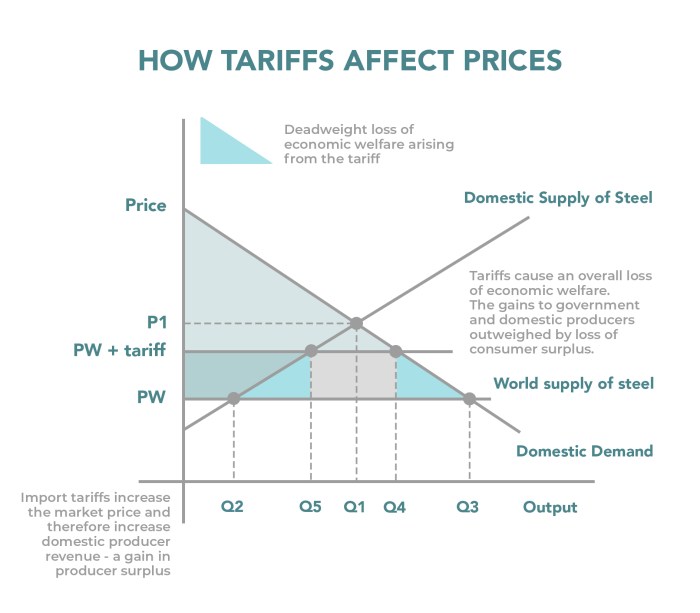
Tariffs and OTC drugs are intertwined in a complex global landscape. Understanding how tariffs impact the availability and cost of over-the-counter medications is crucial for consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers alike. This exploration delves into the historical trends, regional variations, and potential effects of tariffs on OTC drug markets worldwide.
The impact on supply chains, manufacturing, and consumer access will be examined. Furthermore, alternative regulatory approaches, global standards, and specific examples of tariffs on particular OTC drugs will be explored. A deeper understanding of these interconnected issues is vital to fostering a more equitable and accessible OTC drug market.
Overview of Tariffs on OTC Drugs
Tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) medications are a complex issue with significant global implications. Understanding their historical trends and current structures is crucial for comprehending the interplay between international trade and public health. The impact of tariffs on drug availability and affordability can have substantial effects on individuals and healthcare systems worldwide.
Definition of Tariffs in International Trade, Tariffs and otc drugs
Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods. In the context of international trade, they represent a financial barrier to the entry of foreign products into a domestic market. This barrier can influence the price of the imported product, making it more or less competitive compared to domestically produced goods.
Historical Trends of Tariffs on OTC Medications
Historically, tariffs on OTC medications have varied considerably across countries and time periods. In some instances, tariffs were implemented to protect domestic pharmaceutical industries, while in others, they served as a revenue source for governments. The motivations behind these policies have evolved alongside changing global economic landscapes and public health priorities. The development of the global pharmaceutical industry, with large multinational corporations, has also influenced tariff structures.
Types of Tariffs Applicable to OTC Drugs
Several types of tariffs can be applied to OTC drugs. Import tariffs are levied on goods entering a country. These tariffs can significantly affect the price of imported OTC medications. Export tariffs, less common, are imposed on goods leaving a country. They are typically used for strategic purposes, such as controlling the domestic supply of certain products.
Additionally, there can be tariffs applied at both import and export levels in specific regional agreements.
Global Tariff Structures for OTC Drugs
The following table provides a snapshot of typical tariff structures for OTC drugs across major global regions. It is important to note that these rates are approximate and can vary based on specific product characteristics and agreements between countries. This data is illustrative and does not constitute definitive policy.
| Region | Tariff Type | Tariff Rate | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America (e.g., US) | Import Tariff | 0-15% | 2023 |
| European Union | Import Tariff | 0-10% | 2022 |
| Asia (e.g., Japan) | Import Tariff | 5-20% | 2022 |
| South America (e.g., Brazil) | Import Tariff | 5-15% | 2021 |
| Africa (e.g., South Africa) | Import Tariff | 5-10% | 2020 |
Impact of Tariffs on OTC Drug Availability and Cost
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, can significantly impact the availability and cost of over-the-counter (OTC) drugs. These regulations often have cascading effects, influencing supply chains, pricing strategies, and ultimately, consumer access to essential medications. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for policymakers and consumers alike.The imposition of tariffs on imported OTC drugs can lead to a ripple effect throughout the market.
