aggressive cancers tend to grow and spread rapidly, necessitating more aggressive treatment strategies. Slow-growing cancers, on the other hand, may require less intensive interventions, allowing for a more favorable prognosis. A key factor in assessing the type of cancer is the Gleason score, which provides a grading system that helps predict how aggressive the cancer might be.
Comparative Analysis of Survival Rates Across Demographic Groups
Survival rates for prostate cancer can vary across different demographic groups. Race and socioeconomic status can influence access to quality healthcare, impacting early detection and treatment options. Individuals from marginalized communities may face systemic barriers that hinder their ability to receive timely and appropriate care. These disparities highlight the importance of equitable access to healthcare resources for all.
Role of Genetics in Prostate Cancer Survival, Prostate cancer survival rate
Genetic predisposition plays a role in prostate cancer susceptibility and survival. Individuals with a family history of prostate cancer might have a higher risk of developing the disease. Genetic testing can identify specific genetic mutations associated with a higher risk, allowing for more proactive preventative measures and personalized treatment strategies.
Factors Affecting Prostate Cancer Survival – Table
| Factor | Impact on Survival |
|---|---|
| Age | Older age can be associated with a slightly reduced survival rate due to increased risk of comorbidities and potential complications during treatment. |
| Treatment | Prompt and appropriate treatment, including surgery, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy, directly correlates with a higher chance of survival. |
| Stage of Cancer | Early-stage cancers have significantly better survival rates compared to advanced-stage cancers that have spread beyond the prostate. |
| Gleason Score | Higher Gleason scores typically indicate a more aggressive cancer, potentially impacting survival negatively. |
| Overall Health | Pre-existing health conditions and comorbidities can influence the treatment approach and potentially impact the prognosis. |
| Lifestyle | A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, can potentially enhance survival outcomes. |
Treatment and Survival Rates
Prostate cancer, while often treatable, presents a spectrum of treatment approaches, each with varying degrees of effectiveness in extending survival. Understanding how different therapies impact patient outcomes is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into the diverse treatment options and their corresponding survival rates, highlighting the advancements in treatment protocols that have significantly improved patient outcomes over time.Different treatment strategies target prostate cancer at various stages and with varying aggressiveness, resulting in varying degrees of success in extending survival.
Prostate cancer survival rates are a significant concern, and thankfully, they’re improving. While factors like early detection play a crucial role, understanding how other conditions like cerebral palsy life expectancy affect overall well-being can also shed light on broader health trends. Ultimately, continued research into prostate cancer treatment and preventative measures is vital to improving outcomes for patients.
The choice of treatment is a collaborative decision between patients and their healthcare providers, considering factors such as the stage of the cancer, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences.
Surgical Treatment Approaches
Surgical removal of the prostate, often called radical prostatectomy, is a common treatment for localized prostate cancer. This procedure aims to eliminate the cancerous tissue, potentially improving long-term survival rates. The effectiveness of surgery in extending survival varies based on the extent of the cancer’s spread and the patient’s overall health. Surgical outcomes are influenced by the surgeon’s expertise and the patient’s post-operative recovery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) is a common approach, where beams are directed at the prostate from an external source. Intensified radiation, such as Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), helps precisely target the tumor, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. The effectiveness of radiation therapy in extending survival varies depending on the type of radiation, the dose delivered, and the specific characteristics of the cancer.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy aims to reduce the production of hormones that fuel prostate cancer growth. This approach is often used when the cancer has spread beyond the prostate or when other treatments aren’t sufficient. Common types of hormone therapy include androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), which lowers testosterone levels. The impact of hormone therapy on survival depends on the duration of treatment, the patient’s response to the therapy, and the presence of other factors influencing the progression of the cancer.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, using drugs to kill cancer cells, may be used in advanced prostate cancer cases. The effectiveness of chemotherapy in extending survival can vary widely. The type and dosage of chemotherapy drugs, as well as the patient’s overall health, are key factors influencing the outcome. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with other treatments to improve its efficacy and minimize side effects.
