Elderly blood sugar levels chart provides a crucial guide for understanding and managing blood sugar in older adults. Aging brings physiological changes that impact glucose metabolism, making blood sugar management more complex. This comprehensive overview delves into normal ranges, common conditions, monitoring strategies, and lifestyle considerations specific to the elderly. We’ll explore how these factors influence blood sugar levels, from nutrition to medication, offering insights for healthcare providers and caregivers alike.
The physiological changes in glucose metabolism with age are significant, requiring careful attention to blood sugar management. Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can be affected by various factors, and understanding these factors is key to maintaining stable levels. This guide will explore these factors and offer practical strategies for monitoring and managing blood sugar effectively in elderly individuals.
Introduction to Elderly Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, especially as we age. As individuals enter their senior years, their bodies undergo physiological changes that can impact glucose metabolism, potentially leading to challenges in managing blood sugar. Understanding these changes and the factors influencing them is essential for promoting healthy aging and preventing complications associated with diabetes. This knowledge empowers elderly individuals and their caregivers to make informed decisions about lifestyle adjustments and treatment plans.Understanding the physiological shifts in glucose metabolism as we age is vital for effective blood sugar management in the elderly.
Aging often brings about changes in hormone regulation, insulin sensitivity, and the body’s ability to process and utilize glucose efficiently. These alterations can make it more difficult to control blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing or worsening diabetes.
Physiological Changes in Glucose Metabolism with Aging
Aging is associated with a decline in insulin sensitivity, meaning the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin’s signals to absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This reduced sensitivity can lead to higher blood sugar levels. Additionally, age-related changes in the liver’s function can impact glucose production and release, further contributing to fluctuations in blood sugar. Muscle mass often decreases with age, which also affects glucose uptake and utilization.
Factors Contributing to Blood Sugar Fluctuations in the Elderly
Several factors can contribute to fluctuations in blood sugar levels in elderly individuals. These include changes in diet, physical activity levels, and medication regimens. For instance, some medications commonly used for managing other health conditions can impact blood sugar control. Chronic illnesses or conditions that accompany aging, such as kidney disease or cardiovascular issues, can also influence blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, changes in daily routines and lifestyle, such as reduced physical activity or increased stress, can play a role in blood sugar fluctuations.
Keeping track of elderly blood sugar levels is crucial for their health. Understanding how dietary supplements like glucomannan can impact blood sugar is important, too. For example, checking out the glucomannan benefits side effects dosage can offer insights into potential effects on blood sugar levels, which ultimately helps in creating a personalized plan for managing blood sugar for seniors.
Ultimately, monitoring these levels closely is key to maintaining their overall well-being.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Lifestyle Adjustments
Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for elderly individuals with diabetes to track trends and make necessary adjustments to their care plan. Consistent lifestyle adjustments, including a balanced diet rich in whole foods, regular physical activity tailored to their capabilities, and adherence to prescribed medication regimens, are essential for effective blood sugar management. Support from healthcare professionals, family members, and caregivers is also vital in encouraging adherence to these lifestyle changes.
By actively participating in their care and understanding the factors that affect their blood sugar levels, elderly individuals can take an active role in managing their condition and promoting their overall well-being.
Understanding Normal Ranges and Variations
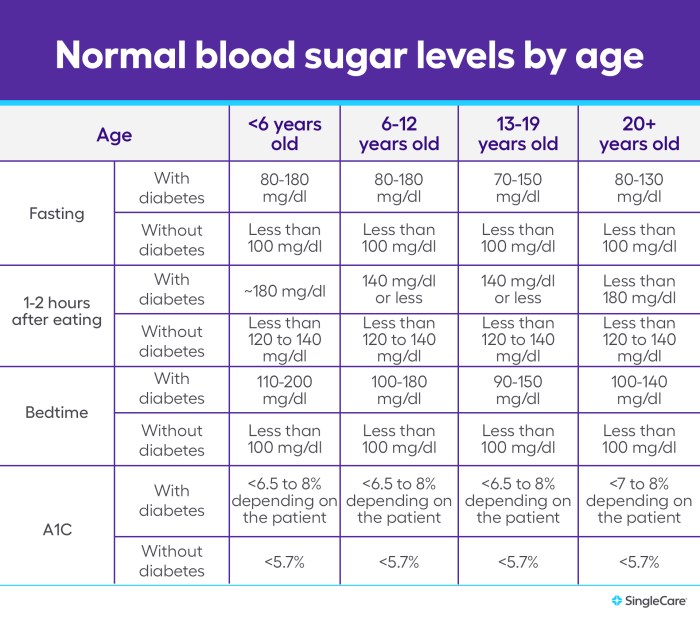
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial, especially as we age. Understanding the normal ranges and potential variations is key to proactive management and early detection of any issues. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being.Blood sugar levels naturally fluctuate throughout the day and are influenced by several factors. For elderly individuals, these fluctuations can be more pronounced due to physiological changes, medications, and lifestyle adjustments.
