Medicares inpatient only list – Medicare inpatient only list details the specific medical services covered exclusively during inpatient stays. Understanding these services is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This guide delves into the specifics of Medicare’s inpatient coverage, from identifying covered services to navigating the reimbursement process and patient rights.
This comprehensive resource provides a detailed look at what constitutes inpatient care under Medicare, the facilities that qualify, and the conditions and procedures typically requiring an inpatient stay. We’ll explore the coverage and reimbursement processes, highlighting potential limitations and exclusions.
Understanding Medicare Inpatient Coverage: Medicares Inpatient Only List
Medicare’s inpatient coverage is a crucial aspect of healthcare access for seniors and those with disabilities. Understanding the specifics of this coverage can help individuals navigate the healthcare system effectively and make informed decisions about their care. This overview will detail the concept of inpatient services, the different types of Medicare plans that cover them, and a comparison to other insurance options.Medicare’s inpatient benefits are designed to cover the costs of care received in a hospital or similar facility when a patient requires a stay for medical treatment.
This contrasts with outpatient care, where patients receive services but do not stay overnight. The focus is on ensuring necessary medical attention and recovery in a controlled environment.
Definition of Inpatient Care
Inpatient care, as it relates to Medicare, refers to medical services provided in a hospital or skilled nursing facility (SNF) when a patient requires continuous medical supervision and overnight stays. This care is distinct from outpatient services, which typically do not require an overnight stay. Examples of inpatient services include hospital stays for surgery, treatment of acute illnesses, or extended rehabilitation.
Types of Medicare Plans Covering Inpatient Services
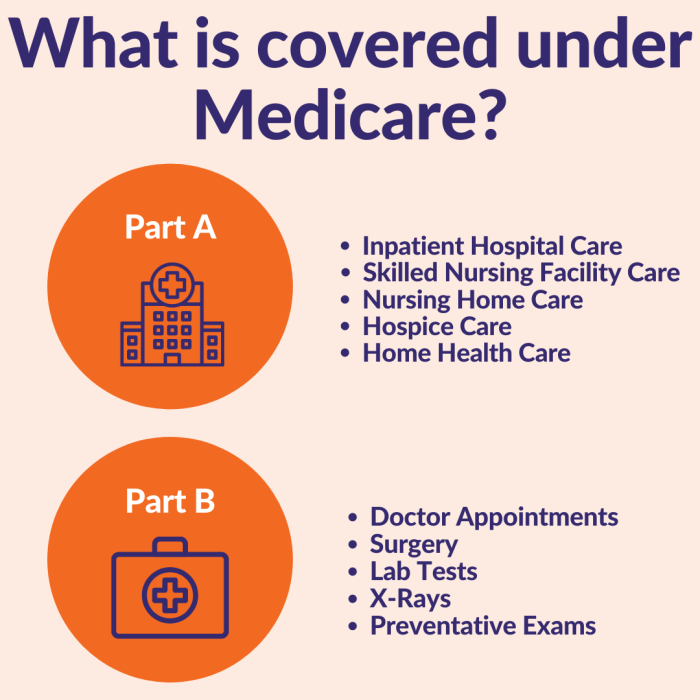
Medicare has several plan options, each with varying degrees of coverage. All plans include Part A, which covers hospital inpatient services under certain conditions. Part A coverage is often paired with other parts to ensure comprehensive benefits.
- Medicare Part A (Hospital Insurance): This part covers the costs of inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, and some hospice care. Eligibility requirements must be met for coverage.
- Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance): This part covers a range of medical services, including some outpatient care, but does not usually cover the full cost of inpatient care on its own. It typically supplements Part A.
- Medicare Advantage Plans: These private plans offered by Medicare providers often include inpatient coverage, but the details and specifics vary by plan. They typically bundle Parts A, B, and sometimes other benefits like prescription drugs.
