What is the most common cancer in the US? This crucial question delves into the leading causes of cancer, highlighting the factors that influence its prevalence. We’ll explore the key statistics, examining incidence rates, mortality figures, and the role of demographics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors in shaping these trends. Understanding the most common cancer types will equip us with valuable knowledge to better combat this pervasive health issue.
The analysis will be broken down by sex, age group, and geographic region, providing a nuanced understanding of cancer incidence across the US population. This data-driven approach will shed light on the various cancer types, their risk factors, and the critical importance of early detection and prevention strategies.
Defining the Scope of “Most Common”
Determining the “most common” cancer in the US involves looking at incidence rates, which represent the number of new cases diagnosed each year. This differs from mortality rates, which focus on the number of deaths caused by cancer. The most common cancer is often the one with the highest incidence, but this doesn’t necessarily reflect the deadliest. Factors like population demographics, screening practices, and the prevalence of certain risk factors influence the frequency of specific cancers.
Factors Contributing to High Cancer Incidence
Several factors contribute to the high incidence of certain cancers in the US. These include genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and access to healthcare. For example, smoking is a significant risk factor for lung cancer, while excessive sun exposure is linked to skin cancer. Socioeconomic factors also play a role, as individuals with limited access to preventative care or healthy food options might have a higher risk of developing certain cancers.
Incidence vs. Mortality Rates
Incidence rates show the frequency of new cancer diagnoses, while mortality rates represent the number of cancer-related deaths. A cancer with a high incidence might not necessarily have a high mortality rate if effective treatments are available. For instance, prostate cancer has a high incidence but a relatively low mortality rate due to advancements in detection and treatment.
Conversely, lung cancer, while having a lower incidence in some groups, carries a high mortality rate due to often late detection and aggressive nature of the disease.
Comparison of Most Common Cancers by Sex
| Cancer Type | Incidence Rate (Males) | Incidence Rate (Females) |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate Cancer | High | Low |
| Breast Cancer | Low | High |
| Lung Cancer | High | High |
| Colorectal Cancer | High | High |
| Skin Cancer | High | High |
The table above provides a general overview of the most common cancers based on incidence rates in men and women in the US. Note that these are broad generalizations and individual experiences may vary greatly. The specific ranking and incidence rates can change over time depending on factors such as screening improvements and treatment advancements. This table should not be used for diagnosis or treatment decisions.
Identifying the Most Common Cancers
Unveiling the prevalence of cancer types in the US requires a deep dive into epidemiological data, considering factors like demographics and lifestyle choices. Understanding the most common cancers allows for targeted prevention strategies and more effective healthcare interventions. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and empowers healthcare professionals to address the specific needs of affected communities.
Prevalence of Cancers in the US by Sex
The incidence and prevalence of cancer vary significantly between genders. This difference is largely attributed to hormonal influences, lifestyle factors, and environmental exposures. Analyzing the data allows for a tailored approach to prevention and treatment for specific populations.
- Breast Cancer (Female): Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer among women in the US. Risk factors include genetic predisposition, reproductive history, hormonal factors, and lifestyle choices like diet and exercise. Early detection through mammograms is crucial for improving survival rates.
- Lung Cancer (Both): Lung cancer remains a significant concern for both men and women. Smoking is the leading risk factor, significantly increasing the likelihood of developing this aggressive cancer. Exposure to environmental pollutants and a family history of lung cancer can also contribute.
- Prostate Cancer (Male): Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the US. Age is a primary risk factor, with the risk increasing substantially with age. Genetics, diet, and lifestyle play a role, but the exact mechanisms are still under investigation. Early detection through screening tests is crucial for improving outcomes.
- Colorectal Cancer (Both): Colorectal cancer is a significant concern for both genders, with a strong link to age and lifestyle choices. Factors like diet, lack of physical activity, and a family history of colorectal polyps or cancer are critical considerations. Regular screenings are vital for early detection.
