Can creatine boost cognition? This intriguing question sparks a fascinating exploration into the potential effects of creatine supplementation on brain function. We’ll delve into the science behind creatine, its role in energy production, and its possible impact on cognitive processes like memory, attention, and processing speed. We’ll examine existing research, discuss potential mechanisms, and consider factors that might influence creatine’s impact on cognition.
Creatine, a naturally occurring compound, plays a vital role in providing energy to cells, including those in the brain. Its supplementation has been linked to enhanced physical performance, but its impact on cognitive function remains a topic of ongoing investigation. This exploration will analyze the existing research to determine whether creatine truly enhances cognitive performance.
Overview of Creatine
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in the body, primarily in muscle tissue. It plays a crucial role in energy production, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity exercise. Understanding its various forms, dosages, and potential side effects is essential for anyone considering creatine supplementation.Creatine’s primary function is to support the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body’s primary energy currency.
During intense workouts, ATP levels deplete rapidly. Creatine helps replenish these stores, allowing for sustained energy and improved performance. This enhanced energy output translates into potentially greater strength, power, and muscle growth.
Creatine Forms and Dosage
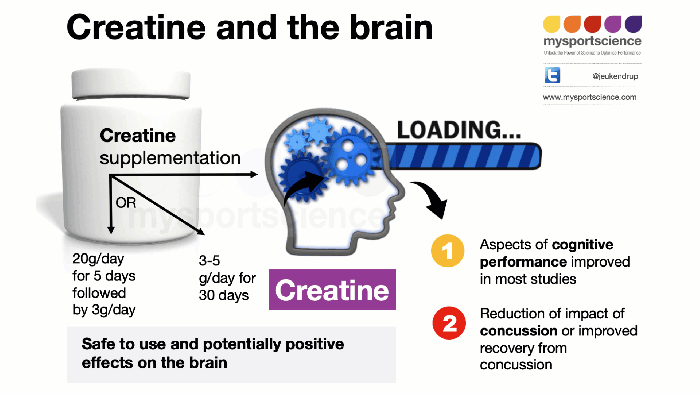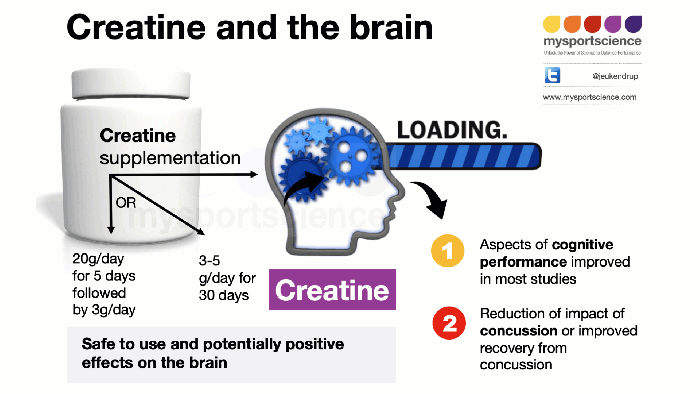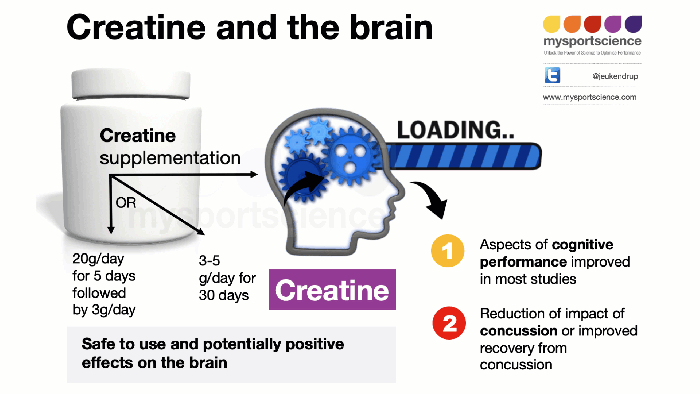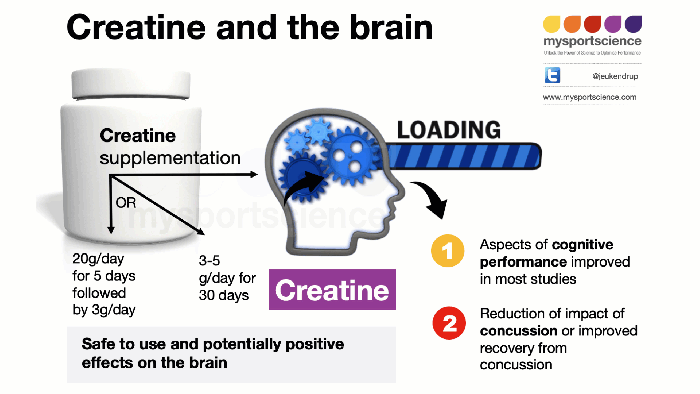
Creatine is available in various forms, including creatine monohydrate powder, capsules, and even liquid solutions. The most common and extensively studied form is creatine monohydrate powder. Capsules provide a convenient way to consume the supplement, while liquid forms often offer faster absorption, though this isn’t universally supported by research.A typical loading phase for creatine supplementation involves taking a higher dose (e.g., 20 grams per day) for a week, followed by a maintenance dose (e.g., 3-5 grams per day).
