Eye injections for AMD offer a potential lifeline for those struggling with age-related macular degeneration. This guide delves into the intricacies of these treatments, exploring the different types of AMD, the medications used in eye injections, and the procedures involved. We’ll also discuss the potential benefits, risks, and post-injection care.
Understanding the specifics of eye injections for AMD, including the types of medications, their mechanisms of action, and the detailed procedures, is crucial for informed decision-making. This detailed guide aims to provide a clear and accessible overview of this complex medical topic.
Introduction to Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)

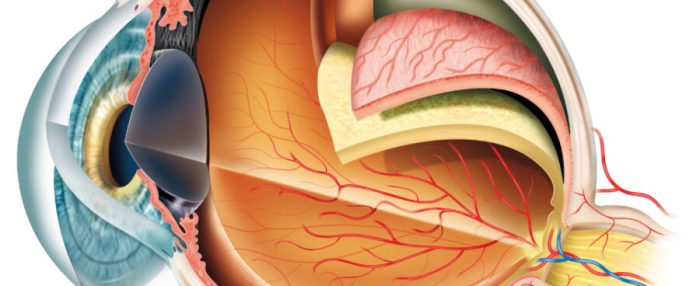
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. It primarily affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision, crucial for tasks like reading, driving, and recognizing faces. Understanding the different types of AMD is essential for appropriate diagnosis and management.AMD typically develops gradually, often without noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
As the disease progresses, the impact on vision can range from minor blurring to significant impairment, potentially leading to legal blindness in severe cases. Early detection and treatment can significantly slow the progression of AMD and preserve vision.
Types of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
AMD is broadly categorized into two main types: wet and dry. These differ significantly in their underlying causes, progression, and treatment options.
Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Dry AMD, the more common type, is characterized by the gradual thinning and deterioration of the cells in the macula. This process, known as drusen formation, involves the accumulation of yellowish deposits (drusen) beneath the retina. While typically progressing slowly, dry AMD can eventually lead to vision loss if left untreated. Early stages often exhibit mild vision changes, such as blurring or difficulty distinguishing fine details.
Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Wet AMD, a more aggressive form, involves the abnormal growth of blood vessels behind the macula. These fragile, leaky blood vessels leak fluid and blood into the macula, leading to rapid vision loss. The leaking blood and fluid damage the light-sensitive cells in the macula, causing distortion and loss of central vision. Vision loss with wet AMD can occur more quickly and severely than with dry AMD.
Comparison of Wet and Dry AMD
| Feature | Wet AMD | Dry AMD |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Cause | Abnormal blood vessel growth (neovascularization) | Thinning and deterioration of macular cells, drusen formation |
| Progression Rate | Rapid, potentially leading to significant vision loss in a short period | Slow, gradual deterioration over time |
| Vision Impact | Sudden or gradual distortion of central vision, blurring, and loss of detail | Gradual blurring of central vision, difficulty reading fine print, loss of detail |
| Treatment | Anti-VEGF injections to stop abnormal blood vessel growth | Often no specific treatment, but lifestyle modifications and supplements may be beneficial |
Overview of Eye Injections for AMD
Eye injections, a crucial part of managing Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), offer a targeted approach to slow or halt the progression of the disease. These injections deliver medications directly to the affected area of the eye, minimizing systemic side effects often associated with oral or other treatments. They are typically administered by an ophthalmologist and can be a vital component of a comprehensive treatment plan.Eye injections work by providing a concentrated dose of medication directly to the back of the eye, where the damage from AMD is occurring.
This precise delivery allows for effective treatment while minimizing the amount of medication needed compared to other methods. This targeted approach aims to reduce inflammation, inhibit further damage to the retina, and promote healthy tissue growth, thereby improving vision and slowing the disease’s progression.
Types of Medications Used
Various medications are employed in eye injections for AMD, each with a unique mechanism of action. These drugs aim to combat the underlying processes driving AMD’s progression, such as inflammation and abnormal blood vessel growth. Understanding the different types and their mechanisms of action is key to grasping the potential benefits and limitations of this treatment approach.
