What vitamin deficiency causes muscle cramps? This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating connection between essential vitamins and those painful muscle spasms. We’ll explore the various vitamins crucial for muscle function, and how their deficiency can trigger cramps. Understanding the specific roles of vitamins like calcium, magnesium, potassium, and vitamin D, along with their impact on muscle contractions, will be key to comprehending this often-misunderstood issue.
Muscle cramps, those sudden, involuntary contractions, can be debilitating. While often attributed to dehydration or overuse, underlying nutritional deficiencies can also be a significant culprit. This article will illuminate the critical link between vitamin deficiencies and muscle cramps, offering valuable insights into the role each vitamin plays in maintaining healthy muscle function.
Introduction to Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions of a muscle or group of muscles. These painful spasms can range from mild discomfort to intense, debilitating pain. While often temporary, they can significantly disrupt daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the causes and triggers of muscle cramps is crucial for effective prevention and management. Many factors contribute to muscle cramps, with nutritional deficiencies being one possible culprit.Muscle cramps typically manifest as a sharp, localized pain in the affected muscle.
The pain can be accompanied by a visible tightening or twitching of the muscle. Symptoms can vary in intensity and duration, from fleeting sensations to prolonged discomfort. The pain is often described as a throbbing or stabbing sensation, depending on the location and severity of the cramp.General causes of muscle cramps include dehydration, strenuous exercise, electrolyte imbalances, and certain medical conditions.
Vitamin deficiencies, particularly of potassium, magnesium, and calcium, are also known to contribute to muscle cramps. These minerals play a crucial role in muscle function, and their absence can disrupt the intricate processes involved in muscle contraction and relaxation.
Types of Muscle Cramps and Potential Triggers
Muscle cramps can be categorized in various ways. This table Artikels different types and potential triggers, including nutritional deficiencies.
| Type of Muscle Cramp | Description | Potential Triggers | Nutritional Deficiencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exercise-induced muscle cramps | Occur during or immediately after physical activity, often in the legs, feet, or calves. | Prolonged or intense exercise, inadequate warm-up, dehydration, poor electrolyte balance. | Low potassium, low magnesium, low calcium. |
| Nocturnal muscle cramps | Occur during sleep, often affecting the legs and feet. | Dehydration, underlying medical conditions, tight muscles, prolonged sitting/standing. | Low magnesium, low calcium, low potassium. |
| Spontaneous muscle cramps | Occur without any apparent trigger, and can happen at any time. | Underlying medical conditions, nerve damage, certain medications. | Low potassium, low magnesium, low calcium, vitamin D deficiency (indirectly impacting calcium absorption). |
| Heat cramps | Associated with prolonged exposure to high temperatures, commonly affecting muscles in the arms, legs, and abdomen. | Excessive sweating, dehydration, intense physical activity in hot environments. | Low sodium, low potassium, low chloride. |
A balanced diet rich in potassium, magnesium, and calcium-rich foods can help prevent these deficiencies and thus reduce the risk of muscle cramps. Regular hydration is also crucial for maintaining optimal electrolyte balance, further minimizing the chances of experiencing cramps.
Vitamin Deficiencies and Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps, those sudden, involuntary contractions of muscle tissue, can be a frustrating and sometimes painful experience. While many factors contribute to muscle cramps, nutrient deficiencies, particularly in certain vitamins, can play a significant role. Understanding the connection between vitamin deficiencies and muscle cramps can help individuals identify potential underlying causes and take proactive steps toward addressing them.
Key Vitamins Associated with Muscle Cramps
Several vitamins are crucial for muscle function, and deficiencies in these vitamins can disrupt normal muscle activity, potentially leading to cramps. The most commonly implicated vitamins include vitamin D, vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B12, and potassium. Understanding their individual roles in muscle function is vital for comprehending how deficiencies can manifest as cramps.
Role of Vitamins in Muscle Function
Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption and muscle contraction. Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is essential for carbohydrate metabolism, providing energy for muscle function. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is involved in energy production, while vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is necessary for protein metabolism, which supports muscle growth and repair. Vitamin B12 is important for red blood cell formation, which carries oxygen essential for muscle activity.
Potassium is an electrolyte crucial for muscle contraction and nerve function. Disruptions in any of these processes can trigger muscle cramps.
