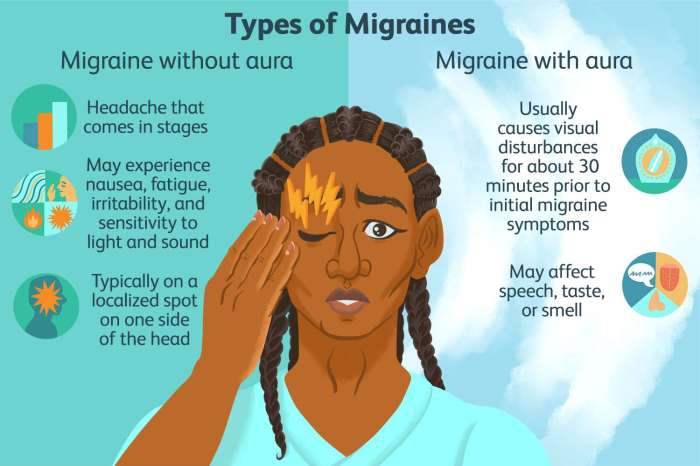
Episodic migraine prevention medications are a crucial aspect of managing these debilitating headaches. This guide delves into the various types of preventative treatments, their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, potential side effects, and important considerations for patient selection. We’ll explore everything from CGRP inhibitors to beta-blockers, providing a comprehensive overview to help you understand the best…
Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Psoriasis A Guide
Anti inflammatory diet for psoriasis – Anti-inflammatory diet for psoriasis is a powerful approach to managing this chronic skin condition. It’s not just about avoiding certain foods, but about understanding how your diet directly impacts inflammation and your psoriasis symptoms. This comprehensive guide explores the principles, food choices, and practical strategies to create a personalized…
Why Is It So Hard to Cut Back on Sodium?
Why is it so hard to cut back on sodium? This isn’t just about willpower; it’s a complex interplay of physiological cravings, ingrained habits, and the pervasive presence of sodium in processed foods. We’ll delve into the science behind salt cravings, explore the sneaky ways food manufacturers add sodium, and uncover the psychological factors that…
Sliver Diamine Fluoride vs Sealants A Deep Dive
Sliver diamine fluoride vs sealants: This comparison explores the two leading preventative dental care methods. Sealants are a popular choice, often seen as a straightforward solution. However, silver diamine fluoride (SDF) offers a unique approach, with both advantages and disadvantages. We’ll examine their application methods, efficacy, patient considerations, safety, and even delve into clinical case…
Conversation Issues Discussing Psoriasis A Deep Dive
Conversation issues discussing psoriasis are complex, encompassing a wide range of challenges faced by those living with the condition. This exploration delves into the nuances of communication, from understanding the emotional toll to navigating difficult conversations in various settings, including family, friendships, and the workplace. We’ll also examine the crucial role of support communities and…
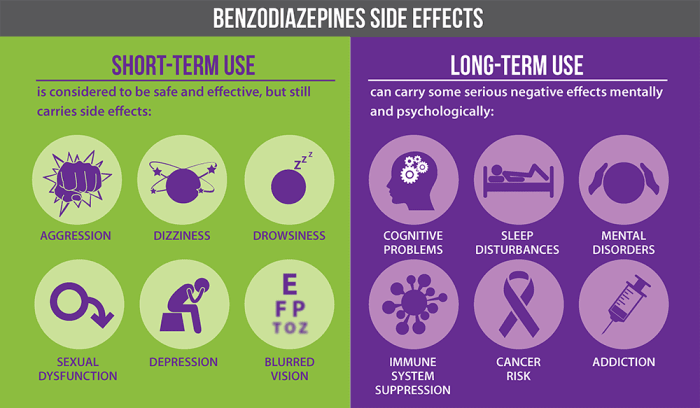
