Tourniquet for first aid kit: This crucial tool is often overlooked, yet it plays a vital role in emergency situations. Knowing how to use it properly can mean the difference between life and death. Different types of tourniquets exist, each with specific characteristics and applications, which we’ll explore in detail. Proper selection, storage, and maintenance are essential to ensure its effectiveness when needed.
This guide will cover everything you need to know about integrating a tourniquet into your first aid kit, including training, protocols, and legal considerations.
From understanding the various tourniquet types and their strengths to recognizing the critical situations where immediate action is necessary, this comprehensive guide empowers you to approach first aid with confidence. We’ll delve into the essential considerations for selecting the right tourniquet, and how to ensure proper storage and maintenance for optimal performance. This knowledge will equip you to act decisively and effectively in emergency situations.
Introduction to Tourniquets in First Aid Kits
Tourniquets are crucial components of any comprehensive first aid kit, serving as a life-saving tool in situations involving severe bleeding. They act as a rapid, effective method to stop uncontrolled blood loss, a leading cause of preventable death in trauma cases. Proper understanding and application of tourniquets are essential for anyone who may encounter such emergencies.Tourniquets work by applying pressure to the blood vessels in a limb, effectively cutting off blood flow.
This intervention is critical when other methods, like direct pressure, are insufficient to control the bleeding. The effectiveness of a tourniquet hinges on proper application, as improper use can lead to nerve damage or tissue necrosis. Knowing when and how to use a tourniquet is a valuable skill in emergency preparedness.
Types of Tourniquets
Tourniquets come in various forms, each with its own application and features. Common types in first aid kits include those designed for both adults and children, ensuring appropriate sizing for different body types. This flexibility in design allows for effective use in a wide range of situations.
Essential Characteristics of a Tourniquet
A reliable tourniquet for a first aid kit should possess several key characteristics. Firstly, it should be easy to apply, minimizing reaction time in critical situations. Secondly, it must be adjustable to accommodate various limb sizes and ensure adequate pressure. Durability and a long lifespan are also crucial, given the potential for repeated use. Finally, a clear and concise application instruction manual is critical to ensuring correct usage.
A crucial item for any well-stocked first aid kit is a tourniquet. Knowing how to use it effectively can be a lifesaver in emergency situations. While focusing on the practical aspects of a tourniquet, it’s also important to consider the nutritional powerhouses that can aid in recovery, like watercress. Learning about the nutritional benefits of watercress, for example, from a site like watercress benefits and nutrition profile , can be incredibly insightful.
Ultimately, the tourniquet is a critical tool for managing life-threatening bleeding, and understanding its use is a vital part of preparedness.
Importance of Proper Tourniquet Application
Correct tourniquet application is paramount to minimize complications. Applying the tourniquet too tightly can lead to nerve damage or tissue damage. Conversely, applying it too loosely may not effectively control the bleeding. The location of application should also follow established protocols, prioritizing critical arteries and minimizing the risk of further harm.
A tourniquet is a crucial item for any first aid kit, and knowing how to use it properly is vital in life-threatening situations. While it’s not something you’d want to use frequently, understanding the potential risks of a severe reaction to gluten allergies, like those often seen in signs of gluten allergy , highlights the importance of preparedness.
Having a well-stocked kit with a functioning tourniquet can make all the difference in a medical emergency.
Tourniquet Types, Materials, and Typical Application
| Tourniquet Type | Material | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Fabric Tourniquet | Strong woven fabric with a tightening mechanism | Suitable for various limb sizes and situations. |
| Military-style tourniquet | Durable, adjustable straps | Ideal for use in high-impact scenarios, often found in military and EMS settings. |
| Improvised Tourniquet | Available from any strong, long material like belts, cloths or even strips of fabric | Can be constructed using available materials in emergency situations, where a specific tourniquet is not readily available. |
Tourniquet Selection for First Aid Kits
Choosing the right tourniquet for your first aid kit is crucial for effective emergency response. A well-selected tourniquet can significantly improve outcomes in life-threatening situations involving severe bleeding. This involves understanding the various types, their pros and cons, and the specific needs of your intended users and the environment where the kit will be used.Proper tourniquet selection requires careful consideration of several factors, from the design and materials to the user’s familiarity and the potential use cases.