Combined Treatment Strategies
Often, a combination of treatments is employed to maximize effectiveness and improve survival rates. For instance, surgery followed by radiation therapy or hormone therapy combined with radiation therapy are common approaches. The survival rates for patients undergoing these combined approaches often surpass those treated with a single modality. The optimal combination of treatments depends on individual patient characteristics and the specific stage of the cancer.
Advancements in Treatment Protocols
Significant advancements in treatment protocols have dramatically improved prostate cancer survival rates over time. These improvements include more precise surgical techniques, advanced radiation therapies, and targeted therapies. New drug therapies are continually being developed, leading to more effective and personalized treatment plans.
Data Organization and Comparison
To effectively compare the effectiveness of different treatment approaches, data should be organized by the following parameters:
- Treatment type: Specify the type of treatment, e.g., radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination.
- Stage of cancer: Classify the cancer based on its spread, such as localized, regional, or distant.
- Patient characteristics: Include details such as age, overall health, and other relevant factors.
- Duration of treatment: Note the length of time the patient received treatment.
- Survival time: Specify the time elapsed from the start of treatment to the patient’s death, if applicable.
Using this structured format, a clear comparison of survival rates can be established.
Treatment Comparison Table
The table below provides a general comparison of average survival rates for different treatment approaches, but it is crucial to remember that individual results can vary significantly.
| Treatment | Average Survival Rate (approximate, in years) | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Radical Prostatectomy | 10+ | Effective for localized cancer; potential for complications |
| Radiation Therapy | 8-12 | Effective for localized cancer; potential for side effects |
| Hormone Therapy | 5-10 | Effective for advanced cancer; long-term treatment required |
| Chemotherapy | 3-7 | Effective in combination with other therapies; high potential for side effects |
| Combination Therapies | 10+ (often higher than single modalities) | Tailored to individual needs; optimal for advanced or aggressive cancers |
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates by Stage
Prostate cancer, while often treatable, has varying outcomes depending on the stage at diagnosis. Understanding the survival rates associated with each stage is crucial for patients and healthcare providers in making informed decisions about treatment plans and prognosis. Early detection and accurate staging are paramount for maximizing chances of successful outcomes.Prostate cancer’s progression from localized to distant disease significantly impacts survival prospects.
The stage of the cancer at diagnosis is a primary determinant of the effectiveness of treatment and the overall prognosis. Factors such as the extent of tumor spread, presence of metastasis, and the patient’s overall health influence the survival rate for each stage.
Staging Classifications
Different systems categorize prostate cancer stages. One common method involves using the TNM system, where T describes the size and extent of the primary tumor, N indicates the involvement of regional lymph nodes, and M signifies the presence of distant metastasis. Other staging systems exist, each with its own criteria for defining the extent of the disease. These systems, while differing in minor details, broadly categorize the cancer based on its characteristics.
Localized Prostate Cancer
Localized prostate cancer is confined to the prostate gland. This early stage offers the highest chances of successful treatment and survival. Five-year survival rates are typically very high, often exceeding 95%. Ten-year survival rates are also generally excellent, often exceeding 90%. This high survival rate reflects the effectiveness of treatments like surgery or radiation therapy when the cancer is localized.
Regional Prostate Cancer
Regional prostate cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland to nearby tissues or regional lymph nodes. Survival rates for this stage are still good, but lower than those for localized disease. Five-year survival rates are often in the 80-90% range. Ten-year survival rates might fall into the 70-80% range. Treatment options for regional disease are more complex and aggressive, often involving a combination of therapies.
Distant Prostate Cancer
Distant prostate cancer has metastasized, meaning the cancer cells have spread to distant organs like bones or lungs. This is the most advanced stage, and survival rates are the lowest. Five-year survival rates are typically in the 50-70% range, depending on the extent of the metastasis. Ten-year survival rates are significantly lower, often below 50%. Treatment focuses on managing the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Importance of Accurate Staging
Accurate staging is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment strategy and predicting the patient’s prognosis. The staging process involves a combination of physical exams, imaging studies (like CT scans or MRIs), and biopsies. A precise staging assessment allows physicians to tailor the treatment approach to the specific characteristics of the cancer.
