Ankylosing spondylitis and teeth problems are intricately linked, creating a complex interplay between spinal health and oral well-being. This exploration delves into the specifics of this connection, examining the common oral health concerns associated with AS, the underlying mechanisms, and effective management strategies.
This comprehensive guide will cover various aspects of oral health in individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS), from the underlying pathophysiology to practical management strategies and dietary considerations. We’ll also explore the impact of medications used to treat AS on oral health, and provide real-world examples through illustrative case studies.
Introduction to Ankylosing Spondylitis and Oral Health
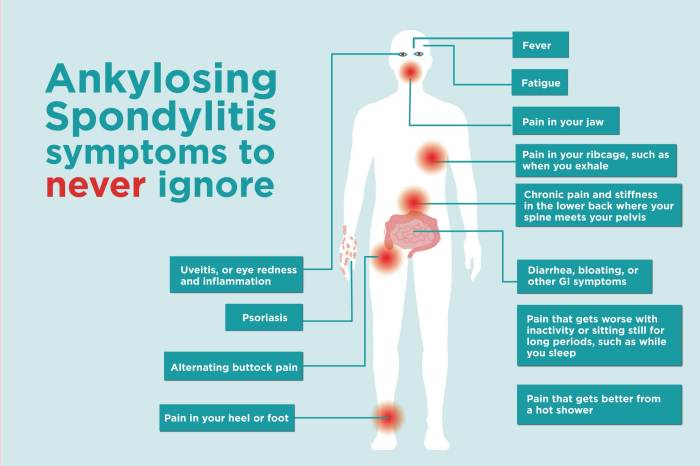
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disease primarily affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints. Characterized by progressive stiffness and pain, AS can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Beyond the musculoskeletal system, AS can also affect other parts of the body, including the mouth and teeth. Understanding the connection between AS and oral health is crucial for comprehensive patient care.The inflammatory process inherent in AS can lead to various oral health complications.
These range from increased risk of gum disease to specific dental issues that can arise due to the disease’s impact on the body’s immune response and systemic inflammation. Early detection and proactive management are vital to prevent more serious problems.
Common Oral Health Concerns in AS
Oral health issues in individuals with AS often stem from the systemic inflammation that characterizes the disease. This inflammation can affect the gums, teeth, and supporting structures. The increased risk of oral complications necessitates vigilant oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups.
- Increased Risk of Periodontitis: The inflammatory response in AS can weaken the supporting tissues around the teeth, leading to periodontal disease (periodontitis). This can result in gum inflammation, bleeding, and eventual tooth loss. The inflammatory cytokines associated with AS directly contribute to the breakdown of periodontal ligaments and alveolar bone.
- Dental Abscesses: Individuals with AS may be more susceptible to dental abscesses due to compromised immune responses and potential difficulties in healing. A compromised immune system can slow the healing process, making individuals more prone to infection. The pain and discomfort associated with abscesses can be significant and require prompt treatment.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Medications used to manage AS can sometimes lead to dry mouth. This reduced saliva production can create an environment favorable to bacterial growth, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease. The decreased saliva flow can also make it harder to maintain oral hygiene.
- Malocclusion and Jaw Pain: AS can cause inflammation and stiffness in the jaw joints, potentially leading to malocclusion (misalignment of teeth). This can result in jaw pain and difficulty chewing, further impacting overall oral health.
Prevalence of Dental Problems in AS
Studies have shown a higher prevalence of oral health problems in individuals with AS compared to the general population. The exact figures can vary based on the specific study and the population sampled. However, the consistent finding is a noticeable increase in issues like periodontal disease and tooth loss. This suggests a direct link between AS and oral health complications, emphasizing the need for comprehensive dental care for individuals with this condition.
Underlying Mechanisms Linking AS and Oral Issues
The underlying mechanisms linking AS and oral health issues are complex and not fully understood. However, the systemic inflammation associated with AS plays a key role. This inflammation can affect various tissues, including those in the mouth. The chronic inflammation and immune system dysregulation in AS are thought to contribute to increased susceptibility to oral infections and impaired healing processes.
This inflammatory response, in turn, may lead to periodontal disease, tooth loss, and other oral complications.
