Steroids topical steroid strengths are crucial for treating various skin conditions. This guide delves into the different potencies, their applications, and potential side effects. Understanding the strengths and appropriate usage is vital for effective treatment and minimizing adverse reactions. We’ll explore the diverse range of skin conditions treatable with topical steroids, examining the factors determining the right strength for each case.
From mild inflammation to severe skin disorders, the right topical steroid strength can significantly impact treatment outcomes. This comprehensive overview will guide you through the potency levels, application methods, and potential side effects associated with various topical steroid strengths. Learn about the importance of following a healthcare professional’s instructions and understanding the unique considerations for specific skin conditions.
Introduction to Topical Steroids
Topical steroids, also known as topical corticosteroids, are a crucial part of treating various skin conditions. They are potent anti-inflammatory medications applied directly to the affected skin area. Their effectiveness stems from their ability to reduce inflammation and itching, often providing significant relief from discomfort and improving the appearance of the skin. Understanding how these medications work is essential for both patients and healthcare providers.Topical corticosteroids exert their effects by decreasing the production of inflammatory mediators within the skin.
This anti-inflammatory action results in a reduction of redness, swelling, and itching, which are common symptoms of many skin conditions. Their mechanisms of action typically involve suppressing the release of substances like histamine and prostaglandins that trigger the inflammatory response. These drugs work by binding to specific receptors in the skin, thus altering cellular processes and reducing inflammation.
Common Skin Conditions Treated with Topical Steroids
Topical steroids are frequently prescribed to treat a variety of skin conditions. These medications effectively address inflammatory skin conditions, including eczema, psoriasis, contact dermatitis, and various forms of allergic reactions. They also play a role in managing conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and some types of acne. The selection of the specific topical steroid and its strength will depend on the severity and type of the skin condition.
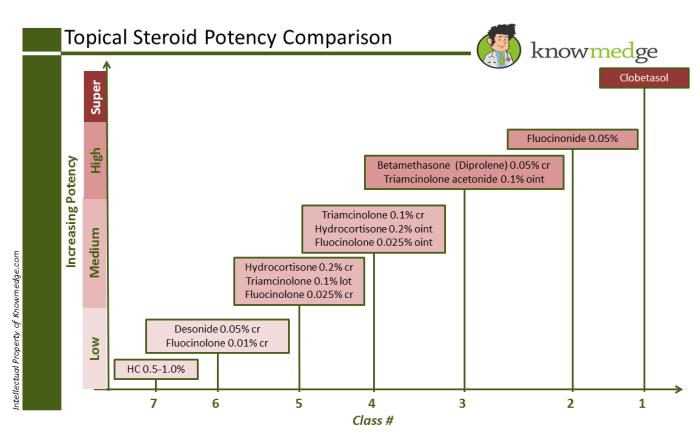
Classes of Topical Steroids
The potency of topical steroids varies significantly. This variation is crucial for treating different skin conditions effectively and minimizing potential side effects. The potency is often categorized into different classes.
| Class | Strength | Examples | Conditions Typically Treated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very High | 0.05% clobetasol propionate | Clobex, Temovate | Severe, recalcitrant eczema; psoriasis plaques |
| High | 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide | Kenalog, Aristocort | Moderate eczema, psoriasis plaques, contact dermatitis |
| Medium | 0.05% betamethasone valerate | Betnovate, Uticort | Mild eczema, seborrheic dermatitis |
| Low | 0.1% hydrocortisone | Hydrocortisone cream, lotion | Mild skin irritations, insect bites, rashes |
The table above highlights the different classes of topical steroids, their typical strengths, examples of available medications, and the types of skin conditions they are often used to treat. The choice of steroid depends on the specific condition and its severity. A healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate strength and type of topical steroid based on the individual patient’s needs.
Topical Steroid Strengths

Choosing the right strength of topical steroid is crucial for effective treatment without causing unwanted side effects. The potency of a topical steroid directly impacts its effectiveness and the potential for adverse reactions. Understanding the different strengths and their appropriate uses is essential for optimal skin health.
Comparing Topical Steroid Strengths
Different strengths of topical steroids are available to address various skin conditions with varying degrees of severity. This section presents a table outlining common strengths and their corresponding brand names, offering a practical overview.
Understanding topical steroid strengths is key for managing skin conditions, but did you know that your health insurance subsidy eligibility might depend on your income? Knowing how to calculate your MAGI, or Modified Adjusted Gross Income, for health insurance subsidy eligibility, is crucial for navigating healthcare costs. This is especially relevant when considering the varying strengths of topical steroids, and how different strengths affect treatment duration and potential side effects.
