Comparing Vyvanse vs Adderall: This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these stimulant medications, exploring their chemical makeup, potential benefits and drawbacks, and patient experiences. We’ll examine the nuances of their formulations, their impact on various conditions, and provide a balanced overview for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Both Vyvanse and Adderall are commonly prescribed stimulants, primarily for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Understanding their differences is crucial for making informed decisions about treatment options. This in-depth comparison aims to equip you with the knowledge to navigate this complex landscape.
Introduction to Stimulant Medications
Stimulant medications are a class of drugs that increase activity in the central nervous system. They achieve this by affecting neurotransmitters, primarily dopamine and norepinephrine, which play crucial roles in regulating attention, focus, and mood. These medications are frequently prescribed to individuals experiencing conditions characterized by reduced attention span or hyperactivity.While stimulants can significantly improve certain symptoms, their use requires careful consideration and monitoring.
Their potential for abuse and side effects necessitates responsible prescription and management. This section will delve into the specifics of stimulant medications, focusing on Vyvanse and Adderall, and their applications.
Types of Stimulant Medications
Stimulant medications come in various forms, each with slightly different mechanisms of action and effects. This diversity is crucial for tailoring treatment to individual needs and minimizing side effects. Two prominent examples are Vyvanse and Adderall.
- Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine dimesylate) is a prodrug, meaning it is inactive until it’s metabolized in the body. This gradual release helps maintain consistent levels of the active component, lisdexamfetamine, in the bloodstream. This is often preferred for its more sustained effect and potential for reduced side effects compared to immediate-release stimulants.
- Adderall (amphetamine salts) is a combination of various amphetamine salts, which act directly on the nervous system to increase the release and/or block the reuptake of neurotransmitters. This immediate effect is why it is often taken multiple times a day to maintain the desired level of stimulation.
Common Conditions for Prescription
Stimulant medications are commonly prescribed for conditions where attention, focus, or impulse control are compromised. These conditions often affect a person’s daily life and functioning.
Comparing Vyvanse and Adderall can be tricky, right? Both are stimulants, but they work a little differently in the body. Understanding how the liver processes these medications is key, and that leads me to wonder about the liver’s remarkable ability to regenerate. You might be surprised to learn how well the liver can repair itself after injury or damage, as discussed in this helpful article about does the liver regenerate.
Ultimately, knowing how the liver handles these medications is crucial when considering which one might be a better fit for you, but this is something you should discuss with your doctor.
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): This neurodevelopmental disorder is characterized by persistent inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Stimulants can help manage these symptoms, enabling individuals with ADHD to improve focus and impulse control in various settings, from school to work and social interactions.
- Narcolepsy: This sleep disorder causes excessive daytime sleepiness and can lead to sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep. Stimulants can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle and reduce the frequency and intensity of these episodes, enabling individuals to maintain alertness and productivity.
Comparison of Active Ingredients
The table below summarizes the active ingredients and their respective forms in Vyvanse and Adderall.
| Medication | Active Ingredient | Form |
|---|---|---|
| Vyvanse | Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate | Prodrug |
| Adderall | Amphetamine salts (dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine) | Immediate release or extended release |
Comparing Chemical Composition and Formulation
Understanding the differences in chemical structure and formulation between Vyvanse and Adderall is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This knowledge helps in tailoring treatment strategies and managing potential side effects. These medications, while both stimulants, operate in slightly different ways within the body, impacting their effects and potential for interaction with other drugs.Vyvanse and Adderall, both central nervous system stimulants, differ significantly in their chemical composition and how they are processed by the body.
This impacts their rate of action and duration of effect, leading to varied clinical responses in individuals.
Chemical Structures of Active Ingredients
The active ingredient in Vyvanse is lisdexamfetamine dimesylate, a prodrug. A prodrug is an inactive compound that is metabolized into an active form within the body. In the case of Vyvanse, lisdexamfetamine is converted to dextroamphetamine, a stimulant. Adderall, on the other hand, contains a mixture of amphetamine salts, primarily dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine. This difference in the chemical structure directly affects how the medication is processed.