How Deficiencies Lead to Muscle Cramps
A deficiency in vitamin D can impair calcium absorption, leading to lower calcium levels in the blood. This can cause muscle spasms and cramps. Similarly, insufficient vitamin B1 can hinder energy production, resulting in muscle fatigue and potential cramps. Vitamin B2 deficiencies affect energy production, impacting muscle function and potentially triggering cramps. Vitamin B6 is critical for protein metabolism, and a deficiency can affect muscle growth and repair, potentially causing cramps.
Vitamin B12 deficiency affects red blood cell formation, hindering oxygen delivery to muscles, which can contribute to muscle fatigue and cramps. Lastly, potassium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction and nerve function. A deficiency can disrupt these processes, triggering muscle cramps. Importantly, these are not the only potential causes for cramps; other factors such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances also contribute.
Comparison of Symptoms
| Vitamin Deficiency | Symptoms of Muscle Cramps | Frequency | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D Deficiency | Muscle weakness, pain, stiffness, and spasms, especially in the legs and back. | Can occur intermittently or consistently. | Often affects the legs, back, and abdomen. |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) Deficiency | Muscle weakness, fatigue, and potentially, numbness or tingling in the extremities. | Symptoms may fluctuate depending on the severity of the deficiency. | Muscle weakness and cramps can occur in various parts of the body. |
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) Deficiency | General weakness, fatigue, and potentially muscle cramps, along with other symptoms such as mouth sores and eye problems. | May be intermittent or consistent, depending on the severity of the deficiency. | Cramps may occur in various muscle groups, including legs and arms. |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) Deficiency | Muscle weakness, fatigue, and potential cramps, alongside other neurological symptoms. | May be intermittent or chronic, depending on the severity of the deficiency. | Cramps can affect different muscle groups, including the legs, arms, and face. |
| Vitamin B12 Deficiency | General fatigue, weakness, tingling in hands and feet, and potential muscle cramps. | Symptoms often emerge gradually. | Muscle cramps may occur in the legs, arms, and other areas. |
| Potassium Deficiency | Muscle weakness, cramps, and potentially irregular heartbeat. | Can occur frequently or intermittently. | Leg cramps are common. |
Calcium Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Calcium plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, including muscle contraction. Without sufficient calcium, muscles may not be able to contract and relax properly, potentially leading to painful muscle cramps. This deficiency, while often overlooked, can significantly impact quality of life.Calcium is essential for maintaining the proper structure and function of muscles. It acts as a vital messenger in the intricate process of muscle contraction.
When calcium levels drop below the necessary threshold, the delicate balance of muscle function is disrupted, increasing the likelihood of painful muscle cramps.
The Role of Calcium in Muscle Function, What vitamin deficiency causes muscle cramps
Calcium ions are critical for the interaction between actin and myosin, the proteins that form the contractile units within muscle fibers. The influx of calcium ions triggers the sliding filament mechanism, enabling muscle contraction. Without adequate calcium, the muscle fibers struggle to contract and relax efficiently, leading to muscle stiffness and potentially painful cramps. Adequate calcium intake is essential for preventing these issues.
How Calcium Deficiency Leads to Muscle Cramps
A deficiency in dietary calcium can result in low blood calcium levels (hypocalcemia). When blood calcium levels drop, the body attempts to maintain a balance by drawing calcium from bones. This process, while necessary for short-term calcium homeostasis, can lead to long-term bone health issues if the deficiency persists. The insufficient calcium in the bloodstream directly affects the ability of muscles to contract and relax properly.
The disruption in the normal calcium signaling pathways leads to muscle spasms and cramps.
Sources of Calcium in the Diet
Maintaining a diet rich in calcium-rich foods is crucial for preventing deficiencies and associated muscle cramps. A variety of food sources provide calcium, catering to diverse dietary needs and preferences.
Muscle cramps can be a real pain, and sometimes it’s not a vitamin deficiency at all. While low potassium is a common culprit, electrolyte imbalances like low sodium can also play a role. Understanding the role of sodium in the body, particularly its crucial function in fluid balance and nerve signals, is key. For a deeper dive into the ins and outs of sodium, check out this informative article on sodium sodium or salt sodium functions sodium and diet.