This process ensures that the chosen tourniquet is both effective and safe to use in a range of situations.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Tourniquets
The selection process for tourniquets involves evaluating different criteria to determine the best fit for a specific first aid kit. Factors like ease of use, size, and cost are critical considerations. The chosen design should be intuitive and allow for rapid application, even under stress. Furthermore, the tourniquet’s size should accommodate a wide range of patients, while the cost should align with the budget constraints.
Comparison of Different Tourniquet Designs
Tourniquets come in various designs, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences allows for a more informed decision. The most common designs include the traditional, the military, and the self-adhering type.
- Traditional Tourniquets: These are often made of cloth or similar material, and they typically require a separate tightening device. They are generally more affordable but may require more practice to apply correctly. The added step of securing the tightening mechanism can increase application time in a critical situation.
- Military-style Tourniquets: Often featuring a ratchet or similar mechanism for controlled tightening, these offer a more streamlined application process. This can be crucial in high-stress situations where speed is of the essence. They often come with more durable materials and a larger size range. However, they tend to be more expensive.
- Self-adhering Tourniquets: These are designed with a strap or material that adheres to the skin. This reduces the need for separate tightening devices, making the application process quicker. However, they may require more care in removing them to avoid skin irritation. The ease of use and speed of application make this a popular choice.
Widely Used and Trusted Tourniquet Models
Several tourniquet models are frequently recommended and used in first aid kits. These are typically chosen based on their effectiveness and user feedback.
- Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT): A popular choice for military and civilian first aid kits, the CAT is known for its ease of use and speed of application. Its design, incorporating a simple ratchet mechanism, allows for quick and efficient tightening. The wide range of sizes and the high reliability of its use are also key factors in its popularity.
- Israeli-style Tourniquets: Often made of sturdy material and featuring a simple tightening mechanism, these tourniquets are known for their durability and effectiveness. Their ease of use and reliability have made them popular choices in various first aid settings.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
Safety and efficacy are paramount when selecting a tourniquet. The chosen model should be easy to use in a variety of situations and ensure minimal risk of complications. Furthermore, the model should be thoroughly tested for safety and effectiveness to avoid unnecessary risk in critical situations.
Tourniquet Model Comparison Table
| Tourniquet Model | Ease of Use | Size Range | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combat Application Tourniquet (CAT) | High | Large | Medium |
| Israeli-style Tourniquet | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Self-adhering Tourniquet | High | Medium | Medium-High |
Storage and Maintenance of Tourniquets
Proper storage and maintenance of tourniquets in a first aid kit are crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and safety. A well-maintained tourniquet is a life-saving tool, ready to be deployed when needed. Neglecting these procedures can compromise the tourniquet’s integrity and potentially lead to serious consequences in an emergency.Tourniquets are essential medical tools, but their effectiveness relies heavily on proper handling and storage.
They need to be easily accessible and ready for use, yet safeguarded from contamination or damage. Careful attention to these details is paramount for optimal performance.
Recommended Storage Procedures
Tourniquets should be stored in a designated area within the first aid kit. A clear, labeled compartment or pouch is essential to ensure quick retrieval without searching. The specific placement depends on the kit’s design and overall layout, but accessibility is key. The tourniquet should be stored in a dry, cool place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
These environmental factors can degrade the material and reduce the tourniquet’s effectiveness over time.
Maintaining Tourniquet Integrity
Regular inspection of the tourniquet is vital. Check for any signs of damage, such as fraying, tears, or broken components. Any damage, no matter how minor, requires immediate replacement of the tourniquet. Periodically inspect the straps and buckles for signs of wear and tear. These components are critical for proper functioning and should be examined regularly.
