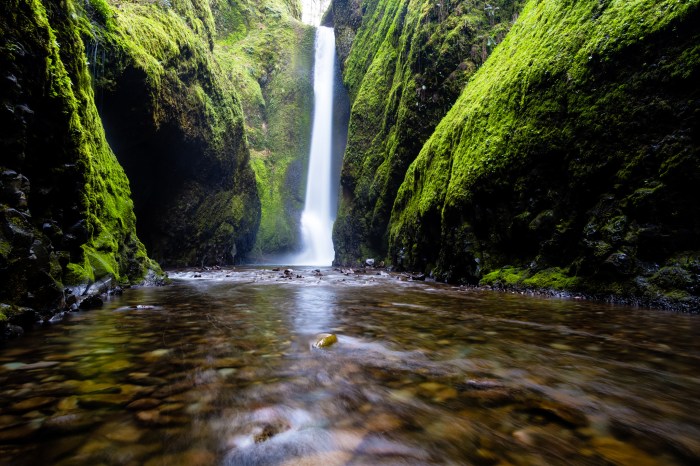
Signs of fibroids breaking down can be a complex and sometimes unsettling experience. This comprehensive guide delves into the various symptoms, potential causes, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options available. We’ll explore how these changes might manifest, potentially differing from other conditions, and examine the possible underlying factors. Understanding the process is crucial for navigating this…
Tag: women’s health
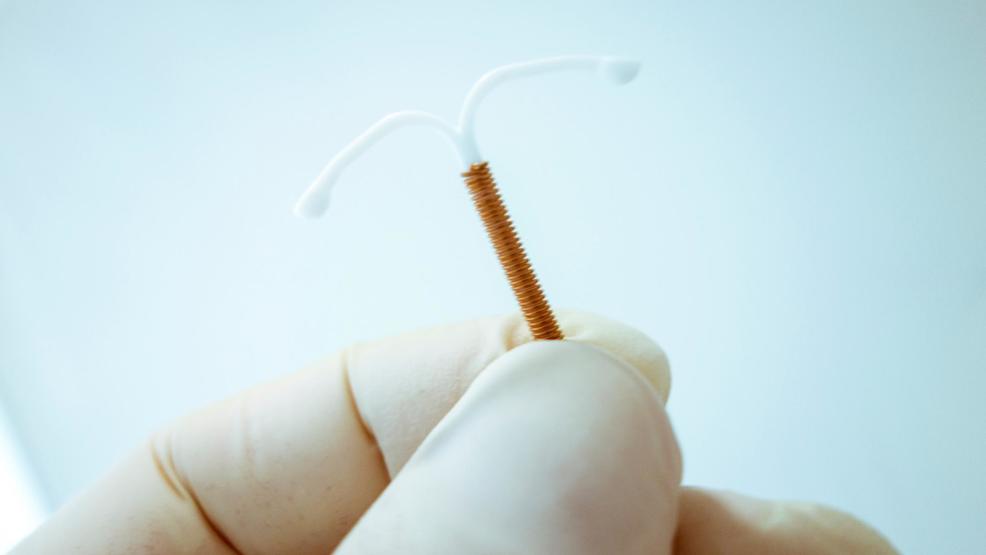
IUD Use in Nulliparous Women A Deep Dive
IUD use in nulliparous women presents a unique set of considerations for women seeking long-term birth control. This comprehensive exploration delves into the various types of IUDs, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects. We’ll specifically examine the advantages, disadvantages, and risks associated with IUD use for women who have not given birth, comparing…
Going to the Gynecologist 101 Your Guide
Going to the gynecologist 101 lays out the essential steps for a comfortable and informative visit. From understanding why you need to see a gynecologist, to preparing for your appointment, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of the entire process. It covers everything from the physical exam to understanding results, and considers the specific needs…
Surgical Management of PMDD A Deep Dive
Surgical management of premenstrual dysphoria disorder is a complex and evolving field, examining the potential of surgical interventions to alleviate the debilitating symptoms of this condition. This in-depth exploration delves into the nuances of PMDD, its diagnosis, and the rationale behind considering surgical approaches. We’ll explore various surgical procedures, evaluating their potential benefits and risks,…
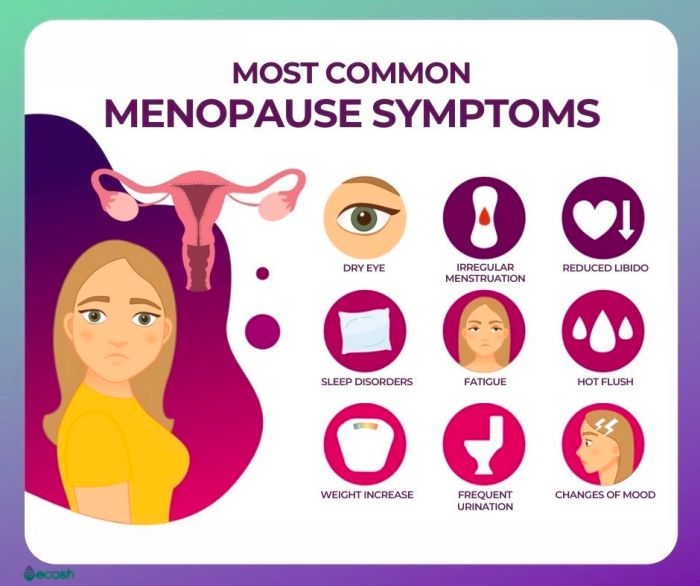
Menopause Facts and Statistics A Deep Dive
Menopause facts and statistics paint a compelling picture of this significant life transition. From global prevalence rates and demographic breakdowns to the intricate interplay of symptoms, health impacts, and management strategies, this exploration provides a comprehensive overview. Understanding the realities of menopause empowers women and healthcare professionals alike. This deep dive examines the prevalence of…
Why Am I So Tired and Have No Energy Female?
Why am I so tired and have no energy female? This pervasive feeling of exhaustion can stem from a multitude of factors, ranging from underlying medical conditions to lifestyle choices. Understanding the potential causes can be crucial in finding solutions and reclaiming your energy. This exploration delves into the complexities of female fatigue, examining everything…
Natural Remedies for Womens Sexual Dysfunction
Natural remedies for sexual dysfunction in women offer a compelling alternative to conventional treatments. This exploration delves into a range of natural approaches, from herbal remedies and nutritional strategies to lifestyle modifications, providing a comprehensive overview of potential solutions. Understanding the diverse factors contributing to sexual dysfunction in women is crucial, and this guide aims…