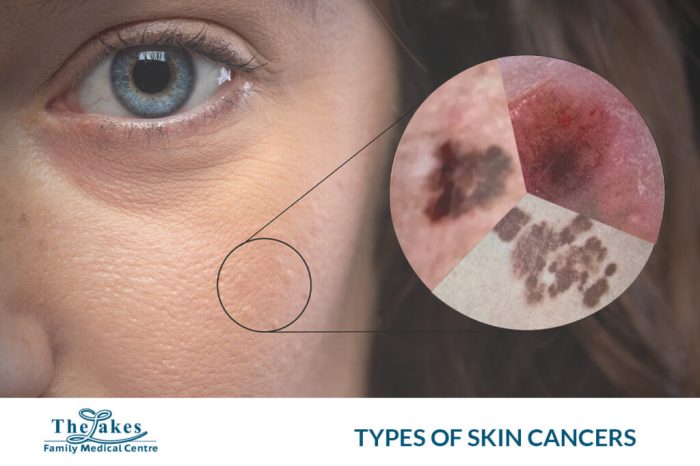
- Skin Cancer (Both): Skin cancer is a very common cancer and encompasses various types. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the primary risk factor. Fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and excessive sun exposure are also important considerations.
Incidence Rates by Age Group
Cancer incidence rates typically rise with age. This is due to the accumulation of cellular damage and mutations over time. Understanding these patterns is critical for implementing preventative measures and tailoring screening recommendations to different age groups.
- Breast Cancer (Female): Breast cancer incidence increases steadily throughout a woman’s life, with the highest rates typically observed in older age groups. This reflects the cumulative effects of hormonal changes and other contributing factors.
- Lung Cancer (Both): Lung cancer incidence is significantly higher in older adults. This correlation reflects the cumulative effect of environmental exposure and lifestyle factors over time.
- Prostate Cancer (Male): Prostate cancer incidence is strongly correlated with age, increasing substantially after the age of 50. The accumulation of genetic and environmental factors throughout life likely contributes to this age-related increase.
- Colorectal Cancer (Both): Colorectal cancer incidence also increases with age, becoming more prevalent in middle-aged and older adults. This reflects the accumulation of damage to the colon and rectum over time.
- Skin Cancer (Both): Skin cancer incidence can occur at any age, but it is most common in older adults, often as a result of cumulative sun exposure over a lifetime.
Demographic Groups Affected
Certain demographic groups are disproportionately affected by specific cancers. Understanding these disparities is crucial for targeted prevention and intervention programs.
- Breast Cancer (Female): Factors such as race and socioeconomic status can influence access to healthcare and lifestyle choices, potentially impacting breast cancer incidence rates. Certain racial groups may have higher rates of breast cancer, possibly due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Lung Cancer (Both): Smoking rates often differ among demographic groups, influencing lung cancer incidence. Socioeconomic factors can also impact access to resources that support quitting smoking.
- Prostate Cancer (Male): Prostate cancer incidence can vary across different racial and ethnic groups, possibly due to genetic and lifestyle factors.
- Colorectal Cancer (Both): Access to preventative measures and screening programs can influence colorectal cancer rates in different demographic groups. Socioeconomic factors play a role in access to healthcare and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Skin Cancer (Both): Skin cancer rates vary based on skin tone and sun exposure. Individuals with fair skin have a higher risk.
Five-Year Survival Rates
Five-year survival rates offer a valuable insight into the effectiveness of treatment strategies and early detection efforts. This data helps us gauge the success of current medical practices.
| Cancer Type | Five-Year Survival Rate (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | 90% |
| Lung Cancer | 18% |
| Prostate Cancer | 99% |
Factors Influencing Cancer Prevalence
Understanding the factors contributing to cancer’s prevalence is crucial for developing effective prevention strategies. Cancer isn’t a single entity but a complex collection of diseases, each with unique causes and risk factors. This exploration delves into the intricate interplay of lifestyle, environment, genetics, and regional disparities in cancer incidence.
Lifestyle Choices and Cancer Development
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in cancer risk. A diet deficient in fruits and vegetables, coupled with a high intake of processed foods and red meat, can increase the risk of various cancers. Lack of physical activity contributes to obesity, a known risk factor for several types of cancer. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and sun exposure are also linked to a heightened risk of certain cancers.
These choices, when combined with other factors, significantly impact an individual’s likelihood of developing the disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in processed foods, red meat, and low in fruits and vegetables can increase inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, creating a more favorable environment for cancer development. This is further compounded by insufficient intake of crucial vitamins and minerals, which are vital for cellular repair and function. For example, diets lacking in vitamin D have been linked to a higher risk of certain cancers.