This loading phase is designed to rapidly saturate muscle creatine stores. However, a loading phase is not strictly necessary, and a lower, consistent daily dose can achieve similar results over a longer period. It’s important to follow the instructions on the product label and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Potential Side Effects
While generally considered safe, creatine supplementation can potentially lead to some side effects in susceptible individuals. Common side effects include weight gain (due to water retention), stomach upset (e.g., cramping, diarrhea), and dehydration. Individuals with pre-existing kidney or liver conditions should exercise caution and consult with a doctor before supplementing with creatine. Proper hydration is crucial when taking creatine.
Comparison of Creatine Types
| Creatine Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Creatine Monohydrate | Most researched and effective form, widely available, relatively inexpensive. | Can cause digestive discomfort in some individuals. |
| Creatine Ethyl Ester | Claimed to be more easily absorbed than creatine monohydrate. | Limited research on long-term effectiveness and safety compared to monohydrate. May not be as effective as monohydrate. |
| Creatine Hydrochloride (HCl) | Potentially better absorption than monohydrate due to improved solubility. | More expensive than monohydrate, some studies show less effectiveness. |
| Buffered Creatine | Reduces potential stomach discomfort associated with monohydrate. | Can be more expensive than monohydrate, and research supporting significant advantages over monohydrate is limited. |
The table above provides a concise comparison of various creatine supplements. The choice of supplement depends on individual needs and preferences, taking into account factors such as cost, potential side effects, and available research.
Cognitive Function
Our brains are incredibly complex machines, constantly processing information and enabling us to learn, remember, and interact with the world around us. Understanding the different aspects of cognitive function, and the physiological mechanisms that support it, is crucial to comprehending how our minds work and how we can optimize performance. This section dives into the core elements of cognition, exploring the intricate interplay of neurotransmitters, brain regions, and external factors that shape our mental capabilities.
Aspects of Cognitive Function
Cognitive function encompasses a broad range of mental processes. Key aspects include memory, attention, and processing speed. Each of these functions relies on intricate networks within the brain, involving specific neurotransmitters and pathways.
Memory
Memory is the ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. Different types of memory exist, each serving distinct purposes. Short-term memory, for example, holds information temporarily, while long-term memory stores information for extended periods. The hippocampus plays a critical role in forming new memories, while the cerebral cortex is essential for long-term storage and retrieval. Neurotransmitters like acetylcholine are vital for memory formation and retrieval.
While the potential cognitive benefits of creatine are intriguing, a lot more research is needed to fully understand its impact on brain function. Factors like age, genetics, and existing health conditions, such as the prevalence of multiple sclerosis (MS), multiple sclerosis MS prevalence and incidence , could influence how creatine affects cognitive performance. Ultimately, more studies are required to determine if creatine can truly boost cognition for everyone.
Attention
Attention is the ability to focus on specific stimuli while filtering out irrelevant information. Sustained attention allows for focused concentration over time, while selective attention allows us to choose which stimuli to process. The prefrontal cortex is a key brain region involved in attentional processes, working in concert with other brain areas to maintain focus. Neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine are involved in modulating attentional control.