- Medicare Supplement Plans (Medigap): These plans supplement Medicare’s coverage gaps, often including some inpatient care expenses that Medicare Part A does not fully cover. They do not directly cover Part A, but assist with co-pays and deductibles.
Comparison with Other Healthcare Insurance Options
Medicare’s inpatient coverage, through Part A and other options, offers a baseline of hospital care benefits. Other insurance plans, such as employer-sponsored health insurance or private insurance plans, might provide more extensive coverage, including potentially higher coverage limits, or more choices for facilities. The specific benefits and limitations of each plan should be carefully reviewed.
Levels of Medicare Coverage for Inpatient Care
| Plan Type | Coverage Details | Limitations | Eligibility Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medicare Part A | Covers inpatient care in hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, and some hospice care. | Coverage is subject to certain conditions, including a deductible and a maximum benefit period. | Must meet specific criteria, including a period of work covered by Social Security. |
| Medicare Part B | Covers some medical services, but not typically the full cost of inpatient care. | Does not cover all inpatient expenses. | Enrollees must be eligible for Medicare Part A. |
| Medicare Advantage Plans | Often include inpatient coverage, but details vary. | Coverage specifics are determined by the plan. | Must be eligible for Medicare Part A and B. |
| Medicare Supplement Plans | Supplement Medicare coverage gaps, often including inpatient care expenses. | Benefits vary by plan. They don’t directly cover Part A, but assist with co-pays and deductibles. | Must be enrolled in Medicare Part A and B. |
Identifying Inpatient-Only Services
Medicare’s inpatient coverage focuses on services necessary for a patient’s stay in a hospital or skilled nursing facility. Understanding which services are considered “inpatient-only” is crucial for navigating the intricacies of Medicare benefits. These services are often essential for a patient’s recovery and well-being during a period of intensive care.Medicare defines inpatient services as those that require the continuous supervision and care provided within a hospital or skilled nursing facility setting.
This differs from outpatient services, which can be provided on a less-intensive, intermittent basis. Crucially, the level of care and the nature of the medical needs dictate whether a service falls under inpatient coverage.
Navigating the Medicare inpatient-only list can be tricky, but focusing on a healthy diet, like incorporating plenty of high protein foods for muscle building here , can be incredibly beneficial. Ultimately, understanding these specific requirements within the Medicare system is key to ensuring smooth healthcare transitions and suitable treatment plans. Knowing what’s covered and what’s not is crucial for patients.
Specific Medical Services Covered Inpatient Only, Medicares inpatient only list
Inpatient-only services are those that are deemed integral to a patient’s care during an extended hospital stay. These services are typically not feasible or appropriate to provide on an outpatient basis, requiring constant monitoring and specialized equipment. Examples include specialized procedures, extensive diagnostics, and intensive therapies directly related to the patient’s acute medical condition.
Criteria for Inpatient-Only Services
A service is considered inpatient-only when it necessitates the specialized environment and continuous monitoring of a hospital or skilled nursing facility. Factors determining this classification include the need for constant medical supervision, the complexity of the procedure, the potential for complications, and the required equipment and resources. In essence, the service is considered integral to the inpatient stay and cannot be effectively or safely provided on an outpatient basis.
Examples of Inpatient-Only Procedures
Many medical procedures and treatments are exclusively provided during an inpatient stay. Examples include:
- Complex surgeries requiring extensive monitoring and post-operative care.
- Intensive respiratory therapies, such as mechanical ventilation, for patients with severe respiratory conditions.
- Continuous monitoring and treatment for patients experiencing acute cardiac events or critical illnesses.
- Diagnostic procedures requiring specialized equipment or facilities not typically found in outpatient settings.
- Treatments that require close observation for potential complications or adverse reactions.
Common Reasons for Inpatient Stays
A variety of medical conditions necessitate inpatient stays. Common reasons include:
- Acute illnesses requiring intensive medical intervention.
- Complex surgical procedures and their associated recovery needs.
