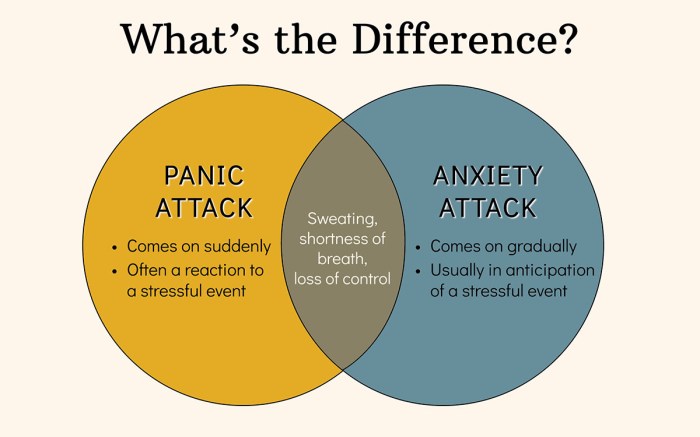
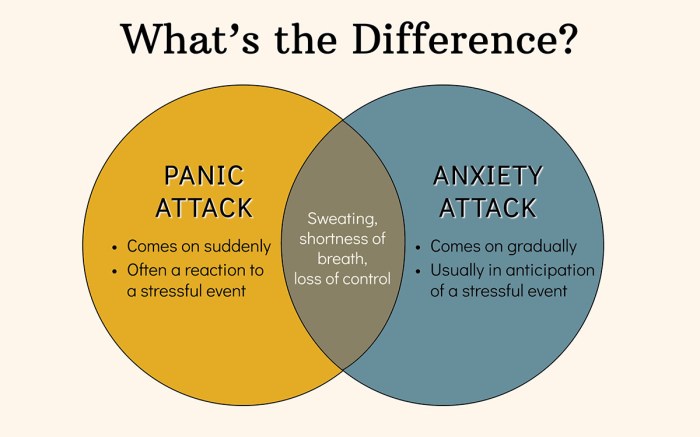
Panic attack vs anxiety attack: This exploration delves into the nuances of these two closely related yet distinct emotional experiences. Understanding their differences is crucial for effective management and treatment. From the physiological responses to the psychological impact, we’ll unravel the complexities of each, highlighting key similarities and contrasting features.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge to differentiate between panic and anxiety attacks. We will examine the symptoms, triggers, and long-term consequences of each, providing a clear picture of how they affect daily life. By understanding the distinctions, individuals can better recognize the type of experience they are facing and take appropriate steps towards managing their well-being.
Defining the Differences: Panic Attack Vs Anxiety Attack
Understanding the nuances between panic attacks and anxiety attacks is crucial for effective self-management and seeking appropriate support. Both conditions involve intense emotional distress, but their physiological and psychological characteristics differ significantly. Recognizing these differences can empower individuals to better identify and address their experiences.Differentiating between panic attacks and anxiety attacks is vital for appropriate intervention. A thorough understanding allows for tailored strategies and support, leading to improved well-being and coping mechanisms.
Both conditions, while distressing, respond differently to various interventions, and self-awareness is key.
Panic Attack Characteristics
Panic attacks are characterized by sudden, intense episodes of fear or discomfort that reach a peak within minutes. Physiological responses include rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, sweating, and trembling. Psychological components include feelings of impending doom, fear of losing control, or fear of dying. These attacks are often unexpected and unpredictable, leaving individuals feeling overwhelmed and vulnerable.
Crucially, panic attacks are not necessarily linked to a specific trigger.
Anxiety Attack Characteristics
Anxiety attacks, on the other hand, are characterized by a more gradual build-up of anxiety, often lasting for extended periods. Physiological responses include muscle tension, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and gastrointestinal issues. Psychological experiences often involve worry, apprehension, and a sense of dread or unease about future events. While anxiety attacks can be triggered by specific situations or thoughts, they can also be more persistent and less intense than panic attacks.
Physiological Responses Comparison
Panic attacks typically involve a surge of the sympathetic nervous system, resulting in rapid heart rate, shortness of breath, and sweating. These physiological responses are immediate and intense. Anxiety attacks, however, often manifest through the chronic activation of the stress response system, leading to more sustained, but less dramatic, physiological changes. This may include muscle tension, digestive issues, and headaches.
