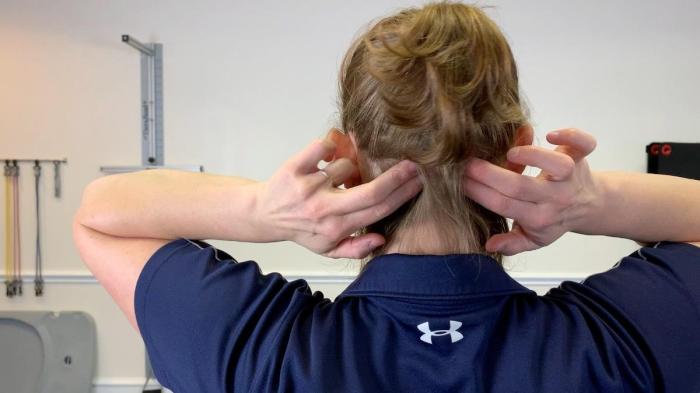
How to relieve a tension headache? This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and effective relief methods for tension headaches. We’ll delve into various home remedies, lifestyle adjustments, and professional help, providing a holistic approach to managing this common ailment.
From understanding the nuances of different headache types to discovering the power of relaxation techniques, this guide equips you with the knowledge to take control of your tension headaches. We’ll also examine dietary considerations and environmental factors that might contribute to your headaches, empowering you to create a personalized plan for prevention and relief.
Understanding Tension Headaches

Tension headaches are a common type of headache, often described as a dull, aching pain that can range from mild to severe. They’re frequently felt as a band-like pressure around the head, and are typically not accompanied by other symptoms like fever or nausea. Understanding the causes and characteristics of tension headaches can help in effective management and prevention.
Characteristics of Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are typically characterized by a dull, aching pain, often described as a tightness or pressure sensation. The pain is usually bilateral, meaning it’s felt on both sides of the head. The intensity of the pain can vary, from a mild discomfort to a severe throbbing sensation. The pain is typically not accompanied by other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light or sound.
These headaches can last from 30 minutes to several hours.
Causes of Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are often triggered by a combination of factors. Stress is a significant contributor, often stemming from mental or emotional strain. Muscle tension in the head, neck, and shoulders, often from poor posture or prolonged periods of stress, can also play a role. Environmental factors like noise, poor lighting, or even exposure to certain smells can sometimes contribute to tension headaches.
Dehydration, lack of sleep, and even certain foods can sometimes act as triggers.
Symptoms Differentiating Tension Headaches from Other Types, How to relieve a tension headache
Distinguishing tension headaches from other types of headaches is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. The following table highlights key differences:
| Headache Type | Symptoms | Triggers | Potential Relief Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tension Headache | Dull, aching pain, pressure, tightness; bilateral; not accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light/sound; lasts from 30 minutes to several hours. | Stress, muscle tension, poor posture, environmental factors (noise, light), dehydration, lack of sleep, certain foods. | Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen); relaxation techniques (e.g., deep breathing, meditation); stress management strategies; applying heat or cold packs; adjusting posture; hydration. |
| Migraine | Throbbing, pulsing pain, often unilateral (one side); accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound; can last for hours or days. | Stress, certain foods (e.g., aged cheeses, chocolate), caffeine withdrawal, hormonal changes, changes in sleep patterns. | Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., triptans); avoiding triggers; relaxation techniques; and in severe cases, prescription medications. |
| Cluster Headache | Severe, piercing pain, typically around one eye; accompanied by tearing, nasal congestion, and eyelid swelling; occurs in clusters, lasting from 15 minutes to 3 hours. | Alcohol consumption, stress, changes in sleep patterns, and environmental factors. | Oxygen therapy, triptans, and in severe cases, prescription medications. |
Home Remedies for Tension Headaches
Tension headaches, often characterized by a dull, aching pain, can be effectively managed with various home remedies. These approaches, when combined with a healthy lifestyle, can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of these headaches. Understanding the mechanisms behind these remedies empowers you to take proactive steps toward managing your pain.
Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques are crucial in managing tension headaches. These methods target the underlying muscle tension that often triggers the pain. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness practices can effectively reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: These exercises involve slow, controlled inhalations and exhalations. Deep breathing helps to calm the nervous system, reducing muscle tension and promoting relaxation. Practicing diaphragmatic breathing, focusing on the abdomen’s rise and fall, can be particularly beneficial.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body. By consciously relaxing these muscles, you can release the physical tension contributing to the headache.
- Mindfulness Practices: Mindfulness meditation encourages focusing on the present moment without judgment. This practice helps to reduce stress and anxiety, often contributing factors to tension headaches. By observing thoughts and sensations without getting carried away, you can better manage stress and tension.
Applying Heat or Cold
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can provide temporary relief from tension headache pain. Heat can help to relax muscles, while cold can help reduce inflammation. The choice between heat and cold depends on individual preferences and perceived effectiveness.
- Heat Therapy: Applying a warm compress, such as a heated towel or a hot water bottle, to the forehead, temples, or neck can help relax tense muscles and improve blood flow to the area. Heat can also promote a sense of comfort and well-being, which can indirectly reduce pain.
- Cold Therapy: Applying a cold compress, such as an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth, to the forehead or temples can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain receptors. Be sure to avoid direct contact with ice to prevent frostbite.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are commonly used to manage mild to moderate tension headache pain. These medications work by reducing inflammation and relieving pain signals. However, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage instructions to avoid potential side effects.
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin): Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps reduce inflammation and pain. It is often effective in relieving tension headaches, but it’s essential to take it as directed.
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol): Acetaminophen is a pain reliever that works by reducing the production of prostaglandins, substances that contribute to pain and inflammation. It can provide relief for tension headaches, but it does not have anti-inflammatory properties.
Comparison of Home Remedies
| Home Remedy | Effectiveness | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxation Techniques | Generally effective in reducing muscle tension and stress, leading to decreased headache frequency. | Minimal side effects, but individual experiences may vary. |
| Heat Therapy | Can provide temporary relief by relaxing muscles and improving blood flow. | Possible skin irritation or discomfort if applied incorrectly. |
| Cold Therapy | May reduce inflammation and numb pain receptors, offering temporary relief. | Potential for skin irritation or frostbite if applied directly or for extended periods. |
| Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers | Often effective in reducing pain and inflammation. | Potential for stomach upset, allergic reactions, or liver damage with prolonged use or exceeding recommended dosages. |
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Tension headaches, while often manageable with over-the-counter pain relievers and home remedies, can be significantly mitigated through lifestyle adjustments. Adopting preventive strategies can reduce the frequency and intensity of these headaches, improving overall well-being. Proactive measures focusing on stress management, regular exercise, and proper sleep patterns play crucial roles in achieving this goal.Understanding the connection between stress and tension headaches is paramount.
Chronic stress triggers the body’s physiological response, leading to muscle tension in the head and neck, a primary contributor to tension headaches. By proactively managing stress, individuals can effectively reduce the likelihood of these headaches. A structured approach to stress reduction can create a positive feedback loop, leading to improved mental and physical health.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress is an unavoidable part of modern life, but learning to manage it effectively is essential for preventing tension headaches. Identifying personal stressors and developing coping mechanisms is crucial. This includes practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation. Engaging in activities that promote mindfulness, such as yoga or tai chi, can also be highly effective.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Slow, deep breaths can calm the nervous system and reduce muscle tension. Incorporating these exercises into daily routines, especially during periods of stress, can be highly beneficial.
- Meditation: Regular meditation practice can help train the mind to focus and reduce anxiety. Even short daily sessions can make a significant difference in managing stress and its associated symptoms.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation: This technique involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups in the body, releasing physical tension that contributes to headaches. Regular practice can significantly reduce muscle tension and associated pain.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Activities like yoga and tai chi promote mindfulness, allowing individuals to focus on the present moment and reduce the impact of stress. This helps regulate the body’s response to stress triggers.