- Critical injuries requiring continuous monitoring and specialized care.
- Conditions requiring ongoing medical treatment and support.
- Conditions requiring specialized equipment or resources that are not available in outpatient settings.
Categorization of Inpatient-Only Services by Medical Specialty
The following table categorizes inpatient-only services based on medical specialties:
| Medical Specialty | Inpatient-Only Services | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiology | Cardiac catheterization, open-heart surgery, cardiac monitoring, intensive cardiac care | These procedures often require specialized equipment, continuous monitoring, and intensive care, making them inpatient-only. |
| Neurology | Stroke treatment, neurosurgery, intensive care for neurological conditions, diagnostic procedures involving specialized equipment. | Stroke treatment, for example, needs constant monitoring and intervention. |
| Pulmonology | Mechanical ventilation, intensive respiratory therapies, management of severe respiratory illnesses. | Conditions like severe pneumonia or acute respiratory distress syndrome often require inpatient management. |
| Surgery | Major surgeries, post-operative care for complex procedures, treatment of surgical complications. | Complex surgeries require specialized care and monitoring, both during and after the operation. |
| Critical Care | Intensive care unit (ICU) stays, advanced life support, critical illness management. | The ICU environment provides constant monitoring and support for critically ill patients. |
Medicare’s Inpatient Facility List
Medicare’s inpatient facility list is a crucial resource for beneficiaries seeking care in approved hospitals and facilities. Understanding the criteria for inclusion on this list ensures that individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare options, relying on facilities that meet specific standards and receive Medicare reimbursement. This section details the process for accessing and understanding the list, along with the factors that influence a facility’s inclusion.Finding the right inpatient facility is vital for effective healthcare.
Medicare’s rigorous standards for facilities ensure beneficiaries receive quality care. This section explores how Medicare selects facilities and what factors determine their inclusion in the program.
Accessing the List of Medicare-Approved Inpatient Facilities
Medicare maintains a comprehensive database of participating facilities. The exact method for accessing this list may vary, potentially involving online searches or contacting Medicare directly. Information is available on the official Medicare website, often through a searchable directory.
Criteria for Medicare Reimbursement
Medicare-approved facilities must meet stringent criteria to ensure quality of care and reimbursement. These criteria are multifaceted and encompass several aspects of the facility’s structure and operations. Facilities must demonstrate adherence to standards, including proper staffing levels, essential medical equipment, and a commitment to patient safety. Facilities meeting these criteria receive reimbursement for services provided to Medicare beneficiaries.
Searching for Facilities by Location, Type, or Specialty
Medicare’s online directories often include search tools allowing users to filter results by location, type of facility (e.g., hospital, skilled nursing facility), and specialty (e.g., cardiology, oncology). Beneficiaries can refine their search to find facilities that meet their specific needs and geographic preferences.
Qualifications for Medicare-Certified Hospitals
| Facility Type | Location | Accreditation | Services Offered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Care Hospitals | Geographically dispersed across the nation | Must hold accreditation from recognized organizations like The Joint Commission | A wide array of medical and surgical services |
| Skilled Nursing Facilities | Located in communities across the country | Must meet standards set by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) | Post-acute care, rehabilitation, and skilled nursing services |
| Psychiatric Hospitals | Nationwide | Accreditation from the Joint Commission or other recognized accrediting bodies | Specialized care for mental health conditions |
These examples illustrate the types of facilities included in the Medicare inpatient list. The specific criteria and requirements vary depending on the facility type.
Factors Affecting Facility Inclusion
A facility’s inclusion in the Medicare inpatient list depends on its ability to meet stringent standards. Factors influencing this decision include compliance with regulations, quality of care measures, and financial stability. Facilities must maintain a certain level of financial stability to ensure continuous operation and appropriate reimbursement practices. A facility’s reputation and history of compliance with Medicare regulations play a significant role in its continued inclusion.