Psychological Experiences Comparison
During a panic attack, the individual experiences a feeling of intense fear and loss of control, often with a sense of impending doom. The psychological experience is overwhelmingly negative and immediate. Anxiety attacks, however, typically involve a sense of worry, apprehension, and dread about future events or situations. The psychological experience is characterized by sustained negativity and often relates to specific stressors or anticipated threats.
Key Differences Table
| Characteristic | Panic Attack | Anxiety Attack | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, sweating, trembling, fear of dying, loss of control. | Muscle tension, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, gastrointestinal issues, worry, apprehension, dread. | Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe distress. |
| Duration | Typically peaks within minutes, lasting for 5-20 minutes. | Can last for hours or even days, with varying intensity. | Duration varies significantly, impacting daily functioning. |
| Triggers | Often unexpected and unpredictable. | Often related to specific situations, thoughts, or stressors. | Triggers can vary greatly, affecting individual experience. |
| Impact | Significant distress, fear, and potential for avoidance behaviors. | Chronic stress, difficulty functioning, and possible impairment in daily activities. | Both can significantly impact daily life and relationships. |
Symptoms and Manifestations
Understanding the physical and psychological symptoms of panic attacks and anxiety attacks is crucial for recognizing and managing these experiences. Recognizing the differences in these symptoms can help differentiate between the two and guide individuals towards appropriate support. Accurate identification of the symptoms can lead to more effective interventions and better overall well-being.
Physical Symptoms of Panic Attacks, Panic attack vs anxiety attack
Panic attacks are often characterized by a sudden surge of intense physical sensations. These sensations can be overwhelming and frightening, leading to a feeling of impending doom. Common physical symptoms include rapid heart palpitations, a pounding or racing heart, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, chest pain or tightness, and feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness. These sensations are often accompanied by nausea, sweating, trembling, or shaking.
The experience can feel like a heart attack, further intensifying the fear and anxiety.
Psychological Symptoms of Panic Attacks
Beyond the physical sensations, panic attacks also manifest in a range of psychological symptoms. Individuals experiencing a panic attack may experience intense fear of dying, losing control, or going crazy. They may feel a sense of detachment from reality, like they are observing themselves from outside their own body. These feelings of fear and impending doom can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function normally.
Figuring out the difference between a panic attack and an anxiety attack can be tricky, but it’s important to understand the distinction. While both involve overwhelming feelings, panic attacks are often sudden and intense, whereas anxiety tends to be more persistent. Knowing these nuances can be vital for self-care, but it’s equally crucial to be mindful of potential health risks, like the potential dangers of certain foods.
For example, while chia seeds are often touted as a superfood, there are some potential downsides to consider, such as dangers of chia seeds related to interactions with certain medications or for individuals with specific health conditions. Ultimately, recognizing the differences between these types of episodes is key to managing your well-being effectively.
Physical Symptoms of Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks, while less intense than panic attacks, can still cause significant distress. Physical symptoms associated with anxiety attacks are often less dramatic than those associated with panic attacks. Common physical symptoms include muscle tension, fatigue, headaches, stomach upset, and a general feeling of unease. These symptoms can persist over longer periods than a panic attack, lasting for days or even weeks.
Psychological Symptoms of Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks are primarily characterized by psychological distress. Common psychological symptoms include persistent worry, nervousness, and restlessness. Individuals may experience a sense of impending doom, but this feeling is less intense than that experienced during a panic attack. They may also feel anxious about a variety of situations or topics, leading to a sense of unease and difficulty concentrating.