Processing Speed
Processing speed refers to the rate at which the brain can perform cognitive tasks. This includes the speed of information processing, decision-making, and reaction time. Factors like age, practice, and individual differences influence processing speed. Neurotransmitters and brain regions involved in processing speed are often interconnected with those supporting memory and attention.
While the potential cognitive benefits of creatine are intriguing, it’s important to consider your overall health, especially if you’re navigating health conditions like PCOS. Understanding your blood tests, particularly when dealing with PCOS, can provide crucial insight into how your body responds to supplements like creatine. For a deeper dive into interpreting those essential health indicators, check out this helpful resource on understanding your blood tests pcos.
Ultimately, a personalized approach to supplement use, guided by your doctor and informed by your blood work, is key to maximizing any potential cognitive gains from creatine.
Physiological Mechanisms
The physiological mechanisms underlying cognitive functions are complex and multifaceted. They involve intricate neural pathways and neurochemical interactions that allow for the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information. These processes are affected by various external factors that can either enhance or impair cognitive function.
Neurotransmitters and Brain Regions
Various neurotransmitters and specific brain regions are crucial for the different cognitive functions. Acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and glutamate are some of the key neurotransmitters involved in memory, attention, and processing speed. The hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and cerebellum are some of the brain regions that are essential for different cognitive functions.
Factors Influencing Cognitive Performance
A multitude of factors influence cognitive performance. These factors range from physiological states to environmental influences. A balanced understanding of these factors can help optimize cognitive function and address potential cognitive impairments.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cognitive Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Sleep | Adequate sleep is essential for memory consolidation and cognitive restoration. | Poor sleep can impair memory, attention, and processing speed. |
| Stress | Chronic stress can negatively impact various cognitive functions. | Increased stress levels can lead to decreased attention, memory problems, and impaired decision-making. |
| Diet | A balanced diet provides essential nutrients for optimal brain function. | Nutrient deficiencies can negatively impact cognitive abilities. |
| Exercise | Regular physical activity can improve cognitive function. | Physical activity can improve memory, attention, and overall cognitive performance. |
| Hydration | Adequate hydration is critical for brain health and function. | Dehydration can lead to cognitive impairments. |
Creatine and its Potential Impact on the Brain
Creatine, a naturally occurring compound primarily known for its role in muscle energy production, has garnered increasing interest for its potential cognitive benefits. While its impact on physical performance is well-documented, research into its effects on the brain is ongoing, revealing promising possibilities for neuroprotection and enhanced cognitive function. This exploration delves into the evidence supporting creatine’s impact on brain health, focusing on its effects on various cognitive functions and the mechanisms by which it might influence brain function.Creatine’s role in cellular energy production extends beyond muscles.
The brain, a highly energy-demanding organ, relies heavily on ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and creatine plays a significant role in supporting this energy supply. This is particularly relevant to cognitive functions that require sustained mental effort. The potential benefits of creatine extend beyond simply providing energy; studies suggest it might also influence neurotransmitter function and protect neurons from damage, contributing to overall brain health.
Evidence Supporting Creatine’s Neuroprotective Potential
Studies investigating creatine’s neuroprotective effects have yielded promising results. Creatine’s ability to buffer cellular stress and maintain optimal energy levels may protect neurons from damage caused by oxidative stress, a key contributor to neurodegenerative diseases. Research has focused on its potential to mitigate the effects of neurological conditions, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. For instance, some studies suggest that creatine supplementation could potentially reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, thus potentially slowing disease progression.
Creatine’s Influence on Different Cognitive Functions
Creatine’s effects on various cognitive functions are being explored. Some studies suggest a positive impact on memory, particularly in tasks involving short-term memory and learning. For example, a study on healthy young adults found that creatine supplementation improved performance in spatial memory tasks. However, the effects on other cognitive domains, such as executive function and attention, are less consistent.