For a detailed guide on MAGI calculation, check out this helpful resource: magi calculation for health insurance subsidy eligibility. Ultimately, choosing the right topical steroid strength involves careful consideration of your individual needs and budget, alongside the correct MAGI calculation.
| Strength | Common Brand Names | Potency |
|---|---|---|
| 0.05% | Hydrocortisone | Low |
| 0.1% | Hydrocortisone | Low |
| 0.5% | Triamcinolone acetonide | Medium |
| 1% | Betamethasone valerate | Medium |
| 2.5% | Fluocinolone acetonide | High |
| 0.05% clobetasol propionate | Temovate | Very High |
Factors Determining Appropriate Strength
Several factors influence the selection of the optimal topical steroid strength. The severity of the skin condition, the location of the affected area, and the patient’s overall health are all critical considerations. A dermatologist can assess these factors and tailor the treatment to the individual’s needs. For example, a mild rash might only require a low-potency steroid, whereas a severe inflammatory condition might necessitate a higher potency option.
Importance of Correct Strength
Using the correct strength of topical steroid is paramount to achieving optimal results while minimizing the risk of adverse effects. Overuse of high-potency steroids can lead to skin thinning, stretch marks, and potentially even fungal infections. Furthermore, inappropriate use can delay healing and increase the likelihood of rebound inflammation.
Steroid Potency and Skin Condition Severity
The potency of the topical steroid should align with the severity of the skin condition. Mild conditions often respond well to low-potency steroids, whereas moderate to severe conditions may require higher potency options. The goal is to use the least potent steroid that effectively controls the inflammation and symptoms.
Strengths and Potential Side Effects
The table below contrasts different potency levels of topical steroids with their potential side effects. It’s crucial to remember that these are not exhaustive lists, and individual reactions can vary. Consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended for personalized advice.
| Potency Level | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|
| Low | Minimal side effects; possible delayed response in severe cases |
| Medium | Potential for skin thinning and atrophy; use for short periods |
| High | Increased risk of skin thinning, striae (stretch marks), and fungal infections; use cautiously and for a limited duration |
| Very High | Significant risk of skin atrophy, striae, and rebound inflammation; use only under strict medical supervision for short periods |
Understanding Potency Levels
Topical steroids come in varying strengths, and understanding these potency levels is crucial for effective and safe treatment. Choosing the right strength is vital, as using a stronger steroid than necessary can lead to unwanted side effects, while a weaker steroid may not provide sufficient relief. This section delves into the different potency classifications and how they affect clinical practice.
Potency Classification Explained
Topical steroids are categorized by their potency, reflecting their ability to reduce inflammation. These categories range from very mild to very strong, allowing physicians to tailor treatment to individual needs. The potency of a topical steroid is determined by its ability to suppress the inflammatory response at the site of application. This is a key factor in choosing the appropriate strength for a particular skin condition.
Different Potency Levels
Topical steroids are categorized into various potency classes, each with a unique strength. These potency levels directly influence the effectiveness and potential side effects of the treatment. The choice of potency depends on the severity of the skin condition and the patient’s individual needs. Factors such as the area of application and the duration of treatment are also considered.
Understanding topical steroid strengths is key, especially if you’re experiencing chest pain when coughing. A common issue is dealing with inflamed areas, and the right strength of topical steroid can make a real difference. If you’re struggling with a persistent cough and chest pain, you might want to explore the potential causes further, such as chest hurts when i cough.
Different strengths target different levels of inflammation, so finding the right one for your specific needs is important. Ultimately, the best course of action is to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate topical steroid strength for your situation.
Examples of Topical Steroids in Each Potency Class
Different topical steroids exhibit varying potencies. The selection of a specific topical steroid is tailored to the specific skin condition and the severity of the inflammatory response. Understanding the potency of different steroids is essential for appropriate clinical management.
Typical Potency Scale and Examples
| Potency Level | Examples | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Very Low | Hydrocortisone 1% | Suitable for mild skin conditions and widespread applications. Often used for initial treatment or as a maintenance therapy. |
| Low | Hydrocortisone valerate 0.2% | Slightly stronger than very low potency, suitable for mild to moderate skin conditions. May be used for limited areas or more persistent conditions. |
| Medium | Triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% | Effective for moderate skin conditions, particularly when used for shorter periods. May be used in limited areas to prevent the development of skin atrophy. |
| High | Fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% | Reserved for moderate to severe skin conditions that haven’t responded to lower potency steroids. Requires careful monitoring due to potential side effects. |
| Very High | Clobetasol propionate 0.05% | Strongest topical steroids. Used for severe, recalcitrant conditions where other treatments have failed. Must be used judiciously to prevent adverse effects like skin thinning. |
Clinical Implications of Varying Potency Levels
The choice of topical steroid potency directly influences the clinical outcomes and potential side effects. Using a stronger steroid than necessary may lead to skin thinning, stretch marks, or other adverse reactions. Conversely, using a weaker steroid may not effectively address the underlying inflammation. Therefore, clinicians must carefully evaluate the patient’s condition and select the appropriate potency level for optimal results.