Keeping track of elderly blood sugar levels is crucial, especially when they’re feeling under the weather. Knowing the dos and don’ts when sick is vital for managing those levels effectively. For instance, following guidelines like staying hydrated and eating light, easily digestible meals, as detailed in this helpful resource on dos donts when sick , can make a real difference.
This will help ensure accurate readings and prevent complications in managing their blood sugar levels.
Knowing these variations allows for a more personalized approach to blood sugar management.
Blood Sugar Ranges: Adults vs. Elderly
Normal blood sugar levels vary slightly between healthy adults and elderly individuals. The following table provides a comparison for reference:
| Category | Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/dL) | 2-Hour Postprandial Blood Sugar (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Adult | 70-100 | < 140 |
| Elderly (General Guideline) | 70-130 | < 160 |
Note that these are general guidelines. Individual variations exist, and consulting a healthcare professional is essential for personalized recommendations.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels in the Elderly
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels in the elderly, which may differ from younger adults. These factors are essential to understand for effective management:
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Physiological Changes | Age-related changes in metabolism and insulin sensitivity can impact how the body processes glucose. |
| Medications | Certain medications, such as diuretics or corticosteroids, can affect blood sugar control. |
| Dietary Changes | Changes in appetite, chewing, or swallowing ability can influence dietary intake, and this, in turn, affects blood sugar levels. |
| Activity Levels | Decreased physical activity can contribute to insulin resistance, affecting blood sugar regulation. |
| Underlying Health Conditions | Chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease can influence blood sugar levels. |
Understanding these factors allows for more tailored strategies for blood sugar management.
Impact of Medications on Blood Sugar Levels
Many medications can affect blood sugar levels in the elderly. The table below highlights some common examples and their potential impact:
| Medication Category | Potential Impact | Example Drugs |
|---|---|---|
| Diuretics | Can increase blood sugar levels | Thiazides, loop diuretics |
| Corticosteroids | Can increase blood sugar levels | Prednisone, methylprednisolone |
| Antipsychotics | Can increase blood sugar levels | Olanzapine, quetiapine |
| Beta-blockers | Can mask symptoms of low blood sugar | Metoprolol, atenolol |
Regular monitoring and communication with a doctor are essential when taking multiple medications.
Symptoms of High and Low Blood Sugar in the Elderly
Symptoms of high and low blood sugar in the elderly can sometimes differ from younger adults. These differences are important to recognize:
| Blood Sugar Level | Potential Symptoms | Differences from Younger Adults |
|---|---|---|
| High (Hyperglycemia) | Increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue | Symptoms may be less pronounced or masked by other conditions. |
| Low (Hypoglycemia) | Confusion, dizziness, sweating, irritability, weakness | Symptoms may be more subtle, or cognitive impairment might be mistaken for other conditions. |
Accurate symptom recognition is vital for prompt intervention.
Role of Nutrition in Blood Sugar Management
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels in the elderly. The table below Artikels important nutritional considerations:
| Dietary Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Portion Control | Maintaining appropriate portion sizes is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. |
| Fiber-Rich Foods | Include foods rich in fiber to slow down glucose absorption. |
| Complex Carbohydrates | Prioritize complex carbohydrates over simple sugars. |
| Protein and Healthy Fats | Include sufficient protein and healthy fats to support overall health and regulate blood sugar. |
Individualized dietary plans should be tailored to specific needs and preferences, under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Common Conditions and Their Impact
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels becomes increasingly crucial as we age. Age-related changes and co-existing conditions can significantly impact glucose control, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of the interplay between various health factors. This section delves into the prevalence of diabetes in the elderly, the impact of age-related conditions on blood sugar control, and the importance of holistic monitoring.The prevalence of diabetes in the elderly is substantial, and its management presents unique challenges.
Many elderly individuals experience a decline in their overall health, making blood sugar control more complex. For example, the presence of other chronic conditions can exacerbate the effects of diabetes and influence the effectiveness of treatment. It is crucial to consider these interactions to optimize care.