Symptom Comparison Table
| Symptom Category | Severity Level | Potential Triggers | Examples of Situations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Symptoms (Panic Attack) | High | Stressful events, caffeine, lack of sleep, underlying health conditions | Public speaking, sudden loud noises, crowded places, arguments |
| High | Stressful events, caffeine, lack of sleep, underlying health conditions | Facing a significant personal challenge, such as job loss or relationship issues | |
| Moderate | Sudden environmental changes, past traumas | Exposure to a phobia, witnessing a traumatic event, or encountering a trigger from the past | |
| Low | Stressful thoughts, emotional overwhelm, and heightened senses | Anticipation of a significant event, such as an important exam or presentation | |
| Psychological Symptoms (Panic Attack) | High | Stressful events, significant life changes, genetic predisposition | Experiencing a sudden, unexpected crisis or a major life event, like a death in the family |
| High | Stressful events, significant life changes, genetic predisposition | Facing overwhelming pressure, such as a demanding job or relationship | |
| Moderate | Sudden environmental changes, past traumas | Exposure to a phobia, witnessing a traumatic event, or encountering a trigger from the past | |
| Low | Stressful thoughts, emotional overwhelm, and heightened senses | Anticipation of a significant event, such as an important exam or presentation | |
| Physical Symptoms (Anxiety Attack) | Moderate | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam |
| Low | Stressful thoughts, emotional overwhelm, and heightened senses | Anticipation of a significant event, such as an important exam or presentation | |
| Low | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam | |
| Low | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam | |
| Psychological Symptoms (Anxiety Attack) | Moderate | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam |
| Low | Stressful thoughts, emotional overwhelm, and heightened senses | Anticipation of a significant event, such as an important exam or presentation | |
| Low | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam | |
| Low | Stressful events, underlying health conditions, medication side effects | Dealing with a stressful deadline at work or preparing for a major exam |
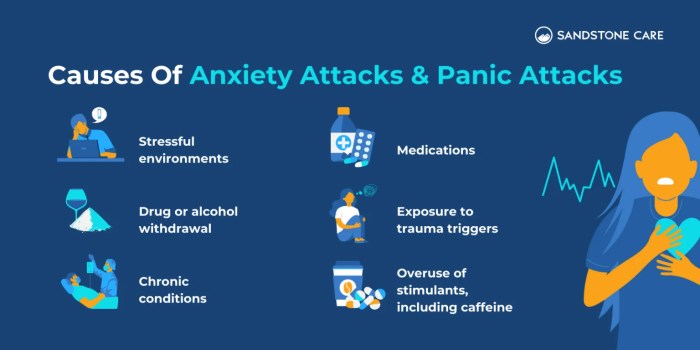
Triggers and Contributing Factors
Understanding the triggers and contributing factors behind panic and anxiety attacks is crucial for effective management and treatment. These factors can vary greatly from person to person, highlighting the complex nature of these conditions. Identifying patterns and triggers allows individuals to proactively address potential stressors and develop coping mechanisms.The interplay between environmental, genetic, and personal experiences shapes the vulnerability to these attacks.
Recognizing these factors allows for a more personalized approach to treatment and support. This knowledge empowers individuals to understand their unique responses and take control of their well-being.
Figuring out the difference between a panic attack and an anxiety attack can be tricky, right? Sometimes, those intense feelings can leave you feeling overwhelmed. Fortunately, when you’re craving a sweet treat, there are delicious options available for those with diabetes. Checking out some go to diabetic desserts can help you satisfy your sweet tooth without derailing your health goals.
Ultimately, understanding the nuances of these emotional responses is key to managing them effectively.
Common Triggers for Panic Attacks
Panic attacks can be triggered by a variety of internal and external factors. Stressful life events, including job loss, relationship problems, or financial difficulties, often act as significant triggers. These events can overwhelm an individual’s coping mechanisms and lead to a heightened state of anxiety, potentially culminating in a panic attack. Substance use, including caffeine, nicotine, and certain recreational drugs, can also induce panic attacks.
These substances can alter brain chemistry and create a physiological response that manifests as a panic attack. Furthermore, certain medical conditions can mimic panic attacks. Understanding the specific symptoms associated with these conditions is essential for proper diagnosis and management.
Common Triggers for Anxiety Attacks
Anxiety attacks, often characterized by persistent worry and apprehension, can be triggered by various factors, frequently centered around social or performance-based situations. Social situations, such as public speaking or meeting new people, can induce anxiety attacks in individuals who experience significant social anxiety. The anticipation of judgment or scrutiny from others can be a significant trigger. Performance pressure, whether in academic, professional, or personal settings, can also contribute to anxiety attacks.
The fear of failure or not meeting expectations can heighten anxiety levels, potentially leading to an anxiety attack.