Mechanisms of Creatine’s Influence on Brain Function
The mechanisms by which creatine might influence brain function are multifaceted. It’s hypothesized that creatine’s role in supporting cellular energy production is a key factor. Increased ATP availability could lead to enhanced neuronal signaling and plasticity, which are essential for cognitive function. Furthermore, creatine’s antioxidant properties could contribute to protecting neurons from damage, reducing oxidative stress, and inflammation.
Types of Studies Investigating Creatine and Cognition, Can creatine boost cognition
Various types of studies have investigated the relationship between creatine and cognition. These include randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing creatine supplementation to a placebo group in healthy individuals and in individuals with neurological conditions. Animal studies have also contributed to our understanding, often showing promising effects in models of neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, some studies have examined the impact of creatine on brain metabolism and neurotransmitter function, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms.
Potential Mechanisms Linking Creatine to Cognition
Creatine, a naturally occurring compound, plays a crucial role in cellular energy production. Its potential impact on cognitive function has garnered significant interest, prompting research into the mechanisms behind this connection. This exploration delves into the possible pathways through which creatine might influence neuronal function, neurotransmitter activity, brain blood flow, and even brain structure.Understanding these mechanisms is essential for evaluating the potential benefits of creatine supplementation for cognitive enhancement.
While promising, more rigorous research is needed to fully elucidate the complex relationship between creatine and cognitive performance.
Creatine’s Role in Cellular Energy Production and Neuronal Function
Creatine phosphate serves as a readily available reservoir of high-energy phosphate bonds within cells. This crucial role in energy production is especially vital for neurons, which require a consistent supply of energy for maintaining electrical signals and carrying out various functions. Increased creatine levels can potentially enhance the efficiency of cellular energy production, providing neurons with the fuel needed for optimal function.
I’ve been curious about whether creatine can actually boost brainpower. While some studies suggest it might improve cognitive function, it’s definitely not a magic bullet. To really get my mind working at peak performance, I’ve been trying to figure out how to stop picking my nails – which is surprisingly tricky! This helpful guide has some interesting tips.
Ultimately, a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and stress management, seems to play a more significant role in cognitive enhancement than just relying on creatine alone. So, while creatine might be a piece of the puzzle, it’s not the whole picture when it comes to boosting brainpower.
This enhancement could translate into improved cognitive processes. For instance, tasks demanding rapid bursts of mental energy, like complex problem-solving or rapid reaction time, might benefit from improved creatine stores.
Creatine and Neurotransmitter Function
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers crucial for communication between neurons. Creatine’s influence on neurotransmitter function is a promising area of research. One potential mechanism involves creatine’s impact on the synthesis or regulation of neurotransmitters like glutamate, a key excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. Changes in glutamate levels could impact cognitive processes such as learning and memory. Furthermore, creatine may influence the reuptake and release of other neurotransmitters, affecting signaling pathways in the brain and potentially impacting various cognitive functions.
Impact of Creatine on Brain Blood Flow
The brain’s intricate network of blood vessels is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients to support neuronal activity. Studies suggest that creatine may influence cerebral blood flow. Improved blood flow to the brain could enhance the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen, supporting neuronal function and potentially improving cognitive processes. Increased blood flow could lead to enhanced neural signaling and improved cognitive performance.
This potential link is particularly relevant to situations where cognitive tasks are demanding, such as during periods of intense mental activity or in conditions associated with impaired blood flow.
Potential Impact of Creatine on Brain Structure
Creatine’s potential impact on brain structure is another area of ongoing research. Some studies have suggested a possible link between creatine supplementation and increased brain volume or specific structural changes within the brain. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and implications of such potential effects. For instance, some studies have shown that creatine may play a role in neuroprotection, potentially mitigating the effects of age-related cognitive decline.
Further research is necessary to clarify the relationship between creatine and structural changes in the brain, as well as the implications for cognitive performance.
Evidence for or Against a Creatine-Cognition Link
Creatine, a naturally occurring compound crucial for energy production in cells, has garnered attention for its potential cognitive benefits. While promising, the evidence linking creatine supplementation to improved cognitive function in healthy individuals is still somewhat mixed. This section delves into the existing research, analyzing study methodologies and findings to evaluate the strength of the creatine-cognition connection.
