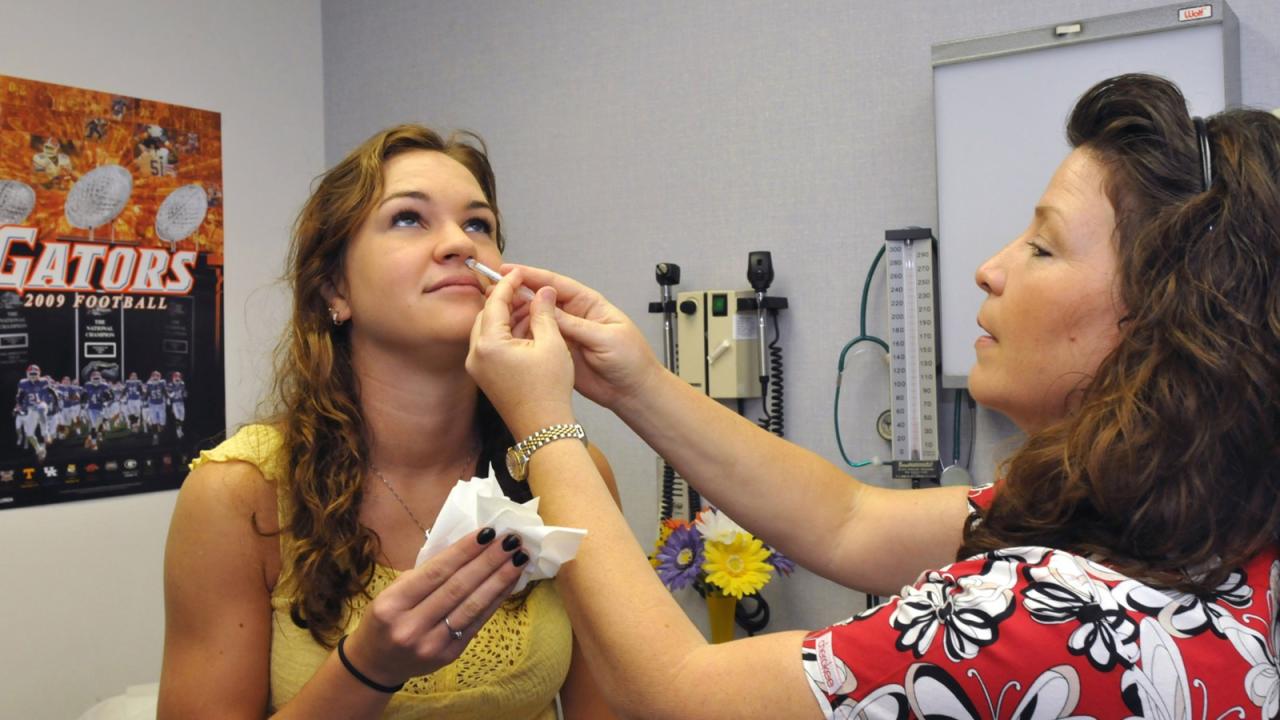
What is the nasal flu vaccine Flumist? This guide dives deep into the nasal spray flu vaccine, exploring its form, benefits, safety, and effectiveness compared to other options. We’ll uncover how it works, who it’s best for, and what to expect from its administration and potential side effects. Prepare to be well-informed! Flumist is a…
Author: admin
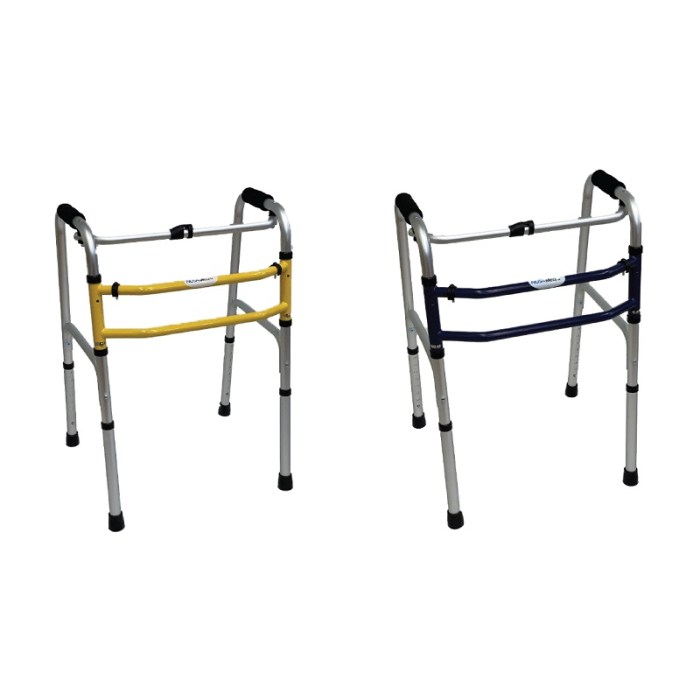
Mobility Aids with Fibromyalgia A Comprehensive Guide
Mobility aids with fibromyalgia are crucial for maintaining independence and managing daily life. This guide delves into various types of mobility aids, from walkers and canes to wheelchairs and scooters, exploring their features and functionalities. We’ll discuss how to choose the right aid based on individual needs and limitations, and how to use them effectively…
Migraine and Mood Swing A Deep Dive
Migraine and mood swing: Understanding the intricate connection between these often-overlooked conditions is crucial for effective management. This exploration delves into the potential mechanisms linking these conditions, examining their impact on daily life, and highlighting various treatment approaches. Migraine headaches, characterized by throbbing pain, often accompany a range of emotional changes. Mood swings, encompassing a…
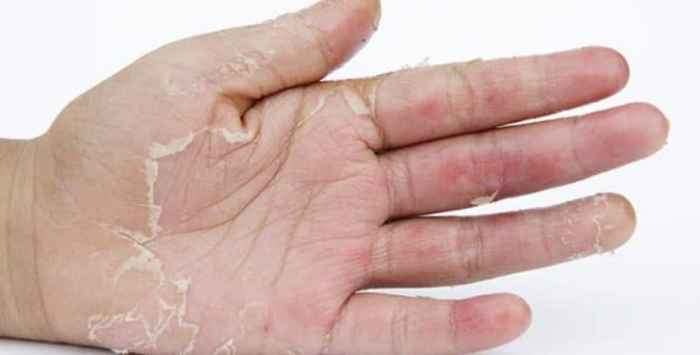
What is Acral Peeling Skin Syndrome? A Deep Dive
What is acral peeling skin syndrome? This condition, characterized by skin peeling primarily on the extremities, presents a fascinating interplay of genetics, environment, and potential causes. Understanding its characteristics, causes, diagnosis, management, and prognosis is crucial for those affected and healthcare professionals alike. This comprehensive exploration delves into the complexities of this often-misunderstood syndrome, offering…
How to Use Saline Nose Drops in Babies A Guide
How to use saline nose drops in babies is a crucial skill for parents. These drops are a common and often effective way to relieve nasal congestion in infants. Understanding the proper administration techniques, potential complications, and alternative solutions is essential for ensuring your baby’s comfort and well-being. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview…