The Role of Genetics and Past Experiences
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of panic and anxiety attacks. Individuals with a family history of anxiety disorders may have a higher likelihood of experiencing these conditions themselves. Research indicates a possible genetic component influencing brain chemistry and neurotransmitter activity, which can increase vulnerability to anxiety and panic attacks. Past experiences, such as trauma or significant stressors, can also significantly influence the development of these conditions.
Adverse childhood experiences, for instance, can contribute to a heightened sensitivity to stress and an increased risk of developing anxiety disorders later in life. These experiences can create long-lasting emotional patterns that increase vulnerability to future triggers.
The Role of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors contribute to the development and manifestation of panic and anxiety attacks. Chronic stress, stemming from demanding work environments, financial pressures, or challenging personal relationships, can significantly increase the likelihood of these attacks. Exposure to traumatic events, such as accidents, natural disasters, or violent crimes, can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a condition often characterized by panic attacks and anxiety.
Furthermore, the presence of chronic illness or significant medical concerns can heighten anxiety levels and increase the risk of panic attacks.
Lifestyle Choices and Their Influence
Lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise, can significantly influence the frequency and severity of panic and anxiety attacks. A diet lacking essential nutrients can impact mood regulation and contribute to anxiety. A balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can promote overall well-being and potentially reduce the intensity of anxiety symptoms. Regular exercise, through its effect on stress hormones, can help regulate mood and reduce the frequency of panic and anxiety attacks.
Lack of sleep and inadequate rest also contribute to heightened anxiety and an increased susceptibility to panic attacks.
Comparison of Triggers
| Trigger Category | Panic Attacks | Anxiety Attacks |
|---|---|---|
| Stressful Events | Job loss, relationship problems, financial difficulties | Public speaking engagements, major life changes |
| Substance Use | Caffeine overdose, drug use, nicotine | Withdrawal from substances, excessive alcohol consumption |
| Social Situations | Overwhelming social gatherings, fear of public scrutiny | Meeting new people, social interactions |
| Performance Pressure | High-stakes exams, competitive environments | Public speaking, performance-based tasks |
| Environmental Factors | Chronic stress, exposure to trauma | Urban environments, noise pollution |
Impact and Consequences
The impact of panic and anxiety attacks extends far beyond the immediate experience of fear and distress. These episodes can significantly disrupt daily life, affecting relationships, work performance, and overall well-being. Understanding these consequences is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support.These attacks, while often perceived as isolated events, can create a cycle of avoidance and anxiety that progressively impacts various aspects of life.
The resulting avoidance behaviors, social isolation, and decreased productivity can have long-lasting effects, hindering personal growth and creating further distress.
Impact on Daily Life
Panic and anxiety attacks can severely disrupt daily routines. Individuals may experience difficulty concentrating, leading to decreased productivity at work or school. This can manifest as missed deadlines, poor performance, and ultimately, job loss or academic setbacks. Furthermore, the unpredictable nature of these attacks can lead to avoidance behaviors, particularly in situations perceived as triggering. This avoidance can range from simple situations, such as public speaking or crowded environments, to more profound limitations on social interaction and participation in daily activities.
Figuring out the difference between a panic attack and anxiety can be tricky, but understanding your body’s responses is key. Sometimes, physical symptoms like skin issues can mimic anxiety. For example, if you’re experiencing persistent skin irritation, it’s worth looking into how to test for atopic dermatitis how to test for atopic dermatitis. This can help you rule out underlying conditions and better understand the root of your anxiety or panic symptoms.
Social Isolation
The fear of experiencing another attack can lead to significant social isolation. Individuals may withdraw from social gatherings, avoid loved ones, or limit their participation in activities they once enjoyed. This isolation can negatively impact relationships, leading to feelings of loneliness and depression. For example, a person who previously enjoyed attending concerts might now avoid them due to the fear of a panic attack in a large, crowded environment.
This avoidance can create a vicious cycle of loneliness and anxiety.
Decreased Productivity
The constant worry and physical symptoms associated with panic and anxiety attacks can lead to a significant decrease in productivity. This can affect work performance, academic success, and even household responsibilities. Missed workdays, reduced efficiency, and an inability to complete tasks effectively can have far-reaching consequences. Imagine an employee who frequently experiences anxiety attacks during presentations, leading to missed deadlines and decreased confidence.