Handling Techniques to Avoid Damage
Avoid unnecessary handling of the tourniquet. Only handle the tourniquet when necessary for inspection or storage. Avoid forceful pulling or bending of the straps, buckles, or any other components. The tourniquet should be handled with care and respect for its function.
Precautions to Prevent Contamination
Always ensure the tourniquet is stored in a clean, sealed container. This helps prevent contamination by dust, dirt, or other foreign materials. Do not expose the tourniquet to potentially contaminated surfaces or fluids. If the tourniquet becomes contaminated, it must be immediately replaced. Contamination can compromise its sterility and potentially introduce pathogens.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Storage and Maintenance
- Inspection: Visually inspect the tourniquet for any signs of damage (tears, fraying, broken parts) or contamination. Any damage or contamination warrants immediate replacement.
- Cleaning (if necessary): If the tourniquet shows signs of contamination, clean it with a suitable disinfectant. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Storage: Store the tourniquet in a clean, dry, and designated area within the first aid kit. Ensure it is properly sealed and labeled for easy retrieval.
- Regular Checks: Schedule regular inspections of the tourniquet, ideally during routine first aid kit checks.
- Replacement: Replace the tourniquet according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or when damage or contamination is observed.
Training and Protocols for Tourniquet Use
Tourniquets, crucial life-saving tools, demand meticulous training and precise protocols for effective application. Proper training ensures responders can confidently and correctly utilize this tool in critical situations, maximizing its potential to save lives. This section delves into the essential training procedures and protocols for tourniquet use, providing a comprehensive guide for first aid responders.The application of a tourniquet is a high-stakes procedure.
Having a tourniquet in your first aid kit is crucial, especially for potential life-saving situations. Knowing how to use it effectively is essential, but so too is understanding how to cope with the emotional and physical challenges of various health conditions. For instance, navigating a condition like wet AMD can be emotionally taxing, but resources like wet amd coping support and living well can provide valuable guidance on maintaining well-being.
Ultimately, preparedness for any situation, whether it’s a medical emergency or dealing with a chronic condition, involves understanding your options and resources, and having a reliable tourniquet is a key element in that preparedness.
A thorough understanding of the circumstances under which a tourniquet is necessary, coupled with practiced application technique, is paramount. Errors in judgment or execution can lead to severe complications, and proper training minimizes these risks.
Necessary Training Procedures
Training for tourniquet application should encompass both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Responders must understand the anatomy and physiology involved, including the critical importance of rapid intervention to prevent or minimize shock and tissue damage. Practical exercises should be performed under supervision, ensuring accuracy and consistency. This includes various scenarios, such as upper and lower extremity bleeding, with varying degrees of severity.
Protocol for Tourniquet Application
The protocol for tourniquet application should be clear, concise, and easily memorized. The critical elements of a tourniquet protocol include a clear decision-making process to determine when a tourniquet is absolutely necessary. It should also detail the precise steps involved in application, from initial assessment to definitive placement.
Steps Involved in Tourniquet Application
The application process must be meticulously explained and demonstrated. It is crucial to emphasize the following steps:
- Initial Assessment: Assess the patient’s condition, determine the extent of bleeding, and identify the location of the wound. Immediate stabilization is essential.
- Positioning: Position the patient appropriately to facilitate the application process. Consider the patient’s comfort and the ease of access to the affected limb.
- Tourniquet Placement: Apply the tourniquet proximal (closer to the heart) to the wound, ensuring proper tension. Avoid placing it directly over joints.
- Application Technique: Tighten the tourniquet using the correct method and tools, ensuring adequate pressure. Never use a tourniquet over clothing. A firm and steady application is crucial.
- Documentation: Record the time the tourniquet was applied and the patient’s condition before, during, and after the procedure.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the patient’s vital signs and look for signs of complications.