Formulations and Processing
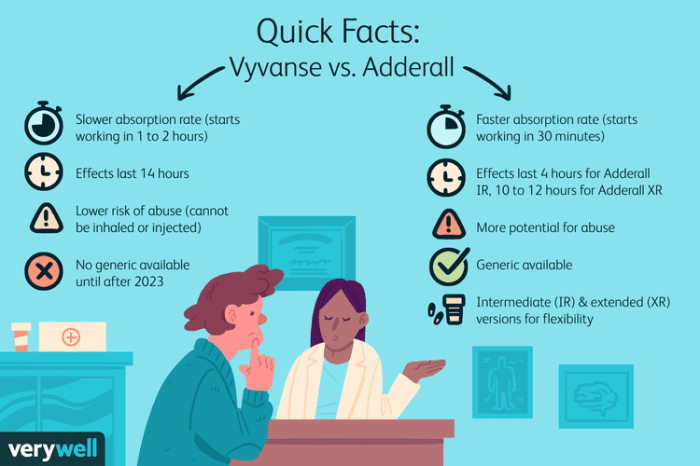
Vyvanse’s formulation differs from Adderall’s in a key way. Vyvanse is designed as a prodrug, which means it is inactive until it’s broken down by the body. This process results in a more sustained release of dextroamphetamine compared to Adderall. Adderall, containing immediate-release amphetamine salts, is absorbed more rapidly. This difference affects how quickly the medication takes effect and how long its effects last.
Rate and Duration of Action
The different formulations directly influence the rate and duration of action. Vyvanse’s sustained-release profile provides a more gradual increase in blood levels of dextroamphetamine, resulting in a longer duration of effect. Adderall, with its immediate-release formula, provides a faster onset but a shorter duration of action. This difference in action is crucial when considering the timing of dosing and the need for potential follow-up doses.
Strengths and Dosages
| Medication | Strengths (mg) | Dosages (mg/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Vyvanse | 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70 | 10–80 mg, typically titrated by the physician |
| Adderall | 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 15, 20, 25, 30 | 5–60 mg, typically titrated by the physician |
This table displays the various strengths and typical dosage ranges for both medications. It’s important to note that dosage recommendations are individualized based on the patient’s specific needs and response to treatment. A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate dosage and monitor the patient closely for optimal results.
Potential Benefits and Effects
Stimulant medications like Vyvanse and Adderall are frequently prescribed to manage attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other conditions. While these medications can significantly improve focus and concentration, they also carry potential risks and side effects. Understanding both the benefits and the drawbacks is crucial for informed decision-making when considering these medications.A crucial aspect of evaluating stimulant medications involves acknowledging their potential to positively impact various aspects of a patient’s life.
However, it’s equally important to consider the possible downsides, which can range from mild discomfort to more severe complications. This section will delve into the potential benefits, side effects, abuse potential, and long-term consequences associated with both Vyvanse and Adderall.
Potential Benefits of Vyvanse and Adderall
These medications work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, which can improve focus, attention, and impulse control. This can lead to significant improvements in academic performance, social interactions, and overall daily functioning for individuals with ADHD. In some cases, these medications can also help manage symptoms of other conditions, such as narcolepsy and certain types of depression.
Patients may experience enhanced productivity, reduced impulsivity, and improved organization.
Potential Side Effects of Vyvanse and Adderall
Stimulant medications, while effective, can induce a range of side effects. These can vary significantly between individuals and depend on factors like dosage, individual physiology, and the presence of other medical conditions. Common side effects include decreased appetite, insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and headaches. In some cases, more serious side effects such as heart palpitations, high blood pressure, or seizures can occur, though these are less frequent.
Abuse Potential and Misuse
Both Vyvanse and Adderall have the potential for abuse and misuse. Their ability to enhance focus and energy makes them attractive to individuals seeking a performance boost or an altered mental state. The risk of dependence and addiction is a concern, especially if the medication is taken in higher doses or for longer durations than prescribed. This risk is further heightened in individuals with a history of substance abuse or mental health disorders.
