How could I not know that I had PCOS until adulthood? This journey explores the often-delayed diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in women. We’ll delve into why diagnosis might be delayed, the impact of this delay on health outcomes, and strategies for improving early detection. Many women experience a range of symptoms, some subtle,…
Author: Albert Quigley
Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis A Deep Dive
Types of rheumatoid arthritis sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into the complexities of this chronic autoimmune disease. We’ll explore the various forms of rheumatoid arthritis, examining their unique characteristics, symptoms, and treatment approaches. Understanding the different types is crucial for effective management and a better quality of life. This…
Aerobic Exercise Fights Stiff Heart
Aerobic exercise fights stiff heart, offering a powerful pathway to a healthier cardiovascular system. This exploration delves into the science behind how regular physical activity can counteract the hardening of arteries, improving heart health and overall well-being. We’ll examine the different types of aerobic exercise, their impact on heart stiffness, and the crucial role of…
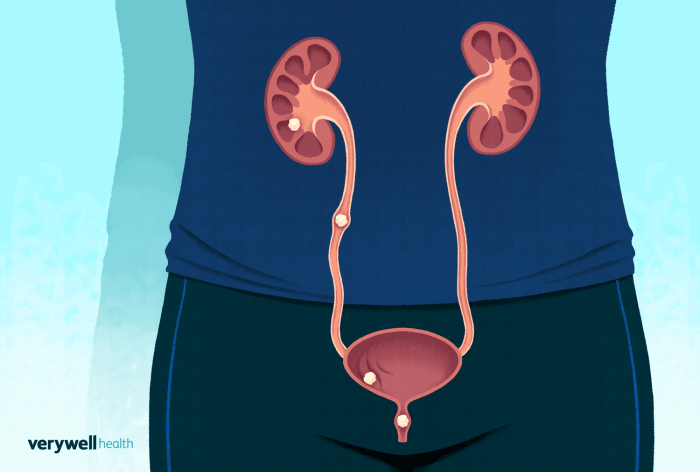
Stages of Passing a Kidney Stone A Comprehensive Guide
Stages of passing a kidney stone can be a truly harrowing experience. This detailed guide delves into the various phases, from the initial agonizing pain to the eventual elimination and recovery. We’ll explore the different types of kidney stones, their formation, and the specific symptoms associated with each stage. Understanding these stages can help you…
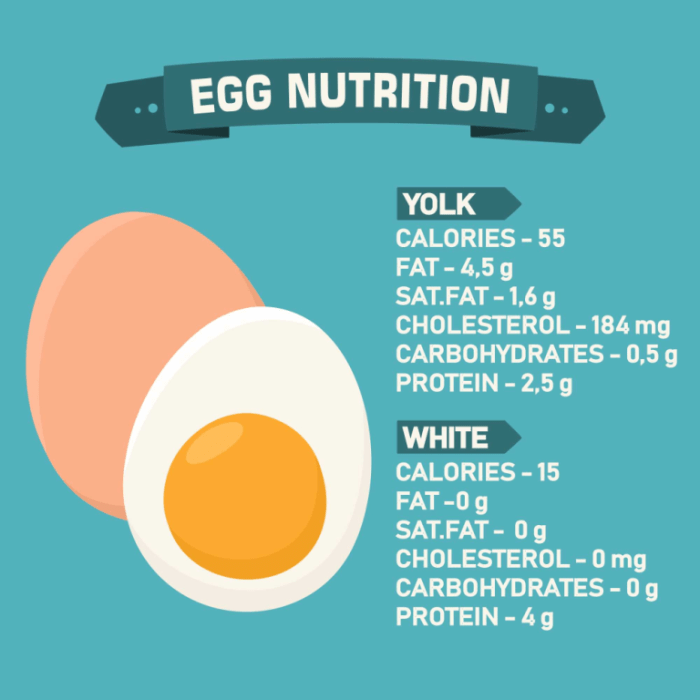
How Much Protein in an Egg A Deep Dive
How much protein in an egg? This question is more than just a simple query; it’s a window into the incredible nutritional powerhouse that is the humble egg. From understanding the protein content differences between the egg white and yolk to exploring the impact of cooking methods, this comprehensive guide delves into the world of…
RSV and Rash Symptoms Link and Treatment
RSV and rash symptoms link and treatment is a crucial topic for parents and caregivers. Understanding the connection between Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and skin rashes can help in early diagnosis and appropriate management. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of rashes associated with RSV, their symptoms, potential causes, diagnostic methods, treatment strategies, and…
What Does Low Serotonin Feel Like? Unveiling the Impact
What does low serotonin feel like? This exploration dives deep into the often-misunderstood world of low serotonin levels, revealing the multifaceted impact they can have on your well-being. We’ll examine the emotional, physical, cognitive, social, and even behavioral changes that can accompany these lower-than-normal serotonin levels. From subtle mood fluctuations to more pronounced symptoms, understanding…
Why Am I Always Constipated? Explained
Why am I always constipated? This frustrating issue affects many, and understanding the root causes is key to finding relief. This in-depth exploration dives into dietary factors, lifestyle habits, potential underlying medical conditions, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and prevention strategies. We’ll cover everything from the foods you eat to the impact of stress and sleep…
What to Eat on Your Period A Guide
What to eat on your period? This isn’t just about cravings; it’s about understanding your body’s unique needs during menstruation. From boosting energy levels to easing discomfort, the right foods can make a real difference. This guide dives deep into the nutritional needs of your cycle, offering practical advice and delicious meal ideas. We’ll explore…
Valine What to Know About This BCAA
Valine what to know about this bcaa – Valine, what to know about this BCAA sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of this branched-chain amino acid. We’ll delve into its chemical structure, role in protein synthesis, and function within the body. Beyond basic science, we’ll also examine its impact on athletes, dietary considerations, and…