Comparison of Survival Rates
| Stage | Five-Year Survival Rate (%) | Ten-Year Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Localized | >95 | >90 |
| Regional | 80-90 | 70-80 |
| Distant | 50-70 | <50 |
This table provides a general overview. Actual survival rates may vary based on individual patient factors, treatment effectiveness, and other influencing variables.
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates and Research
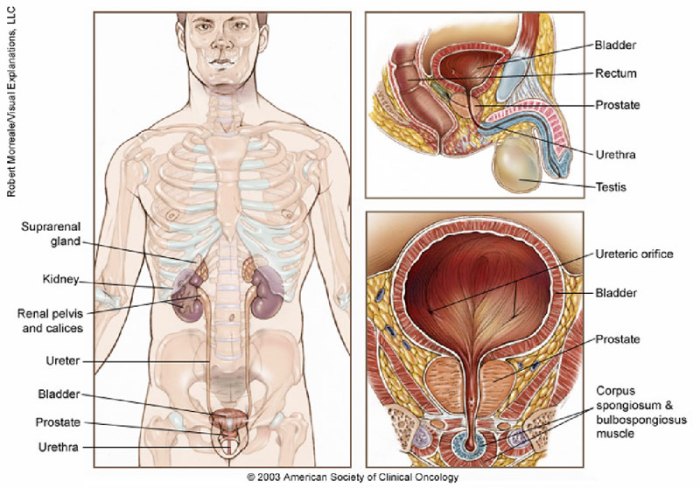
Prostate cancer, while often treatable, requires ongoing research to improve outcomes and patient quality of life. Understanding the current landscape of research efforts, clinical trials, and emerging therapies is crucial for individuals facing this diagnosis and their families. This exploration delves into the multifaceted aspects of prostate cancer research, emphasizing its impact on survival rates.Ongoing research endeavors are actively striving to improve the effectiveness of prostate cancer treatments and enhance the overall survival rates.
These efforts span various avenues, including the development of novel therapies, refinement of existing treatments, and the exploration of personalized medicine approaches.
Current Research Efforts
Research in prostate cancer is a dynamic field, with ongoing studies investigating diverse aspects of the disease. Scientists are actively pursuing novel therapeutic strategies and exploring the molecular underpinnings of prostate cancer progression. This investigation encompasses a broad spectrum of approaches, from innovative drug combinations to targeted therapies.
Impact of Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a vital role in evaluating new therapies and treatments for prostate cancer. The results of these trials often provide crucial data for understanding treatment efficacy and potential side effects. Positive outcomes from clinical trials can significantly impact treatment protocols and lead to improvements in patient survival. For instance, a recent clinical trial exploring a novel immunotherapy approach demonstrated promising results in reducing tumor size and increasing overall survival rates in a subset of patients.
Role of Screening and Early Detection
Early detection of prostate cancer is critical for improving treatment outcomes and survival rates. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening, while controversial, remains a significant tool for early detection. However, the effectiveness of PSA screening in reducing mortality rates is still a subject of debate. Further research is needed to optimize screening strategies and refine diagnostic tools to achieve greater accuracy and minimize false positives.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
New and emerging treatments for prostate cancer are continuously being investigated. Immunotherapy, targeted therapies, and novel radiation approaches are among the promising areas of research. For example, advancements in immunotherapy are exploring ways to harness the body’s immune system to target and destroy prostate cancer cells, potentially offering long-term remission for some patients. The use of personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatment strategies based on individual genetic profiles, is also gaining momentum.
Challenges and Opportunities in Prostate Cancer Research
Despite significant advancements, challenges remain in prostate cancer research and treatment. These include developing more effective therapies for advanced stages of the disease, minimizing side effects associated with existing treatments, and improving the accuracy of early detection methods. Nevertheless, opportunities exist for leveraging cutting-edge technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to personalize treatments and predict patient responses to therapies.