Ultimately, while sodium is important, a vitamin deficiency is still a likely cause of muscle cramps if sodium levels are within a normal range.
| Food Category | Specific Foods | Approximate Calcium Content (mg per serving) | Preparation Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Products | Milk, yogurt, cheese | Vary depending on type and serving size | Choose low-fat or fat-free options for reduced calorie intake. |
| Leafy Green Vegetables | Kale, collard greens, bok choy | Moderately high | Cooked leafy greens often have increased calcium bioavailability. |
| Fortified Foods | Orange juice, tofu, cereals | Vary depending on fortification | Read labels carefully to determine calcium content. |
| Other Sources | Almonds, sesame seeds, canned salmon (with bones) | Moderately high in some | Include in a balanced diet for additional calcium intake. |
Note: The calcium content in foods can vary depending on preparation methods and specific types of food. Consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized dietary recommendations for optimal calcium intake.
Magnesium Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Magnesium plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, and its importance extends to muscle health. This crucial mineral is essential for proper muscle contraction and relaxation. Without adequate magnesium levels, muscles can experience spasms and painful cramps, disrupting daily activities. Understanding the intricate relationship between magnesium and muscle function is key to addressing these debilitating issues.Magnesium is a fundamental element in the intricate dance of muscle contractions.
It acts as a catalyst, facilitating the movement of calcium ions within the muscle cells. Calcium, as we discussed earlier, is vital for triggering the process of muscle contraction. Magnesium helps regulate calcium levels, ensuring a smooth and controlled contraction-relaxation cycle. When magnesium levels are insufficient, this delicate balance is disrupted, leading to an uncontrolled influx of calcium ions into the muscle cells.
This, in turn, triggers sustained muscle contractions, resulting in painful cramps. This disruption is a common cause of muscle spasms and cramps.
Magnesium’s Role in Muscle Function
Magnesium is critical for the proper functioning of muscle cells. It helps maintain the electrical signals that control muscle contractions. Without sufficient magnesium, these signals can become erratic, leading to uncontrolled muscle spasms and the painful cramps we often experience. Furthermore, magnesium aids in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy source for muscle contractions.
Insufficient magnesium hinders ATP production, making muscles less efficient and more susceptible to cramping.
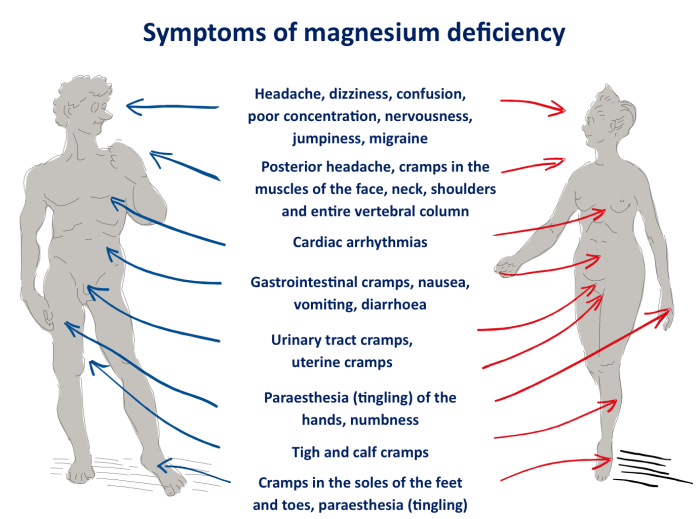
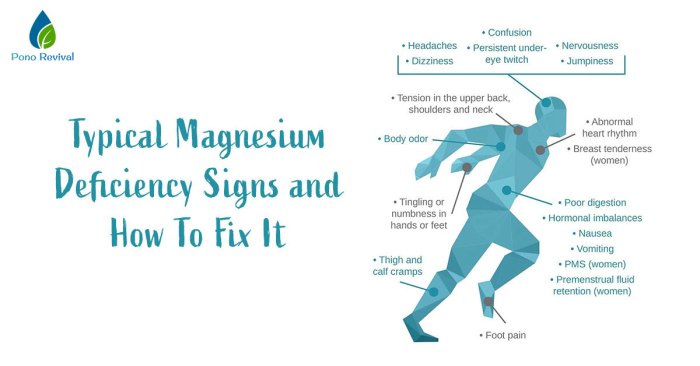
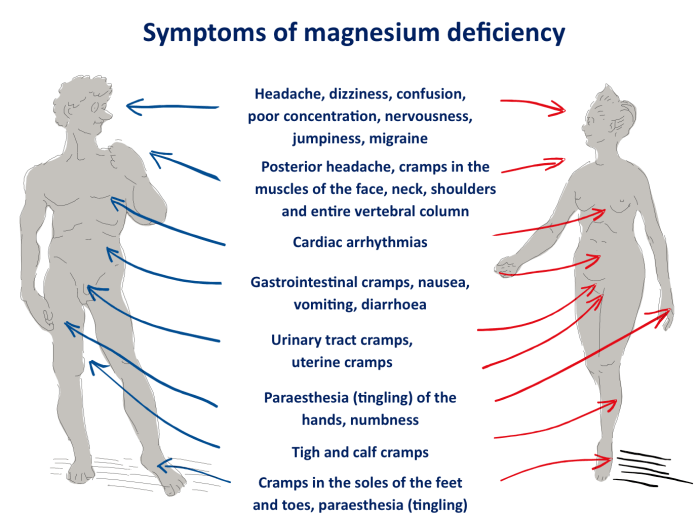
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency can manifest in various ways, affecting different parts of the body. The symptoms often overlap with those of calcium deficiency, making diagnosis challenging. Understanding the unique characteristics of magnesium deficiency symptoms is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Foods Rich in Magnesium