Prevalence of Diabetes in the Elderly
Diabetes is a common condition affecting a significant portion of the elderly population. Studies have shown a rise in diabetes diagnoses as individuals age, often attributed to lifestyle changes and the development of other health problems. The increasing prevalence of diabetes in the elderly necessitates tailored strategies for diagnosis, management, and prevention.
Impact of Age-Related Conditions on Blood Sugar Control
Age-related conditions can significantly impact blood sugar control. Conditions such as arthritis, cognitive decline, and other chronic illnesses can interfere with medication adherence, physical activity, and overall health management. For instance, joint pain associated with arthritis can limit mobility, impacting the ability to engage in regular exercise, which is vital for regulating blood sugar levels. Similarly, cognitive decline can affect a person’s ability to remember and follow treatment plans.
Keeping track of elderly blood sugar levels is crucial for their health, but sometimes dietary changes intended to improve other aspects, like cholesterol, can have unexpected consequences. For instance, a diet rich in fiber, while great for lowering cholesterol, can sometimes lead to issues with blood sugar regulation if too much fiber is consumed, as discussed in this article about too much fiber in cholesterol lowering diet.
Ultimately, a balanced approach, considering the individual needs of the elderly, is key when adjusting diets to manage both blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Proper management of these underlying conditions is critical for effective blood sugar control.
Relationship Between Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar Levels in Elderly Individuals
Blood pressure and blood sugar levels are closely intertwined in elderly individuals. High blood pressure can worsen the complications associated with poorly controlled blood sugar. Conversely, uncontrolled blood sugar can also elevate blood pressure. These factors often co-occur, necessitating a holistic approach to managing both conditions. For example, an elderly individual with hypertension may experience elevated blood glucose levels, further impacting their cardiovascular health.
A comprehensive approach to monitoring and managing both conditions is crucial.
Common Complications Arising from Poorly Controlled Blood Sugar Levels in the Elderly
Poorly controlled blood sugar levels in the elderly can lead to various complications. These include cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy (nerve damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), and retinopathy (eye damage). For example, prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, leading to cardiovascular issues such as heart attack and stroke. These complications can significantly impact the quality of life and necessitate ongoing management.
Significance of Monitoring Blood Sugar in Conjunction with Other Health Indicators for Elderly Patients
Comprehensive monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential, but it should not be considered in isolation. It is vital to track other health indicators, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and kidney function. This holistic approach allows for a more accurate assessment of the patient’s overall health status and guides treatment strategies accordingly. For example, monitoring kidney function alongside blood sugar is critical in patients with pre-existing kidney disease.
The interconnectedness of various health parameters underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to care.
Impact of Social Determinants of Health on Blood Sugar Management in the Elderly
Social determinants of health, including access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, and social support networks, significantly influence blood sugar management in the elderly. Individuals with limited access to healthcare or financial resources may have difficulty adhering to treatment plans and accessing necessary medications. Moreover, social isolation can negatively impact self-care behaviors and contribute to poor blood sugar control. For example, an elderly individual living alone with limited financial resources may face challenges in obtaining necessary groceries or managing medications.
Addressing these social determinants is crucial for optimizing blood sugar control and improving overall well-being.
Monitoring and Management Strategies
Managing blood sugar levels effectively in elderly individuals requires a multifaceted approach that considers their unique needs and abilities. This involves a combination of careful monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and appropriate medication choices. A tailored strategy is crucial to ensure optimal health and well-being.
Blood Sugar Monitoring Methods for the Elderly
Elderly individuals may face challenges in performing complex tasks, affecting their ability to monitor blood sugar levels consistently. Therefore, selecting suitable methods is paramount.
- Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): This remains a common method. However, for those with visual impairments or dexterity issues, larger sized glucose meters with large display screens and simplified testing procedures are essential. Consider using test strips with larger numbers or using a lancing device with a larger needle size. Caregivers can assist in the process.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM systems offer real-time glucose readings, providing valuable insights into glucose fluctuations. While generally effective, some elderly individuals may find the technology challenging to use. Clear instructions and caregiver support are crucial.
- Regular Blood Tests: Routine blood tests, performed by healthcare professionals, provide a comprehensive picture of blood sugar control over time. These tests can identify patterns and help adjust treatment plans.
Role of Exercise and Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, promoting efficient glucose uptake. For elderly individuals, the focus should be on manageable activities that maintain cardiovascular health and strength.