Study Methodologies Investigating Creatine and Cognition
Various methodologies are employed in studies investigating the relationship between creatine supplementation and cognitive performance. A crucial aspect is the inclusion of control groups. These groups, receiving either a placebo or no intervention, provide a baseline for comparison, allowing researchers to isolate the effects of creatine supplementation. Furthermore, rigorous protocols are necessary to minimize the influence of confounding factors like diet, exercise, and pre-existing conditions.
Randomization of participants is also critical, ensuring that the groups are as similar as possible, minimizing bias and maximizing the validity of the results.
Evidence Table: Creatine and Cognitive Performance in Healthy Individuals
| Study | Methodology | Cognitive Domains Assessed | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supplement Study 1 (Example) | Healthy adults, 20-35 years old, randomized into creatine or placebo groups for 8 weeks. Cognitive tests included memory, processing speed, and attention. | Memory, processing speed, attention, working memory | Creatine group showed a statistically significant improvement in working memory tasks compared to the placebo group. |
| Study 2 (Example) | Healthy adults, 25-45 years old, randomized into creatine or placebo groups for 12 weeks. Cognitive tests focused on executive function and verbal fluency. | Executive function, verbal fluency | No significant difference in cognitive performance was observed between the creatine and placebo groups. |
| Study 3 (Example) | Healthy young adults, 18-25 years old, randomized into high-dose creatine or placebo groups for 6 weeks. Evaluated attention, reaction time, and spatial reasoning. | Attention, reaction time, spatial reasoning | High-dose creatine group exhibited improved reaction time compared to the placebo group. |
Contrasting Results from Different Studies
The table above highlights the varied findings regarding creatine’s impact on cognitive function. Crucially, discrepancies exist in the magnitude and nature of observed effects. Some studies demonstrate statistically significant improvements in specific cognitive domains, while others find no significant differences between creatine and placebo groups.
Factors Contributing to Varying Results
Several factors could contribute to the inconsistent findings across studies. These include variations in study design, such as duration of supplementation, dosage, and the specific cognitive domains assessed. Furthermore, participant characteristics, including age, gender, and pre-existing health conditions, can influence the response to creatine supplementation. Finally, the specific cognitive tests used may affect the results.
Factors Affecting Creatine’s Impact on Cognition
Creatine supplementation has garnered attention for its potential cognitive benefits, but its effects aren’t universal. Numerous factors can influence how creatine impacts cognitive performance, making it crucial to understand these nuances before drawing definitive conclusions. This section delves into the variables that can modify the response to creatine, including pre-existing health conditions, dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and potential interactions with other substances.Individual variations in response to creatine supplementation are substantial.
Factors like pre-existing health conditions, age, and genetic predispositions play a significant role in how the body processes and utilizes creatine, impacting its potential impact on cognitive function. The effectiveness of creatine’s cognitive benefits is not a one-size-fits-all scenario.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can affect how the body absorbs and utilizes creatine, potentially diminishing or enhancing its impact on cognition. Individuals with kidney or liver issues, for instance, might need to be cautious about creatine supplementation, as their kidneys and livers play a role in creatine metabolism. Consult with a healthcare professional before supplementing with creatine if you have any pre-existing health concerns.
Conditions such as diabetes or hypothyroidism may also influence how creatine affects cognitive performance.
Age
Age-related changes in muscle mass and function can influence creatine’s effect on cognitive performance. While creatine supplementation might offer benefits for cognitive function in some age groups, its effects may vary in individuals with age-related cognitive decline. Further research is needed to fully understand the interplay between age and creatine’s impact on cognition.
Individual Genetic Predisposition
Genetic variations can influence how efficiently the body synthesizes and utilizes creatine. Individuals with specific genetic variations might experience different responses to creatine supplementation, affecting its cognitive benefits. Research is ongoing to identify the specific genetic markers associated with creatine’s impact on cognition.
Diet and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for optimizing the effects of creatine supplementation on cognition. A balanced diet rich in carbohydrates can support creatine uptake, while sufficient hydration is crucial for overall bodily function, potentially impacting cognitive performance. Adequate hydration helps maintain cellular function, which may support the positive cognitive effects of creatine.