Benzodiazepines Uses, Types, and Risks
Uses types and risks of benzodiazepines – Benzodiazepines: Uses, Types, and Risks sets the stage for a detailed exploration of these medications. This in-depth look will cover everything from their chemical makeup and mechanism of action to their various applications, potential dangers, and long-term considerations. We’ll analyze different types, examining their potency, duration, and common…
Diagnosis and Testing for HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Diagnosis and testing for her2 positive breast cancer – Diagnosis and testing for HER2-positive breast cancer is crucial for effective treatment. This comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of identifying this aggressive form of breast cancer, from understanding the role of the HER2 protein to the various diagnostic tests used. We’ll explore the nuances of…
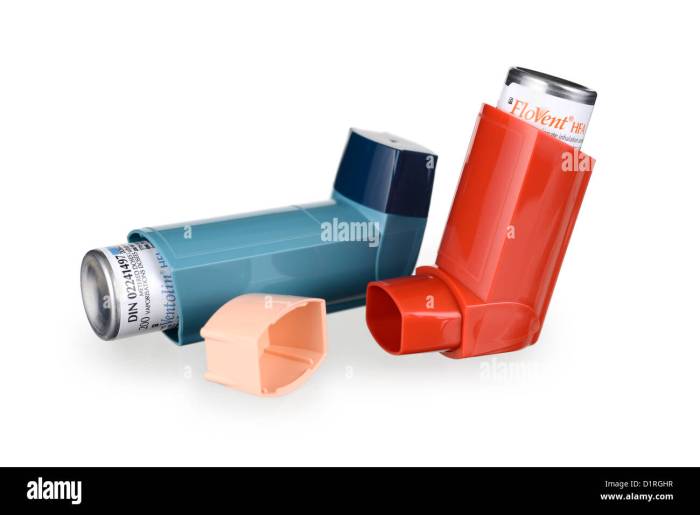
Flovent, Qvar, Pulmicort, Alvesco, or Asmanex A Deep Dive
Flovent qvar pulmicort alvesco or asmanex – Flovent, Qvar, Pulmicort, Alvesco, or Asmanex – these inhaled corticosteroids are frequently prescribed for respiratory conditions. Understanding their similarities and differences, mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making. This comprehensive guide dives into each medication, comparing their effectiveness, usage, and considerations for patients….
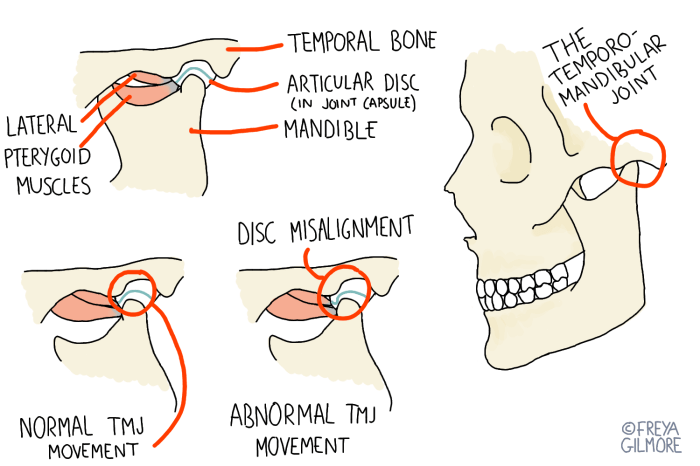
What is TMJ Disorder? A Deep Dive
What is TMJ disorder? This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, exploring everything from their intricate anatomy to effective treatment options. Understanding the structure and function of the TMJ is crucial to grasping the various types of TMJ disorders and their associated symptoms. We’ll also explore the causes, diagnosis, and…
Autoimmunity Neuroinflammation in Fibromyalgia Unveiling the Link
Autoimmunity neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia is a fascinating and complex area of research. This condition, characterized by widespread pain and fatigue, is increasingly understood to involve interactions between the immune system and the nervous system. We’ll delve into the potential mechanisms by which these processes intertwine, exploring the suspected roles of autoimmunity and neuroinflammation in the…