Comparison of Oral Health Issues
| Disease | Oral Health Issues |
|---|---|
| Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) | Increased risk of periodontitis, dental abscesses, dry mouth, malocclusion, and jaw pain. |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Increased risk of periodontitis, tooth loss, and dental erosion. |
| Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) | Increased risk of oral ulcers, dry mouth, and dental erosion. |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Increased risk of periodontitis, delayed wound healing, and oral fungal infections. |
The table above provides a brief comparison of common oral health issues across different conditions. Note that these are not exhaustive lists and individual experiences may vary. The presence of these issues should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
Specific Dental Problems in AS
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. However, the inflammatory process can extend to other parts of the body, including the oral cavity. This often leads to a range of dental issues that can significantly impact the quality of life for individuals with AS. Understanding these specific problems is crucial for early detection, appropriate management, and improved overall health outcomes.
Common Dental Problems in AS, Ankylosing spondylitis and teeth problems
Dental problems in AS are often a consequence of the systemic inflammation characteristic of the disease. This inflammation can affect the supporting structures of the teeth, including the periodontal ligaments and bone, leading to a range of complications. Additionally, some medications used to treat AS may contribute to dental issues.
Hey everyone, I’ve been doing some research on ankylosing spondylitis and the potential dental issues it can cause. It’s a tricky condition, and sometimes the symptoms can be confusing. For example, if you’re experiencing pain in your jaw or teeth, along with inflammation in other parts of your body, it could be related. Sometimes, a persistent cough with a white mucus production, like you might find out more about in this article on coughing up white mucous , could also be a sign of something else going on.
It’s important to remember that ankylosing spondylitis and potential dental problems can often be interconnected. More research is needed to fully understand these complex relationships.
- Periodontal Disease: Inflammation of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth is a frequent occurrence in AS. The inflammatory response, often exacerbated by systemic inflammation, can lead to gingivitis and periodontitis, potentially causing bone loss around the teeth. This is often associated with persistent inflammation, causing pain, bleeding gums, and eventually tooth loss. The frequency of this problem tends to be higher in individuals with more active disease, impacting both younger and older AS patients.
- Tooth Erosion: The chronic inflammation in AS can influence the production of stomach acid, leading to increased gastric acid reflux. This can result in the erosion of tooth enamel, potentially exposing the dentin and increasing the risk of sensitivity and cavities. This is a significant issue as it can occur in any age group and impacts the longevity and health of the teeth.
It is more noticeable in individuals with frequent or uncontrolled reflux.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Some medications used to manage AS can have a side effect of reducing saliva production. This can create a dry mouth environment, increasing the risk of cavities and oral infections. Dry mouth can affect patients of all ages with varying severity.
- Jaw Joint Issues: Inflammation can also affect the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jaw to the skull. This can lead to pain, limited movement, and clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth. This is a problem that may affect patients of all ages, especially those with significant spine involvement.
Frequency of Dental Problems by Age
The prevalence of dental issues in AS patients can vary based on age and disease activity. Younger patients, in particular, might experience more frequent and severe periodontal disease as the disease is more active in their bodies. While older patients may have established disease, the long-term impact on their oral health is still significant. The precise frequency of each issue requires further research, and studies may need to be tailored to specific age groups and disease severity.
Impact on Overall Health
Dental problems in AS are not just localized to the mouth. They can significantly impact overall health and well-being. Infections in the mouth can spread to other parts of the body, potentially exacerbating existing AS symptoms or causing new complications. Poor oral hygiene and untreated dental issues can contribute to systemic inflammation, further impacting the disease progression.
Severity of Dental Problems in AS
| Dental Problem | Potential Severity | Impact on Overall Health |
|---|---|---|
| Periodontal Disease | Moderate to Severe (depending on progression) | Increased risk of tooth loss, systemic inflammation |
| Tooth Erosion | Mild to Moderate (depending on acid reflux) | Increased sensitivity, increased risk of cavities |
| Xerostomia | Mild to Moderate (depending on medication) | Increased risk of oral infections, cavities |
| TMJ Issues | Mild to Severe (depending on involvement) | Pain, limited jaw movement, difficulty chewing |
Oral Health Management Strategies
Maintaining optimal oral health is crucial for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The chronic inflammation associated with AS can impact various aspects of the body, including the mouth and teeth. Effective oral hygiene practices, coupled with regular dental check-ups, are vital for preventing and managing potential dental problems that can arise from AS. Early detection and intervention are key to preserving oral health and overall well-being.Proper oral care plays a significant role in mitigating the risk of dental complications.
Addressing any potential issues promptly can prevent the progression of problems, leading to more extensive and costly interventions later on. This proactive approach ensures the preservation of healthy teeth and gums, which contributes to overall comfort and quality of life.