Regular Exercise
Physical activity is a powerful stress reliever and has been shown to reduce the frequency and severity of tension headaches. Exercise releases endorphins, natural mood boosters that can alleviate stress and pain. The endorphins act as natural pain relievers and improve overall well-being. Finding activities you enjoy, whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, or dancing, is key to maintaining a regular exercise routine.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities like running, swimming, or cycling increase blood flow and release endorphins, which can help reduce stress and tension in the body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio most days of the week.
- Strength Training: Strengthening the neck and shoulder muscles can help improve posture and reduce strain, thus lessening the likelihood of tension headaches.
- Flexibility and Stretching: Yoga, Pilates, and stretching exercises can improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and promote relaxation, reducing the risk of tension headaches.
Proper Sleep Hygiene
Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, directly impacting headache frequency. Insufficient sleep can exacerbate stress and muscle tension, increasing the likelihood of tension headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a conducive sleep environment can greatly improve sleep quality.
- Consistent Sleep Schedule: Going to bed and waking up around the same time each day, even on weekends, regulates the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, improving sleep quality.
- Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Establish a relaxing routine before bed, such as taking a warm bath, reading, or listening to calming music, to signal to the body that it’s time to wind down.
- Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. A comfortable mattress and pillows are also essential for a good night’s sleep.
Daily Routine for Managing Stress and Preventing Headaches
This flowchart visually illustrates a daily routine designed to manage stress and prevent tension headaches. It emphasizes the importance of incorporating stress-reducing activities throughout the day, ensuring a balance between work, relaxation, and sleep. By prioritizing stress management and adopting healthy habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of tension headaches.
Professional Help and Treatment Options
Sometimes, tension headaches can be persistent and disruptive to daily life, making it challenging to manage them effectively at home. In such cases, seeking professional help is crucial for comprehensive management and long-term relief. Understanding the different treatment options available can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their care.Professional intervention can provide a deeper understanding of the underlying causes contributing to the headaches and develop tailored strategies to address them.
This can involve identifying potential triggers, exploring stress management techniques, and implementing lifestyle adjustments.
When to Seek Professional Medical Attention
Tension headaches, while often manageable at home, warrant professional attention when they exhibit concerning characteristics. These include increased frequency, severity, or duration of headaches, or when accompanied by other symptoms like fever, stiff neck, or visual disturbances. Experiencing sudden, intense headaches, particularly those differing significantly from previous patterns, should also prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. If a headache is accompanied by neurological symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, or weakness, immediate medical attention is crucial.
Types of Professional Help
Various healthcare professionals can provide support for tension headaches. Physical therapists can help identify and correct posture and muscle imbalances that might contribute to headaches. Massage therapy can alleviate muscle tension and promote relaxation, reducing headache pain. Counseling or therapy can address underlying stress and anxiety, which are often linked to tension headaches. A mental health professional can help develop coping mechanisms for managing stress and improving overall well-being.
Role of Medication
Medications play a significant role in managing tension headaches. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can effectively alleviate mild to moderate pain. However, for more severe or frequent headaches, prescription medications might be necessary. These medications can include triptans, which are specifically designed to target migraine headaches but can also sometimes be helpful in treating tension headaches, or muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms.
A doctor can assess the individual’s needs and determine the most suitable medication and dosage.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment Option | Suitable for | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks ||—|—|—|—|| Over-the-counter pain relievers (e.g., ibuprofen, acetaminophen) | Mild to moderate tension headaches | Quick relief, readily available, generally safe | May not be effective for severe headaches, potential for side effects with overuse || Prescription medications (e.g., triptans, muscle relaxants) | Moderate to severe tension headaches, or when OTC meds are ineffective | Potentially more effective pain relief, targeted approach | Can have side effects, require a doctor’s prescription, potential for dependence with overuse || Physical therapy | Tension headaches linked to posture or muscle imbalances | Improved posture, reduced muscle tension, long-term relief | Requires consistent effort and time commitment, might not address underlying psychological factors || Massage therapy | Tension headaches related to muscle tension | Relaxation, reduced muscle tension, pain relief | May not address underlying causes, short-term relief only || Counseling/Therapy | Tension headaches linked to stress or anxiety | Improved coping mechanisms, stress reduction, long-term well-being | Requires commitment and time, may not provide immediate pain relief |
Relaxation Techniques for Tension Headaches
Tension headaches, often triggered by stress and muscle tension, can be effectively managed through various relaxation techniques. These methods can help calm the nervous system, reduce muscle contractions, and promote a sense of well-being, easing headache pain. Learning and incorporating these techniques into your daily routine can significantly contribute to preventing and managing tension headaches.