The potential for diversion and illegal use of these medications must be acknowledged and monitored.
Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of stimulant medications like Vyvanse and Adderall are an area of ongoing research. While many individuals experience positive outcomes with appropriate use and monitoring, long-term use can potentially lead to changes in brain development or other health complications. Some studies suggest potential impacts on appetite, sleep patterns, and emotional regulation over time. Further research is necessary to fully understand these potential effects.
Long-term consequences may include cognitive changes, mood swings, or social difficulties. Furthermore, prolonged use can lead to tolerance, necessitating higher doses to maintain the same effect.
Table of Common Side Effects
| Side Effect | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Decreased Appetite | Common |
| Insomnia | Common |
| Headaches | Common |
| Anxiety | Common |
| Irritability | Common |
| Heart Palpitations | Uncommon |
| High Blood Pressure | Uncommon |
| Seizures | Rare |
Note: This table represents a general overview and individual experiences may vary. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Considerations for Patients and Prescribers
Choosing between stimulant medications like Vyvanse and Adderall requires careful consideration of individual needs and potential risks. A thorough understanding of the patient’s medical history, specific symptoms, and potential side effects is crucial for both the patient and the prescribing physician. Properly managing these medications demands a collaborative approach, prioritizing patient well-being and adherence to treatment plans.
Importance of Thorough Medical Evaluation, Comparing vyvanse vs adderall
A comprehensive medical evaluation is paramount before prescribing any stimulant medication. This evaluation should include a detailed patient history, a physical examination, and potentially, neuropsychological testing. Identifying pre-existing conditions, such as cardiovascular issues, anxiety disorders, or a history of substance abuse, is vital. These conditions can significantly impact how a patient responds to stimulants and may necessitate careful monitoring and dosage adjustments.
A thorough evaluation helps to tailor the treatment plan to the individual patient’s specific needs and circumstances.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Vyvanse and Adderall
Several factors influence the selection of either Vyvanse or Adderall. The specific chemical makeup of each medication results in distinct effects and potential side effects. For instance, Vyvanse’s unique formulation may lead to a more sustained release of the active compound, potentially resulting in fewer fluctuations in blood levels compared to Adderall. The patient’s specific needs and response to medication should also be taken into account.
Some individuals may experience a more favorable response to one medication over the other. Additionally, the patient’s overall medical history and potential for adverse reactions should be carefully assessed.
Strategies for Managing Potential Side Effects
Managing potential side effects is a critical aspect of stimulant medication treatment. Strategies for managing these effects often include adjusting dosages, adding counseling or behavioral therapy, and providing clear communication about expected side effects. Regular monitoring of the patient’s blood pressure and heart rate is important. For example, a patient experiencing significant insomnia may benefit from adjusting the medication schedule or considering a sleep aid.
Similarly, anxiety can be addressed through counseling or medication management strategies. Open communication between the patient and the prescriber is crucial for managing side effects effectively and tailoring the treatment plan to the individual.
Importance of Adherence to Prescribed Dosages and Treatment Plans
Adherence to the prescribed dosage and treatment plan is critical for optimal outcomes. This includes taking the medication at the prescribed times and following the instructions provided by the healthcare provider. Non-adherence can lead to ineffective treatment and potentially increased risk of side effects. Clear communication between the patient and prescriber is essential to address any concerns or difficulties with adherence.
For example, a patient struggling with remembering medication times may benefit from utilizing reminders, such as medication organizers or mobile phone apps.
