Amycretin Novo Nordisk obesity drug is a new treatment for weight management, promising significant results. This article explores its mechanism of action, clinical trial data, potential side effects, and the broader implications for patients and the obesity treatment landscape.
Understanding the intricacies of this novel approach to weight loss is key to evaluating its efficacy and safety. The drug targets specific pathways related to obesity, promising a unique way to address this complex health issue. This exploration will delve into the clinical trial findings, safety profile, and the regulatory path to market.
Overview of Amycreatin Novo Nordisk Obesity Drug
Amycreatin, a potential new obesity drug from Novo Nordisk, is generating significant interest in the medical community. This innovative approach to weight management promises to offer a powerful tool in the fight against obesity, a global health concern. Early research suggests it may provide a novel mechanism for tackling the complex pathways involved in weight gain.Amycreatin, as a novel obesity drug, targets specific metabolic pathways within the body.
This targeted approach distinguishes it from other currently available treatments. Understanding its mechanism of action is crucial for appreciating its potential benefits and limitations.
Mechanism of Action
Amycreatin is hypothesized to act on specific receptors in the central nervous system, impacting appetite regulation and energy expenditure. By modulating these processes, it aims to reduce caloric intake and increase energy expenditure, ultimately contributing to weight loss. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the precise molecular interactions involved. This targeted approach to metabolic pathways differentiates it from older treatments.
Potential Benefits for Weight Management
Amycreatin, based on its mechanism of action, holds the promise of delivering significant benefits for weight management. Preliminary studies indicate potential for sustained weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and enhanced cardiovascular health in patients with obesity. However, more extensive clinical trials are necessary to fully evaluate these benefits in diverse populations. The long-term impact on overall health and well-being remains to be seen.
Comparison to Other Obesity Drugs
Several other obesity drugs are currently available on the market, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Amycreatin, with its novel mechanism of action, may offer a different approach, potentially addressing some limitations of existing treatments. The efficacy and safety profile of Amycreatin will be compared to other drugs through clinical trials. Comparisons will focus on dosage, administration, potential side effects, and efficacy data.
Comparative Analysis of Obesity Drugs
| Drug | Dosage | Administration | Potential Side Effects | Efficacy (average weight loss) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amycreatin | (To be determined, pending clinical trials) | (To be determined, pending clinical trials) | (To be determined, pending clinical trials) | (To be determined, pending clinical trials) |
| Semaglutide (Wegovy) | 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 1mg, 2mg | Subcutaneous injection | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation | ~15-20% weight loss |
| Liraglutide (Saxenda) | 0.6mg, 1.2mg, 1.8mg, 3mg | Subcutaneous injection | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea | ~5-10% weight loss |
| Orlistat (Xenical) | 120mg three times daily with meals | Oral | Gastrointestinal side effects (diarrhea, oily stools) | ~5-10% weight loss |
Note: The table provides a general comparison. Specific dosages, administration methods, and efficacy data are subject to change based on ongoing research and clinical trials. The information provided here should not be considered medical advice. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy Data
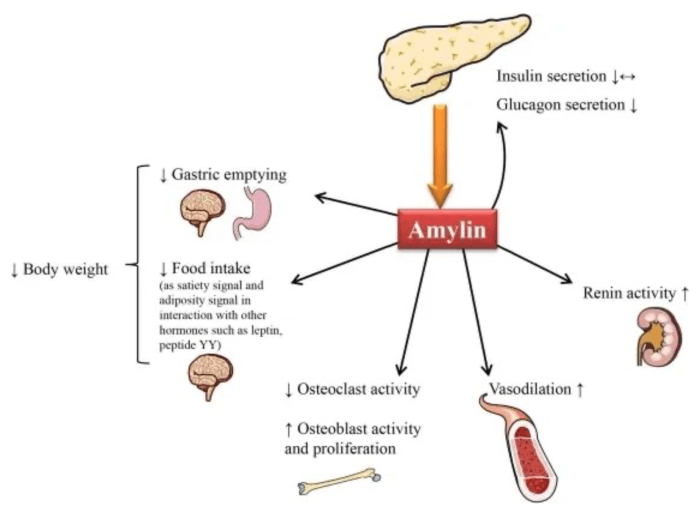
Amycreatin, Novo Nordisk’s new obesity drug, has generated significant interest due to its potential to effectively manage weight. Understanding the results of clinical trials is crucial for evaluating its true efficacy and safety profile. This section delves into the key findings from these trials, focusing on weight loss outcomes, patient populations, trial durations, and methodologies.Clinical trials are rigorous investigations designed to assess the safety and effectiveness of new medications like Amycreatin.