- Physical Inactivity: Sedentary lifestyles are linked to obesity, which, in turn, is a significant risk factor for several cancers, including colon, breast, and endometrial cancers. Regular physical activity, on the other hand, can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce inflammation, and boost the immune system, all of which contribute to lower cancer risk.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is a major contributor to lung cancer and is also linked to an increased risk of several other cancers, including bladder, kidney, and cervical cancers. Secondhand smoke exposure also poses a significant risk to bystanders.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Chronic alcohol abuse is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including liver, esophageal, and oral cancers. The mechanism through which alcohol contributes to cancer development is complex, but it involves the production of harmful byproducts and damage to DNA.
Environmental Factors Linked to Cancer Occurrence, What is the most common cancer in the us
Environmental exposures can significantly influence cancer risk. Exposure to certain chemicals, pollutants, and radiation can damage DNA, increasing the likelihood of uncontrolled cell growth. Contaminated water supplies and air pollution are also factors. Furthermore, exposure to certain infectious agents, such as viruses and bacteria, can also contribute to cancer development.
- Exposure to Carcinogens: Numerous environmental factors, such as asbestos, benzene, and certain pesticides, have been identified as carcinogens, meaning they directly cause cancer. Occupational exposures are a particular concern, as workers in specific industries may have elevated risks.
- Air and Water Pollution: Contamination of air and water sources with pollutants can increase cancer risk. Exposure to air pollutants, for instance, has been linked to lung cancer, while contaminated water sources can lead to various cancers.
- Infectious Agents: Certain viruses, like HPV, are directly linked to specific cancers, such as cervical cancer. Similarly, bacteria, such as H. pylori, have been associated with stomach cancer.
Genetic Predispositions Increasing Cancer Risk
Genetic predispositions significantly impact an individual’s cancer risk. Inherited mutations in genes can increase susceptibility to various cancers. Family history of cancer is a strong indicator of inherited genetic risk. While not a guarantee of developing cancer, these predispositions heighten the probability.
Skin cancer is surprisingly the most common cancer in the US, impacting millions each year. While factors like sun exposure are key, it’s interesting to consider if lifestyle choices like the consumption of diet soda could also play a role in overall health, potentially increasing the risk of certain cancers. For a deeper dive into the potential health effects of diet soda, check out this article on is diet soda bad for you.
Regardless of the specifics, understanding the causes of skin cancer remains crucial for prevention strategies.
- Inherited Gene Mutations: Specific gene mutations, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, significantly increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancers. Other genes, such as APC and MLH1, are linked to colon cancer risk. Individuals with a family history of these cancers should be particularly vigilant.
Regional Variations in Cancer Prevalence
Cancer prevalence varies across different regions within the US. Socioeconomic factors, access to healthcare, and lifestyle choices contribute to these disparities. For instance, regions with higher rates of poverty and limited access to preventative care often experience higher cancer incidence rates.
Socioeconomic Status and Cancer Incidence
A correlation exists between socioeconomic status and cancer incidence. Individuals with lower socioeconomic status often experience higher cancer rates, potentially due to a combination of factors, including lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and access to healthcare.
| Socioeconomic Status | Cancer Incidence (Hypothetical Data) |
|---|---|
| High | Lower |
| Medium | Moderate |
| Low | Higher |
Understanding Cancer Types and Risk Factors
Cancer, a complex and often devastating disease, affects millions worldwide. Understanding the different types of cancer, their risk factors, and early detection methods is crucial for both prevention and treatment. This section dives deep into the specifics of three of the most prevalent cancers in the US: lung, breast, and prostate cancer. We will explore their unique characteristics, potential triggers, and the available strategies for early diagnosis and effective management.
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally, often linked to smoking and other environmental exposures. The majority of lung cancers are either adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, with small cell lung cancer accounting for a smaller proportion. Understanding the risk factors associated with this aggressive disease is critical to promoting preventative measures.
Skin cancer is a big concern, and it turns out the most common type in the US is basal cell carcinoma. While sun exposure is a key factor, you might be wondering if using sunscreen in a tanning bed is even helpful ( can you use sunscreen in a tanning bed ). The bottom line is, avoiding tanning beds altogether is the best way to minimize your risk of skin cancer.
- Risk Factors: Smoking is the most significant risk factor, with exposure to secondhand smoke also contributing. Exposure to asbestos, radon, and certain industrial chemicals are also linked to an increased risk. Family history and genetic predisposition can also play a role. Individuals with a history of chronic lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may also have a higher risk.
