Major depressive disorder medications are a crucial aspect of treatment for those struggling with this condition. This guide delves into the various types of medications used, exploring their mechanisms of action, effectiveness, and potential side effects. We’ll also examine factors influencing medication selection, patient adherence strategies, and emerging treatment directions. Get a deeper understanding of…
Tag: treatment
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome vs Fibromyalgia A Deep Dive
Chronic fatigue syndrome vs fibromyalgia: Understanding these conditions is crucial for those affected and those supporting them. This exploration delves into the complexities of diagnosing, treating, and living with these often-misunderstood illnesses. We’ll examine their shared and distinct symptoms, explore the challenges in diagnosis, and investigate the potential underlying mechanisms. Both conditions significantly impact daily…
Antibiotics for Sinus Infection A Comprehensive Guide
Antibiotics for sinus infection sets the stage for a deep dive into the world of sinus health. We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments, highlighting the crucial role of antibiotics in resolving bacterial infections. Understanding the different types of antibiotics, their mechanisms, and potential side effects is key to making informed decisions about your health….
Life Expectancy in Parkinsons Disease
Life expectancy in parkinsons disease – Life expectancy in Parkinson’s disease is a complex issue, influenced by various factors. This exploration delves into the average lifespan of individuals diagnosed with Parkinson’s, examining the impact of disease progression, comorbidities, treatment strategies, and lifestyle choices. We’ll also look at historical trends, the role of support systems, and…
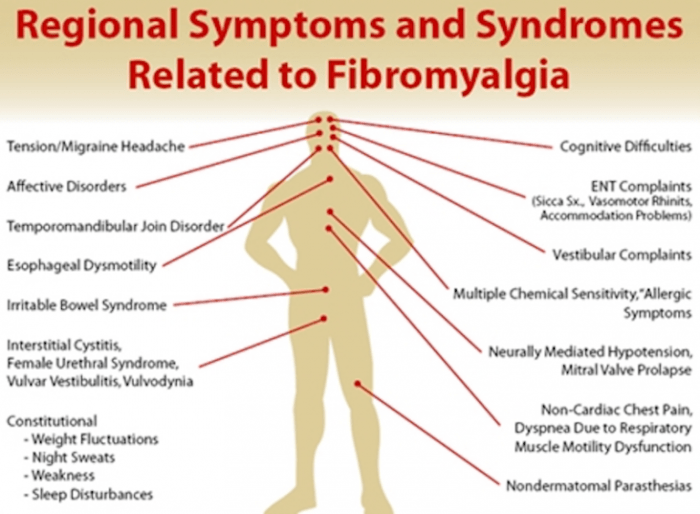
Fibromyalgia Primary or Secondary Unveiling the Types
Fibromyalgia primary or secondary is a complex condition that often stumps doctors and patients alike. Understanding the distinctions between primary and secondary forms is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective management. This exploration delves into the characteristics, causes, and treatment approaches for both, offering a comprehensive guide for anyone affected by or seeking to understand…