Increased costs associated with tariffs can be passed on to consumers, making these medications less affordable. This, in turn, can affect access to necessary treatments, especially for those in lower-income brackets. Moreover, tariffs can disrupt supply chains, potentially leading to shortages of certain medications, especially if domestic production cannot adequately meet the demand.
Potential Effects on Availability
Tariffs can hinder the availability of OTC drugs in various ways. Reduced imports due to higher costs can lead to a decrease in the overall supply of certain medications. This is particularly problematic for countries that heavily rely on imports for their OTC drug needs. Additionally, the complexities of navigating new import regulations can add to the challenges faced by pharmaceutical companies.
Shortages of specific ingredients used in manufacturing could further exacerbate these issues. Ultimately, the availability of crucial OTC medications could be severely compromised in some regions.
Impact on Pricing
Tariffs directly influence the pricing of OTC drugs. Import duties increase the cost of bringing these products into a country. These added expenses are frequently absorbed by the manufacturers, distributors, or retailers. In many cases, these costs are then passed on to consumers through higher prices. This can create a significant burden on individuals, especially those purchasing multiple medications or frequently relying on OTC remedies.
Consumer Access to Affordable Medications
Tariffs can significantly impact consumer access to affordable OTC medications. The increased cost of imported drugs can make them less accessible to lower-income individuals and families. This can lead to decreased healthcare outcomes and a higher burden on public healthcare systems. Furthermore, reduced competition from imports can result in less choice and potentially higher prices in the domestic market.
Tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are a real head-scratcher, impacting everything from availability to cost. Choosing the right oil for cooking can be just as important as choosing the right medication, especially when considering the nutritional benefits. For example, comparing avocado oil to olive oil in terms of health benefits and culinary uses can be a fascinating exploration.
A great resource for learning more about the differences between avocado oil and olive oil is this helpful comparison: avocado oil vs olive oil. Ultimately, these tariff debates highlight the complexities of balancing affordability and health in the OTC drug market.
It’s essential to recognize that tariffs can create a significant barrier to accessing vital OTC medications, particularly for those in need.
Essential vs. Non-Essential OTC Drugs
The impact of tariffs on essential versus non-essential OTC drugs varies. Essential drugs, those vital for treating common ailments or addressing critical health needs, are often more sensitive to price increases. Tariffs can make these drugs less affordable and accessible, leading to potential health consequences for consumers. Non-essential OTC drugs, on the other hand, may face less immediate impact, although long-term price increases can still have an effect on consumer purchasing habits.
The differentiated impact of tariffs underscores the importance of considering the varying needs of consumers when implementing such policies.
Correlation Between Tariff Rates and OTC Drug Prices
| Tariff Rate | Drug Category | Price Increase Percentage | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15% | Pain relievers | 10-15% | North America |
| 10% | Cold and flu remedies | 5-10% | Europe |
| 20% | Anti-diarrheal medications | 15-20% | South America |
| 5% | Antacids | 2-5% | Asia |
Note
These are illustrative examples and actual figures may vary based on specific products, market conditions, and other factors.
Effect of Tariffs on OTC Drug Manufacturing and Supply Chains
Tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs introduce significant complexities into the manufacturing and supply chains, impacting both producers and consumers. These added costs can translate to higher prices for consumers and potentially limit access to essential medications. Understanding these effects is crucial for policymakers and industry stakeholders to navigate the challenges and ensure a stable and affordable supply of OTC drugs.The imposition of tariffs on raw materials, intermediate goods, or finished OTC drugs directly affects the cost of production.