Monitoring Tools for Patients and Prescribers
Monitoring tools play a crucial role in both patient and prescriber management. For patients, tools like daily symptom logs, medication adherence trackers, and sleep diaries can provide valuable data to track treatment progress and identify potential issues. Prescribers can utilize electronic health records (EHRs) to track patient responses to treatment, monitor vital signs, and communicate effectively. These tools allow for proactive identification of potential side effects or treatment adjustments, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Key Considerations for Patient Selection and Management
| Criterion | Vyvanse Considerations | Adderall Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Medical History | Consider potential for sustained-release effect and its impact on patients with specific medical conditions. | Assess for potential for more rapid fluctuations in blood levels and its impact on patients with specific medical conditions. |
| Patient Response | Monitor for sustained effects and potential for reduced side effects. | Monitor for potential for more pronounced effects and potential for more frequent side effects. |
| Side Effect Management | Strategies may focus on sustained release to minimize fluctuations in response. | Strategies may focus on adjusting dosages and timing to manage potential side effects. |
| Adherence | Potential for better adherence due to sustained release. | Potential for better adherence if the medication aligns with patient preferences and daily routines. |
| Monitoring | Regular monitoring of sustained effects and potential side effects. | Regular monitoring of response, fluctuations, and potential side effects. |
Interactions and Contraindications
Understanding the potential interactions and contraindications of Vyvanse and Adderall is crucial for safe and effective use. These stimulants, while often helpful for ADHD and other conditions, can interact with other medications and pre-existing medical issues. A thorough understanding of these factors allows both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about treatment.
Potential Drug Interactions
Medication interactions can significantly alter the effects of Vyvanse and Adderall, potentially leading to adverse reactions or diminished effectiveness. Many medications can affect the metabolism or absorption of these stimulants. Careful consideration of all concurrent medications is vital.
Numerous drugs can interact with stimulants. This includes, but is not limited to, antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors), and certain antibiotics. These interactions can result in increased or decreased stimulant levels in the bloodstream, potentially leading to unwanted side effects.
| Medication Class | Potential Interaction | Example |
|---|---|---|
| MAOIs | Potentially dangerous hypertensive crisis | Taking an MAOI with a stimulant can cause dangerously high blood pressure. |
| Antidepressants (certain types) | Increased stimulant effects or side effects | Combining certain antidepressants with stimulants may amplify the stimulant’s effects or increase the risk of side effects like anxiety or insomnia. |
| Anti-anxiety medications | Reduced effectiveness of either medication | Combining an anti-anxiety medication with a stimulant could decrease the effectiveness of both. |
| Certain antibiotics | Altered metabolism of the stimulant | Some antibiotics can impact how the body processes stimulants, potentially leading to higher or lower levels in the blood. |
Contraindications
Certain medical conditions can make Vyvanse and Adderall unsuitable for use. A thorough medical history is critical to identifying potential contraindications. It’s vital that patients and prescribers fully understand these conditions.
Conditions like uncontrolled high blood pressure, severe anxiety, and pre-existing heart conditions are contraindications to stimulant use. Stimulants can exacerbate these conditions, potentially leading to serious health risks. Furthermore, individuals with a history of drug abuse or dependence should be closely monitored and carefully evaluated for stimulant use.
- Uncontrolled High Blood Pressure: Stimulants can elevate blood pressure, potentially leading to a hypertensive crisis in those with pre-existing or uncontrolled hypertension.
- Severe Anxiety or Panic Disorder: Stimulants can exacerbate anxiety symptoms in individuals prone to anxiety disorders. In severe cases, this can lead to panic attacks or increased anxiety.
- Heart Conditions: Stimulants can affect heart rate and blood pressure. Pre-existing heart conditions, including cardiovascular disease, may be worsened by stimulant use. Patients with a history of heart problems should be closely monitored.
- Drug Dependence or Abuse History: Stimulant use in individuals with a history of drug dependence or abuse can increase the risk of addiction or relapse.
- Important Note: This list is not exhaustive. A thorough medical evaluation by a healthcare provider is essential to determine if Vyvanse or Adderall is appropriate for an individual.
Importance of Disclosure
Full disclosure of all medications and supplements is critical for accurate prescribing and avoiding potentially harmful interactions. This includes over-the-counter medications, herbal remedies, and dietary supplements. Failure to disclose these substances can lead to unexpected reactions or complications.