Eye injections for AMD are a fascinating treatment option, but it’s important to understand the broader context of similar genetic conditions. For example, learning about conditions like familial dysautonomia, which impacts the autonomic nervous system, can offer a helpful perspective on how genetic factors can affect various parts of the body. Understanding an overview of familial dysautonomia can help to highlight the complexities of eye health treatments, and ultimately, inform choices about eye injections for AMD.
Mechanisms of Action of Medications
The medications used in eye injections for AMD often target specific pathways implicated in the development and progression of AMD. Some drugs work by reducing inflammation, while others aim to inhibit the growth of abnormal blood vessels that contribute to the disease’s progression. These mechanisms of action can be categorized broadly into targeting inflammatory responses and controlling angiogenesis.
Common Medications Used in Eye Injections
Understanding the different medications used in eye injections provides a clearer picture of how these treatments work to combat AMD. The following table Artikels some common medications, their brand names, and the general effects they aim to achieve.
Eye injections for AMD can be a complex treatment, and it’s important to explore all avenues for improving overall health. While focusing on treatments like these, it’s also worthwhile to consider complementary therapies like contrast baths, which can improve circulation and potentially support overall well-being. A great resource on the benefits of contrast bath in physical therapy can offer insights into how these baths might be integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan for managing AMD.
Ultimately, the best approach is often a multifaceted one, combining medical interventions with lifestyle choices.
| Medication | Brand Name | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Ranibizumab | Lucentis | Targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein that stimulates abnormal blood vessel growth, effectively reducing the growth of new blood vessels in the retina. |
| Aflibercept | Eylea | Similar to ranibizumab, aflibercept also targets VEGF, but it’s a more comprehensive inhibitor. It binds to and neutralizes a wider range of VEGF proteins, potentially offering more extensive inhibition of abnormal blood vessel growth. |
| Bevacizumab | Avastin | While primarily used for other conditions, bevacizumab can be used in some cases for AMD. It targets VEGF, a protein that promotes blood vessel growth. Its use is less common for AMD compared to Lucentis and Eylea. |
| Brolucizumab | Ruytell | Targets VEGF. This newer medication has shown promise in providing long-term effectiveness with fewer injections. |
Procedures and Techniques for Eye Injections
Getting injections directly into your eye might sound scary, but it’s a common and often effective treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). These injections deliver medication that can help slow the progression of the disease and improve vision. The process is carefully controlled and performed by trained ophthalmologists, using specialized equipment to minimize discomfort and maximize safety.
Preparing for the Procedure
Before the injection, you’ll likely have a pre-procedure evaluation. This includes a thorough examination of your eye to assess the condition and identify the optimal injection site. The doctor will also discuss any allergies or medical conditions you might have that could affect the procedure. This careful preparation ensures the injection is as safe and effective as possible.
The Injection Process
The injection itself is typically a quick procedure, often taking less than 15 minutes. The area around your eye will be numbed with anesthetic eye drops to minimize discomfort. The doctor will carefully position the injection site and use a tiny needle to deliver the medication.
Equipment Used
Several specialized tools are used for this procedure. A surgical microscope allows the doctor to see the area clearly and precisely. A special needle, very thin and precisely calibrated, delivers the medication. A topical anesthetic numbs the eye. Sterile solutions and instruments are used to maintain cleanliness and prevent infection.
The doctor also uses a device to keep your eye steady during the procedure, which minimizes any discomfort and increases precision.
Step-by-Step Procedure
This table Artikels the key steps involved in the eye injection procedure:
This detailed step-by-step process ensures a safe and effective procedure.
Benefits and Risks of Eye Injections
Eye injections, a crucial treatment for Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD), offer hope for slowing or halting vision loss. However, like any medical procedure, they come with potential benefits and risks. Understanding these factors is essential for patients to make informed decisions alongside their ophthalmologists.The effectiveness of these injections varies depending on the individual, the type of AMD, and the specific medication used.