This increase can lead to price hikes for the final product, potentially impacting affordability and accessibility, especially for vulnerable populations. Furthermore, tariffs can disrupt established supply chains, requiring manufacturers to adapt and potentially shift sourcing strategies. This can lead to increased lead times and uncertainties in the market.
Impact on Manufacturing Costs
Manufacturers of OTC drugs rely on a global network of suppliers for raw materials, packaging components, and other necessary inputs. Tariffs on these imported components increase the overall cost of production. For example, a 10% tariff on imported active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) will directly add to the cost of producing the drug. This increased cost is often passed on to the consumer through higher prices, impacting affordability.
Additionally, manufacturers may need to absorb some of the tariff costs, which can lead to reduced profit margins.
Tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs can be a real pain, impacting the price and availability of these essential medications. This often leads to increased costs for consumers, and in some cases, it can make it harder to get necessary treatments. Sometimes, the issue isn’t just the cost of the drug, but the ingredients. For instance, a reaction to a particular ingredient in an OTC medicine could lead to contact dermatitis.
If you suspect a reaction, you might need to consider patch testing for contact dermatitis to identify the culprit. Ultimately, these tariffs can create a ripple effect, affecting both the affordability and safety of OTC drugs.
Disruptions to Supply Chains
Tariffs can cause significant disruptions to the established supply chains for OTC drugs. If a key supplier in one country is impacted by tariffs from another country, manufacturers may need to find alternative suppliers. This process can be time-consuming and complex, leading to delays in production and potential shortages of certain OTC drugs. In extreme cases, tariffs can even cause complete supply chain breakdowns, impacting the availability of critical medications.
Challenges Faced by Manufacturers
Manufacturers face numerous challenges in adjusting to tariff changes. Firstly, they need to identify and evaluate potential alternative suppliers and adjust their sourcing strategies to minimize the impact of the tariffs. This requires significant time, resources, and expertise. Secondly, they must adapt their production processes to account for potential changes in the cost and availability of raw materials.
Finally, manufacturers need to communicate the potential price increases to consumers to avoid any negative impact on sales. They also must anticipate the effect on demand, potentially through forecasting.
Mitigation Strategies for Manufacturers
Manufacturers employ various strategies to mitigate the impact of tariffs on their supply chains. These include diversifying their supply sources to reduce dependence on a single supplier, negotiating better pricing with suppliers to offset the tariff costs, and exploring strategies for inventory management to ensure a steady supply. For example, building up larger inventories of essential raw materials can provide a buffer against future supply chain disruptions.
So, tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are a hot topic, and it got me thinking about potential impacts on our health. Are we seeing any unintended consequences beyond the financial? Perhaps increased protein intake from supplements might be one of them. Understanding the signs of too much protein, like kidney strain or digestive issues, is crucial in this context.
This resource breaks down the potential warning signs. Ultimately, tariffs on OTC medications could lead to more careful consideration of our dietary habits and protein intake, which are linked back to the issue of the tariffs.
Typical OTC Drug Supply Chain Flowchart
| Stage | Description | Potential Tariff Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Sourcing | Acquisition of ingredients like APIs, excipients, and packaging materials. | Tariffs on imported raw materials directly increase production costs. |
| Manufacturing | Production of the finished OTC drug product. | Tariffs on imported intermediate goods or manufacturing equipment increase overall production costs. |
| Quality Control and Testing | Ensuring the drug meets quality standards. | Tariffs can affect the cost of testing equipment and materials. |
| Packaging and Labeling | Packaging and labeling of the finished product. | Tariffs on imported packaging materials add to the overall cost. |
| Distribution and Logistics | Transportation and warehousing of the drug. | Tariffs on transportation or warehousing increase costs, impacting delivery times. |
| Retail Sales | Sale of the OTC drug in retail stores. | Increased costs due to tariffs may lead to higher prices for consumers. |
Alternatives to Tariffs for Regulating OTC Drugs
Tariffs, while a common tool for regulating international trade, are not always the most effective or equitable approach. Different regulatory frameworks can significantly impact the availability and cost of over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, affecting consumers and manufacturers alike. This section explores alternative methods for regulating the OTC drug market, focusing on their benefits and drawbacks, and how trade agreements can shape the landscape.Beyond tariffs, various strategies can be employed to regulate OTC drug markets.