A balanced diet is crucial for maintaining adequate magnesium levels. Many foods are excellent sources of this essential mineral. These include leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Dark chocolate, while a treat, also contains a significant amount of magnesium. Consuming a variety of these foods can help ensure sufficient intake.
- Leafy green vegetables, like spinach and kale, are packed with magnesium.
- Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and pumpkin seeds, are excellent sources of magnesium.
- Whole grains, like brown rice and quinoa, provide magnesium along with other essential nutrients.
- Legumes, including beans and lentils, are a great source of magnesium.
- Certain fish and seafood contain magnesium.
Comparison of Calcium and Magnesium Deficiencies
The symptoms of calcium and magnesium deficiencies can overlap, making accurate diagnosis crucial. A detailed understanding of these differences can aid in determining the specific deficiency and its treatment.
| Characteristic | Calcium Deficiency | Magnesium Deficiency | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle Cramps | Often localized, especially in hands and feet | Often widespread, affecting multiple muscle groups | Muscle cramps, spasms, twitches |
| Fatigue | Can occur, but may be less pronounced | Frequently reported, potentially severe | Weakness, lethargy, tiredness |
| Nerve Function | Can affect nerve conduction, leading to tingling or numbness | Can disrupt nerve signals, leading to muscle spasms | Tingling, numbness, seizures |
| Heart Health | Can potentially affect heart rhythm | May impact heart function, including irregular heartbeats | Irregular heartbeat, palpitations |
Potassium Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Potassium plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, and its importance in muscle contraction is significant. Without adequate potassium levels, the proper transmission of nerve impulses and muscle relaxation can be compromised, potentially leading to muscle cramps. Understanding the connection between potassium deficiency and muscle cramps is crucial for preventative measures and effective treatment.
The Significance of Potassium in Muscle Function
Potassium is an essential electrolyte that helps maintain the proper balance of fluids inside and outside muscle cells. This balance is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses and for muscle contraction and relaxation. When potassium levels are low, this delicate balance is disrupted, which can lead to a variety of symptoms, including muscle cramps. Potassium is also essential for nerve function and regulating blood pressure.
The Relationship Between Potassium Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Potassium deficiency, also known as hypokalemia, can disrupt the electrical signals that control muscle contractions. This disruption can result in involuntary muscle spasms and cramps, particularly in the legs, feet, and arms. Other symptoms may include fatigue, weakness, and irregular heartbeat. The severity of symptoms varies depending on the degree of potassium deficiency. In severe cases, hypokalemia can be life-threatening.
Potassium-Rich Foods
A balanced diet is key to maintaining adequate potassium levels. Many fruits, vegetables, and dairy products are excellent sources of potassium. Examples include bananas, oranges, potatoes, sweet potatoes, spinach, yogurt, and beans. Incorporating these foods into your daily diet can help prevent potassium deficiency and its associated symptoms, such as muscle cramps.
