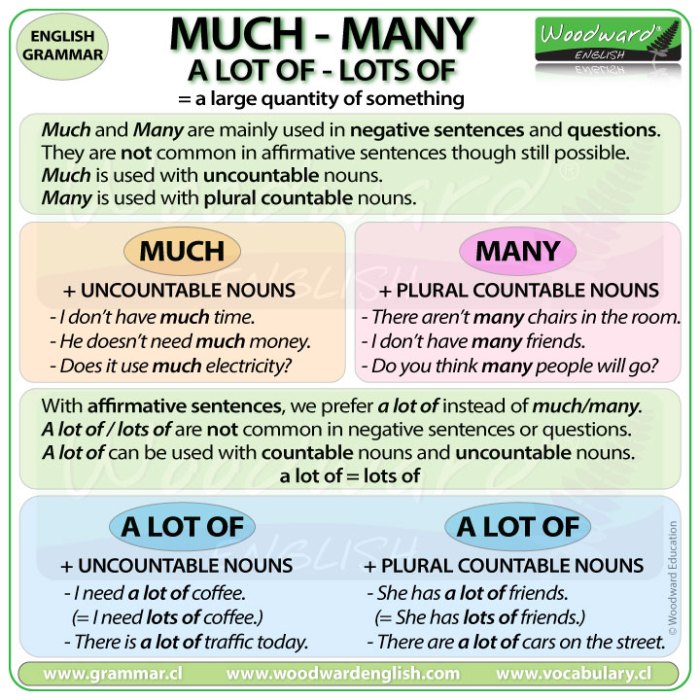
How much water is too much? This seemingly simple question delves into a complex interplay of physiology, individual needs, and potential risks. Understanding the optimal hydration levels for different people is crucial for maintaining good health, but exceeding those levels can lead to a condition known as water intoxication.
This exploration examines the nuances of excessive water intake, outlining the dangers, symptoms, and preventative measures. We’ll consider various factors like age, activity level, and health conditions to understand how much water is truly the right amount for each individual.
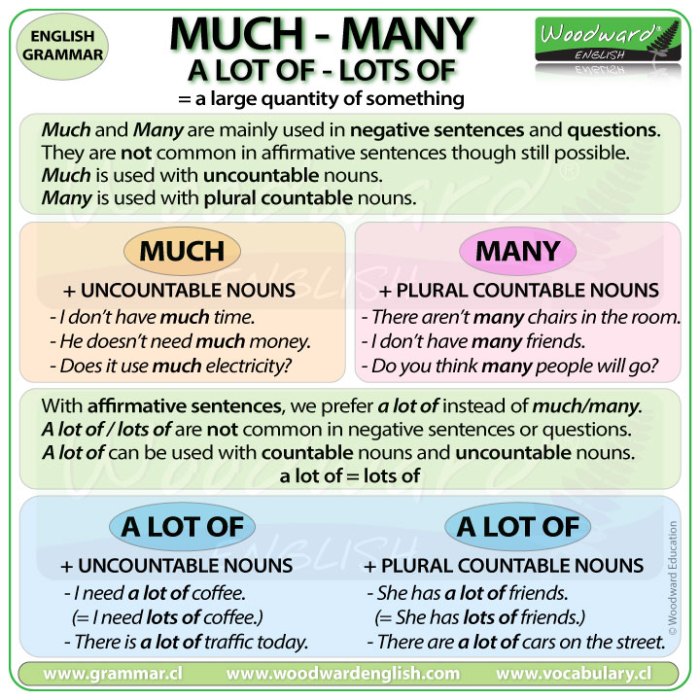
Defining “Too Much Water”
Excessive water intake, while seemingly beneficial, can become detrimental to human health. Understanding the limits of hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal well-being. Water is essential for numerous bodily functions, but like any vital nutrient, an imbalance can lead to serious complications. This discussion will delve into the definition of excessive water intake, its physiological consequences, and the varying needs of different individuals.Water toxicity, or water intoxication, is a condition that arises when the body absorbs more water than it can effectively eliminate.