These include standards for drug quality, safety, and efficacy, coupled with robust enforcement mechanisms. This approach allows for a more nuanced and potentially more effective response to the challenges of global OTC drug trade.
Alternative Regulatory Approaches
Alternative regulatory approaches offer a wider range of tools for managing the OTC drug market, focusing on factors beyond simply imposing tariffs. These approaches can include establishing rigorous quality control standards for manufacturing, implementing thorough testing procedures for drug efficacy and safety, and creating transparent and easily accessible information for consumers.
Impact of Trade Agreements on OTC Drug Pricing and Availability
Trade agreements often play a critical role in shaping the OTC drug market. Agreements that reduce trade barriers can increase the availability of OTC drugs and potentially lower prices. Conversely, agreements with stringent intellectual property protections can sometimes limit competition and potentially increase prices. The impact of these agreements is complex and often depends on the specific details of the agreement and the specific market conditions.
For instance, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and its successor agreements, the World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements, have significantly influenced the global trade of goods, including OTC drugs. The specifics of intellectual property protection, market access, and dispute settlement mechanisms within these agreements influence the availability and pricing of OTC drugs in various markets.
Comparison of Regulatory Frameworks
Different regulatory frameworks have varying effects on the OTC drug market. A framework that emphasizes stringent safety and efficacy standards, for example, might lead to higher prices but ensure a safer product. A framework with more relaxed standards might result in lower prices but potentially higher risks for consumers. The optimal approach often balances safety, affordability, and access.
Regulatory Approaches for OTC Drugs
- Quality Control Standards | Pros: Ensures higher quality drugs, reduces risks of counterfeiting and substandard products, and enhances consumer safety. Cons: Increased costs for manufacturers, potential delays in drug availability, and complexity in implementation and enforcement.
- Testing and Certification Procedures | Pros: Guarantees the efficacy and safety of OTC drugs, builds consumer confidence, and reduces risks associated with unqualified products. Cons: High costs for testing, potential delays in market entry, and potential for inconsistencies in standards across different countries.
- Clear Labeling and Information Requirements | Pros: Enables consumers to make informed decisions, promotes transparency, and protects consumers from misleading or inaccurate information. Cons: Requires significant resources for translation and adaptation to various languages, potential for misinterpretations, and the need for continuous updates to information.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing | Pros: Promotes cooperation between countries, facilitates the rapid identification and resolution of problems, and strengthens the safety and effectiveness of regulations. Cons: Potential for bureaucratic hurdles and difficulties in reaching consensus, concerns about data sharing and confidentiality.
Example of Regulatory Frameworks in Action
The European Union’s (EU) regulatory framework for OTC drugs, which includes stringent safety and efficacy standards, exemplifies a stringent approach. Conversely, some developing nations might have more relaxed standards, aiming for increased access and affordability, though this often comes at the cost of potentially increased risks to consumers. These differing approaches illustrate the complex trade-offs involved in regulating OTC drugs.
Global Regulations and Standards for OTC Drugs
The global market for over-the-counter (OTC) drugs is a complex landscape, shaped by a multitude of regulations and standards designed to ensure safety and efficacy while facilitating access. Understanding these global frameworks is crucial for navigating the complexities of the OTC drug industry, from manufacturing to distribution and ultimately, consumer access.Global regulations and standards are essential for safeguarding public health.