Patients should provide a complete list of all medications, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, and any other substances they are taking, to their healthcare providers. This proactive approach helps prevent potentially serious interactions and ensures the safest possible treatment plan.
Examples of Contraindicated Situations
Contraindications can manifest in various scenarios. Consider a patient with a history of hypertension taking Vyvanse and concurrently taking an over-the-counter cold medication containing pseudoephedrine. The combination of Vyvanse and pseudoephedrine could potentially elevate blood pressure to dangerous levels.
Another example involves a patient with known heart arrhythmias who is prescribed Adderall. The stimulant properties of Adderall could exacerbate the arrhythmias, potentially leading to serious complications. These examples highlight the importance of thorough disclosure and comprehensive medical evaluation before initiating stimulant therapy.
Patient Experiences and Perspectives: Comparing Vyvanse Vs Adderall
The journey of managing ADHD or other conditions often involves more than just medication. Patient experiences with stimulants like Vyvanse and Adderall are diverse, influenced by individual factors, treatment approaches, and the specific needs of each person. Understanding these perspectives is crucial for healthcare providers to tailor effective and compassionate care.Patient experiences with stimulants like Vyvanse and Adderall vary significantly.
This section will delve into common experiences, the potential emotional and psychological impacts, and the importance of open communication between patients and their healthcare providers. Examples of both positive and negative feedback will be shared, highlighting the nuanced reality of medication use.
Common Experiences with Vyvanse and Adderall
Patient experiences with Vyvanse and Adderall frequently include both positive and negative effects. Some common experiences include improvements in focus, reduced impulsivity, and increased motivation. Conversely, some patients report side effects like anxiety, insomnia, appetite suppression, and mood swings.
Emotional and Psychological Impacts
Stimulant medications can have a profound impact on emotional and psychological well-being. Positive impacts can include improved self-esteem, reduced feelings of inadequacy, and enhanced social functioning. However, negative impacts like heightened anxiety, irritability, or even depression are also possible and should be monitored closely. The specific emotional response varies greatly between individuals, and careful observation is crucial.
Positive and Negative Patient Feedback
Positive feedback often emphasizes improved concentration, enhanced academic performance, and a greater sense of control over daily tasks. Patients may feel more productive and engaged in their work and personal life. However, negative feedback frequently points to unwanted side effects like difficulty sleeping, decreased appetite, and increased anxiety. Some patients report that the medication does not adequately address their specific needs or causes undesirable emotional reactions.
Importance of Open Communication
Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is paramount. Patients should feel comfortable discussing their experiences, both positive and negative, with their doctors. This allows for adjustments to the medication regimen or treatment plan to maximize benefits and minimize adverse effects. Regular check-ins and honest dialogue are essential for managing potential side effects and ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
Patient Testimonials
“Since starting Vyvanse, I’ve been able to focus better at work and finally finish projects. It’s made a huge difference in my productivity and confidence.”
John Doe
“Adderall initially helped me manage my impulsivity, but I started experiencing significant anxiety and insomnia. My doctor and I worked together to adjust the dosage, and things have improved considerably.”
Jane Smith
“I was initially hesitant about taking any medication, but Vyvanse has helped me feel more in control of my ADHD symptoms. I can now focus on my studies without feeling overwhelmed.”
David Lee
Clinical Research and Studies

Clinical studies play a crucial role in evaluating the effectiveness and safety of medications like Vyvanse and Adderall. These studies help clinicians and patients make informed decisions about treatment options. Rigorous research designs and analysis methods are essential to ensure the validity and reliability of findings.
Summary of Comparative Studies
Numerous studies have investigated the effectiveness of Vyvanse and Adderall in treating attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). These studies often compare the two medications in terms of symptom reduction, side effect profiles, and overall treatment response. The results can vary depending on the specific study design, patient population, and outcome measures.