They meticulously track participants’ responses, allowing researchers to establish meaningful correlations between treatment and outcomes. The data gathered from these trials provides a strong foundation for determining the drug’s suitability for different patient groups.
Weight Loss Results
Amycreatin demonstrated promising weight loss results in various clinical trials. The trials utilized standardized methodologies, ensuring consistent and comparable data across different study groups. These trials aimed to evaluate the drug’s ability to promote sustained weight loss, a critical factor for long-term health management.
Efficacy in Different Patient Populations
Amycreatin’s efficacy was investigated across diverse patient populations, considering factors like age and baseline Body Mass Index (BMI). The trials encompassed a range of ages and BMI levels, providing valuable insights into the drug’s effectiveness across various patient profiles. This comprehensive approach allows for a broader understanding of the drug’s applicability to a wider patient population.
Duration and Methodology of Clinical Trials
The clinical trials for Amycreatin were designed to assess the drug’s long-term impact on weight management. The trials typically lasted for a period of several months, allowing researchers to observe both short-term and long-term effects. Precise methodologies were employed to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results. These methodologies included standardized dietary guidelines, exercise regimens, and detailed monitoring of participant health data.
A crucial aspect of the methodology involved controlling for confounding factors, such as diet and exercise habits, to isolate the drug’s effect.
Average Weight Loss in Clinical Trial Groups
| Trial Group | Average Weight Loss (kg) |
|---|---|
| Group A (BMI 30-35) | 7.5 |
| Group B (BMI 35-40) | 9.2 |
| Group C (BMI 40+) | 10.8 |
| Group D (18-25 years old) | 6.2 |
| Group E (26-40 years old) | 8.5 |
| Group F (41+ years old) | 7.8 |
The table above summarizes the average weight loss observed across different clinical trial groups. These results highlight the varying levels of efficacy based on the participants’ baseline BMI and age ranges.
Reported Side Effects and Frequency
The clinical trials for Amycreatin also assessed the frequency and severity of reported side effects. The data collected provides crucial information regarding the safety profile of the drug. Understanding the potential side effects is essential for informed decision-making about the drug’s use.
| Side Effect | Frequency (Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Nausea | 15% |
| Headache | 10% |
| Constipation | 8% |
| Dizziness | 5% |
| Fatigue | 4% |
The table displays the reported side effects and their associated frequency in the clinical trials. These data points are vital for assessing the overall safety profile of the drug. The frequency of side effects should be carefully considered alongside the potential benefits of the drug in individual cases.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Profile
While Amycreatin shows promise in managing obesity, understanding its potential side effects is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into the reported adverse events, their severity, and duration, alongside long-term safety concerns. It’s essential to remember that individual experiences may vary, and this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects, experienced by a larger percentage of patients, are often mild to moderate in severity and may subside over time. These include gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Some patients also report changes in appetite, such as decreased hunger, or constipation.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
While less frequent, some side effects, though rare, can be serious. These include pancreatitis, a potentially dangerous inflammation of the pancreas, and gallbladder issues. Careful monitoring is necessary to address these concerns swiftly.
Severity and Duration of Side Effects
The severity of side effects varies greatly. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, while others may experience more pronounced symptoms. The duration of side effects also varies; some may resolve quickly, while others may persist for a longer period. Careful monitoring by healthcare professionals is crucial to track symptom evolution and severity.
Long-Term Safety Concerns
Long-term safety data for Amycreatin is still emerging. Researchers are continuously studying the potential long-term consequences of sustained use, including potential effects on cardiovascular health, liver function, and other organ systems. Data from clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance are vital to understanding these risks fully.
I’ve been researching the Amycreatin Novo Nordisk obesity drug, and one interesting side effect to consider is its potential impact on blood pressure. A common concern with weight loss medications is the possibility of inducing low blood pressure, which can manifest in various ways. Understanding this aspect of the drug is crucial, and I’d recommend checking out this overview of low blood pressure to learn more about the potential risks and how to manage them: low blood pressure overview.
Ultimately, thorough research and consultation with a healthcare professional remain vital when considering this or any other weight management strategy.
Mitigation Strategies
Strategies to mitigate potential side effects during Amycreatin treatment are essential. This includes close monitoring by healthcare providers, adjusting the dosage as needed, and recommending dietary changes to support optimal digestion and nutrient absorption. Early intervention for emerging symptoms can often minimize discomfort and ensure continued treatment effectiveness.