Recognizing When a Tourniquet is Needed
A tourniquet should only be used in situations where significant, uncontrolled bleeding threatens a person’s life. Factors that necessitate its use include a high-pressure arterial bleed that is not controllable by other methods, like direct pressure or pressure points.
Situations Requiring a Tourniquet
| Injury Type | Description | Justification for Tourniquet Use |
|---|---|---|
| Severe Arterial Bleeding | High-pressure bleeding from an artery, often spurting blood. | Immediate intervention is crucial to stop the bleeding. |
| Massive Blood Loss | Large volume of blood loss, often accompanied by rapid pulse weakening and shock. | Significant blood loss demands immediate intervention to prevent death. |
| Uncontrollable Venous Bleeding | Uncontrollable bleeding from a vein, potentially severe. | If other methods fail, a tourniquet might be necessary. |
| Amputations | Severed limbs, often with significant arterial bleeding. | Stop bleeding to prevent further shock and potential organ damage. |
| Severe Trauma | Wounds that cannot be controlled by direct pressure. | The severity of the injury and uncontrolled bleeding necessitate immediate action. |
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Tourniquet use in emergency situations carries significant legal and ethical weight. Understanding the potential implications and responsibilities associated with deploying a tourniquet is crucial for both medical professionals and laypeople who may find themselves in a position to assist. This section delves into the legal frameworks, ethical considerations, and practical steps to navigate potential legal issues that might arise from using a tourniquet.
Legal Implications of Tourniquet Use
The legal landscape surrounding tourniquet use varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances. Generally, individuals acting in good faith and within the scope of their training or reasonable actions are protected from liability. However, misuse or failure to follow established protocols can expose individuals to potential legal challenges. The key lies in adhering to best practices and documenting the situation thoroughly.
Ethical Considerations for Tourniquet Deployment
Ethical considerations are intertwined with legal ones. The decision to use a tourniquet should always prioritize the patient’s well-being and safety. Factors such as the severity of the bleeding, the potential for further harm if not used, and the availability of other resources should be weighed carefully. Ethical considerations include ensuring the patient’s comfort and dignity throughout the process, and promptly seeking additional medical help.
Guidelines and Regulations Concerning Tourniquet Use
Various organizations, such as the American College of Surgeons (ACS), provide guidelines and protocols for tourniquet use. These resources emphasize the importance of proper training, consistent application techniques, and meticulous documentation. These guidelines aim to minimize risks while maximizing the chances of successful outcomes. Adhering to these protocols is critical for minimizing legal and ethical challenges.
Addressing Potential Legal Issues
In the unfortunate event of a legal challenge related to tourniquet use, a thorough understanding of the incident is essential. This includes a detailed account of the situation, the steps taken, and the reasons for using the tourniquet. Maintaining accurate records, including photos and documentation of the injuries, can provide valuable support during any legal proceedings. Seeking legal counsel specializing in medical malpractice cases is recommended.
Table of Key Legal Considerations and Actions
| Key Legal Consideration | Corresponding Actions |
|---|---|
| Proper Training and Certification | Ensure all individuals deploying tourniquets possess appropriate training and certification. |
| Documentation of Incident | Maintain a detailed record of the incident, including time of application, location, and circumstances surrounding the tourniquet use. |
| Patient Consent (if possible) | Obtain consent from the patient, if possible and appropriate, prior to applying the tourniquet. |
| Immediate Medical Intervention | Prioritize rapid transport to a medical facility and continuous monitoring of the patient’s condition after tourniquet application. |
| Following Protocols | Adhere to established protocols and guidelines for tourniquet use, and ensure that the tourniquet was used correctly. |
First Aid Kit Design Considerations

Optimizing a first aid kit for tourniquet use involves careful planning beyond simply including the device. A well-designed kit will ensure the tourniquet is readily accessible, protected from damage, and easily deployed during a critical situation. Proper placement and material selection are key elements for ensuring both the safety of the tourniquet and the efficiency of its deployment.