This process ensures that only facilities with the capacity and commitment to high-quality care are recognized.
Conditions and Procedures
Understanding Medicare’s inpatient coverage requires a grasp of the specific medical conditions and procedures that frequently necessitate a stay in a hospital. Inpatient care is crucial for patients with complex illnesses or injuries demanding continuous monitoring, specialized interventions, and potentially extensive treatment regimens. This section will delve into such conditions and procedures.
Conditions Requiring Inpatient Care
Inpatient care is often necessary for conditions requiring constant monitoring and intensive treatment. These conditions typically involve significant risks, complications, or the need for immediate intervention. For instance, a patient experiencing a severe heart attack may require immediate monitoring and interventions like angioplasty, which are typically performed in a hospital setting. The level of care required for certain conditions dictates whether an inpatient stay is necessary.
- Severe Infections: Sepsis, pneumonia, and other severe infections often demand hospitalization for intensive care, intravenous antibiotics, and fluid management. The need for close monitoring of vital signs and response to treatment is paramount.
- Major Trauma: Patients with significant injuries from accidents or violence frequently require inpatient care. The severity of the injuries, potential for complications, and the need for surgical interventions often necessitate a hospital stay. For example, a patient with multiple fractures or a head injury might require extended observation and specialized care.
- Acute Neurological Conditions: Conditions like strokes, brain tumors, and severe headaches frequently demand inpatient care for close monitoring of neurological function and management of potential complications. Continuous monitoring for changes in condition and swift response to neurological deterioration are critical.
- Major Surgical Procedures: Procedures such as open heart surgery, complex joint replacements, and extensive abdominal surgeries necessitate inpatient care to manage post-operative complications and ensure patient recovery. Patients undergoing these procedures may require extensive observation and specialized care during their recovery period.
- Critical Medical Illnesses: Conditions such as severe kidney failure, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and organ failure often demand inpatient care for intensive supportive care and management of organ dysfunction. Continuous monitoring and interventions, such as dialysis, are often necessary.
Procedures Performed During Inpatient Stays
Certain procedures can only be performed in a hospital setting due to the required resources and specialized personnel. These procedures often carry significant risks and require meticulous care and close monitoring.
- Surgical Procedures: Many complex surgical procedures, including open-heart surgery, organ transplants, and major orthopedic surgeries, require specialized equipment, skilled surgeons, and intensive care units for post-operative monitoring and treatment.
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Procedures: Procedures within an intensive care unit (ICU) are often performed to stabilize patients with critical illnesses. These procedures can include mechanical ventilation, dialysis, and other life-support measures.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Some diagnostic procedures, such as complex imaging studies, require specialized equipment and trained personnel that are only available in a hospital setting. Examples include angiograms, biopsies, and certain types of neuroimaging.
- Endoscopic Procedures: Some endoscopic procedures, particularly those requiring extensive manipulation or interventions, are often performed in a hospital setting due to the need for rapid response to complications and the availability of specialized equipment and personnel.
Rationale for Inpatient Care
Inpatient care offers the necessary resources and environment for the comprehensive management of complex conditions. The availability of specialized equipment, personnel, and support systems is crucial in cases where patients require constant monitoring, intensive treatment, or the need for immediate intervention. The rationale for inpatient care stems from the risk of complications, the necessity for specialized care, and the need for a structured environment.