Preventive Measures for Maintaining Oral Health
Preventive measures are essential for preserving oral health in individuals with AS. A comprehensive approach encompassing both daily oral hygiene practices and regular professional dental care is vital. A consistent routine of brushing and flossing, combined with a balanced diet and avoidance of sugary drinks and snacks, are critical steps.
Strategies for Early Detection and Intervention of Dental Problems
Early detection and intervention of dental problems are paramount in AS. Individuals with AS should prioritize regular dental check-ups, including visual assessments, radiographic imaging (like X-rays), and periodontal examinations. These evaluations can identify potential issues such as gum disease, tooth decay, or bone loss in the jaw early on, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
Role of Oral Hygiene Practices in Managing AS-Related Dental Issues
Oral hygiene practices play a significant role in managing AS-related dental issues. Daily brushing, flossing, and rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash are crucial. These practices help remove plaque and bacteria, which can contribute to gum disease and tooth decay. Furthermore, a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals contributes to overall oral health. Regular use of fluoride toothpaste further strengthens tooth enamel.
Importance of Regular Dental Check-ups and Professional Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for maintaining optimal oral health in AS. These visits allow dentists to monitor the patient’s oral condition, identify any potential issues early, and provide personalized treatment plans. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup that can be missed during daily brushing and flossing, preventing gum disease and tooth decay.
Need for Customized Treatment Plans for AS Patients
Customized treatment plans are necessary for AS patients. Dentists should consider the unique challenges and needs of individuals with AS when creating a treatment plan. This involves understanding the potential impact of the disease on oral health, such as the reduced jaw movement or potential for inflammation in the mouth. This proactive approach ensures effective and personalized care.
Step-by-Step Guide for Oral Hygiene in AS Patients
A consistent and comprehensive oral hygiene routine is crucial for managing dental health in individuals with AS. This detailed step-by-step guide Artikels the essential practices:
| Step | Action | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste | Twice a day (morning and night) |
| 2 | Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth | Daily |
| 3 | Use an antiseptic mouthwash | Once or twice daily |
| 4 | Eat a balanced diet low in sugar | Daily |
| 5 | Visit the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings | Every 3-6 months |
| 6 | Report any pain, swelling, or discomfort to the dentist immediately | As needed |
Dietary Recommendations and Oral Health: Ankylosing Spondylitis And Teeth Problems
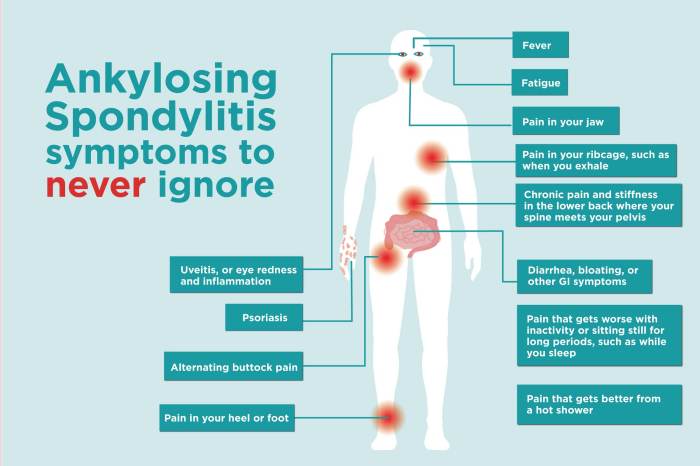
Eating well is crucial for overall health, and this is especially true for individuals with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Maintaining a healthy diet can significantly impact oral health, potentially reducing the risk of dental problems often associated with AS. Understanding the connection between diet and oral health in AS is essential for proactively managing the condition.A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, plays a vital role in supporting the overall well-being of those with AS.
Proper nutrition aids in maintaining strong bones and teeth, essential for preventing dental issues that can be exacerbated by the inflammatory processes common in AS. This section delves into dietary considerations for individuals with AS, providing specific recommendations to minimize dental problems.
Dietary Considerations for Oral Health in AS
A diet rich in vitamins and minerals is important for oral health. Nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and vitamin C are crucial for maintaining strong teeth and gums. The inflammatory processes often associated with AS can impact the absorption and utilization of these essential nutrients. A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help mitigate this impact.