Tourniquet Compartment Design, Tourniquet for first aid kit
A dedicated compartment for the tourniquet is crucial. It should be easily accessible yet secure enough to prevent accidental deployment or damage to the tourniquet itself. The compartment should be designed to prevent the tourniquet from becoming entangled with other items within the kit.
Tourniquet Placement Within the Kit
The tourniquet should be positioned in a location that is easily grasped during a fast-paced emergency. Avoid placing it in a spot that might obscure other essential items or require significant searching. A good example is placing the tourniquet in a front, easily accessible pocket or compartment, ideally with a quick-release mechanism. For instance, a Velcro-fastened flap on a compartment would allow for rapid deployment.
Kit Configuration Examples
Several configurations can optimize tourniquet placement. A modular kit, with separate compartments for different categories of supplies, can easily accommodate a dedicated tourniquet compartment. A structured, layered kit with a front-facing pocket specifically for the tourniquet is also effective. A kit with a large, open compartment might not provide sufficient protection for the tourniquet, and may allow for entanglement with other items.
A smaller, zippered compartment could be used to maintain order and prevent items from shifting.
Material Selection for Tourniquet Compartment
The ideal material for a tourniquet compartment should be sturdy enough to withstand the rigors of transport and storage, while also allowing for easy access and retrieval. Water resistance is also crucial to protect the tourniquet from moisture damage. A durable, waterproof, and tear-resistant material like a high-quality nylon or a reinforced polyester is recommended. This would prevent the tourniquet from getting damaged during transportation or exposure to the elements.
The material should be lightweight, minimizing the overall weight of the kit.
Ideal Tourniquet Packaging
Proper packaging for the tourniquet is vital for its protection. The tourniquet should be packaged individually, in a waterproof, tear-resistant, and clear or transparent pouch or container, ideally with clear labeling and instructions. This individual packaging will prevent the tourniquet from being damaged or getting contaminated.
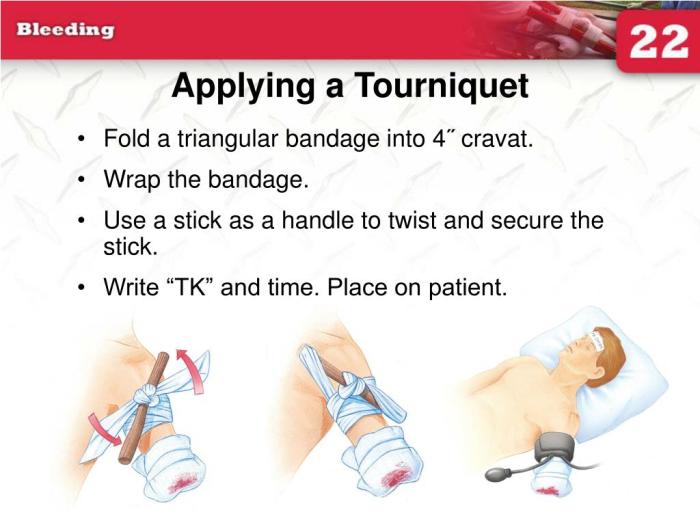
Tourniquet Application Illustrations
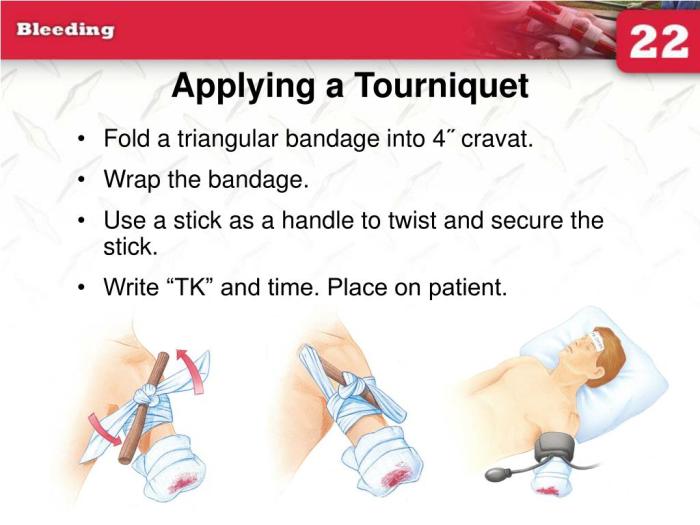
Tourniquets are critical life-saving tools in emergency situations, but their effective use requires precise application techniques. Incorrect application can lead to severe complications, such as nerve damage, tissue damage, or even limb loss. Mastering the correct procedures is crucial for anyone handling a tourniquet. Proper application minimizes harm and maximizes the chances of a positive outcome.