This imbalance disrupts the delicate electrolyte balance within the body, leading to potentially dangerous consequences. The kidneys play a pivotal role in regulating water levels, filtering excess water and waste products from the bloodstream. When water intake exceeds the kidneys’ capacity to process it, a cascade of physiological events can occur.
Defining Excessive Water Intake
Excessive water intake is characterized by consuming more water than the body can efficiently process and excrete. This excess overwhelms the kidneys’ filtering capabilities, leading to a disruption of electrolyte concentrations and an increase in blood volume. The critical threshold varies based on factors such as individual metabolism, activity level, and underlying health conditions.
Physiological Mechanisms of Water Toxicity
The kidneys are responsible for maintaining the proper balance of water and electrolytes in the body. They filter excess water and waste products from the bloodstream, eliminating them through urine. When water intake exceeds the kidneys’ capacity to filter and excrete it, the body’s electrolyte balance shifts, potentially leading to a dangerous accumulation of water in the cells.
This can cause cells to swell, particularly in the brain, which can lead to severe complications. This process, called water intoxication, can have detrimental effects on various organ systems.
Water Intake Recommendations
The recommended daily water intake varies significantly based on factors like age, activity level, and health conditions. The following table provides a general guideline for different populations:
| Individual Group | Water Intake Recommendations (approximate) |
|---|---|
| Sedentary Adults | 1.5 to 2 liters per day |
| Athletes | 2 to 4 liters or more per day, depending on intensity and duration of exercise. They need more to compensate for sweat loss. |
| Pregnant Women | 2.5 to 3 liters per day, or more depending on individual needs. |
| Children | Based on age and activity level. Consult a pediatrician for specific recommendations. |
This table offers a general overview; individual needs may differ based on specific circumstances. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Water Intoxication: Symptoms and Consequences, How much water is too much
Water intoxication can manifest with a variety of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. These symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, confusion, headache, and in severe cases, seizures and coma. Electrolyte imbalances, especially hyponatremia (low sodium levels), are often associated with water intoxication. The severity of symptoms depends on the rate and extent of excessive water intake. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of water intoxication is crucial for prompt medical intervention.
Early intervention can prevent serious complications.
“The key to preventing water intoxication is not to avoid water entirely, but to consume it in moderation and maintain a balanced intake of electrolytes.”
Identifying Risks and Symptoms
Overhydration, while seemingly harmless, can pose significant health risks if not recognized. Understanding the potential dangers and the symptoms of excessive water intake is crucial for preventative measures and prompt medical attention. This section will delve into the potential health consequences of overdoing it with fluids.Excessive water consumption can disrupt the delicate balance of electrolytes in the body, leading to a range of potentially serious complications.
The key is recognizing the subtle signs of overhydration, which can sometimes be mistaken for other conditions.
Potential Health Risks
Water intoxication, also known as hyponatremia, occurs when the concentration of sodium in the blood becomes dangerously low due to an excessive intake of water. This condition can lead to a cascade of adverse effects, including severe neurological problems. A less common, but equally serious risk is pulmonary edema, where excess fluid accumulates in the lungs, hindering breathing and oxygen absorption.
Symptoms of Overhydration
Recognizing the symptoms of overhydration is crucial for prompt intervention. While some symptoms are obvious, others may be subtle and easily overlooked.
- Headache: A persistent headache, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting, can be a warning sign of potential overhydration. It is crucial to differentiate this from other potential causes.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms, often accompanied by dizziness and confusion, are common indicators of fluid imbalance in the body.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Sudden changes in mental state, such as confusion, disorientation, and difficulty concentrating, could signal a disruption in electrolyte balance. This can be especially noticeable in individuals with underlying medical conditions.
- Muscle Weakness and Cramps: Muscle weakness, particularly in the extremities, and muscle cramps can result from the body’s struggle to maintain electrolyte balance.
- Seizures: Severe cases of water intoxication can lead to seizures, which are a significant medical emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
- Loss of Consciousness: In extreme cases, overhydration can lead to a loss of consciousness, a critical sign that immediate medical intervention is necessary.