Exercise and Lifestyle Choices
Exercise and lifestyle choices significantly interact with creatine supplementation to influence cognitive function. Individuals engaging in regular physical activity may experience more pronounced benefits from creatine supplementation, possibly due to increased muscle protein synthesis and improved blood flow to the brain. Stress levels and sleep quality also play a role. Adequate sleep is essential for cognitive function, and chronic stress can negatively impact cognitive performance, which may interact with creatine supplementation.
Interactions with Other Supplements and Medications
Creatine may interact with other dietary supplements or medications, either positively or negatively affecting cognitive function. For instance, creatine and caffeine are commonly consumed together, but the combined effects on cognition are not fully understood. The synergistic or antagonistic effects of creatine with other supplements require further investigation. It’s important to disclose all supplements and medications to a healthcare provider before supplementing with creatine.
Consult a doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure about possible interactions.
Future Directions and Research Needs

The current research on creatine and cognitive function is promising but still leaves significant gaps in our understanding. To truly harness the potential benefits of creatine for cognitive enhancement, we need more robust and well-designed studies. This involves exploring different populations, cognitive domains, and testing various creatine administration protocols to gain a more complete picture.
Investigating Specific Cognitive Domains
The impact of creatine on cognition is not uniform across all cognitive functions. While some studies show improvements in memory and attention, others have yielded mixed results. Future research should meticulously investigate specific cognitive domains like working memory, executive function, and processing speed, focusing on the underlying mechanisms at play. Detailed assessments of these specific domains are crucial for understanding the nuanced effects of creatine supplementation.
For instance, a study might focus on the impact of creatine on working memory tasks involving complex information processing.
Exploring Different Populations and Demographics
Current research predominantly focuses on healthy young adults. To determine the generalizability and potential therapeutic applications of creatine for cognitive enhancement, future studies should investigate its effects across various populations, including older adults, individuals with cognitive impairments, and those with specific neurological conditions. This approach will help to understand if the benefits extend beyond the typical healthy population.
Examining creatine’s effects on age-related cognitive decline, for example, is a significant area for future research.
Optimizing Creatine Administration Protocols
Different creatine supplementation strategies might yield varying cognitive outcomes. Future studies should explore different dosing regimens, timing of administration, and duration of supplementation. For instance, a study could compare the effects of daily low-dose creatine intake with high-dose creatine loading protocols on cognitive performance. This exploration will help determine the optimal creatine regimen for maximizing cognitive benefits.
Also, understanding the interaction of creatine with other dietary supplements and medications is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
Investigating Underlying Mechanisms
While several potential mechanisms link creatine to cognition, further research is needed to elucidate the precise pathways involved. Future studies should delve deeper into the molecular and cellular mechanisms, such as creatine’s role in energy production, neurotransmitter regulation, and neuronal plasticity. Examining the effects of creatine on brain metabolites and neural activity using advanced neuroimaging techniques would greatly contribute to our understanding.
Addressing the Need for Longitudinal Studies
Many current studies are short-term, observing effects over a few weeks. Longitudinal studies following participants over months or years are essential to assess the long-term impact of creatine supplementation on cognitive function and potential health implications. Such studies would offer a more realistic perspective on creatine’s influence on cognitive development and maintenance throughout life. Observing potential cumulative effects of creatine supplementation over time would provide valuable insight.
Addressing Research Gaps and Ethical Considerations
Current research lacks consistency in methodologies, making comparisons across studies challenging. Future studies must adhere to rigorous protocols, standardizing variables like participant demographics, cognitive assessment tools, and creatine dosage. Ensuring ethical considerations are carefully addressed, including potential side effects and interactions with other medications, is crucial for the responsible advancement of this research area. A detailed protocol outlining participant safety measures is essential for any future studies.
Summary: Can Creatine Boost Cognition
In conclusion, while the evidence for creatine boosting cognition is promising, it’s not conclusive. More research, particularly studies with larger sample sizes and diverse populations, is needed to solidify our understanding. Factors like individual differences, pre-existing health conditions, and the specific type of creatine used can all play a role in determining its impact. This exploration underscores the importance of consulting with healthcare professionals before incorporating creatine or any other supplement into your routine.