Careful consideration of potential risks, coupled with a realistic understanding of benefits, empowers patients to navigate this treatment option effectively.
Potential Benefits of Eye Injections
Eye injections, particularly those containing anti-VEGF medications, aim to reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. This targeted approach can slow the progression of vision loss in AMD patients. By decreasing the leakage and inflammation associated with these abnormal blood vessels, vision can be preserved. Some patients report improved visual acuity, allowing them to engage in activities they previously found difficult.
For instance, tasks like reading, driving, or recognizing faces may become easier.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Eye Injections
While eye injections offer significant potential benefits, they are not without risks. Common side effects include mild discomfort, such as pain, redness, or swelling around the injection site. These typically subside within a few days. More serious, though less frequent, risks include increased eye pressure, infection, and bleeding inside the eye. Understanding the potential side effects and the likelihood of their occurrence allows for proactive management by the patient and healthcare provider.
Comparison of Risks and Benefits of Different Injection Types
Different types of injections may carry varying degrees of risk and offer different benefits. For example, injections containing anti-VEGF medications are commonly used, offering a high potential for slowing the progression of AMD, but they might cause some side effects like mild inflammation or bleeding. Other types of injections might have different side effects or efficacy levels. A crucial discussion with the ophthalmologist is necessary to weigh the benefits against the potential risks for each individual patient.
Summary of Benefits and Risks
| Benefit/Risk | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Visual Acuity | Patients may experience enhanced clarity and sharpness of vision. | Moderate |
| Slowed Progression of AMD | Treatment can halt or slow the deterioration of vision associated with AMD. | High |
| Reduced Leakage and Inflammation | Injections aim to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth, minimizing retinal damage. | Moderate |
| Pain/Discomfort | Mild to moderate pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site. | Low |
| Increased Eye Pressure | Potentially leading to discomfort or other complications. | Moderate |
| Infection | Rare but possible complication requiring prompt medical attention. | High |
| Bleeding Inside the Eye | A serious complication requiring immediate medical intervention. | High |
Patient Selection and Preparation

Choosing the right patient for eye injections in AMD is crucial for maximizing treatment success and minimizing potential risks. Careful patient selection and meticulous preparation are paramount to ensuring a safe and effective procedure. This involves a thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, current eye health, and overall well-being. Understanding the nuances of the process allows for a personalized approach that optimizes outcomes.
Criteria for Patient Selection
Selecting suitable patients for eye injections requires careful consideration of several factors. These factors are designed to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from the treatment and minimize complications. Age-related macular degeneration, in its various forms, necessitates a tailored approach, understanding that each patient presents unique characteristics.
- Presence of active AMD: Patients must exhibit active, progressive AMD in a form that is responsive to the targeted injection. This involves evaluating the progression of vision loss and the underlying pathology. For example, a patient with wet AMD experiencing rapid vision decline is a prime candidate for injection therapy, while a patient with dry AMD may not be an appropriate candidate unless the dry form is exhibiting signs of progression.
- Stable General Health: Patients should have a stable overall health status, minimizing the risk of complications related to the procedure itself or the medication. Any underlying medical conditions, such as uncontrolled hypertension or diabetes, need to be well-managed. For instance, a patient with uncontrolled diabetes may experience increased bleeding risk during the procedure, and thus requires careful consideration.
- Understanding of the Procedure: Patients must demonstrate a clear understanding of the procedure, including its potential benefits and risks. This crucial element involves comprehensive counseling and open communication. Patients must be able to follow instructions and comply with post-injection care instructions.
- Visual Acuity: Assessing baseline visual acuity is essential to monitor treatment effectiveness. Ideally, the patient’s visual acuity is measurable and demonstrably affected by the AMD. This allows for an objective measure of the treatment’s success and a baseline for comparison over time.