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments for Potassium Deficiency
| Symptoms | Causes | Treatments | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle cramps, particularly in the legs and feet | Inadequate dietary intake of potassium, excessive potassium loss through urine (diuretic use, vomiting, diarrhea), certain medications (diuretics), and underlying health conditions (kidney disease, Cushing’s syndrome) | Dietary changes to include potassium-rich foods, potassium supplements (under medical supervision), and addressing any underlying medical conditions. | Muscle cramps can be a sign of several other conditions. Consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. |
| Fatigue and weakness | Similar to muscle cramps, potassium deficiency, excessive fluid loss, and other underlying health conditions can cause fatigue and weakness. | Increasing potassium intake, ensuring adequate hydration, and treating underlying medical conditions. | Fatigue and weakness are common symptoms, and it is crucial to consult a doctor to determine the root cause. |
| Irregular heartbeat | Potassium plays a crucial role in regulating heart function. Low potassium levels can disrupt the electrical signals in the heart, potentially leading to abnormal heart rhythms. | Potassium supplementation under medical guidance, addressing the underlying causes, and monitoring heart rate and rhythm. | Irregular heartbeats require immediate medical attention. |
| Nausea and vomiting | Electrolyte imbalance, including potassium deficiency, can contribute to nausea and vomiting. | Replenishing potassium levels and treating the underlying cause of the nausea and vomiting. | Consult a doctor for any severe or persistent nausea and vomiting. |
Vitamin D Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Vitamin D, often dubbed the “sunshine vitamin,” plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, including muscle function. It’s essential for calcium absorption, a key mineral for strong bones and healthy muscles. A deficiency in vitamin D can disrupt this process, potentially leading to a variety of symptoms, including muscle cramps. Understanding the connection between vitamin D, calcium, and muscle function is key to addressing this issue.Vitamin D’s impact on muscle function extends beyond its role in calcium absorption.
Magnesium deficiency is a common culprit behind those pesky muscle cramps. Understanding the progression of health conditions like type 2 diabetes is also important, as it can sometimes be linked to muscle issues. For example, exploring the stages of type 2 diabetes can reveal potential underlying causes. While other factors can contribute, magnesium is often a key player in preventing muscle cramps.
It directly influences muscle protein synthesis and repair. Adequate vitamin D levels are necessary for optimal muscle contraction and relaxation. A deficiency can result in muscle weakness, fatigue, and an increased susceptibility to muscle cramps. These cramps can be particularly problematic, affecting daily activities and overall well-being.
The Role of Vitamin D in Calcium Absorption
Vitamin D is a critical factor in the absorption of calcium from the digestive system. It acts like a key, unlocking the mechanism for calcium to enter the bloodstream and be utilized by the body. Without sufficient vitamin D, calcium absorption is compromised, leading to lower calcium levels, which can strain the muscles and increase the likelihood of cramps.
This connection highlights the importance of maintaining healthy vitamin D levels for optimal calcium utilization.
Vitamin D’s Influence on Muscle Function
Vitamin D directly impacts muscle protein synthesis and repair. It plays a key role in the process of muscle contraction and relaxation. A deficiency in vitamin D can disrupt these processes, potentially leading to muscle weakness, fatigue, and an increased risk of muscle cramps. This is because the muscles may not receive the necessary calcium and other minerals for optimal function.
Importance of Sun Exposure
Sunlight is a primary source of vitamin D for the body. When skin is exposed to sunlight, the body converts a precursor molecule into active vitamin D. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy vitamin D levels. Regular sun exposure, within safe limits, is essential for preventing deficiencies and supporting overall well-being. Spending time outdoors, particularly during midday hours, can significantly contribute to vitamin D production.
However, it’s important to remember that excessive sun exposure can have detrimental health effects, so moderation is key.
Vitamin D Sources
Adequate intake of vitamin D can be achieved through a combination of dietary sources and sun exposure. Understanding the various sources and their respective vitamin D content can help individuals create a balanced diet.
| Food Source | Vitamin D Content (IU) | Serving Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty Fish (Salmon, Tuna, Mackerel) | 100-400 | 3 ounces | Excellent source of vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids. |
| Egg Yolks | 10-20 | 1 large egg | A modest but reliable source of vitamin D. |
| Fortified Foods (Milk, Yogurt, Cereals) | 2-100 | Serving size varies | Often fortified with vitamin D, offering a convenient way to increase intake. |
| Mushrooms | 2-20 | 1 cup | Exposure to UV light can increase vitamin D content. |
Other Potential Contributing Factors
Muscle cramps, unfortunately, aren’t always caused by a simple vitamin deficiency. Several other factors can play a significant role in their onset, often interacting with and exacerbating the effects of nutrient deficiencies. Understanding these additional contributors is crucial for a comprehensive approach to preventing and managing muscle cramps.