Methodologies Used in Studies
The methodologies employed in these studies vary, but commonly involve randomized controlled trials (RCTs). RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating treatment efficacy. In these trials, participants are randomly assigned to receive either Vyvanse, Adderall, or a placebo. Researchers meticulously monitor and record participant responses, such as symptom severity, medication adherence, and adverse events. Statistical analyses are then performed to determine if there are significant differences in treatment outcomes between the groups.
Different outcome measures, like the ADHD Rating Scale, are used to assess improvement in various symptoms. These studies often have a specific duration, for example, 8 weeks, during which data is collected and analyzed.
Results of Studies
Studies consistently demonstrate that both Vyvanse and Adderall are effective in improving ADHD symptoms. However, subtle differences in their effects and side-effect profiles can emerge. Some studies suggest a slightly different duration of action, with Vyvanse potentially having a more sustained release effect, leading to a more stable concentration of the medication in the bloodstream. Others point to potential differences in side effects like appetite suppression or insomnia.
The results often need to be interpreted cautiously, considering the specific design and context of each study.
Comparing Vyvanse and Adderall can be tricky, right? It’s a bit like figuring out the differences between gout and rheumatoid arthritis – both can cause painful inflammation, but the underlying causes and treatment approaches differ significantly. Learning about the specifics of each condition, like gout vs rheumatoid arthritis , can help you better understand your own health needs.
Ultimately, consulting a doctor is key for accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans, regardless of whether you’re comparing stimulants or dealing with inflammatory conditions.
Limitations of Studies and Implications
Limitations in clinical studies often include sample size, the specific patient populations studied, and the duration of the study. Small sample sizes might not allow for generalizability of the results to a wider population. The specific characteristics of the patients involved in a study, like age, gender, or co-occurring conditions, can also influence the findings. Furthermore, the relatively short duration of some studies might not fully capture the long-term effects of the medications.
The implications of these limitations are that results need to be interpreted in context. Further research with larger samples, diverse patient populations, and longer follow-up periods is needed to fully understand the differences and similarities between Vyvanse and Adderall.
Table Summarizing Key Findings
| Study Feature | Vyvanse | Adderall | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symptom Improvement (e.g., Inattention, Hyperactivity) | Significant improvement observed in most studies. | Significant improvement observed in most studies. | Both medications show similar effectiveness. |
| Duration of Action | Potentially more sustained release effect, leading to more stable plasma levels. | Shorter duration of action, requiring more frequent dosing. | Sustained release is a potential advantage of Vyvanse. |
| Side Effect Profile | Potential for fewer side effects, particularly in relation to appetite suppression, compared to Adderall. | May lead to more pronounced side effects such as appetite suppression and insomnia. | Side effects are not always consistent between patients. |
| Patient Population | Findings may vary based on patient characteristics (age, comorbidities). | Findings may vary based on patient characteristics (age, comorbidities). | More studies with diverse populations are needed. |
| Study Duration | Results are often based on relatively short durations. | Results are often based on relatively short durations. | Long-term effects require further research. |
Practical Advice for Choosing the Right Medication
Choosing the right stimulant medication, like Vyvanse or Adderall, is a crucial step in managing ADHD or other conditions. It’s not a one-size-fits-all process; individual responses vary greatly. This section provides practical advice for patients and families, emphasizing the importance of ongoing monitoring and personalized treatment approaches.Selecting the appropriate medication requires careful consideration of various factors, including the specific symptoms, individual needs, and potential side effects.
It’s not about simply comparing chemical compositions, but about understanding how each medication might affect a particular person.
Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
Effective medication management isn’t a static process. Symptoms can fluctuate, and medication responses can change over time. Regular check-ups and adjustments to the dosage or medication type are essential to ensure optimal efficacy and minimize side effects. A healthcare provider should monitor the patient’s progress closely and make necessary modifications to the treatment plan based on observed changes.
This proactive approach helps maintain the best possible outcome for the patient.
Comparing Vyvanse and Adderall can be tricky, and often involves considering potential side effects. One important factor to remember is that both medications can sometimes affect the digestive system. This is something to consider alongside learning more about irritable bowel syndrome, which can also cause significant digestive issues. Facts about irritable bowel syndrome are crucial to understanding this broader context when weighing the pros and cons of each medication.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on individual needs and how each medication affects the patient’s overall well-being.