Pre-Injection Preparation
Thorough pre-injection preparation significantly reduces the risk of complications and improves patient comfort. A meticulous approach, involving both the patient and the medical team, is crucial for a successful outcome.
- Medical History Review: A comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history, including any allergies, previous eye surgeries, and current medications, is vital. This step helps identify potential risks and allows for appropriate adjustments in treatment plans or the choice of medication.
- Comprehensive Eye Exam: A comprehensive eye exam is performed to assess the extent and type of AMD, the health of the eye, and the location of any potential injection site. This examination also allows the ophthalmologist to evaluate the retinal condition in detail. This crucial step helps in precisely targeting the injection for maximum effectiveness.
- Medication Adjustment (if needed): Any medications that may interact with the injection are identified and addressed. For example, blood thinners might need adjustment. This is essential to minimize potential complications.
- Patient Education: Thorough patient education is vital to address any concerns and ensure the patient understands the procedure and post-procedure care. This process builds confidence and reduces anxiety.
Patient Counseling Before the Procedure, Eye injections for amd
Patient counseling is a critical component of the pre-injection preparation. It ensures that patients are fully informed and empowered to make informed decisions. Open communication fosters trust and reduces anxiety.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Detailed Explanation of Procedure | A clear explanation of the procedure, including the steps involved, the use of anesthesia, and potential sensations during the procedure. |
| Discussion of Potential Risks and Benefits | A thorough discussion of potential complications, such as infection, bleeding, or vision changes, alongside the potential benefits of the injection. |
| Answering Questions | Creating a supportive environment where patients can ask questions and address any concerns. |
| Post-Procedure Instructions | Providing clear and concise instructions on post-procedure care, including activity restrictions, medication use, and follow-up appointments. |
Post-Injection Care and Follow-up
Taking care of your eyes after an injection for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is crucial for optimal healing and preventing complications. Proper post-injection care, coupled with diligent follow-up appointments, significantly improves the chances of a successful treatment outcome and minimizes potential risks. This section details the necessary steps for successful post-injection recovery and highlights the importance of adhering to your ophthalmologist’s instructions.Following the injection, your eye may experience some temporary discomfort or changes in vision.
It’s essential to understand these potential responses and how to manage them effectively. Understanding the potential complications and recognizing their warning signs is critical for early intervention and minimizing their impact. The information presented here aims to empower you with the knowledge needed to navigate this process and promote your well-being.
Eye injections for AMD can be expensive, and understanding your coinsurance how to calculate how much you’ll owe is crucial. Knowing the amount you’ll pay out-of-pocket can help you budget for these important treatments. This proactive approach is key to managing the cost of eye injections for AMD effectively.
Post-Injection Care Instructions
Adherence to post-injection care instructions is essential for a smooth recovery. These instructions are tailored to individual cases and should be strictly followed as prescribed by your ophthalmologist. A key aspect of this care involves avoiding strenuous activities that could potentially increase intraocular pressure (IOP). These activities include heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, and excessive bending. This precaution is crucial to prevent potential complications.
- Rest and Avoiding Strenuous Activities: For the first 24-48 hours following the injection, minimize strenuous activities. This period allows the eye to heal without unnecessary strain. Light activity is generally permissible, but avoid any actions that may elevate intraocular pressure (IOP).
- Eye Protection: Avoid rubbing or touching the injected eye. Wear protective eyewear as advised by your ophthalmologist to prevent injury. This includes using sunglasses to block UV rays.
- Medication Adherence: Take all prescribed medications as directed, including any pain relievers or eye drops. Adherence to the medication schedule is critical for managing potential inflammation or discomfort.
- Hydration: Maintaining proper hydration is essential for overall health and well-being. Drink plenty of water to support the healing process.
- Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments diligently. These appointments allow your ophthalmologist to monitor the healing process, detect any potential complications, and adjust treatment as needed.
