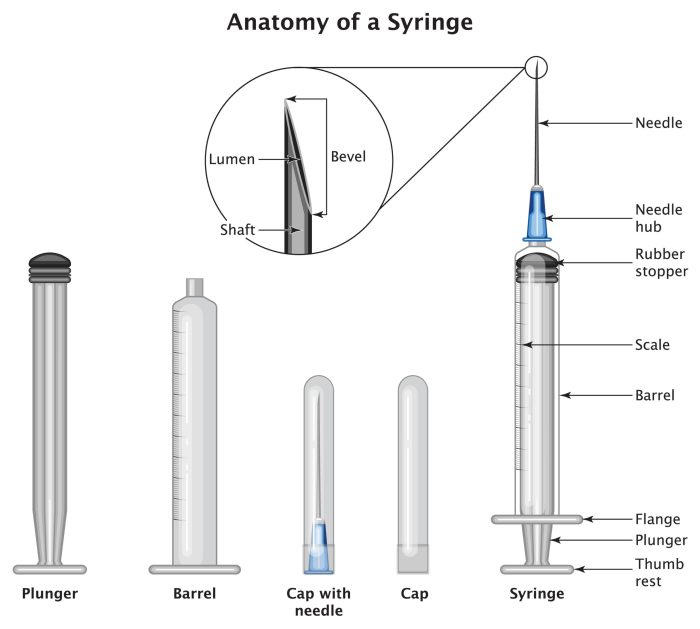
How to select the correct needle size for an injection is crucial for patient safety. Using the wrong size can lead to complications, from discomfort to serious health risks. This comprehensive guide will delve into the factors influencing needle size selection, the methods for determining the appropriate gauge, and the essential safety precautions to follow….
How to Reduce Uric Acid A Comprehensive Guide
How to reduce uric acid? This comprehensive guide delves into various strategies, from dietary adjustments to lifestyle modifications, and even medication considerations. High uric acid levels, or hyperuricemia, can lead to painful gout and other health problems. Understanding the factors contributing to elevated uric acid and implementing effective management strategies is key to maintaining overall…
Why Does Alcohol Make Me Sleepy? Unveiling the Reasons
Why does alcohol make me sleepy? This seemingly simple question delves into a complex interplay of physiological responses, individual differences, and potential interactions. From the initial impact on brain function to long-term consequences, understanding this phenomenon is key to responsible alcohol consumption and overall well-being. This exploration examines the science behind alcohol’s sleep-inducing effects, considering…
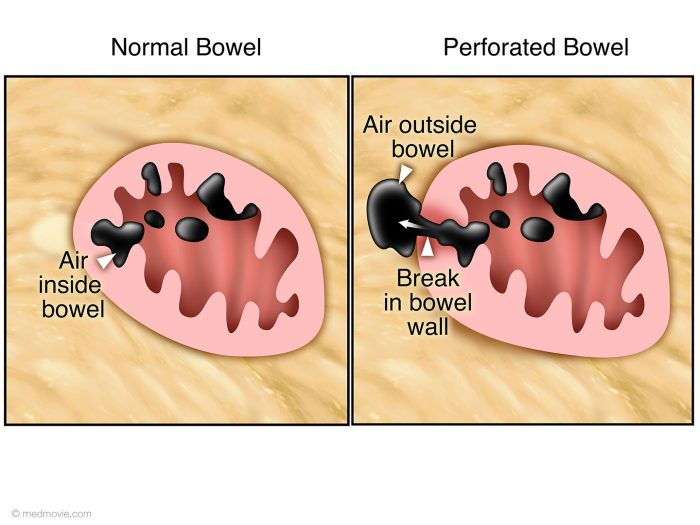
Whats a Bowel Perforation? A Deep Dive
Whats a bowel perforation – What’s a bowel perforation? It’s a serious medical condition where a hole develops in the wall of the intestines. This can happen spontaneously, due to trauma, or various underlying conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for anyone seeking knowledge about this potentially life-threatening…
Paxlovid Mouth What to Do
Paxlovid mouth what to do? This guide explores the potential oral side effects of Paxlovid, offering practical strategies for managing discomfort, and highlighting the crucial role of professional interventions and patient self-care. Many users experience oral issues while taking Paxlovid, ranging from dry mouth and sores to more severe complications. Understanding the potential problems, along…
Low Iron Level Causes Understanding the Factors
Low iron level causes are multifaceted, stemming from a variety of dietary, physiological, and medical factors. From dietary deficiencies to blood loss, and absorption issues, this comprehensive guide explores the intricate web of causes contributing to low iron levels. We’ll delve into the specific roles of diet, blood loss, absorption, and other potential contributing factors,…
Comparing Vyvanse vs Adderall A Deep Dive
Comparing Vyvanse vs Adderall: This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these stimulant medications, exploring their chemical makeup, potential benefits and drawbacks, and patient experiences. We’ll examine the nuances of their formulations, their impact on various conditions, and provide a balanced overview for patients and healthcare providers alike. Both Vyvanse and Adderall are commonly…
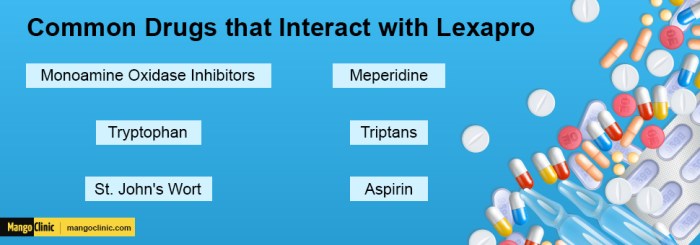
Prozac Fluoxetine vs Lexapro Escitalopram A Deep Dive
Prozac fluoxetine vs lexapro escitalopram: A comparison of these two popular antidepressants, both Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), is crucial for individuals seeking effective treatment. This in-depth look examines their mechanisms of action, common side effects, dosage ranges, and potential interactions. Understanding the nuances between these drugs empowers informed decision-making with a healthcare professional. This…
Acne and Oily Skin Your Complete Guide
Acne and oily skin can be a real challenge, affecting self-esteem and confidence. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, types, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, home remedies, skincare routines, and even how your skin reacts to products. We’ll explore everything from hormonal imbalances and genetics to dietary choices, environmental factors, and stress levels. We’ll cover various…
Surgery Not Needed for Rotator Cuff Tears Alternatives Explored
Surgery not needed for rotator cuff tears is a growing area of interest for those experiencing pain and discomfort in their shoulders. This in-depth exploration delves into the various non-surgical treatment options available, providing a comprehensive overview of how to effectively manage rotator cuff tears without resorting to surgery. From physical therapy and medication to…