Specific Dietary Recommendations
Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential vitamins and minerals that support oral health. Furthermore, limiting sugary drinks and foods can help prevent tooth decay, a common concern in AS. It’s important to remember that the impact of diet on oral health is interconnected with the overall management of AS.
Impact of Certain Foods and Drinks
Sugary foods and drinks are detrimental to oral health. They create an acidic environment in the mouth that can erode tooth enamel and increase the risk of cavities. Frequent consumption of sugary snacks and beverages can lead to significant dental problems. Similarly, highly acidic foods and drinks can also contribute to enamel erosion. It is recommended to consume these items in moderation.
Influence of Diet on Dental Problem Progression
The progression of dental problems in AS can be influenced by diet. A diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken teeth and gums, making them more susceptible to decay and inflammation. This, in conjunction with the inflammatory aspects of AS, can create a vicious cycle. Therefore, a well-balanced diet is crucial for managing both AS and potential dental complications.
Role of Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining oral health. Saliva, produced by the salivary glands, helps to wash away food particles and neutralize acids in the mouth. Dehydration can lead to reduced saliva production, increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Regular consumption of water is essential to maintaining optimal oral health.
Dealing with ankylosing spondylitis can sometimes lead to tricky dental issues. Inflammation can affect the jaw, making teeth extra sensitive and potentially impacting your overall oral health. This is something I’ve been researching more recently, and I’ve learned that weight changes and birth control pill effectiveness weight and birth control pill effectiveness can play a role in a person’s overall health.
This is an area I’m keen to explore further in relation to the impact on ankylosing spondylitis and teeth problems.
Healthy and Unhealthy Food Choices
| Healthy Food Choices | Unhealthy Food Choices |
|---|---|
| Fruits (apples, berries, bananas) | Sugary snacks (candy, cookies) |
| Vegetables (carrots, celery) | Sugary drinks (soda, juice) |
| Dairy products (milk, yogurt) | Highly processed foods |
| Whole grains (brown rice, whole wheat bread) | Sticky candy (trolli, gummy bears) |
| Lean protein (fish, chicken) | Excessive consumption of acidic foods and drinks |
The table above highlights some healthy and unhealthy food choices for individuals with AS. This is not an exhaustive list, but it serves as a guide for making informed dietary decisions. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations based on individual needs and circumstances.
Impact of Medications on Oral Health
Medications used to manage ankylosing spondylitis (AS) can have a significant impact on overall health, including oral health. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for proactive management and maintaining good oral hygiene. This section will delve into the ways certain medications can affect the mouth, offering strategies for mitigating any issues and emphasizing the importance of open communication with healthcare providers.Medications for AS, while vital for symptom control, can sometimes lead to adverse effects in the oral cavity.
Ankylosing spondylitis can sometimes lead to dental issues, like gum inflammation and tooth loss. Understanding your oral health is crucial, but did you know that knowing your skin type can be just as important for overall well-being? Taking the time to learn how to know your skin type can help you choose the best skincare routine.
Ultimately, paying attention to these factors can help you better manage ankylosing spondylitis symptoms, including any related dental problems.
These effects range from dry mouth to increased susceptibility to infections and even changes in tooth structure. This section will provide specific examples of medications commonly prescribed for AS and the potential oral side effects they might cause. By understanding these potential issues, patients can take proactive steps to protect their oral health and work with their healthcare team to optimize treatment strategies.
Common Medications and Potential Oral Side Effects
A variety of medications can be used to treat AS, each with its own set of potential side effects. The following table Artikels some commonly used medications and their potential impact on oral health.
| Medication | Potential Oral Side Effects | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Increased risk of mouth sores, dry mouth, gum inflammation, and ulcers. | Use of mouthwash and regular dental visits. |
| Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNF inhibitors) | Increased risk of oral infections, particularly fungal infections. | Good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and prompt treatment of any oral infections. |
| Biologics | Similar to TNF inhibitors, with a possible increased risk of oral infections. | Good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and prompt treatment of any oral infections. |
| Corticosteroids | Significant risk of dry mouth (xerostomia), increased risk of oral infections, gum inflammation, and delayed wound healing. Can also cause tooth decay and bone loss. | Frequent sips of water, sugar-free gum or candies, use of saliva substitutes, and diligent oral hygiene. |
| Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) | Can contribute to dry mouth, and possible increased risk of oral infections. | Frequent sips of water, sugar-free gum or candies, use of saliva substitutes, and diligent oral hygiene. |
Importance of Open Communication
Open and honest communication between patients and their healthcare providers is paramount in managing potential oral health issues arising from AS medications. Patients should proactively discuss any oral symptoms, including dryness, sores, or pain, with their doctors. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing more serious complications. Healthcare providers should actively inquire about patients’ oral health routines and any medication-related side effects.