Factors Increasing Risk of Water Intoxication
Several factors can increase an individual’s susceptibility to water intoxication. Understanding these factors can help mitigate the risk.
- Prolonged Intense Exercise: Athletes engaging in prolonged and strenuous physical activity, especially in hot and humid conditions, are at higher risk of overhydration if they consume large volumes of water without adequate electrolyte replacement.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Individuals with kidney problems, heart conditions, or other underlying medical conditions may be more vulnerable to the effects of overhydration. Their bodies might not be able to process fluids at the same rate as healthy individuals.
- Inadequate Electrolyte Intake: Consuming excessive amounts of water without replenishing essential electrolytes, like sodium, can disrupt the body’s fluid balance, increasing the risk of water intoxication.
- Rapid Water Intake: Rapidly consuming large quantities of water can overwhelm the body’s ability to regulate fluid levels.
Severity Levels of Water Intoxication
The severity of water intoxication can vary, ranging from mild to severe cases. Early detection and appropriate medical intervention are critical in each situation.
| Severity Level | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Mild | Headache, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, and slight confusion. |
| Moderate | Severe headache, seizures, loss of consciousness, and difficulty breathing. |
| Severe | Coma, respiratory arrest, and potentially fatal complications. |
Understanding Water Intake Patterns
Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, but the ideal water intake varies significantly from person to person. Understanding the factors that influence individual water needs helps us determine the right amount for our bodies. This is particularly important because consuming excessive water can have negative consequences.Knowing how much water you should drink is not a one-size-fits-all answer.
Your individual water needs are influenced by various factors, and these factors are interconnected and play a significant role in determining your hydration requirements. Recognizing these factors can help you tailor your hydration strategy to your unique circumstances.
Factors Influencing Water Needs
Understanding the variables impacting your water intake allows for a personalized approach to hydration. Different factors play a critical role in determining how much water your body requires.
| Category | Factors | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Climate | Temperature and humidity | Living in a hot and humid climate increases sweat loss and thus, water needs. Similarly, cold weather can also affect water needs, though to a lesser degree. |
| Activity Level | Exercise intensity and duration | Athletes and individuals engaged in strenuous physical activity need more water to compensate for sweat loss. Sedentary individuals may require less, but still need to maintain adequate hydration. |
| Diet | Food composition | Foods with high water content, like fruits and vegetables, contribute to overall hydration. Conversely, consuming highly processed foods or those high in sodium can increase water loss. |
| Health Conditions | Medical conditions and medications | Certain medical conditions, like kidney disease, may require specific hydration guidelines. Medications can also influence fluid balance and water needs. |
| Pregnancy and Breastfeeding | Physiological changes | Pregnant and breastfeeding women require increased water intake to support the growing needs of the developing fetus or infant. |
Monitoring Daily Water Intake
Various methods can help track your daily water intake and ensure you’re meeting your hydration needs. It’s important to select a method that works best for your lifestyle.
- Tracking Apps
- These apps provide a structured way to log water intake throughout the day. They offer reminders and visual representations of progress. However, accuracy depends on user consistency and input accuracy.
- Measuring Urine Output
- Monitoring the color and volume of urine can provide a natural indicator of hydration status. Pale yellow urine usually signifies adequate hydration. Darker yellow urine might indicate dehydration. This method doesn’t replace other methods, but can be a useful complementary approach.
Consequences of Excessive Water Intake
While it’s important to stay hydrated, consistently exceeding recommended water intake levels can lead to negative health consequences.
Excessive water intake can potentially dilute electrolytes in the blood, leading to hyponatremia.
This condition can cause a range of symptoms, from nausea and headache to more severe complications like seizures and coma. Symptoms often manifest gradually, so recognizing early signs is crucial. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for addressing any concerns regarding water intake. Individual responses to excessive water intake can vary significantly, so understanding your body’s signals is key to maintaining a healthy hydration balance.
Managing Water Consumption
Knowing how much water you need and how to consume it effectively is crucial for overall health. Overhydration, just as dehydration, can lead to serious health problems. This section provides practical strategies for maintaining a healthy water balance.Effective water management isn’t just about drinking enough; it’s about understanding your body’s signals and adapting your intake to your individual needs.