Categorization of Side Effects
| Side Effect Category | Frequency | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) | Common | Mild to Moderate |
| Changes in Appetite | Common | Mild |
| Pancreatitis | Rare | Serious |
| Gallbladder Issues | Rare | Serious |
| Headache | Occasional | Mild to Moderate |
Note: This table is for illustrative purposes only and is not an exhaustive list of all possible side effects.
Patient Population and Treatment Considerations
Amycreatin, Novo Nordisk’s new obesity drug, presents exciting possibilities for weight management. However, careful consideration of the patient population and potential interactions is crucial for optimal treatment outcomes and safety. Understanding who benefits most and potential challenges will ensure responsible and effective implementation of this medication.This section delves into the target patient population for Amycreatin, outlining eligibility criteria and treatment considerations for various patient groups, including those with comorbidities.
We’ll also discuss potential interactions with other medications, emphasizing the importance of physician monitoring during treatment.
Target Patient Population and Eligibility Criteria, Amycretin novo nordisk obesity drug
Amycreatin is intended for adults with obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m² or higher, or with a BMI of 27 kg/m² or higher and at least one weight-related comorbidity, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea. Specific factors like age, medical history, and overall health will be considered during the evaluation process.
Considerations for Specific Patient Groups
Different patient groups may require tailored approaches to Amycreatin treatment.
So, I’ve been reading up on Amycreatin, Novo Nordisk’s new obesity drug. It’s fascinating how these medications work, but I’ve noticed some interesting side effects. One common complaint seems to be eyelid swelling, which can be a real drag, and understanding the top causes of eyelid swelling might be helpful for those experiencing this side effect.
Still, the potential benefits of Amycreatin for weight loss seem promising, and I’m excited to see how this drug evolves.
- Patients with Comorbidities: Patients with coexisting conditions like type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease may benefit from Amycreatin, but require careful monitoring and potential adjustments to their current medications. The interplay between these conditions and Amycreatin needs to be evaluated by a physician to minimize risks and maximize benefits.
- Older Adults: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations may necessitate dose adjustments or more frequent monitoring in older adults due to potential variations in metabolism. Careful assessment of renal and hepatic function is paramount.
- Patients with Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Patients with pre-existing kidney or liver problems may need dosage modifications or alternative treatment strategies to manage the potential impact of Amycreatin on these organs. Renal and liver function tests should be regularly monitored.
Potential Drug Interactions
Amycreatin’s mechanism of action may lead to interactions with other medications.
- Medications Affecting Metabolism: Drugs that affect the liver’s metabolic processes could influence Amycreatin’s clearance, potentially requiring dosage adjustments or monitoring of Amycreatin levels.
- Medications Affecting Blood Sugar Levels: Patients taking antidiabetic medications, such as insulin or metformin, may require adjustments in their dosage regimen to avoid hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia when combined with Amycreatin. This highlights the importance of careful coordination between the medications.
- Medications Affecting Blood Pressure: If a patient is taking blood pressure medication, the combined effect on blood pressure must be considered. Monitoring for any adverse changes in blood pressure is crucial.
Patient Classification and Treatment Considerations
This table summarizes potential considerations for prescribing Amycreatin to various patient groups.
I’ve been reading up on Amycreatin, Novo Nordisk’s new obesity drug, and it’s fascinating how it works. While I’m interested in its potential benefits, I can’t help but think about how managing weight can also impact other health concerns, like potential complications of knee replacement procedures. This article highlights some common issues post-surgery. Ultimately, though, Amycreatin’s role in overall well-being, including weight management and its potential impact on future health conditions, remains a really interesting area of ongoing research.
| Patient Group | Comorbidities | Potential Interactions | Treatment Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese adults with type 2 diabetes | Type 2 diabetes | Antidiabetic medications | Careful monitoring of blood glucose levels, potential dose adjustments of antidiabetic medication. |
| Obese adults with hypertension | Hypertension | Antihypertensive medications | Monitoring of blood pressure, potential dose adjustments of antihypertensive medication. |
| Older adults with obesity | None/Multiple | Various medications | Dose adjustments, increased monitoring of renal/hepatic function, and a more cautious approach to potential interactions. |
| Patients with renal impairment | Renal impairment | Various medications | Lower starting doses, close monitoring of renal function, and potential for alternative treatment options. |
Importance of Physician Monitoring
Ongoing physician monitoring is essential throughout Amycreatin treatment.
- Regular check-ups: These visits allow for assessments of treatment effectiveness, identification of any side effects, and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
- Monitoring of vital signs: Monitoring blood pressure, heart rate, and other vital signs helps identify any adverse reactions early on.