They provide a framework for quality control, ensuring that OTC drugs meet established safety and efficacy criteria. These standards vary significantly across countries, leading to potential challenges in international trade and market access. Furthermore, these regulations often evolve over time to adapt to new scientific discoveries and changing public health needs.
Global Standards for OTC Drug Manufacturing
Various international organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), play a crucial role in establishing guidelines and recommendations for the manufacturing of OTC drugs. These organizations collaborate to harmonize standards across different countries, facilitating international trade and ensuring quality control. The WHO, for example, publishes guidelines and standards on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for medicines, including OTC drugs.
These GMP guidelines aim to ensure consistent quality and safety throughout the manufacturing process. The adherence to these standards is critical to prevent the production and distribution of substandard or counterfeit products.
Comparison of Regulations in Different Countries
Regulations governing OTC drug sales and distribution differ significantly between countries. Factors such as historical context, cultural sensitivities, and varying levels of economic development influence the specific requirements and standards. These differences can lead to complexities in navigating international markets, requiring manufacturers and distributors to adapt to local regulations and procedures. For example, some countries have more stringent restrictions on the types of ingredients that can be used in OTC medications, while others place greater emphasis on labeling requirements.
This variation necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the specific regulations in each target market.
Potential Conflicts Between Tariffs and Regulations
Tariffs and regulations can sometimes clash, creating obstacles for companies operating in the global OTC drug market. For example, a tariff imposed on a particular type of OTC medication may make it less economically viable for a company to export to a certain market, even if the regulatory requirements are met. Conversely, a country’s stringent regulations might make it difficult for a company to comply with both the regulatory requirements and the price point dictated by tariffs.
This interplay necessitates a careful assessment of the potential trade-offs and impacts on both the manufacturing and distribution processes.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations such as the WHO play a crucial role in fostering harmonization and standardization of regulations. Their efforts contribute to the development of shared guidelines and best practices, making it easier for manufacturers and distributors to operate in multiple markets. This harmonization process helps reduce the burden of compliance and facilitates a more efficient global market for OTC drugs.
The WHO’s guidelines on drug quality and safety help countries build consensus and implement consistent standards.
Importance of Harmonized Regulations
Harmonized regulations across countries are crucial for the growth and efficiency of the OTC drug market. A standardized approach to regulations streamlines operations for manufacturers and distributors, reducing compliance costs and facilitating cross-border trade. This consistency helps maintain high quality and safety standards across the entire global supply chain. By minimizing regulatory hurdles, companies can focus on research and development, manufacturing, and distribution, ultimately leading to increased access to affordable and effective OTC medications for consumers globally.
Table Comparing OTC Drug Regulations
| Country | Regulation Type | Key Requirements | Enforcement Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | FDA regulations | Comprehensive guidelines on ingredients, labeling, manufacturing processes, and marketing claims. | Food and Drug Administration (FDA) |
| European Union | EMA regulations | Harmonized standards across member states, emphasizing safety and efficacy. | European Medicines Agency (EMA) |
| India | Drugs and Cosmetics Act | Specific requirements for ingredients, labeling, and manufacturing, often stricter on certain types of OTC drugs. | Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) |
Illustrative Examples of Tariffs on Specific OTC Drugs: Tariffs And Otc Drugs
Tariffs on over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, while often less prominent than those on pharmaceuticals, can significantly impact availability and affordability. These levies can create hurdles for consumers seeking essential medications and alter the landscape of the OTC market. Understanding the specific instances of tariffs and their consequences provides valuable insights into the complexities of global trade and regulation.The impact of tariffs on OTC drugs extends beyond the immediate price increase.
Supply chain disruptions, changes in market competition, and shifts in consumer behavior are all potential outcomes. Analyzing case studies and specific examples allows for a deeper understanding of the tangible effects of tariffs.