Dehydration
Dehydration significantly impairs the body’s ability to regulate electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, and calcium. This imbalance can directly trigger muscle spasms. Athletes, particularly those participating in intense or prolonged physical activity, are especially vulnerable to dehydration-induced cramps. Similarly, individuals in hot climates or those with underlying health conditions that increase fluid loss are also at higher risk.
The body’s ability to utilize and store vitamins is impacted by hydration levels, further highlighting the interplay between dehydration and vitamin deficiencies.
Overexertion and Overtraining
Excessive physical activity, especially without adequate rest and recovery, can lead to muscle fatigue and strain. This increased stress on muscles can trigger micro-tears and inflammation, creating an environment conducive to cramps. Chronic overtraining can also disrupt the body’s ability to maintain optimal electrolyte balance, making it more susceptible to muscle cramps, especially if combined with inadequate nutrient intake.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, like nerve disorders, thyroid problems, and kidney disease, can increase the likelihood of muscle cramps. These conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the nervous system and muscles, impacting the body’s ability to regulate muscle contractions. Moreover, these conditions can lead to electrolyte imbalances, which further contributes to the risk of cramps. The relationship between these conditions and vitamin deficiencies can be complex, as some conditions might directly impact nutrient absorption or excretion.
Medications
Some medications can induce muscle cramps as a side effect. Diuretics, for instance, can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly potassium loss. Certain statins, commonly prescribed for cholesterol management, have also been linked to muscle cramps. When considering medications and vitamin deficiencies, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach to managing both the medication side effects and potential underlying deficiencies.
Lifestyle Factors
Poor posture and repetitive movements can strain specific muscle groups, increasing the risk of cramps. Similarly, prolonged periods of sitting or standing without adequate movement can contribute to muscle stiffness and fatigue. Lifestyle factors can also influence vitamin intake, such as a diet lacking in fruits and vegetables. These interactions between lifestyle choices and vitamin intake highlight the need for a holistic approach to muscle cramp prevention.
Muscle cramps can be a real pain, and often a deficiency in magnesium is the culprit. While magnesium is crucial for muscle function, a good way to potentially supplement your diet and potentially improve magnesium levels is by exploring different teas, like black tea vs green tea. Ultimately, though, if you’re experiencing persistent muscle cramps, it’s always best to consult a doctor to pinpoint the exact cause and get personalized advice on how to address it.
Table of Potential Causes of Muscle Cramps
| Potential Cause | Description | Relationship to Vitamin Deficiencies | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | Insufficient water intake disrupts electrolyte balance. | Dehydration can exacerbate existing vitamin deficiencies, particularly those related to electrolytes. | Prolonged exercise without adequate hydration, hot weather exposure. |
| Overexertion/Overtraining | Excessive physical activity without adequate rest and recovery. | Overexertion can deplete the body’s vitamin stores, leading to deficiencies. | Intense training schedules, lack of rest between workouts. |
| Underlying Medical Conditions | Nerve disorders, thyroid problems, kidney disease, etc. | Underlying conditions can disrupt nutrient absorption and metabolism, contributing to deficiencies. | Diabetes, multiple sclerosis, chronic kidney disease. |
| Medications | Certain medications can cause muscle cramps as a side effect. | Some medications, like diuretics, can induce electrolyte imbalances, impacting vitamin levels. | Diuretics, statins. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Poor posture, repetitive movements, prolonged sitting/standing. | Poor lifestyle choices can negatively affect dietary intake of vitamins. | Sedentary lifestyle, improper posture during work. |
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being, including muscle function. It provides the necessary nutrients to support muscle growth, repair, and contraction. Proper nutrition plays a vital role in preventing muscle cramps, particularly those related to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals. Consuming a balanced diet rich in these nutrients ensures adequate intake of crucial elements for optimal muscle health.A balanced diet is more than just eating the right foods; it’s about eating a variety of foods that provide the right mix of vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
This variety is essential to ensure the body receives all the nutrients it needs to function optimally. Muscle cramps can often be attributed to insufficient intake of specific vitamins and minerals, and a balanced diet helps prevent such deficiencies.