Deep Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises are simple yet powerful tools for reducing stress and promoting relaxation. They work by slowing your heart rate, lowering blood pressure, and calming the nervous system. This relaxation response can alleviate muscle tension and reduce headache pain.
Tension headaches can be a real pain, right? A good way to relieve them is by applying gentle pressure to the temples and massaging the surrounding muscles. Sometimes, if you’re dealing with digestive issues that exacerbate the headache, learning more about medications like bentyl dicyclomine might be helpful. For example, what you need to know about bentyl dicyclomine could shed light on how it works and its potential side effects.
Ultimately, though, finding the right combination of relaxation techniques and perhaps lifestyle changes is key to getting rid of those nagging tension headaches for good.
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen. Inhale deeply through your nose, feeling your abdomen rise as your diaphragm expands. Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your abdomen to fall. Repeat this process for several minutes, focusing on the rhythm of your breath. This technique can be practiced anywhere, anytime.
- Box Breathing: Inhale for a count of four, hold your breath for a count of four, exhale for a count of four, and hold your breath for a count of four. Repeat this cycle for several minutes. This structured breathing pattern can help regulate your nervous system and reduce anxiety.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation involves systematically tensing and releasing different muscle groups in your body. This process helps identify and release physical tension, a significant contributor to tension headaches. By consciously relaxing your muscles, you can reduce overall stress and promote a more relaxed state.
- Identify Muscle Groups: Start by focusing on a specific muscle group, such as your forehead muscles. Slowly tense the muscles, holding the tension for a few seconds.
- Release the Tension: Release the tension gradually, allowing the muscles to relax completely. Notice the difference between the tense and relaxed states.
- Repeat with Other Muscle Groups: Continue this process with other muscle groups, such as your shoulders, back, and neck, moving systematically through your body.
- Focus on Sensations: Pay close attention to the sensations of tension and relaxation in each muscle group. This awareness will help you identify areas of tension more effectively.
Mindfulness Meditation
Mindfulness meditation involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. This practice can help reduce stress, improve focus, and increase self-awareness. The increased awareness of the present can lessen the mind’s tendency to dwell on worries and stressors that can trigger tension headaches.
- Find a Comfortable Position: Sit or lie down in a comfortable position. Close your eyes gently.
- Focus on Your Breath: Bring your attention to the sensation of your breath entering and leaving your body. Notice the rise and fall of your chest or abdomen.
- Acknowledge Thoughts and Sensations: As thoughts or sensations arise, acknowledge them without judgment and gently redirect your attention back to your breath.
- Practice Regularly: Consistency is key to reaping the benefits of mindfulness meditation. Aim for regular practice, even if it’s just for a few minutes each day.
Dietary Considerations
Diet plays a significant role in managing tension headaches. Certain foods can trigger or worsen these headaches, while others can provide relief and support overall well-being. Understanding these dietary connections can be a powerful tool in preventing and managing tension headaches effectively.Many people experience headaches in response to specific dietary components. These responses can vary greatly from person to person, highlighting the importance of individual dietary awareness.
Identifying personal triggers can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of tension headaches.
Foods That May Trigger Tension Headaches
Some foods and drinks are more likely to trigger tension headaches than others. This is often due to their effects on blood vessels, hormones, or the body’s overall inflammatory response. Understanding these potential triggers can help individuals proactively manage their headache risk.
- Processed Foods: High in sodium, sugar, and unhealthy fats, processed foods can lead to dehydration, blood vessel constriction, and inflammation, all of which may contribute to headaches. Examples include packaged snacks, fast food, and many convenience foods.
- Tyramine-Rich Foods: Certain foods, such as aged cheeses, cured meats, fermented foods, and alcoholic beverages, contain tyramine, a substance that can cause blood vessel dilation. This dilation may contribute to headaches in some individuals. It’s important to note that individual sensitivities vary.