Figuring out how much water is too much can be tricky, especially when dealing with chronic pain. Sometimes, medications like buprenorphine for chronic pain management buprenorphine for chronic pain management can affect your fluid balance. Ultimately, it’s crucial to listen to your body and consult a doctor for personalized advice on hydration levels, especially when taking certain medications.
Overhydration can be just as harmful as dehydration, so finding that sweet spot is key.
By recognizing your personal water requirements and developing healthy habits, you can prevent the negative consequences of both insufficient and excessive water consumption.
Safe and Effective Strategies for Managing Water Intake
Maintaining a healthy water balance involves a combination of mindful consumption and understanding your body’s cues. Simple strategies can make a significant difference in your daily water intake management.
- Listen to your thirst cues. Your body’s thirst mechanism is a natural signal. Ignoring it can lead to overhydration or dehydration. Paying attention to your body’s cues and adjusting your intake accordingly is key to maintaining optimal hydration.
- Maintain a consistent hydration schedule. Instead of waiting until you’re extremely thirsty, aim for regular water intake throughout the day. This could involve setting reminders on your phone or carrying a reusable water bottle to ensure consistent hydration.
- Track your water intake. Keeping a log of your water consumption can help you identify patterns and adjust your intake as needed. This method can be helpful in understanding your individual water needs over time.
Identifying Personal Water Intake Needs
Determining your ideal water intake involves considering several factors. A personalized approach is essential for optimal hydration.
- Consider your activity level. More physically active individuals need more water to compensate for sweat loss. If you exercise regularly, you should adjust your water intake to account for increased perspiration.
- Evaluate your climate. Hot and humid climates require more water intake to replace fluids lost through perspiration. In these conditions, increasing your water intake is vital.
- Take note of your health conditions. Certain medical conditions can affect fluid needs. If you have any pre-existing health concerns, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance on water intake.
Practical Tips for Avoiding Excessive Water Consumption
While drinking enough water is important, excessive water intake can also be harmful. Strategies to avoid overconsumption are essential for overall well-being.
- Avoid excessive intake in a short period. Instead of gulping large amounts of water at once, sip consistently throughout the day. This approach can help prevent sudden water overload.
- Pay attention to signs of overhydration. Symptoms such as nausea, headache, and swelling can indicate excessive water intake. If you experience these symptoms, reduce your water intake and seek medical advice if necessary.
- Be mindful of other fluid sources. Beverages like juice, tea, and coffee contribute to your total fluid intake. Consider these sources when calculating your overall water intake to prevent overconsumption.
Listening to Your Body’s Signals Regarding Thirst
Understanding your body’s thirst cues is essential for managing water intake effectively. Recognizing these cues helps maintain a healthy hydration balance.
Thirst is a natural physiological response indicating a need for water. It’s essential to listen to these signals and act accordingly. Ignoring thirst can lead to dehydration, while excessive consumption can cause water intoxication. The key is to maintain a balance, which involves understanding and responding to your body’s cues.
So, how much water is actually too much? It’s a tricky question, especially when you consider how your body reacts to excess fluids. For instance, if you’re dealing with an allergy to bandages and adhesives, allergy to bandages and adhesives can be triggered by the moisture-wicking properties of certain materials, making excess water a possible contributor to the issue.
Ultimately, listening to your body and understanding your individual limits is key when it comes to water intake.
Case Studies and Examples
Water intoxication, while less common than dehydration, is a serious health concern. Understanding how different individuals can be susceptible, and the potential consequences of overhydration, is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Different lifestyles and activity levels can significantly impact an individual’s water needs, making it important to personalize water intake strategies.The following examples illustrate the various ways individuals can experience water intoxication, emphasizing the importance of mindful water consumption.
We’ll look at a hypothetical marathon runner, and discuss the factors that can lead to unintentional overhydration, as well as the available treatment options.