This negatively impacts their professional reputation and career prospects.
Impact on Relationships and Work Performance
Panic and anxiety attacks can strain relationships with friends, family, and partners. The unpredictable nature of these episodes can lead to misunderstandings, frustration, and feelings of resentment. Similarly, in the workplace, repeated attacks can negatively affect job performance, leading to missed deadlines, errors, and conflicts with colleagues. This can create a challenging environment for both the individual experiencing the attacks and those around them.
Long-Term Consequences
Untreated panic and anxiety attacks can have profound long-term consequences. Chronic anxiety can lead to physical health problems such as cardiovascular issues, digestive problems, and sleep disturbances. Furthermore, the constant fear and avoidance behaviors can create a sense of hopelessness and despair, increasing the risk of developing depression or other mental health conditions. The long-term impact can be devastating, affecting various aspects of life, including career, relationships, and overall well-being.
Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
| Aspect of Life | Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Health | Increased heart rate, shortness of breath, sweating, dizziness | Chronic health problems (e.g., cardiovascular issues, digestive problems), sleep disturbances |
| Mental Health | Fear, worry, sense of impending doom, feelings of inadequacy | Depression, hopelessness, anxiety disorders, social isolation |
| Relationships | Strained communication, misunderstandings, conflict | Loss of relationships, social isolation, decreased intimacy |
| Work/Academics | Missed deadlines, decreased productivity, reduced performance, difficulty concentrating | Job loss, academic setbacks, difficulty maintaining employment, decreased earning potential |
| Daily Life | Difficulty with daily tasks, avoidance behaviors, decreased participation in activities | Reduced quality of life, inability to pursue personal goals, limited social interaction |
Seeking Professional Help
Facing panic and anxiety attacks can be incredibly isolating and overwhelming. The good news is that help is available, and seeking professional guidance is a crucial step toward managing these conditions effectively. It’s a sign of strength, not weakness, to acknowledge the need for support and actively work towards a healthier state of mind.Understanding that panic and anxiety disorders are treatable conditions is fundamental to taking the first step towards recovery.
Seeking professional help empowers individuals to navigate these challenges with the right tools and strategies. This process allows for a deeper understanding of the specific triggers, contributing factors, and best approaches for managing symptoms.
Mental Health Professionals
Various mental health professionals can provide support for panic and anxiety disorders. Psychologists, psychiatrists, and therapists are trained to diagnose and treat these conditions. Psychologists often specialize in talk therapy, focusing on understanding the root causes of anxiety and developing coping mechanisms. Psychiatrists, who are medical doctors, can prescribe medication alongside therapy. Therapists, encompassing various specializations, offer diverse approaches to address the unique needs of each individual.
Types of Treatments
Several effective treatments are available for panic and anxiety disorders. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely used approach that helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns contributing to anxiety. Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to feared situations, reducing their anxiety responses over time. Mindfulness-based therapies, such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), teach individuals to focus on the present moment, reducing rumination and anxiety.
Medication
Medication can be a valuable tool in managing panic and anxiety symptoms, often used in conjunction with therapy. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are commonly prescribed antidepressants that can help regulate mood and reduce anxiety. Other medications, like benzodiazepines, may be used short-term to manage acute anxiety attacks, but their long-term use is often not recommended due to potential dependence.
It’s crucial to discuss medication options with a psychiatrist to determine the most suitable approach for individual needs.
Steps in Seeking Professional Help
Identifying the need for professional help is the first step. The next step involves reaching out to a primary care physician or a mental health professional. A consultation will involve discussing symptoms, medical history, and personal experiences. Thereafter, a personalized treatment plan can be developed. This plan often involves a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments.
Consistent engagement in the treatment plan is essential for achieving optimal results. This might involve regular therapy sessions, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications. Finally, ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed are crucial for long-term well-being.
Self-Management Strategies
Taking control of your anxiety and panic responses is crucial for improving your overall well-being. Learning effective self-management strategies empowers you to navigate challenging situations with greater resilience and confidence. These techniques are not a replacement for professional help, but rather valuable tools to use alongside therapy or medication, if applicable.Implementing these strategies consistently can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of panic and anxiety attacks, making daily life more manageable and enjoyable.