Healthy Diet for Muscle Health
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides the building blocks for strong, healthy muscles. These foods contain the essential vitamins and minerals that support muscle function. Adequate hydration is also critical for optimal muscle performance and prevention of cramps.
Healthy Meal Suggestions
A balanced diet should encompass a variety of foods that provide a range of essential nutrients. This includes a mix of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. The following table provides examples of healthy meals incorporating foods high in vitamins and minerals crucial for muscle health.
| Meal | Protein Source | Fruits/Vegetables | Grains/Starches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast (Oatmeal with Berries and Nuts) | Nuts (almonds, walnuts) | Berries (strawberries, blueberries) | Oatmeal |
| Lunch (Chicken Salad Sandwich on Whole Wheat Bread) | Chicken breast | Lettuce, tomato, cucumber | Whole wheat bread |
| Dinner (Salmon with Roasted Vegetables and Quinoa) | Salmon | Broccoli, carrots, bell peppers | Quinoa |
| Snack (Greek Yogurt with Fruit and Granola) | Greek yogurt | Banana, apple | Granola (whole grain) |
Diagnosis and Treatment: What Vitamin Deficiency Causes Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps, while often harmless, can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the diagnosis and appropriate treatment is crucial for effective management and preventing recurrence. Proper diagnosis involves identifying the underlying cause, which might be a vitamin deficiency or other contributing factors. This section delves into the diagnostic process and Artikels various treatment options.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Seeking professional medical advice is paramount when experiencing persistent or severe muscle cramps. A healthcare provider can accurately assess the situation, rule out any serious underlying medical conditions, and guide you towards the most suitable treatment plan. Self-treating can be risky, potentially masking a more significant health problem.
Methods for Diagnosing Vitamin Deficiencies
Several methods are employed to diagnose vitamin deficiencies. These include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history, including dietary habits, lifestyle factors, and any existing health conditions, is essential. A physical examination, focusing on muscle strength and tone, can provide further insights. For example, a doctor might ask about dietary habits and note any unusual symptoms in addition to muscle cramps.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests are crucial for measuring the levels of various vitamins and minerals in the blood. These tests can detect deficiencies in vitamins like D, B12, calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Specific blood tests will be ordered depending on the suspected deficiency and the overall health picture.
- Dietary Analysis: A detailed dietary analysis can highlight potential dietary deficiencies that might contribute to muscle cramps. This can include assessing food intake and identifying potential gaps in essential nutrients.
- Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, might be necessary to rule out other medical conditions that can mimic muscle cramps, such as nerve compression or bone problems. For instance, an MRI scan could help identify nerve impingement, a possible cause of persistent cramps.
Treatment Options for Muscle Cramps
Effective treatment for muscle cramps focuses on addressing the underlying cause. If a vitamin deficiency is identified, supplementation is often part of the solution.
Treatment Summary Table
| Treatment | Description | Effectiveness | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin Supplements (as prescribed) | Replenishing deficient vitamins, such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, or vitamin D, through oral supplements. | Generally effective if the deficiency is confirmed and supplementation is appropriate. | Supplements should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Dosage and type should be tailored to the specific deficiency and individual needs. Overdosing on supplements can have negative effects. |
| Dietary Modifications | Increasing intake of foods rich in the deficient vitamin. | Can be effective in combination with supplements, especially for mild deficiencies. | Dietary changes should be made gradually and in consultation with a nutritionist or dietician to ensure a balanced intake of all essential nutrients. Some dietary changes may not be suitable for everyone. |
| Hydration | Maintaining adequate fluid intake, particularly during and after physical activity. | Crucial for preventing and treating muscle cramps, regardless of the cause. | Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can mitigate many instances of muscle cramps. |
| Physical Therapy | Stretching, massage, and other physical therapy techniques to improve muscle flexibility and reduce cramping. | Can be beneficial for treating chronic or recurring muscle cramps. | Physical therapy should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and condition. It can be particularly useful in combination with other treatments. |
Last Point
In conclusion, understanding the connection between vitamin deficiencies and muscle cramps is crucial for preventative measures and effective treatment. A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins, coupled with adequate hydration, is vital in maintaining healthy muscle function. This article has highlighted the key vitamins involved and how their deficiencies can manifest as muscle cramps. However, proper diagnosis and treatment always require consultation with a healthcare professional.
If you experience persistent muscle cramps, seeking professional advice is strongly recommended to uncover the root cause and implement the most appropriate course of action.