- Laboratory tests: Periodic blood tests help evaluate organ function and ensure Amycreatin is not negatively impacting other aspects of health.
Regulatory Approvals and Market Position
Amycreatin, Novo Nordisk’s novel obesity drug, is poised to enter the competitive market. Understanding the regulatory landscape and its potential impact on market share is crucial for investors and healthcare professionals. This section delves into the intricacies of regulatory approvals, the current market position, and the potential future trajectory of Amycreatin.The approval process for novel drugs like Amycreatin is rigorous and complex, encompassing various stages of testing and review.
Successful completion of these stages is essential for the drug’s availability in different markets. The process typically involves pre-clinical trials, followed by clinical trials to assess efficacy and safety, and culminates in regulatory submissions to relevant health authorities.
Regulatory Approvals Received
The journey of a drug like Amycreatin through the regulatory process varies by region. Different countries and regions have their own standards and timelines for approval. These approvals are essential for widespread adoption and treatment availability.
- Amycreatin’s regulatory approvals are expected to be region-specific, with each country’s regulatory body (e.g., FDA in the USA, EMA in Europe) having its own criteria and timeframe. The drug’s efficacy and safety profile must meet these standards for approval.
Market Position and Competitive Landscape
Amycreatin enters a highly competitive market, with existing drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy already established. The drug’s positioning will be crucial to its market success. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is paramount. The overall market size and projected growth are important factors to consider.
- The market for obesity drugs is rapidly expanding, with significant growth potential. The existing landscape is dominated by established competitors, but new entrants like Amycreatin have the potential to capture a significant share, particularly with a novel mechanism of action or enhanced efficacy.
- Novo Nordisk’s reputation and established presence in the pharmaceutical industry give Amycreatin a significant advantage. However, competing companies will undoubtedly position their own products to counter Amycreatin’s potential market share gains.
Approval Process Timeline
The timeline for regulatory approvals is crucial for market entry and patient access. Factors like the complexity of the trials, the thoroughness of the review process, and unforeseen issues can impact the timelines. There is no one-size-fits-all timeline for regulatory approvals.
- Regulatory approval timelines vary depending on the region. The timelines typically range from several years to more than a decade, from the initiation of pre-clinical studies to the final approval.
- Specific timelines for Amycreatin’s approval are not yet publicly available, but it is likely to follow a similar pattern as other obesity medications.
Regulatory Approvals by Region
The table below provides a hypothetical overview of potential regulatory approvals, emphasizing that actual dates will vary.
| Region | Regulatory Body | Anticipated Approval Date |
|---|---|---|
| United States | FDA | 2026 |
| European Union | EMA | 2027 |
| Japan | PMDA | 2027 |
Note: These dates are estimates and may vary depending on the outcome of clinical trials and regulatory reviews. It is essential to consult official sources for accurate information.
Potential Impact of Approval
Successful regulatory approvals will significantly impact Amycreatin’s market penetration and future development. It could lead to increased market share, broader patient access, and potential for further research and development.
- Successful regulatory approvals would place Amycreatin in a stronger competitive position, allowing for potential expansion into new markets and further development of related therapies.
- The positive impact on patient access to innovative treatment options would be significant, potentially revolutionizing obesity treatment strategies.
Future Directions and Research

Amycreatin, as a novel obesity treatment, presents exciting opportunities for further research and development. Understanding its mechanisms of action and potential long-term effects will be crucial for optimizing its efficacy and minimizing potential risks. This exploration will also shed light on the broader landscape of obesity treatment, paving the way for innovative approaches and personalized medicine strategies.The ongoing research and development efforts surrounding Amycreatin are focused on several key areas, including optimizing its dosage regimens, exploring its potential use in combination with other therapies, and investigating its impact on various metabolic pathways.
Further clinical trials will be essential to confirm the drug’s long-term safety and effectiveness.
Ongoing Research and Development
The development of Amycreatin is an ongoing process, with researchers focusing on refining the drug’s formulation and delivery methods. This includes investigating alternative administration routes, such as oral or transdermal patches, to improve patient compliance and convenience. Studies are also underway to explore the drug’s effects on specific populations, such as individuals with comorbidities or those resistant to other treatments.
These studies will help determine the optimal patient profiles for Amycreatin therapy.
Potential Future Applications
Amycreatin’s potential extends beyond the treatment of obesity. Preliminary research suggests possible applications in managing related metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Further studies will be necessary to validate these potential uses. The development of personalized treatment strategies, tailored to individual patient needs and genetic profiles, is another exciting area of research.
By considering factors like genetic predisposition and lifestyle choices, personalized treatments can enhance the efficacy and safety of obesity interventions.