By incorporating these practices into your routine, you can build coping mechanisms that support your mental health and overall well-being.
Relaxation Techniques for Panic Attacks
Effective relaxation techniques can help calm the body and mind during a panic attack. These methods focus on slowing down your heart rate, regulating breathing, and reducing physical tension. Learning these techniques empowers you to manage your responses to anxiety-provoking situations.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises are fundamental for managing panic attacks. They help regulate your nervous system and promote a sense of calm. These techniques focus on slow, controlled inhalations and exhalations, which can help reduce feelings of panic and anxiety.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in your body. This process helps release physical tension that often accompanies anxiety and panic attacks. By focusing on the physical sensations, you can learn to recognize and manage the physical manifestations of anxiety.
Relaxation Techniques for Anxiety Attacks
Relaxation techniques are crucial in managing anxiety attacks. They help calm the body and mind, reducing the intensity of anxiety symptoms. By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can develop coping mechanisms for managing anxiety-provoking situations.
- Mindfulness Exercises: Mindfulness exercises focus on present-moment awareness. They involve paying attention to your thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations without judgment. By practicing mindfulness, you can learn to observe and accept your anxiety without getting swept away by it.
- Meditation: Meditation practices, including guided meditations, help cultivate a sense of inner peace and calmness. These techniques involve focusing on your breath or a specific mantra to quiet the mind and reduce anxiety. Regular meditation can help you develop a stronger sense of self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Coping Mechanisms for Anxiety-Provoking Situations
Developing coping mechanisms is essential for managing anxiety-provoking situations. These strategies provide practical tools to navigate stressful encounters and reduce the intensity of anxiety responses.
- Cognitive Restructuring: This technique involves identifying and challenging negative or unhelpful thoughts that contribute to anxiety. By replacing negative thoughts with more realistic and positive ones, you can change your emotional response to stressful situations.
- Problem-Solving: Addressing the root cause of anxiety-provoking situations can significantly reduce anxiety levels. Breaking down problems into smaller, manageable steps can provide a sense of control and reduce feelings of overwhelm.
Practical Strategies for Managing Anxiety and Panic Symptoms
Implementing practical strategies into your daily life is crucial for managing anxiety and panic symptoms. These strategies help you develop coping mechanisms and reduce the frequency and intensity of these experiences.
- Establishing a Routine: Maintaining a consistent daily routine can provide a sense of structure and predictability, reducing feelings of anxiety and promoting a sense of control.
- Time Management: Effective time management techniques help prevent feelings of being overwhelmed and reduce stress associated with deadlines and responsibilities. By prioritizing tasks and planning your time effectively, you can maintain a sense of control and reduce the likelihood of experiencing anxiety.
Relaxation Techniques Table
| Technique | Benefits | Step-by-Step Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Reduces heart rate, promotes relaxation, and calms the nervous system. | 1. Find a comfortable position. 2. Inhale deeply through your nose, filling your lungs. 3. Hold your breath for a few seconds. 4. Exhale slowly through your mouth, releasing tension. 5. Repeat for several minutes. |
| Progressive Muscle Relaxation | Releases physical tension, reduces anxiety, and promotes relaxation. | 1. Identify a muscle group to tense. 2. Tense the muscles for a few seconds. 3. Release the tension and feel the relaxation. 4. Repeat with other muscle groups. |
| Mindfulness Exercises | Increases awareness of thoughts and feelings without judgment, promoting calmness. | 1. Find a comfortable position. 2. Focus on your breath. 3. Notice your thoughts and feelings without judgment. 4. Return your focus to your breath. |
| Meditation | Promotes inner peace, reduces anxiety, and improves focus. | 1. Find a quiet space. 2. Find a comfortable position. 3. Focus on your breath. 4. Observe your thoughts and feelings without judgment. |
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, while panic and anxiety attacks share some overlapping symptoms, they represent distinct experiences with different physiological and psychological underpinnings. Understanding the unique characteristics of each—from the sudden surge of panic to the persistent worry of anxiety—is key to effective self-management and seeking appropriate professional help. This knowledge empowers individuals to navigate these challenges with greater awareness and resilience.