Role of a Healthcare Provider in Decision-Making
A healthcare provider plays a vital role in guiding the selection and management of stimulant medications. They assess individual needs, considering medical history, current symptoms, and potential risks. They evaluate the patient’s response to the medication, adjusting dosages and medications as needed. This ongoing dialogue between the patient, family, and healthcare provider is critical for tailoring the treatment to the unique circumstances of each individual.
Open communication is key to ensuring the best possible outcome.
Personalized Treatment Approaches
A one-size-fits-all approach to medication management is generally ineffective. Individual responses to stimulants vary considerably. Therefore, a personalized treatment approach is crucial. Factors like age, pre-existing conditions, and even lifestyle choices influence how a person responds to a particular medication. A healthcare provider should consider these factors when determining the best course of action.
Examples of Different Treatment Approaches for Different Patient Profiles
Different patient profiles may benefit from different treatment approaches. For example, a young adult with ADHD and a history of anxiety might respond better to a lower initial dose of Vyvanse, allowing for careful monitoring of anxiety symptoms. Alternatively, an adolescent with predominantly inattentive symptoms might benefit from a gradual increase in Adderall dosage, observing the effects on focus and concentration.
An older adult with co-occurring conditions might require a more cautious approach, starting with a lower dose of either medication and titrating upwards as tolerated. These are just illustrative examples, and the specific approach should always be determined in consultation with a healthcare provider. The ultimate goal is to find the medication and dosage that best supports the patient’s individual needs and overall well-being.
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the nuances of Vyvanse and Adderall requires looking at how they impact real people. This section provides hypothetical case studies and personal experiences to paint a clearer picture of the potential benefits and challenges associated with each medication.
Hypothetical Case Study
A 10-year-old boy, Leo, was struggling with ADHD. His parents tried various behavioral therapies, but his symptoms persisted. He was diagnosed with ADHD, and his doctor prescribed Vyvanse. After a few weeks of adjusting the dosage, Leo’s focus improved significantly in school. He completed assignments without needing constant reminders, and his social interactions became more controlled.
His teachers reported noticeable improvements in his classroom behavior and academic performance. This positive response was sustained over several months.
Patient Experience with Vyvanse
Sarah, a 25-year-old software engineer, experienced a noticeable shift in her productivity and focus after starting Vyvanse. She found it easier to concentrate on complex tasks and stay on track throughout the workday. Prior to taking Vyvanse, she frequently struggled with procrastination and felt overwhelmed by the sheer volume of work. The medication helped her manage her workload effectively, resulting in increased output and reduced stress.
However, she noted some initial side effects, such as mild insomnia and occasional headaches, that subsided after a few weeks.
Patient Experience with Adderall
Mark, a 32-year-old entrepreneur, had been using Adderall for several years to manage his ADHD. He found that Adderall consistently helped him maintain a high level of focus and motivation, crucial for his demanding work schedule. He effectively managed multiple projects and deadlines, leading to increased efficiency and a sense of accomplishment. He reported feeling energized and alert, which allowed him to make quick decisions and take decisive actions.
However, he did experience occasional anxiety and restlessness if the dosage was too high.
Tablet Forms of Vyvanse and Adderall


Vyvanse tablets are typically extended-release, meaning the medication is absorbed slowly over a longer period. This results in a more sustained effect compared to immediate-release formulations. Adderall comes in both immediate-release and extended-release forms. Immediate-release Adderall provides a faster onset of action, while extended-release Adderall offers a more controlled and sustained effect. The different release profiles lead to varying effects and potential side effects.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, choosing between Vyvanse and Adderall is a personal decision that should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional. This comparison has highlighted the key differences between these medications, but ultimately, individual responses vary. Factors such as side effects, potential interactions, and personal experiences must be carefully considered to ensure the most effective and safe treatment plan.