Tourniquet Application for Upper Arm Injuries
Correct application of a tourniquet on the upper arm is vital for controlling severe bleeding. A poorly placed tourniquet can cause irreparable harm. The illustration below demonstrates the proper technique for upper arm tourniquet application:
Imagine a diagram depicting the upper arm. The tourniquet is placed snugly around the upper arm, approximately 2 inches above the elbow. The tourniquet should be positioned in a straight line with the arm’s axis, not twisted or angled. The tightening mechanism should be visible and easily accessible. A second person or medical professional should apply firm pressure over the artery, perpendicular to the skin, to further compress the bleeding source.
Tourniquet Application for Lower Leg Injuries
For lower leg injuries, the application technique is slightly different from the upper arm. Understanding the anatomy and blood flow in the lower leg is critical. Incorrect application can lead to severe complications.
Imagine a diagram depicting the lower leg. The tourniquet is placed approximately 2 inches above the knee. The tourniquet should be positioned in a straight line with the leg’s axis. A second person or medical professional should apply firm pressure over the artery, perpendicular to the skin, to further compress the bleeding source. The tourniquet should be tightened until the bleeding stops, but not excessively.
Tourniquet Application for Thigh Injuries
Applying a tourniquet to the thigh requires careful consideration of the location and pressure points. The illustration below depicts the proper technique for thigh injuries:
Imagine a diagram depicting the thigh. The tourniquet is placed approximately 2 inches above the knee. The tourniquet should be positioned in a straight line with the leg’s axis. The tightening mechanism should be visible and easily accessible. A second person or medical professional should apply firm pressure over the artery, perpendicular to the skin, to further compress the bleeding source.
Step-by-Step Illustrated Guide for Limb Injuries
Proper tourniquet application involves a series of steps for different limb injuries. This guide helps in applying tourniquets to various injuries:
- Assess the situation: Determine the severity of the bleeding and the need for a tourniquet. The presence of severe, uncontrolled bleeding usually indicates a tourniquet is necessary.
- Select the appropriate tourniquet: Choose a tourniquet suitable for the size of the limb.
- Apply the tourniquet: Position the tourniquet 2 inches above the injury site, ensuring it is aligned with the limb’s axis.
- Tighten the tourniquet: Tighten the tourniquet until bleeding stops. Do not overtighten.
- Document the time: Record the time the tourniquet was applied.
- Continuously monitor the patient: Monitor the patient’s vital signs and for any signs of complications.
- Transport to medical facility: Immediately transport the patient to a medical facility for further treatment.
Final Conclusion: Tourniquet For First Aid Kit
In conclusion, equipping your first aid kit with a tourniquet is a critical decision. Proper understanding of selection, storage, and application procedures is paramount. This comprehensive guide has highlighted the significance of training and protocols, as well as the legal and ethical considerations. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you’re not just adding a tool, but potentially saving a life.
Remember, knowledge is power, and preparedness is key in times of crisis.