Importance of Follow-up Appointments
Regular follow-up appointments are vital for monitoring treatment effectiveness and identifying potential complications early. These appointments allow your ophthalmologist to assess the condition of your eye, evaluate the treatment’s impact, and adjust the course of action as necessary. Missing appointments can lead to delayed detection of potential problems and impede the achievement of optimal results.
Potential Post-Injection Complications
While eye injections for AMD are generally safe, some potential complications can arise. These complications are usually temporary and manageable with appropriate medical intervention.
- Eye Pain or Discomfort: Mild to moderate discomfort is common after the injection. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate discomfort. Severe or persistent pain warrants immediate medical attention.
- Eye Swelling or Redness: Swelling and redness around the injection site are possible side effects. These usually resolve within a few days. Persistent or increasing swelling or redness requires medical evaluation.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary blurred vision is a common occurrence following the injection. This usually subsides within a few days. If the blurred vision persists or worsens, seek immediate medical attention.
- Increased Intraocular Pressure (IOP): In rare cases, eye injections can lead to a temporary increase in IOP. This is usually managed with eye drops. Symptoms of increased IOP include severe eye pain, headache, or vision changes.
Managing Post-Injection Complications
If you experience any of the potential complications, promptly contact your ophthalmologist. They will assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment. Early intervention is crucial to minimize the impact of these complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
Long-Term Outcomes and Management
Eye injections for age-related macular degeneration (AMD) are a crucial treatment option, offering the potential to significantly improve vision and slow the progression of the disease. However, like any medical intervention, they come with potential long-term effects and require careful management to optimize outcomes and minimize complications. Understanding these long-term implications is vital for both patients and healthcare providers.
Long-Term Outcomes of Eye Injections
The long-term outcomes of anti-VEGF injections for AMD vary depending on several factors, including the individual’s specific disease progression, the type of injection used, and the adherence to prescribed follow-up care. While injections can significantly stabilize vision loss and even improve it in some cases, complete restoration of lost vision is not always achievable. Some patients experience sustained improvement, while others may experience a gradual decline in vision over time, despite ongoing treatment.
This highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and adjusting treatment strategies as needed.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Effective long-term management involves a proactive approach focused on maintaining optimal eye health and addressing any emerging complications. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor the progression of AMD, adjust treatment strategies, and identify any potential side effects. This includes assessing the effectiveness of the injections, evaluating any changes in vision, and managing any associated symptoms. Communication between the patient and ophthalmologist is critical for successful long-term management.
Patients should actively participate in their care, reporting any changes in vision or discomfort promptly.
Potential Long-Term Complications
While eye injections are generally safe, potential complications can occur. These can include, but are not limited to, increased intraocular pressure, infections, and retinal detachment. The risk of each complication varies based on the individual and the specifics of their treatment. Early detection and prompt management of these complications are crucial to minimize their impact on vision.
In some cases, additional treatments, such as laser surgery, may be necessary to address these complications.
Comparison of Long-Term Effects of Different AMD Treatments
| Treatment | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|
| Anti-VEGF injections (e.g., ranibizumab, aflibercept) | Generally well-tolerated, with potential for sustained vision improvement or stabilization. Long-term complications like increased intraocular pressure, infections, and retinal detachment are possible, though less frequent with careful monitoring. |
| Laser therapy | Can be effective in treating some forms of AMD, particularly geographic atrophy. Long-term effects can include vision loss in the treated area, and potential for further progression of the disease in other parts of the retina. |
| Vitrectomy | Considered a more invasive procedure, potentially leading to a higher risk of complications, including infections, retinal detachment, and bleeding. However, it may be beneficial in specific cases where other treatments have failed. Long-term effects can vary widely depending on the individual and the severity of the AMD. |
Ultimate Conclusion: Eye Injections For Amd
In conclusion, eye injections for AMD present a complex but potentially beneficial treatment option for certain cases of macular degeneration. Careful consideration of individual patient needs, potential risks and benefits, and the meticulous post-injection care are essential. This comprehensive guide provides a foundational understanding, encouraging further research and consultation with qualified medical professionals.