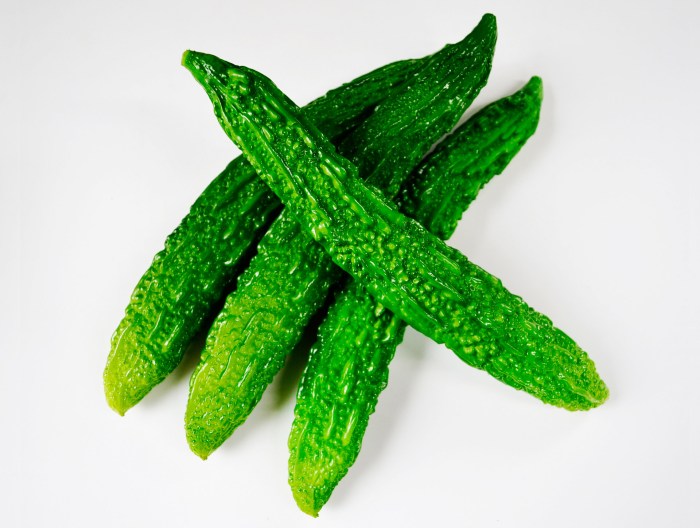
Bitter Melon Benefits and Nutrition A Deep Dive
Bitter melon benefits and nutrition are a fascinating area of study. This comprehensive exploration dives into the remarkable properties of this often-overlooked fruit, examining its history, nutritional profile, potential health advantages, and culinary applications. From its use in traditional medicine to modern research, we’ll uncover the multifaceted nature of bitter melon. Bitter melon, known scientifically…
What Foods Cause High Triglycerides? A Deep Dive
What foods cause high triglycerides? This comprehensive guide explores the surprising array of dietary culprits contributing to elevated triglyceride levels. We’ll uncover the nutritional content of various foods, from processed delights to healthy staples, and examine how different types of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins impact triglyceride production. Understanding these connections empowers you to make informed…
Brown vs White Eggs A Deep Dive
Brown vs white eggs – a seemingly simple comparison, but a fascinating exploration into the world of poultry and food production. From the subtle differences in shell color to the nuances in taste and culinary applications, this comprehensive guide delves into the specifics of both types. We’ll examine their nutritional profiles, production methods, and consumer…
Warning Signs of a Dying Liver Early Detection
Warning signs of a dying liver can be subtle, often appearing as mild discomfort or vague symptoms. Understanding these early indicators is crucial for timely intervention. This exploration delves into the intricate workings of the liver, highlighting its vital roles in detoxification, digestion, and metabolism. We’ll examine various stages of liver dysfunction, from early warning…
Foods Rich in Vitamin D Your Daily Dose
Foods rich in vitamin d are crucial for overall health, supporting everything from strong bones to a robust immune system. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of vitamin D-rich foods, exploring their nutritional benefits, preparation methods, and dietary considerations. We’ll uncover the best sources, from familiar favorites to surprising plant-based options, and provide actionable…