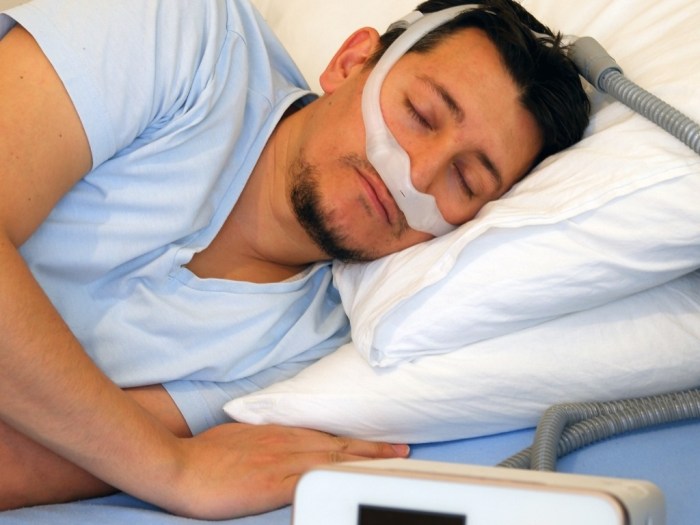
What is the difference between CPAP and BiPAP? Understanding these two therapies is crucial for anyone struggling with sleep apnea. CPAP and BiPAP machines deliver pressurized air to keep your airways open during sleep, preventing interruptions to your breathing. However, they differ in how they achieve this, leading to distinct advantages and disadvantages for different…
Author: Albert Quigley
Computer Headaches Causes and Solutions
Is working at my computer causing my headaches? This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted reasons behind computer-related headaches, delving into everything from ergonomic setups to lifestyle factors and potential underlying medical conditions. We’ll unpack the science behind why staring at a screen all day can lead to pain and discomfort, and provide practical solutions to…
HATTR Amyloidosis Life Expectancy A Deep Dive
HATTR amyloidosis life expectancy is a critical factor for patients and their families. This exploration delves into the complexities of this disease, examining the factors influencing survival and the impact on overall well-being. We’ll discuss the various aspects of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis, all while providing a comprehensive understanding of this challenging condition. From the…
How Much Protein in Milk? A Deep Dive
How much protein in milk? This question is crucial for anyone looking to understand the nutritional value of milk and milk alternatives. From cow’s milk to almond milk, different types contain varying amounts of protein, impacting their suitability for different dietary needs. This comprehensive guide explores the protein content of various milk types, examining factors…
How Can You Prevent Colds? A Complete Guide
How can you prevent colds? This comprehensive guide delves into various strategies, from simple hygiene practices to boosting your immunity. We’ll explore everything from meticulous handwashing to the impact of environmental factors, offering actionable advice to keep you healthy throughout the year. Discover practical tips and tricks to avoid those pesky colds, and learn how…
Do Wireless Bluetooth Headphones Cause Cancer?
Do wireless Bluetooth headphones cause cancer? This question sparks considerable debate, raising concerns about the potential health risks associated with RF radiation emitted by these devices. Understanding the science behind RF radiation, examining existing research, and exploring regulatory standards is crucial to form a balanced perspective on this issue. This exploration delves into the scientific…
Is Zyn Bad for Your Heart?
Is Zyn bad for your heart? This question is important for anyone considering using Zyn, a popular energy product. Understanding the ingredients, typical dosages, and potential cardiovascular effects is key to making informed decisions about your health. We’ll delve into the details, examining the possible links between Zyn and heart health, and provide a comprehensive…
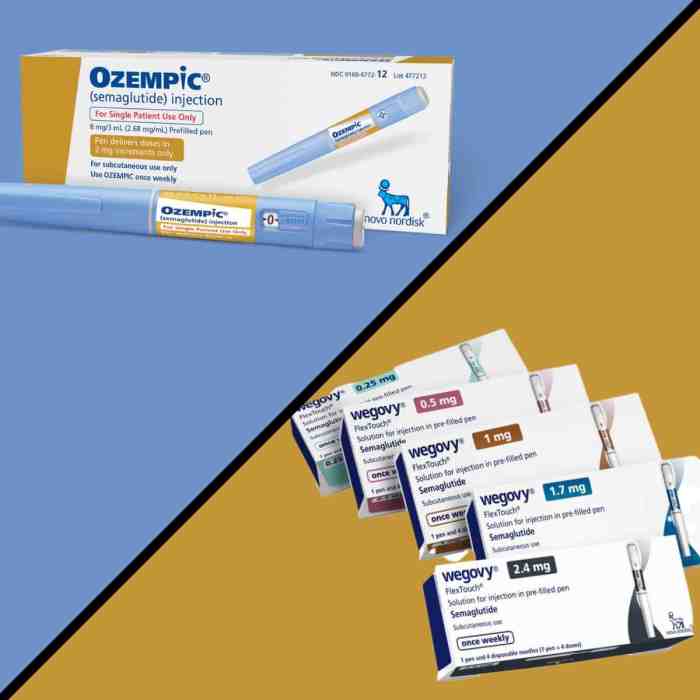
Ozempic Approved Kidney Disease Risk Reduced
Ozempic approved to reduce kidney disease risk is a significant development in healthcare. This groundbreaking approval opens up exciting possibilities for managing and potentially preventing kidney disease, a condition affecting millions worldwide. The approval hinges on research exploring Ozempic’s mechanisms of action, clinical trials, and the potential interplay with existing kidney disease risk factors. We’ll…
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome vs Fibromyalgia A Deep Dive
Chronic fatigue syndrome vs fibromyalgia: Understanding these conditions is crucial for those affected and those supporting them. This exploration delves into the complexities of diagnosing, treating, and living with these often-misunderstood illnesses. We’ll examine their shared and distinct symptoms, explore the challenges in diagnosis, and investigate the potential underlying mechanisms. Both conditions significantly impact daily…
Two Dates a Day for Health Benefits A Deep Dive
Two dates a day for health benefits: This post explores the potential advantages of incorporating two dates daily into your diet. From understanding the nutritional powerhouse that dates are, to learning how to incorporate them into various meals and snacks, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll examine different date types, preparation methods, potential…