- Caffeine: While caffeine can initially provide a headache-relieving effect, its withdrawal can trigger headaches in some people. For those sensitive to caffeine, consistent intake or sudden cessation can cause tension headaches. Excessive caffeine intake can also lead to dehydration and other potential headache triggers.
- Chocolate: The theobromine and caffeine content in chocolate can trigger headaches in susceptible individuals. The intensity of the reaction can differ widely based on individual tolerance levels.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can dehydrate the body, leading to headaches in some people. The combination of alcohol and other triggers, like tyramine-rich foods, can exacerbate the risk.
Healthy Dietary Choices for Headache Relief
Maintaining a balanced diet with specific nutrients can support overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of tension headaches. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Quick tension headache relief often involves gentle stretching and massage. But did you know that sleep disturbances, like those associated with sleep apnea, can sometimes contribute to headaches? Understanding if sleep apnea might be a factor in your weight gain could be key to finding lasting relief. Investigate further by reading about does sleep apnea cause weight gain and consider how better sleep might help manage the headaches.
Once you’ve addressed any underlying issues, you can return to tried-and-true tension headache remedies, like a cool compress or a relaxing bath.
- Hydration: Water is crucial for overall health and can help prevent dehydration-related headaches. Maintaining proper hydration is essential for preventing tension headaches.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which support overall health and may reduce inflammation, potentially contributing to headache relief. A variety of colorful fruits and vegetables provide diverse nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains provide fiber, which aids digestion and promotes regularity. Maintaining a regular digestive system can contribute to overall well-being, potentially reducing the likelihood of tension headaches.
- Healthy Fats: Including healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and seeds can contribute to overall health and potentially reduce inflammation.
Dietary Strategies for Tension Headache Management
A well-structured diet can significantly impact tension headache management. The following table Artikels potential impacts of various food types on headaches and suggests healthy alternatives.
| Food Type | Potential Impact on Headaches | Suggested Alternatives |
|---|---|---|
| Processed Meats (e.g., salami, bologna) | May trigger headaches due to high sodium and potential tyramine content. | Lean poultry, fish, or beans. |
| Aged Cheeses (e.g., cheddar, parmesan) | May trigger headaches due to tyramine content. | Fresh mozzarella, cottage cheese, or yogurt. |
| Sugary Drinks (e.g., soda, juice) | Can lead to dehydration and exacerbate headaches. | Water, unsweetened tea, or herbal infusions. |
| Chocolate | May trigger headaches in sensitive individuals due to caffeine and theobromine. | Fruits, nuts, or seeds. |
| Alcohol | Can dehydrate the body and potentially worsen headaches. | Water, unsweetened tea, or herbal infusions. |
Environmental Factors Affecting Tension Headaches
Our environment plays a significant role in our overall well-being, and this includes our susceptibility to tension headaches. Understanding how factors like noise, light, and temperature can trigger or exacerbate these headaches is crucial for effective prevention and management. These external stressors can trigger a cascade of physiological responses that manifest as head pain.Environmental factors often act as subtle triggers, increasing tension and contributing to the development of tension headaches.
Recognizing these triggers allows us to proactively adjust our surroundings to create a more supportive and less headache-inducing environment.
Environmental Stressors and Mitigation Strategies
Environmental stressors can significantly impact our ability to relax and reduce muscle tension, a primary contributor to tension headaches. Identifying these stressors and implementing effective mitigation strategies is key to headache prevention.