Improved understanding of the genetic drivers of prostate cancer could lead to the development of more targeted and effective therapies.
Research Areas and Potential Impact on Survival
| Research Area | Potential Impact on Survival |
|---|---|
| Immunotherapy | Targeted immune responses against cancer cells, potentially leading to longer remission periods and increased overall survival. |
| Targeted Therapies | Precise targeting of specific genetic mutations driving cancer growth, resulting in more effective treatment and potentially reduced side effects. |
| Personalized Medicine | Tailoring treatment plans based on individual genetic profiles, potentially improving treatment efficacy and reducing the risk of adverse events. |
| Early Detection Strategies | Improving the accuracy and sensitivity of diagnostic tools, leading to earlier intervention and improved outcomes. |
| Novel Drug Combinations | Combining existing therapies in novel ways, potentially enhancing treatment efficacy and reducing resistance development. |
Visual Representation of Data
Understanding prostate cancer survival rates requires more than just numbers. Visual representations offer a powerful way to grasp the complexities and nuances of this disease. Graphs and charts can clearly illustrate trends, highlight key factors, and ultimately, provide a more impactful understanding of patient outcomes. By visually displaying data, we can identify patterns and potential areas for improvement in treatment and care.
Overall Survival Rates Across Stages and Treatments
Visualizing survival rates across different stages and treatment approaches provides a clear picture of the disease’s progression and how treatment choices impact outcomes. A stacked bar chart, for example, could display 5-year survival rates for each stage (localized, regional, distant) with separate sections representing different treatment modalities (surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy). This would allow for direct comparisons of survival probabilities based on stage and treatment.
Such a chart can immediately highlight the impact of early detection and aggressive treatment in the localized stage, where survival rates are significantly higher.
Factors Impacting Survival
A scatter plot can effectively demonstrate the influence of various factors on survival. The x-axis could represent age, while the y-axis could display the 5-year survival rate. Different colors or markers could represent different treatment types, allowing for a visual comparison of survival rates across age groups and treatments. For example, a point clustered in the upper right quadrant of the scatter plot would indicate a higher survival rate among older patients who received a specific treatment.
This type of visualization can help identify patient groups that might benefit from specific interventions or strategies. Another visual could show survival rates by stage of disease, with lines representing different treatment approaches.
5-Year Survival Rates by Stage
A bar chart is an ideal choice for comparing 5-year survival rates across different stages of prostate cancer. The x-axis would represent the stage (e.g., localized, regional, distant), and the y-axis would display the corresponding 5-year survival rate. Different colors could be used to distinguish between different treatment groups, further clarifying the impact of treatment choices on survival rates.
For example, the bar for localized prostate cancer would likely be significantly higher than the bar for distant prostate cancer.
Improvement in Survival Rates Over Time
A line graph would effectively illustrate the improvement in prostate cancer survival rates over time. The x-axis would represent the year, and the y-axis would represent the 5-year survival rate. The graph would ideally show a clear upward trend, reflecting the advancements in early detection, treatment techniques, and overall understanding of the disease. The inclusion of a line representing the average survival rate for a specific historical period (e.g., 1990-2000) alongside the modern line would highlight the substantial progress in the field.
Impact of Treatment Strategies
A combination of pie charts and bar charts could visually demonstrate the impact of different treatment strategies. A pie chart could represent the proportion of patients who received different treatment options (surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, chemotherapy). A bar chart could then overlay this, showing the 5-year survival rates associated with each treatment type. This combined visualization provides a comprehensive understanding of the treatment landscape and its correlation with survival outcomes.
For example, a pie chart could display the distribution of treatments for localized prostate cancer and the bar chart associated with this would highlight that surgical treatment often correlates with significantly higher 5-year survival rates.
Final Summary: Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
In conclusion, prostate cancer survival rates vary significantly depending on the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, treatment options, and individual factors. Early detection remains paramount in improving outcomes, and advancements in treatment are continually improving patient survival. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the key elements influencing prostate cancer survival. It’s important to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
Consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.