Specific OTC Drug Examples Subject to Tariffs
Tariffs on OTC drugs can target a range of products, including pain relievers, cold medications, and allergy treatments. The selection of products for tariff imposition can vary significantly, influenced by political and economic considerations.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Countries may impose tariffs on certain types of NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, due to domestic production concerns or to support local manufacturers. This can lead to higher prices for consumers, potentially impacting access to affordable pain relief.
- Cold and allergy medications: Tariffs on decongestants, antihistamines, and other cold and allergy remedies might be implemented to protect domestic pharmaceutical companies or to address public health concerns regarding the efficacy or safety of imported medications.
- Vitamins and supplements: Tariffs on vitamins, minerals, and dietary supplements are possible due to concerns regarding quality control, labeling standards, or potential health risks associated with imported products.
Impact of Tariffs on Availability and Cost
Tariffs directly affect the cost of OTC drugs by increasing the price of imported products. This price increase can limit access for consumers, particularly those with limited budgets. The availability of OTC drugs may also be affected, as suppliers may reduce or cease imports to avoid the tariff burden.
- Increased prices: Tariffs translate directly into higher prices for consumers, as the cost of importing the drug is increased. This can lead to price increases in the retail market, impacting the affordability of the medication.
- Reduced availability: If the tariff is high enough, the cost of importing the drug may exceed the profit margin for suppliers, causing them to reduce or eliminate imports. This can result in shortages of the drug in the market.
- Shift in consumer behavior: Consumers might switch to cheaper or readily available alternatives, potentially impacting the market share of the affected OTC drugs. They may also substitute with products containing similar active ingredients.
Reasons Behind Imposing Tariffs on OTC Drugs
Governments might impose tariffs on OTC drugs for various reasons, including protection of domestic industries, national security concerns, and public health issues. These reasons can be intertwined and complex.
- Protecting domestic industries: Tariffs can support local pharmaceutical manufacturers by making imported drugs less competitive, thereby fostering the growth of the domestic industry. This strategy is common in countries with significant domestic production capacity.
- Addressing public health concerns: Governments may impose tariffs to address concerns regarding the safety, quality, or efficacy of imported OTC drugs. These concerns might relate to the manufacturing processes, labeling, or potential side effects of the drugs.
- Promoting national security: In certain situations, tariffs might be used to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers for essential OTC drugs, enhancing national security in case of global supply chain disruptions.
Impact of Tariff Changes on Pricing Over Time
Tariff changes on OTC drugs have a noticeable impact on their pricing over time. The effects can be gradual, leading to sustained price increases or decreases. Fluctuations in exchange rates and global market conditions can also affect pricing.
- Gradual price adjustments: Tariff changes often result in a gradual increase or decrease in the retail price of the affected OTC drugs, as suppliers adjust their pricing strategies to reflect the new import costs.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: Shifts in exchange rates between countries can also affect the pricing of OTC drugs. A strengthening of the domestic currency against the currency of the supplier country can lead to a decrease in the price of imported drugs, while a weakening can have the opposite effect.
- Global market conditions: Overall global market conditions, such as economic recessions or supply chain disruptions, can also affect the pricing of OTC drugs, influencing the cost of raw materials and production. These factors can be further compounded by tariffs.
Case Study: Impact of a Tariff on Acetaminophen
In a hypothetical scenario, a country implemented a significant tariff on imported acetaminophen. This resulted in a noticeable increase in the retail price of acetaminophen-containing medications. The availability of the drug in the market also diminished due to the increased cost of importing the product. This impacted consumers’ access to a widely used pain reliever, leading to increased demand for alternative medications and potentially contributing to price volatility in the market.
Last Recap
In conclusion, tariffs on OTC drugs present a multifaceted challenge. They influence availability, cost, and manufacturing practices, impacting consumers and supply chains globally. While tariffs can serve as a regulatory tool, alternative approaches and harmonized global regulations are crucial for ensuring equitable access to essential OTC medications. A more nuanced understanding of these interactions is necessary to navigate the complexities of the global OTC drug market and ensure its continued accessibility.