Varied Susceptibility to Water Intoxication
Different individuals experience varying degrees of water intake requirements based on their activity levels, diets, and overall health. Athletes, particularly those engaging in prolonged high-intensity exercise, may be at a higher risk of water intoxication if they don’t carefully monitor their fluid intake. Furthermore, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney or heart problems, may need to adjust their water intake even more cautiously.
Hypothetical Marathon Runner Case
Consider a hypothetical marathon runner who, driven by a desire to perform at their best, consumed large volumes of water during and after the race. They might experience symptoms such as nausea, headache, confusion, and muscle weakness, which could be indications of water intoxication. The symptoms could range from mild discomfort to potentially life-threatening conditions.
Unintentional Overhydration
Several factors can contribute to an individual unknowingly consuming excessive amounts of water. These include:
- Intense Physical Activity: Prolonged and strenuous exercise can lead to an increased thirst and subsequent urge to drink large amounts of water, potentially surpassing the body’s natural capacity to process it. In these situations, athletes should focus on gradual hydration throughout the exercise and be mindful of their body’s signals.
- Inadequate Electrolyte Intake: When individuals consume large amounts of water without replacing lost electrolytes, they risk an imbalance in their body’s internal chemistry. Electrolytes, such as sodium, play a critical role in maintaining fluid balance and nerve function. A balanced electrolyte intake is crucial, especially for those engaging in prolonged physical activities.
- Misinterpretation of Thirst Signals: Some individuals may not accurately perceive their thirst signals, potentially leading to excessive water consumption. Regular self-assessment and understanding of individual hydration needs is key.
- Certain Medications: Some medications can influence water retention or require specific fluid intake recommendations, which may increase the risk of overhydration. Consult with a doctor for guidance on appropriate fluid intake.
Treatment Options for Water Intoxication
Treatment for water intoxication focuses on restoring the body’s electrolyte balance and addressing any related symptoms. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if symptoms arise. The following are possible approaches:
- Slowing Water Intake: Reducing or ceasing the intake of water and focusing on electrolyte replacement is a critical first step. Medical professionals can provide specific instructions on how to gradually adjust water consumption.
- Electrolyte Replacement: Oral or intravenous rehydration solutions containing electrolytes can help restore the body’s electrolyte balance and counteract the effects of water intoxication.
- Medical Monitoring: Close monitoring by medical professionals is essential to track the individual’s response to treatment and ensure proper recovery. This may include observation for changes in vital signs and potential complications.
Preventing Overhydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for health, but too much water can be just as detrimental. Understanding how to avoid water intoxication is vital for maintaining well-being. This section delves into preventative measures and potential warning signs to help you stay safe.Overhydration, while less common than dehydration, is a serious medical concern that can lead to potentially life-threatening complications.
Recognizing the signs and knowing how to mitigate risk is essential for protecting your health.
Preventative Measures to Avoid Water Intoxication
Strategies to minimize the risk of water intoxication involve careful monitoring of water intake, especially in situations where excessive fluid intake is likely. Understanding your body’s needs and adjusting consumption accordingly is key.
- Listen to your body’s signals.
- Avoid excessive water intake during strenuous exercise or in hot environments.
- Don’t drink large quantities of water all at once.
- Be mindful of water intake, especially if you have conditions like kidney or heart problems, or if you are taking certain medications.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on water intake.
Situations of High Risk for Overhydration
Certain activities and conditions increase the likelihood of water intoxication. Awareness of these situations is critical for proactive safety.
While it’s crucial to stay hydrated, excessive water intake can be problematic. It’s a bit like anything else; too much isn’t always good. Knowing what foods to avoid when you’re struggling with constipation can be just as important as adjusting your water intake. For instance, foods high in fiber and those that are hard to digest can make matters worse.
Check out this guide on foods to avoid when you are constipated for more details. Ultimately, finding the right balance of hydration is key, and understanding what your body needs is crucial to avoid any potential issues.
- Marathon runners or endurance athletes: Prolonged strenuous activity in hot conditions can lead to excessive fluid intake if not managed carefully.
- Individuals with kidney or heart conditions: Pre-existing conditions can affect the body’s ability to process water efficiently, increasing the risk of overhydration.
- People taking certain medications: Some medications can alter water balance, increasing the risk of water intoxication.
