Does birth control make you moody? This is a question that affects many women, and understanding the connection between hormonal birth control and mood is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. We’ll explore the hormonal shifts associated with various birth control methods, examining how they might impact mood, and discuss individual variations and…
Tag: women’s health
Winter Skin Tips for Women with PCOS
Winter skin tips for women with PCOS offer a comprehensive guide to navigating the unique challenges of winter skin health. This guide delves into understanding PCOS, crafting tailored skincare routines, dietary recommendations, lifestyle adjustments, and addressing specific winter skin concerns. Learn how to manage breakouts, dryness, and other common issues, all while considering the unique…
Celiac Disease Symptoms in Women A Deep Dive
Celiac disease symptoms in women often manifest differently than in men, leading to unique challenges in diagnosis and management. This comprehensive guide explores the spectrum of symptoms, from common gastrointestinal issues to less-obvious non-gastrointestinal problems, providing valuable insights for women experiencing potential symptoms. The prevalence of celiac disease in women compared to men, along with…
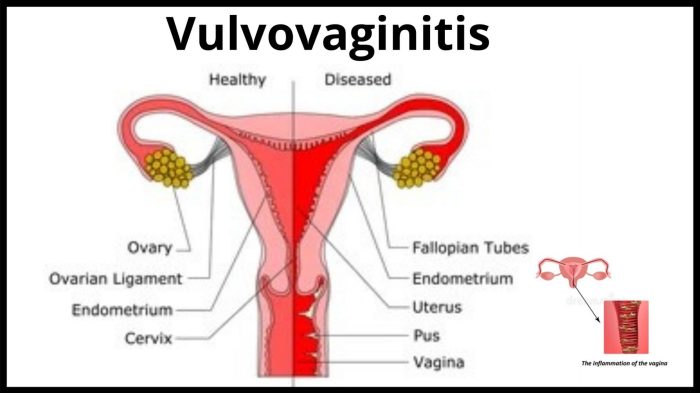
What Does Vulvovaginitis Look Like? A Guide
What does vulvovaginitis look like? Understanding the visual cues and symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. This guide delves into the appearance of vulvovaginitis, covering everything from common symptoms to visual characteristics across different types. We’ll explore the various presentations, potential underlying causes, and when to seek medical attention. This comprehensive overview will…
Heart Attack in Women Understanding the Differences
Heart attack in women is a critical health issue often misunderstood and under-recognized. Women experience heart attacks differently than men, with symptoms often masked or misconstrued. This detailed look delves into the unique symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic challenges, and treatment options specific to women. Recognizing the variations is crucial for early detection and effective intervention….
Older Women and the HPV Vaccine Protecting Health
Older women and the HPV vaccine: Understanding vaccination rates, health concerns, and effective strategies is crucial for promoting the well-being of this demographic. The discussion delves into vaccination rates across different age groups of older women, highlighting potential barriers and reasons for variations. It also explores the potential health risks associated with HPV infection, the…
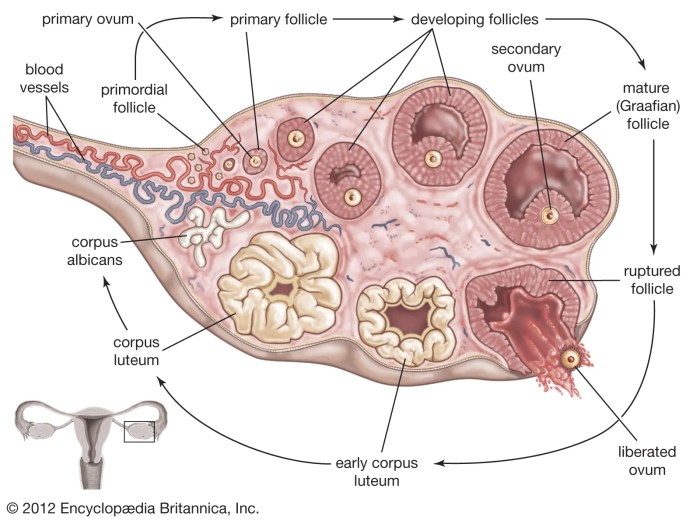
Things to Know About Your Ovaries and Ovulation
Things to know about your ovaries and ovulation: Dive deep into the fascinating world of female reproductive health. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate workings of your ovaries, the crucial ovulation process, and the overall menstrual cycle. From understanding ovarian anatomy to recognizing potential health concerns and fertility, you’ll gain valuable insights into your body’s…
How to Check Your IUD Strings A Guide
How to check your IUD strings is a crucial aspect of IUD care. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding the purpose and appearance of IUD strings to identifying potential issues and knowing when to seek professional help. We’ll cover everything from self-assessment techniques to recognizing normal versus abnormal findings, empowering you to maintain…
Bacterial Vaginosis Keeps Coming Back Understanding Recurrence
Bacterial vaginosis keeps coming back, frustrating many women. This recurring infection can be challenging to manage, impacting quality of life. This blog post delves into the reasons behind these recurring episodes, exploring everything from lifestyle factors to potential underlying health conditions. We’ll also look at diagnostic considerations, treatment strategies, and preventive measures you can take…
PCOS Truths Hidden in Plain Sight
Things no one tells you about PCOS. This isn’t just about the obvious symptoms like irregular periods and acne. It’s about the hidden struggles, the emotional toll, and the often-overlooked challenges women face navigating this condition. We’ll delve into the nuances, separating fact from fiction, and sharing real experiences that shed light on the often-unseen…