Figuring out Medicare’s inpatient-only list can be tricky, but it’s crucial for understanding your coverage. Sometimes, seemingly minor issues like a yeast infection vs. a UTI can become complicated when considering hospitalization. For a helpful guide to differentiating between these conditions, check out this article on yeast infection vs uti. Ultimately, knowing the specifics of the Medicare inpatient list helps you make informed choices about your healthcare, ensuring you’re getting the right care at the right time.
| Condition | Treatment Type | Rationale for Inpatient Care | Typical Procedures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Severe Sepsis | Infectious Disease | Close monitoring of vital signs, rapid administration of antibiotics, and intensive supportive care. | Blood cultures, intravenous antibiotics, fluid management, hemodynamic monitoring. |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction (Heart Attack) | Cardiology | Immediate intervention, monitoring for complications, and potentially invasive procedures. | Angioplasty, stent placement, cardiac catheterization, electrocardiograms (ECGs). |
| Complex Fractures | Orthopedics | Immobilization, pain management, and potential surgical intervention to stabilize fractures. | Surgical repair, casting, traction, pain medication, physical therapy. |
| Stroke | Neurology | Monitoring neurological function, managing potential complications, and administering clot-busting medications (if applicable). | CT scans, MRI scans, medication administration, physical therapy. |
Coverage and Reimbursement
Medicare’s reimbursement process for inpatient services is complex, encompassing a variety of factors that influence the amount paid to hospitals and other healthcare providers. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone seeking to understand how Medicare covers inpatient care. This section will detail the reimbursement process, explore influential factors, and discuss limitations within Medicare’s inpatient coverage.
Medicare Reimbursement Process
Medicare’s reimbursement for inpatient services involves several steps. Claims are submitted by healthcare providers, who detail the services provided and the associated costs. Medicare then reviews these claims against its payment policies and guidelines. This review process considers various factors like the type of service, the facility’s location, and the patient’s diagnosis. If the claim meets Medicare’s criteria, payment is made to the provider.
In the event of a dispute, a formal appeal process is available to address concerns.
Navigating the Medicare inpatient-only list can be tricky, but fascinating research into plant polyphenols, like the study on plant polyphenols slow aging study , might offer a surprising connection. While the Medicare list focuses on specific facilities, perhaps these powerful plant compounds could offer alternative avenues for proactive health management, potentially impacting future hospital stays. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of the Medicare inpatient list remains crucial for informed healthcare decisions.
Factors Affecting Reimbursement Rates
Several factors influence the reimbursement rates Medicare pays for inpatient stays. These factors include the type of facility (e.g., acute care hospitals, skilled nursing facilities), the specific services provided, and the geographic location of the facility. Additionally, the patient’s diagnosis and the length of the stay significantly impact the reimbursement amount. The complexity of the patient’s care and the resources required for their treatment also play a role.
Limitations and Exclusions in Coverage
Medicare inpatient coverage has specific limitations and exclusions. Services that are considered experimental or not medically necessary are often excluded. Additionally, some services might be covered only under specific circumstances, such as when they are provided as part of a bundled payment arrangement. Certain facilities may also fall outside of Medicare’s coverage network. These exclusions ensure that Medicare resources are used effectively and efficiently.
Medicare’s Payment Structure for Inpatient Facilities
Medicare employs a multifaceted payment structure for inpatient facilities. This includes a variety of payment methodologies, such as diagnosis-related groups (DRGs) for acute care hospitals. These DRGs classify patients based on their diagnoses and procedures, creating a standardized approach to reimbursement. Additionally, different payment models may apply to skilled nursing facilities and other inpatient settings. This structure aims to ensure fair and consistent reimbursement across various facilities and patient populations.
Accessing Medicare Guidelines on Reimbursement
Medicare’s guidelines on reimbursement are readily available online. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) website provides detailed information on payment policies, methodologies, and claim processing procedures. This resource is essential for healthcare providers, facilities, and individuals seeking to understand how Medicare covers inpatient care. Detailed information is often organized by specific types of services or facility types.
CMS provides downloadable documents, frequently asked questions, and links to relevant regulations.
Patient Rights and Responsibilities

Navigating the complexities of inpatient Medicare care can be challenging. Understanding your rights and responsibilities as a patient is crucial for a positive and effective experience. This section Artikels your rights and responsibilities, providing clarity and empowerment throughout your stay.Patients in Medicare-covered inpatient facilities have specific rights and obligations that must be respected. Knowing these rights and fulfilling your responsibilities ensures a smooth and appropriate experience.