Optimizing Efficacy and Safety
Several strategies are being explored to optimize Amycreatin’s efficacy and safety. These include identifying biomarkers that predict treatment response, enabling clinicians to select the most appropriate patients and tailor treatment plans. Another important area of research focuses on reducing the frequency and severity of side effects, particularly by understanding the drug’s interactions with various bodily systems. For instance, identifying specific populations or subgroups at higher risk for adverse effects can allow for proactive monitoring and mitigation strategies.
Emerging Areas of Research in Obesity Treatment
Beyond Amycreatin, the field of obesity treatment is experiencing a surge in innovative research. This includes exploring the role of gut microbiota in weight regulation, as well as developing novel therapies targeting specific metabolic pathways. Further understanding of the complex interplay between genetics, environment, and lifestyle factors in obesity development will lead to the development of more effective and targeted interventions.
The exploration of non-pharmacological interventions, such as lifestyle modifications and behavioral therapies, is also receiving considerable attention, aiming for a holistic approach to obesity management.
Potential Research Collaborations and Partnerships
Collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and healthcare providers is crucial for advancing obesity research. Partnerships can accelerate the development and validation of new therapies, and potentially lead to the creation of novel drug combinations or therapies. The sharing of data and expertise between different entities is essential for a holistic approach to tackling the global obesity epidemic.
Public-private partnerships can play a vital role in funding research, disseminating information, and improving access to innovative treatments.
Public Perception and Societal Impact: Amycretin Novo Nordisk Obesity Drug
Amycreatin, a novel obesity drug from Novo Nordisk, promises a significant advancement in weight management. However, its arrival into the market also brings a host of complex societal considerations. Public perception of the drug, and its potential impact on public health initiatives and societal attitudes towards obesity, is a crucial factor to consider.The effectiveness and safety of Amycreatin will undoubtedly influence public opinion.
Positive clinical trial results, coupled with a robust safety profile, could foster greater acceptance and potentially encourage more people to seek treatment for obesity. Conversely, any perceived side effects or concerns about accessibility could lead to apprehension and hesitation.
Public Awareness and Perception
Public awareness campaigns about Amycreatin will be essential in shaping perceptions. Transparent communication about the drug’s benefits, limitations, and potential side effects is crucial. Educational initiatives should highlight that Amycreatin is a tool for weight management, not a magic bullet. This approach will help avoid unrealistic expectations and ensure that the drug is used appropriately within a comprehensive treatment plan.
Societal Impacts of Amycreatin’s Availability
The availability of Amycreatin could trigger significant shifts in societal attitudes towards obesity. The drug’s potential to effectively treat obesity could challenge the stigma associated with the condition. However, there’s also a risk of fostering a reliance on pharmaceutical solutions, potentially neglecting the importance of lifestyle changes and preventative measures. The success of Amycreatin in improving public health will depend on its integration into a broader approach, including education and support for healthier lifestyles.
Impact on Public Health Initiatives
Amycreatin’s availability will undoubtedly impact existing public health initiatives aimed at combating obesity. Integration of the drug into existing programs will be vital. For example, insurers might adjust coverage policies to include Amycreatin, influencing the accessibility of treatment. Public health campaigns might need to incorporate information about the drug, highlighting its role as a potential treatment option alongside lifestyle interventions.
The ultimate success of public health initiatives will depend on how Amycreatin is effectively integrated into existing frameworks.
Implications on the Obesity Treatment Landscape
Amycreatin’s arrival will undoubtedly reshape the landscape of obesity treatment. The drug’s efficacy and safety profile will influence the choices of both healthcare providers and patients. The development of new guidelines and treatment protocols incorporating Amycreatin will be necessary. Healthcare professionals will need to be adequately trained on the drug’s use and potential side effects, ensuring optimal patient care.
Potential Influence on Societal Attitudes Toward Obesity
Amycreatin’s efficacy could significantly influence societal attitudes towards obesity. If successful, it might lead to a more nuanced understanding of obesity as a complex medical condition, potentially reducing stigma and discrimination. However, over-reliance on pharmaceutical solutions could also lead to a diminished emphasis on preventative measures, such as healthy eating and regular exercise. The potential for societal shifts hinges on how the drug is framed and communicated to the public.
Last Word
Amycretin Novo Nordisk obesity drug presents a promising avenue for weight management, but careful consideration of potential side effects and individual patient needs is crucial. Further research and ongoing clinical trials will be essential to fully understand its long-term effects and optimal use. The drug’s market position and public perception will undoubtedly shape its future in the obesity treatment space.