This proactive approach fosters a collaborative partnership, ensuring the best possible management of both AS and its potential oral consequences.
Medication Interactions
Some medications used to treat AS may interact with certain oral care products. Patients should always inform their dentist or pharmacist about all medications they are taking, including those for AS. This information is vital for preventing any potential adverse reactions.
Conclusion
Effective management of ankylosing spondylitis necessitates a comprehensive approach that considers both the systemic effects of the disease and the potential oral health complications. Proactive communication, understanding of potential side effects, and diligent oral hygiene practices are crucial for maintaining optimal oral health while managing AS.
Illustrative Case Studies and Examples
Understanding the connection between ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and oral health requires looking at real-life examples. These case studies illustrate how AS can impact oral health, highlight successful management strategies, and emphasize the importance of early intervention. By examining individual experiences, we can better appreciate the multifaceted nature of this connection and the crucial role of proactive oral care in managing AS.
Case Study: The Impact of AS on Oral Health
A 30-year-old woman diagnosed with AS experienced significant stiffness and pain in her spine, impacting her posture and daily activities. Simultaneously, she developed noticeable gum inflammation and tooth sensitivity. X-rays revealed progressive bone erosion around the teeth, a common finding in individuals with AS. Her dental hygiene was subpar due to the pain and discomfort associated with AS, leading to worsening periodontal disease.
This case demonstrates how AS-related inflammation and reduced mobility can negatively affect oral hygiene practices and ultimately lead to significant oral health issues.
Case Study: Successful Oral Health Management in an AS Patient
A 45-year-old man with AS actively participated in a comprehensive oral health management plan. He worked closely with his dentist and a registered dietitian to identify and address specific needs. His plan included regular dental check-ups, tailored oral hygiene instructions, and dietary modifications to minimize the risk of further complications. This proactive approach allowed him to maintain good oral health, despite the challenges of AS.
His positive experience underscores the importance of individualized management strategies for effective oral health maintenance in AS patients.
Case Study: The Importance of Early Intervention
A 22-year-old diagnosed with AS sought dental care only after experiencing severe pain and noticeable swelling. By that point, the condition had progressed significantly, necessitating extensive dental procedures. Had he sought dental care earlier, the damage could have been minimized, and potentially prevented. This case highlights the significance of early dental check-ups and proactive oral health management for individuals with AS, emphasizing the potential for more effective treatment outcomes when interventions are initiated sooner.
Case Study: Dietary Impact on Oral Health in AS
A 38-year-old AS patient struggled with maintaining good oral hygiene due to limited mobility and pain. She often relied on soft, sugary foods, which contributed to frequent episodes of plaque buildup. By incorporating more crunchy fruits and vegetables into her diet, she improved her oral hygiene practices, reducing plaque and gum inflammation. This experience emphasizes the connection between dietary choices and oral health in individuals with AS, highlighting the need for a balanced diet rich in nutrients and fibers to support optimal oral health.
Illustrative Case Examples
- A 28-year-old female with AS experienced significant tooth mobility due to the progression of the disease. Treatment involved a combination of medication and oral physiotherapy to improve jaw muscle function, along with regular dental check-ups and targeted oral hygiene strategies.
- A 42-year-old male with AS had severe gum inflammation. His dental care included a thorough oral hygiene instruction program, a tailored dietary recommendation, and regular periodontal maintenance. The plan helped control the inflammation and prevent further damage.
- A 35-year-old female with AS developed significant oral dryness as a side effect of her medications. She implemented strategies to increase saliva production and maintain good oral hygiene, including sugar-free gum, and oral moisturizers.
- A 50-year-old male with AS and a history of poor oral hygiene developed severe tooth decay. Through a comprehensive approach combining improved oral hygiene practices, regular dental visits, and a dietary consultation, his oral health improved significantly.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the connection between ankylosing spondylitis and oral health is undeniable. Understanding the specific dental problems, preventive measures, and management strategies is crucial for improving the overall health and quality of life for those affected by AS. Maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals about medication choices and oral health is essential for successful management. This comprehensive overview provides a foundation for navigating the challenges and empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards optimal oral health.