- Consult with a healthcare professional: Before initiating any exercise program, a consultation with a doctor is essential to determine appropriate exercises and safety measures.
- Tailored Exercise Regimen: The program should consider the individual’s physical capabilities, health conditions, and preferences. This could include walking, swimming, or chair exercises.
- Consistency: Even short bursts of activity throughout the day can be beneficial. Regularity is key to achieving the desired effect.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels, especially for elderly individuals with diabetes. Nutrient-rich foods and portion control are essential.
- Prioritize whole foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in the diet. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive saturated fats.
- Control portion sizes: Overeating can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar spikes. Using smaller plates and mindful eating can be helpful.
- Regular meals: Eating at regular intervals helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
Sample Meal Plan for Elderly Individuals with Diabetes
A sample meal plan for elderly individuals with diabetes might include:* Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries and a sprinkle of nuts, or a small portion of whole-wheat toast with avocado and a hard-boiled egg.
Lunch
A salad with grilled chicken or fish, a small portion of brown rice, and plenty of vegetables.
Dinner
Baked salmon with roasted vegetables and a side of quinoa.
Snacks
Fruits like apples or oranges, or a handful of almonds.
Comparison of Diabetes Medications, Elderly blood sugar levels chart
| Medication Type | Potential Benefits | Potential Side Effects | Suitability for Elderly Patients |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Generally well-tolerated, effective in lowering blood sugar | Gastrointestinal upset, vitamin B12 deficiency | Often suitable, especially for type 2 diabetes. Monitor for side effects, especially in those with kidney issues. |
| Sulfonylureas | Effective in lowering blood sugar | Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), weight gain | May not be as suitable for elderly individuals due to risk of hypoglycemia. Close monitoring is necessary. |
| Insulin | Precise control of blood sugar | Hypoglycemia, weight gain, injection site reactions | Can be effective, but requires careful dosage adjustment and monitoring. Needs support and education for elderly patients. |
Strategies to Improve Adherence to Blood Sugar Management Plans
Elderly individuals may face challenges in adhering to complex blood sugar management plans. Simplifying the plan, providing clear and concise information, and involving caregivers are essential strategies.
- Simplify the plan: Reduce the number of medications or testing requirements whenever possible. This can improve adherence.
- Clear and concise information: Provide easily understandable instructions and educational materials about the plan.
- Involve caregivers: Educate caregivers about the plan and empower them to support the individual in managing their blood sugar.
Lifestyle Considerations for the Elderly
Managing blood sugar levels effectively in elderly individuals requires a holistic approach that considers the unique challenges and opportunities presented by aging. Adapting lifestyle choices to accommodate physical limitations, fostering emotional well-being, and establishing strong support systems are crucial components of successful blood sugar management in this population.Elderly individuals often face limitations in mobility and physical activity, impacting their ability to engage in traditional exercise routines.
However, this does not mean that physical activity should be entirely disregarded. Finding age-appropriate activities and incorporating them into daily life is paramount. Modifications in meal preparation and portion control are also essential to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, considering the potential for changes in appetite and dietary needs associated with aging.
Adapting Lifestyle Choices for Limited Mobility
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for managing blood sugar levels, but physical limitations can pose challenges. Strategies to address these limitations include modifying exercise routines to accommodate physical limitations, exploring adaptive equipment and assistive technologies to facilitate movement and participation in activities, and ensuring access to safe and accessible environments for physical activity. Examples include chair exercises, gentle stretching routines, or using stationary bikes or walking machines that can be adjusted to accommodate physical limitations.
Importance of Emotional Well-being and Stress Management
Emotional well-being plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels. Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar control, and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the effects of stress. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or joining support groups, can help to mitigate the impact of stress on blood sugar levels. Engaging in hobbies, social activities, and spending time with loved ones can contribute to emotional well-being and a sense of purpose, which in turn can positively influence blood sugar management.
Support Systems and Resources for Elderly Individuals
Accessing appropriate support systems and resources is critical for successful blood sugar management in the elderly. Community-based programs, senior centers, and support groups can provide valuable resources and connections. These programs can offer education, support, and a sense of community, empowering individuals to manage their condition effectively. Family members and caregivers play a significant role in providing practical support, such as assistance with meal preparation, medication reminders, and transportation to appointments.
Communication between Healthcare Providers and Patients
Open and effective communication between healthcare providers and elderly patients is essential for successful blood sugar management. This involves clear communication of treatment plans, medication instructions, and blood sugar monitoring guidelines. Regular check-ups and discussions about any concerns or challenges are crucial for addressing any potential issues promptly and ensuring that the treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s needs.