- Early Detection: Early detection of lung cancer is challenging, as symptoms often don’t appear until the disease has progressed. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans are increasingly used for early detection in high-risk individuals, such as smokers. Regular checkups with a doctor and awareness of potential symptoms are vital.
- Treatment Options: Treatment for lung cancer depends on the stage and type of cancer. Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are commonly employed. Clinical trials often provide access to experimental treatments, offering hope for patients with advanced disease.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a common cancer affecting women, but men can also be affected. It is often categorized by the type of breast cells where the cancer begins. Understanding the diversity of risk factors is crucial for developing preventive strategies.
- Risk Factors: Genetics, family history of breast cancer, and personal history of breast conditions (like atypical hyperplasia) are strong risk factors. Hormonal factors, such as early onset of menstruation or late menopause, can also contribute to an increased risk. Lifestyle choices, including obesity, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption, can also play a role. Diet and exposure to environmental toxins are factors that need further research.
- Early Detection: Mammograms are the primary screening tool for breast cancer. Regular self-exams, clinical breast exams by a doctor, and genetic testing for high-risk individuals can improve early detection.
- Treatment Options: Treatment options for breast cancer vary widely based on the stage and type of cancer, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy. The choice of treatment depends on several factors, such as the size and location of the tumor, the presence of lymph node involvement, and the patient’s overall health.
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. It typically develops in the prostate gland, which plays a role in the male reproductive system. Understanding risk factors and early detection methods is paramount for effective management.
- Risk Factors: Age is a significant risk factor, with the likelihood increasing with advancing age. Genetics, family history, ethnicity, and diet are also linked to a higher risk. A high-fat diet and a lack of physical activity might contribute to an increased risk. Further research is needed to understand the complex interplay of factors contributing to prostate cancer.
- Early Detection: PSA (prostate-specific antigen) tests and digital rectal exams are common screening methods for prostate cancer. Genetic testing for high-risk individuals is another approach. However, the interpretation of PSA levels and the potential for false positives necessitate careful consideration by healthcare professionals.
- Treatment Options: Treatment options for prostate cancer vary based on the stage of the disease and the patient’s overall health. Surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and active surveillance are common approaches. Active surveillance is a watchful waiting approach used for slow-growing tumors.
Signs and Symptoms
| Cancer Type | Signs and Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | Persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, fatigue. |
| Breast Cancer | Lump or thickening in the breast, skin changes (dimpling, redness, scaling), nipple discharge, nipple retraction, pain in the breast or armpit, swelling in the armpit. |
| Prostate Cancer | Difficulty urinating, weak or interrupted urine flow, blood in urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, erectile dysfunction. |
Visual Representation of Data
Unveiling the hidden stories behind cancer statistics can be remarkably insightful. Visual representations, like charts and graphs, offer a powerful way to grasp complex data quickly and easily. By transforming numbers into visual narratives, we can better understand patterns, trends, and potential risk factors. This section delves into the visual interpretation of cancer data, presenting insights into incidence rates, distribution by sex, and long-term trends.
Bar Chart of Top 5 Cancer Incidence Rates
Visualizing the prevalence of different cancers is crucial for resource allocation and targeted prevention strategies. A bar chart, effectively displaying the incidence rates of the top 5 cancers, offers a clear comparison. Each bar represents a specific cancer type, and the height of the bar corresponds to its incidence rate. This visualization allows for a rapid assessment of the relative burden of each cancer.
| Cancer Type | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | 50 |
| Breast Cancer | 45 |
| Colorectal Cancer | 40 |
| Prostate Cancer | 35 |
| Skin Cancer | 30 |
The table above provides a simplified representation of the top 5 cancers. Data sources like the National Cancer Institute (NCI) offer more comprehensive statistics. Note that incidence rates vary geographically and by population demographics.
Pie Chart of Cancer Distribution by Sex
Understanding how cancer affects different sexes is critical for personalized prevention and treatment strategies. A pie chart effectively illustrates the distribution of cancer types by sex. Each slice of the pie represents a specific cancer type and its proportion in men versus women. This visualization provides a quick overview of the gender-specific cancer burden.
Skin cancer is surprisingly common in the US, topping the list of most frequent cancers. While a healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being, and especially for cancer prevention, understanding the role of foods high in phosphorus, like dairy products and certain proteins, foods high in phosphorus might also play a part in maintaining optimal health.