This section dives deep into these areas, emphasizing the importance of patient advocacy and understanding the appeals process.
Patient Rights in Medicare Inpatient Facilities
Medicare Artikels specific rights for patients receiving inpatient care. These rights are designed to ensure quality care and patient autonomy.
- Right to Information: Patients have the right to receive clear and understandable information about their medical condition, treatment options, and the facility’s policies. This includes details about the care plan, potential risks, and the costs involved.
- Right to Refuse Treatment: Patients have the right to refuse any medical treatment, even if recommended by the healthcare team. This right is crucial for maintaining patient autonomy and respecting personal choices.
- Right to Privacy and Confidentiality: All patient information is confidential and must be protected. Patients have the right to privacy during their stay and access to their medical records.
- Right to Participate in Decisions: Patients have the right to be involved in decisions related to their care. This includes discussing treatment options, goals of care, and preferences for care.
- Right to a Safe Environment: Patients have the right to a safe and secure environment free from abuse, neglect, and discrimination. This includes proper safety measures to prevent falls and ensure overall well-being.
Patient Responsibilities During Inpatient Stay
Understanding your responsibilities as an inpatient is equally vital. Your cooperation contributes to a positive and productive experience.
- Adhering to Treatment Plan: Patients are expected to follow the treatment plan prescribed by their healthcare team. This includes taking medications as directed and participating in scheduled therapies.
- Communicating Concerns: If a patient has any concerns about their care, they should promptly communicate them to the appropriate healthcare professional. This is vital for addressing any issues proactively.
- Following Facility Policies: Inpatient facilities have established policies that all patients must follow. This includes guidelines on visiting hours, noise levels, and other regulations designed to maintain a safe and orderly environment.
- Providing Accurate Information: Patients must provide accurate and complete information about their medical history, allergies, and other relevant details. This is crucial for the healthcare team to provide appropriate care.
- Respecting Others: Maintaining a respectful attitude towards healthcare staff and fellow patients is essential for creating a positive environment for everyone.
Appealing Decisions Related to Inpatient Care Coverage
Medicare offers a process for appealing decisions related to inpatient care coverage. This process provides patients with a means to contest decisions if they disagree with them.
- Understanding the Appeal Process: Familiarize yourself with the specific steps and deadlines involved in appealing a Medicare decision regarding inpatient care coverage. Each facility and case has unique steps to follow. Review the Medicare website for detailed instructions.
- Documenting the Appeal: Thoroughly document all relevant information supporting your appeal, including medical records, supporting documentation, and any communication with healthcare providers. This ensures your appeal is well-supported.
- Contacting Medicare: Contact Medicare to inquire about the appeals process for inpatient coverage issues. This will ensure you have access to the necessary information and guidance to successfully navigate the process.
Importance of Understanding Patient Rights and Responsibilities
Comprehending your rights and responsibilities empowers you to actively participate in your care and advocate for your needs. This proactive approach leads to a better experience and improved outcomes.
Examples of Situations Requiring Patient Advocacy
There are situations where patients might need to advocate for their rights. Examples include:
- Disagreement with a Treatment Plan: If a patient feels a treatment plan isn’t suitable or doesn’t align with their goals, they should express their concerns and seek clarification.
- Concerns about the Quality of Care: If a patient observes issues with the quality of care, they should communicate these concerns to the appropriate authorities to ensure prompt resolution.
- Questions Regarding Coverage Decisions: When there are questions about whether a specific procedure or service is covered under Medicare, patients should initiate communication to clarify the details.
Summary
In conclusion, navigating Medicare’s inpatient-only list requires a thorough understanding of coverage criteria, facility requirements, and patient rights. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, enabling informed decision-making for patients and healthcare professionals. Understanding the specifics of inpatient services empowers individuals to make the best choices regarding their healthcare.

