6 foods to help soothe ibs symptoms naturally offer a natural approach to managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). This guide explores specific foods, their potential benefits, and how they can help alleviate IBS symptoms. We’ll delve into the science behind these foods and provide practical dietary recommendations for incorporating them into your daily life. IBS…
Author: Jaiden Mayer
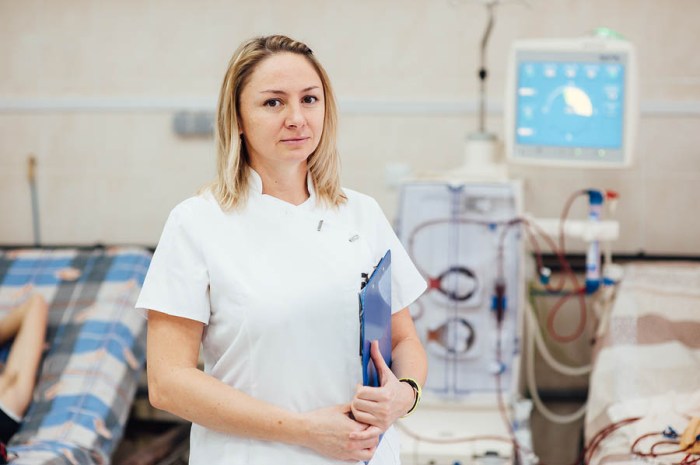
Chronic Kidney Disease Life Expectancy A Comprehensive Guide
Chronic kidney disease life expectancy is a crucial aspect of understanding this complex health condition. This guide delves into the stages of CKD, their impact on lifespan, and the various treatment options available. We’ll explore how treatment effectiveness, lifestyle modifications, and overall health factors influence the trajectory of life expectancy in CKD patients. From the…
Avoid Drinking Water After 4 PM Myth or Reality?
Avoid drinking water after 4pm – Avoid drinking water after 4 PM. Is this a sound hydration strategy, or a harmful misconception? This post explores the potential health implications of restricting water intake after 4 pm, debunking common myths and offering alternative, evidence-based approaches to managing your hydration needs throughout the day. We’ll delve into…
Ways to Clear Blocked Sinuses A Comprehensive Guide
Ways to clear blocked sinuses is a multifaceted topic that dives into various approaches, from simple home remedies to advanced medical interventions. This guide explores the anatomy of sinuses, pinpointing common and uncommon causes of blockages, and distinguishing between acute and chronic cases. It further details effective home remedies, over-the-counter medications, and when medical intervention…
Sitting and Brain Volume A Deep Dive
Sitting and brain volume sets the stage for this fascinating exploration, delving into the complex relationship between our sedentary lifestyles and the structure of our brains. We’ll examine how prolonged sitting might affect brain volume, considering various factors like posture, lifestyle, and specific brain regions impacted. Prepare to uncover the potential mechanisms and explore strategies…
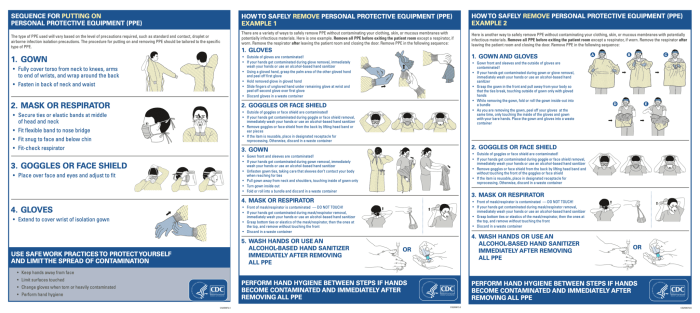
When You Cant Get a Diagnosis A Deep Dive
When you cant get a diagnosis – When you can’t get a diagnosis, the journey can feel isolating and overwhelming. This exploration delves into the complexities of navigating the healthcare system when a diagnosis eludes you. We’ll uncover the emotional, practical, and financial burdens of diagnostic uncertainty, examine the diagnostic process, and offer coping strategies…
How to Get More Fiber in Your Diet A Guide
How to get more fiber in your diet is a crucial aspect of a healthy lifestyle. Fiber is more than just a buzzword; it plays a vital role in digestion, blood sugar control, and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide dives deep into understanding dietary fiber, exploring various fiber-rich foods, and providing practical strategies to boost…
Acid Reflux and Shortness of Breath A Deep Dive
Acid reflux and shortness of breath are often intertwined, creating a complex medical puzzle. Understanding the connection between these seemingly disparate symptoms is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. This exploration delves into the physiological mechanisms, potential underlying conditions, diagnostic procedures, management strategies, and ultimately, the prognosis for individuals experiencing both acid reflux and…