Tension headaches can be a real pain, literally! A great way to ease the pressure is applying a cold compress to your forehead. Sometimes, underlying conditions like fibromyalgia primary or secondary fibromyalgia primary or secondary can contribute to headaches. If you’re dealing with chronic tension headaches, it’s always best to consult a doctor to rule out any underlying issues and get personalized advice on the best relief methods.
| Factor | Potential Impact | Strategies for Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Loud, sudden, or persistent noise can stimulate the nervous system, leading to muscle tension and headaches. A noisy environment can disrupt sleep and increase stress levels, contributing to headache frequency. |
|
| Light | Fluctuating or intense light can strain the eyes, leading to muscle tension in the head and neck. Harsh lighting can be particularly disruptive, making it difficult to relax. |
|
| Temperature | Extreme temperatures, whether too hot or too cold, can trigger vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) or vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) in the head, potentially leading to discomfort and headaches. |
|
| Environmental Pollution | Air pollution, including smoke and certain chemical pollutants, can irritate the respiratory system and lead to tension headaches. |
|
Specific Examples of Environmental Stressors
Specific environmental stressors can trigger headaches in individuals. For example, a sudden loud noise from a construction site, bright fluorescent lights in an office, or a stuffy room during a heatwave can all contribute to headache development.
Visual Aids and Illustrations: How To Relieve A Tension Headache
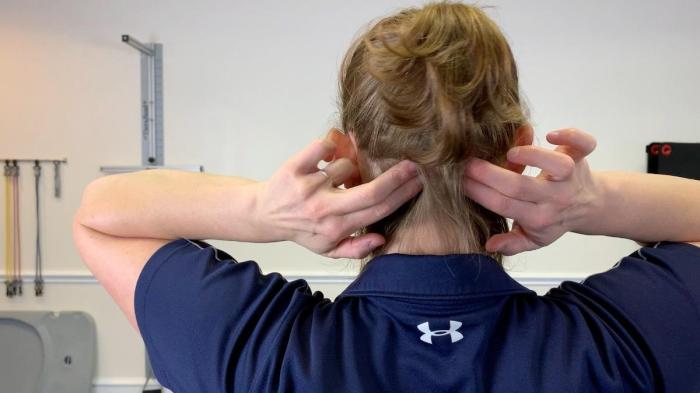
Understanding tension headaches goes beyond just knowing the symptoms. Visual aids can significantly enhance our comprehension of the underlying mechanisms and the body’s response to this common ailment. Visual representations can make complex concepts easier to grasp, helping us identify triggers and develop more effective coping strategies.
Tension Headache Anatomy
Tension headaches are characterized by a dull, aching pain that typically wraps around the head, like a tight band. The pain often feels like a squeezing or pressing sensation, and it’s usually bilateral, meaning it’s present on both sides of the head. The intensity can vary from mild to moderate, and it frequently worsens with stress or physical exertion.
Crucially, tension headaches are not typically accompanied by nausea or vomiting, a key distinction from other types of headaches.
Muscle Involvement in Tension Headaches
The muscles of the head and neck play a critical role in tension headaches. These muscles, when subjected to prolonged stress or tension, can become tight and painful. A visual representation of these muscles would show the scalp muscles, the muscles at the base of the skull, and the neck muscles, all interconnected and susceptible to tension. The diagram should emphasize the interconnectedness of these muscles, showcasing how tension in one area can radiate and affect others, triggering a headache.
For instance, the sternocleidomastoid muscle, located on the side of the neck, and the trapezius muscle, spanning the upper back and neck, are often implicated. Their chronic contraction can lead to significant pain and discomfort, contributing to the headache’s manifestation.
Stress and the Body’s Physical Response (Headaches)
Stress triggers a complex cascade of physiological responses within the body. A diagram illustrating this connection would depict a simplified representation of the stress response pathway. The diagram would start with a stressor (e.g., work deadlines, relationship issues) and then show how this stressor triggers the release of hormones like cortisol. This hormonal response, in turn, can lead to muscle tension, increased blood pressure, and altered brain activity, all contributing factors to a tension headache.
A crucial part of this visual representation would be the feedback loop, showing how the headache itself can then exacerbate the stress response, creating a vicious cycle. A simple example would be a student facing an impending exam. The stress of the exam (the stressor) triggers the release of cortisol, leading to muscle tension in the neck and head.
This tension then triggers the headache, and the pain and discomfort further increase the stress, creating a continuous cycle.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, effectively managing tension headaches involves a multifaceted approach. By understanding the root causes, implementing helpful home remedies, making lifestyle adjustments, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, you can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of your headaches. This guide provides a roadmap to empower you to take charge of your well-being and achieve lasting relief.