- Individuals with a history of water intoxication: Those who have experienced water intoxication in the past may be more vulnerable to future occurrences.
- Unintentional or compulsive water intake: Individuals who consume large volumes of water for non-physiological reasons are at risk.
Potential Warning Signs of Overhydration
Recognizing the symptoms of overhydration is crucial for timely intervention. Prompt recognition can prevent serious complications.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Nausea and vomiting | Feeling unwell with an urge to vomit. |
| Headache | A persistent pain in the head. |
| Confusion and disorientation | Difficulty in thinking clearly and understanding surroundings. |
| Seizures | Uncontrolled muscle spasms. |
| Loss of consciousness | Inability to respond to stimuli. |
Education and Awareness in Preventing Water Intoxication
Public education plays a vital role in preventing water intoxication. Dissemination of information about the dangers and preventative measures is crucial for public health.Promoting awareness of the risks associated with overhydration, including the symptoms and situations of heightened vulnerability, is essential for preventing adverse outcomes. Educational campaigns can effectively reduce the incidence of water intoxication.
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the delicate balance of hydration is crucial. While water is essential for life, excessive intake can be harmful. This section explores real-world scenarios to highlight the risks associated with overhydration and the importance of personalized water intake recommendations.
Desert Hike Mishap
A common scenario where overhydration becomes a concern is during extended hikes in desert environments. Imagine a hiker embarking on a multi-day trek through the scorching sands. Driven by the intense heat and exertion, the hiker drinks copious amounts of water, believing more is always better. This, however, can lead to a dangerous condition called water intoxication, also known as hyponatremia.
The rapid influx of water dilutes the sodium levels in the bloodstream, potentially causing severe symptoms such as nausea, headache, confusion, and even seizures. The body’s natural regulatory mechanisms, designed to maintain electrolyte balance, can be overwhelmed by this rapid hydration, particularly when combined with physical exertion. This emphasizes the critical need for gradual hydration and awareness of individual needs in extreme conditions.
Case Study: Child with Kidney Condition
Children with certain kidney conditions require careful monitoring of their water intake. A young patient with impaired kidney function may have difficulty filtering excess water from the body. In such cases, adjusted water intake recommendations are necessary to prevent water overload. Doctors closely monitor the child’s urine output, weight, and electrolyte levels to ensure appropriate hydration. This ensures the child receives the necessary fluids without jeopardizing their kidney health.
Individualized hydration plans are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Impact of Activities and Climate
Different activities and climates significantly affect water needs. An athlete engaged in strenuous physical activity, particularly in a hot climate, requires a higher fluid intake to compensate for sweat loss. However, even in these situations, excessive water intake can be detrimental. Similarly, individuals living in arid regions need to carefully manage their water intake to prevent dehydration, but also to avoid overhydration.
Acclimatization to different climates plays a crucial role in determining appropriate hydration strategies. Factors like duration and intensity of activity, ambient temperature, and humidity all contribute to the optimal water intake for each individual.
Water Intake and Kidney Function
The following graphic illustrates the relationship between water intake and kidney function. Note that the graph will not be displayed here, as it is not possible to include images. However, a well-designed graph would depict a healthy range of water intake that corresponds with proper kidney function. As water intake increases beyond this range, the graph would show a decline in kidney function, highlighting the risks of overhydration.
The graph would illustrate the optimal level of water intake for maintaining kidney health.
Overhydration puts excessive strain on the kidneys. The kidneys’ role in regulating fluid balance becomes compromised, leading to a potential accumulation of water in the body’s tissues and organs. In extreme cases, this can lead to serious health complications. This graphic would clearly show the crucial balance needed between sufficient water intake and avoiding overhydration.
Closing Notes: How Much Water Is Too Much
In conclusion, while staying hydrated is vital, understanding the potential risks of overhydration is equally important. By recognizing the signs of water intoxication and adopting responsible water consumption habits, we can ensure we’re nourishing our bodies without jeopardizing our health. The key takeaway? Listen to your body, adjust your intake based on your specific needs, and prioritize a balanced approach to hydration.