Adjustments in Healthcare Plans for Elderly Patients
Healthcare plans for elderly patients with blood sugar issues must be flexible and adaptable to accommodate the unique needs and limitations of this population. This includes recognizing that elderly individuals may have co-existing medical conditions that need to be considered in the overall management of blood sugar. Regular assessments and adjustments to treatment plans based on individual responses and progress are crucial.
Role of Family Members in Support
Family members play a vital role in supporting elderly individuals managing their blood sugar levels. Education about the condition, active participation in care, and emotional support are crucial for the success of blood sugar management. Family members can assist with medication reminders, blood sugar monitoring, and help maintain a healthy lifestyle. Strong family support systems can significantly improve the quality of life and outcomes for elderly individuals.
Illustrative Examples and Case Studies
Understanding blood sugar fluctuations in elderly individuals requires a nuanced approach. Factors like age-related changes in metabolism, concurrent health conditions, and medication interactions play crucial roles. This section explores illustrative examples, case studies, and preventative measures to better manage blood sugar in this demographic.
Typical Blood Sugar Fluctuations in Elderly Individuals with Specific Health Conditions
Age-related changes in the body’s ability to process glucose can result in varying blood sugar patterns. For instance, individuals with type 2 diabetes and hypertension often experience more pronounced fluctuations, particularly after meals or during periods of stress. Similarly, those with hypothyroidism may exhibit a tendency towards slightly elevated blood sugar levels due to the impact of the thyroid hormone on metabolism.
These variations underscore the importance of personalized management plans.
Case Study: Successful Blood Sugar Management Program for an Elderly Individual
Agnes, a 78-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes, initially struggled with inconsistent blood sugar levels. Her management program involved a combination of lifestyle modifications and medication adjustments. A registered dietitian designed a meal plan tailored to her preferences and nutritional needs, focusing on portion control and balanced meals. Regular exercise, including walking and gentle yoga, was incorporated into her daily routine, helping to improve insulin sensitivity.
Medication adjustments, in consultation with her physician, further stabilized her blood sugar levels. Through consistent monitoring and proactive adjustments, Agnes achieved significant improvements in her overall health and well-being.
Preventative Measures to Improve Blood Sugar Control in the Elderly
Implementing preventative measures can significantly improve blood sugar control in the elderly. These measures include maintaining a healthy weight, following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and engaging in regular physical activity. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and proactive communication with healthcare providers are also essential. Consistent medication adherence, when prescribed, is critical for effective blood sugar management.
“Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, is crucial for preventing and managing blood sugar fluctuations in elderly individuals.”
Illustrative Scenarios of Managing Blood Sugar Issues During Specific Events in the Elderly
Managing blood sugar during events like holidays or social gatherings requires careful planning and adjustments. During holidays, individuals may consume larger portions of high-carbohydrate foods, necessitating increased awareness of portion sizes and mindful choices. Similarly, managing blood sugar during periods of stress or illness requires careful monitoring and possible adjustments to medication or dietary intake. A pre-planned strategy is often beneficial to help mitigate these fluctuations.
Visual Representation of the Relationship Between Diet, Exercise, and Blood Sugar Control for the Elderly
| Factor | Description | Impact on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein | Stabilizes blood sugar levels, providing sustained energy |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity, including walking, swimming, or yoga | Improves insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels |
| Blood Sugar Control | Consistent monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle adjustments | Reduces risk of complications and improves overall health |
Typical Blood Sugar Patterns in Elderly Individuals with Different Levels of Activity and Dietary Habits
| Activity Level | Dietary Habits | Typical Blood Sugar Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary | High in processed foods, sugary drinks | Tendency towards higher blood sugar levels, especially after meals |
| Moderate | Balanced diet, moderate portions | Stable blood sugar levels with slight fluctuations after meals |
| Active | Balanced diet, regular meals | Stable blood sugar levels with minimal fluctuations |
End of Discussion: Elderly Blood Sugar Levels Chart

In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels in the elderly requires a holistic approach that considers the unique challenges associated with aging. Understanding normal ranges, common conditions, and appropriate monitoring strategies is crucial. By adopting a balanced lifestyle, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, and medication adherence, elderly individuals can maintain healthy blood sugar levels and overall well-being. Remember, open communication between healthcare providers, patients, and family members is essential for successful management.