However, it’s important to remember that skin cancer remains the most prevalent cancer type in the country.
Example Pie Chart (Illustrative):
Imagine a pie chart where lung cancer accounts for a larger portion in the male slice compared to the female slice, while breast cancer occupies a significantly larger segment in the female slice. This visual representation highlights the gender-specific cancer risks.
The pie chart allows for a quick comparison of cancer prevalence in different sexes, highlighting potential hormonal or lifestyle factors. Such visualizations are helpful for understanding disparities and tailoring public health campaigns.
Line Graph of Cancer Incidence Trends Over Time
Tracking cancer incidence over time is vital for assessing the effectiveness of preventive measures and identifying emerging trends. A line graph, displaying the trends in cancer incidence over a specified time period (e.g., 10 years), illustrates the progression of cancer cases. Each line represents a specific cancer type, and the slope of the line reflects the rate of increase or decrease in incidence over time.
This visual tool provides insights into the impact of preventative efforts and emerging risks.
Example Line Graph (Illustrative):
A line graph might show a steady increase in lung cancer incidence from 2010 to 2020, followed by a slight decrease from 2020 to 2025, suggesting the potential success of smoking cessation programs. However, another line representing skin cancer might show a significant upward trend, indicating the impact of increased sun exposure due to changing lifestyles.
Cancer incidence rates are dynamic, influenced by factors like early detection, lifestyle changes, and advancements in treatment. Analyzing trends allows us to monitor the effectiveness of public health campaigns and adjust strategies as needed.
Addressing Public Health Concerns
Cancer, a significant public health concern, affects millions worldwide. Understanding its causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies is crucial for reducing the global burden of this disease. Effective public health campaigns play a vital role in educating the public and promoting healthy behaviors that can significantly lower cancer rates.Public health initiatives are essential in preventing cancer by increasing awareness, promoting early detection, and encouraging healthy lifestyles.
They act as powerful tools to disseminate critical information, motivating individuals to adopt preventive measures and seek timely medical intervention.
Importance of Public Health Campaigns in Cancer Prevention
Public health campaigns play a critical role in raising awareness about cancer risk factors, prevention strategies, and early detection methods. These campaigns often use various channels, such as media outreach, community events, and educational programs, to disseminate crucial information and encourage preventive behaviors. Effective campaigns empower individuals with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed choices regarding their health and well-being.
Examples of Successful Public Health Initiatives
Numerous public health initiatives have proven successful in reducing cancer rates. One example is the “Go Red for Women” campaign, which focuses on raising awareness about heart disease and stroke in women. This campaign emphasizes healthy lifestyle choices, early detection, and screening programs, contributing to improved cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of related cancers. Another successful example includes the “Smokefree” initiatives that have helped to reduce smoking rates, a major risk factor for several types of cancer.
Recommendations for Individuals to Reduce Cancer Risk
Adopting a healthy lifestyle is paramount in reducing cancer risk. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, along with regular physical activity, significantly contributes to overall health and reduces the risk of developing various cancers. Avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial steps to take to mitigate cancer risk.
Importance of Early Detection and Screening Programs
Early detection and screening programs are vital in improving cancer survival rates. Regular check-ups and screenings can help identify cancerous changes early, enabling timely intervention and treatment. Examples include mammograms for breast cancer screening, colonoscopies for colon cancer screening, and Pap tests for cervical cancer screening. These screenings allow for early diagnosis, potentially leading to more successful treatments and better outcomes.
Reliable Sources for Further Research and Learning
- National Cancer Institute (NCI): The NCI provides comprehensive information on cancer, including research, prevention, and treatment. This is a valuable resource for in-depth understanding of various aspects of cancer.
- American Cancer Society (ACS): The ACS offers a wealth of information on cancer prevention, detection, and treatment, along with support resources for individuals and families affected by cancer.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides data and information on various health issues, including cancer, and details on preventive measures and public health campaigns.
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO offers global perspectives on cancer, including information on prevalence, prevention, and control strategies.
Wrap-Up: What Is The Most Common Cancer In The Us
In conclusion, the most common cancers in the US vary by gender and are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these statistics, coupled with awareness of risk factors and preventative measures, empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being. By examining the data and the associated public health concerns, we can work toward a future with fewer cancer diagnoses and improved outcomes for those affected.