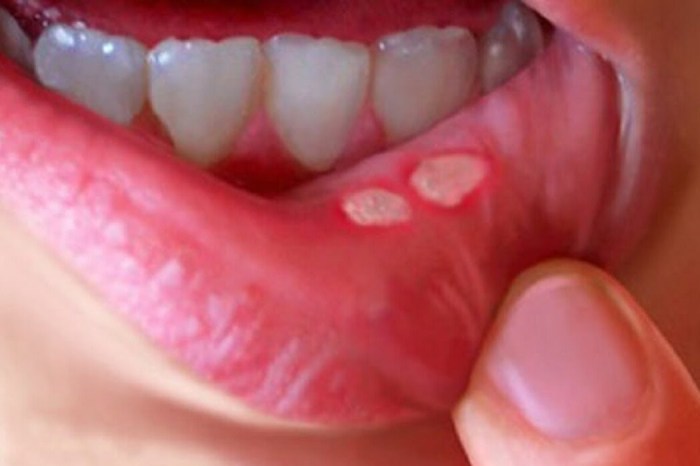
Canker sore on tongue, those pesky little ulcers that pop up in the mouth, can be incredibly frustrating. This guide dives deep into understanding these painful sores, from their causes and symptoms to effective home remedies and when to seek professional help. We’ll explore everything you need to know about identifying, treating, and preventing canker…
Ella vs Plan B Contraceptive Comparison
Ella vs Plan B: This in-depth comparison explores the key differences between EllaOne and Plan B, two emergency contraceptive options. We’ll delve into their active ingredients, potential side effects, effectiveness, cost, and accessibility. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their reproductive health. From active ingredients and dosages to potential side effects…
Allergy Medication and Airport Security A Guide
Allergy medication and airport security can be a tricky combination. Navigating airport security with allergy medications requires careful planning and understanding of regulations. This guide will walk you through the policies, challenges, and solutions for travelers with allergies, ensuring a smoother and less stressful experience. Airport security policies regarding medications vary, but generally, prescription medications…
Is Blood Pressure Higher in the Morning? Exploring the Why
Is blood pressure higher in the morning? Yes, it often is, and understanding why this happens is crucial for managing your overall health. Our bodies have a natural rhythm, or circadian rhythm, that influences many functions, including blood pressure. This morning peak in blood pressure isn’t necessarily a cause for alarm, but knowing the factors…
L-Theanine and Magnesium A Powerful Duo
L theanine and magnesium – L-theanine and magnesium, a powerful duo for well-being. This exploration dives into the individual properties of each, delving into their potential synergistic effects when combined. We’ll uncover the science behind their interaction, exploring their impact on stress, cognition, and sleep. Expect a detailed look at dosage ranges, potential benefits, and…
Does the Pill Work for PMDD Treatment?
Does the pill work as a PMDD treatment? This in-depth exploration delves into the complex relationship between hormonal birth control and Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD). We’ll examine the science behind the pill, its potential benefits, and drawbacks, while also considering individual variability and alternative approaches. Understanding the intricacies of PMDD management is crucial for navigating…
Right Handed Left Handed Stroke Differences
Right handed left handed stroke different reveals fascinating variations in how we write. From the subtle grip to the trajectory of our strokes, there’s a world of difference between right and left-handed individuals. This exploration dives into the characteristics of each hand’s writing style, the impact on writing tools, the developmental stages of learning, and…
De Novo Metastatic Breast Cancer A Deep Dive
De novo metastatic breast cancer presents a unique challenge, representing breast cancer that spreads to other parts of the body from the start, without any prior evidence of local or regional spread. This contrasts with other forms of metastatic breast cancer, and understanding its distinct characteristics, risk factors, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options is crucial…
Fish Oil Supplements AFib Risk A Deep Dive
Fish oil supplements AFib risk is a complex issue, with ongoing research attempting to unravel the potential connections between these dietary supplements and the development of Atrial Fibrillation (AFib). This blog post delves into the science behind fish oil’s purported cardiovascular benefits and examines the existing evidence linking fish oil intake to AFib risk. We’ll…
How to Eat During an IBD Flare-Up
How to eat during an ibd flare up – How to eat during an IBD flare-up is crucial for managing symptoms and promoting healing. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of dietary strategies, from understanding the disease to specific recommendations and safe food preparation. It delves into the nuances of IBD flare-ups, highlighting the importance…