Application and Usage Guidelines
Proper application of topical steroids is crucial for maximizing effectiveness and minimizing potential side effects. Incorrect application can lead to inconsistent results and increased risk of complications. Adherence to the prescribed guidelines is paramount for achieving optimal outcomes.Careful attention to application techniques, frequency, and duration is essential for managing skin conditions effectively. Overuse can lead to unwanted side effects, while insufficient application may not provide adequate relief.
This section will detail the proper methods for applying topical steroids, highlighting the importance of avoiding overuse and carefully monitoring treated areas.
Proper Application Techniques
Applying topical steroids correctly is essential for their effectiveness. Using clean hands and applying the medication to the affected area as directed by your healthcare professional is crucial. Using a thin layer of medication is typically sufficient. Rubbing vigorously can be counterproductive, and excessive pressure should be avoided.
Frequency and Duration of Application
The frequency and duration of topical steroid application are determined by the specific condition and the prescribed strength of the medication. A healthcare professional will tailor a treatment plan to individual needs. The duration of treatment should be determined by the healthcare provider, as continued use beyond the prescribed period can lead to potential complications.
Avoiding Overuse and Potential Side Effects
Overuse of topical steroids can lead to a range of side effects, including skin thinning, redness, irritation, and even the development of fungal infections. These adverse reactions can often be avoided by adhering strictly to the prescribed application guidelines. It’s crucial to follow the dosage and frequency recommended by your healthcare provider.
Importance of Monitoring Treated Areas
Careful monitoring of treated areas is essential for detecting any adverse reactions or unexpected side effects. Regular observation of the treated area can help identify issues early on. Changes in skin appearance, such as increased redness, swelling, or unusual discharge, should be promptly reported to your healthcare provider.
Adherence to Prescribed Guidelines
Following the guidelines provided by your healthcare professional is essential for the successful and safe management of your skin condition. This includes understanding the prescribed strength, frequency, and duration of application. It’s critical to adhere to the instructions provided by your doctor to prevent unwanted side effects and achieve the best possible results. A healthcare provider can assess your individual needs and tailor a treatment plan that best suits your condition.
It’s crucial to contact your doctor with any concerns or questions.
Example Application Schedule (Illustrative – Consult your doctor):
| Day | Application Time | Frequency | Duration (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1-7 | Morning and Evening | Twice daily | 1 |
| Day 8-14 | Morning and Evening | Twice daily | 2 |
| Day 15-21 | Morning | Once daily | 3 |
This is a sample schedule and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Your doctor will provide a tailored treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Topical steroids, while effective for many skin conditions, can have side effects. Understanding these potential issues and the precautions to take is crucial for safe and effective use. Proper application and adherence to dosage instructions are vital in minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.Topical steroid use, despite its localized application, can sometimes lead to systemic effects or reactions in susceptible individuals.
The severity and type of side effects depend heavily on the potency of the steroid and the duration of treatment. Knowing the potential side effects and recognizing the signs of problems is essential for prompt intervention and avoiding complications.
Potential Side Effects
Topical steroids, while generally safe when used correctly, can lead to various side effects. These range from mild and temporary to more severe and persistent, and understanding these is crucial for patient management. It’s important to be aware that the risk of side effects increases with higher potency and prolonged use.
- Skin Irritation and Irritation Worsening: Burning, itching, redness, and dryness are common initial reactions. These can sometimes worsen the original skin condition, particularly if the steroid is not applied correctly or if the skin is already compromised.
- Thinning of the Skin (Atrophy): Prolonged use of potent topical steroids can lead to thinning of the skin, making it more fragile and prone to bruising. This is particularly true for prolonged or frequent use of higher potency topical steroids. This effect can be minimized by using the lowest effective potency for the shortest duration possible.
- Striae (Stretch Marks): In some cases, prolonged use of topical steroids, especially in areas prone to stretching, can lead to the formation of stretch marks.
- Perioral Dermatitis: This skin condition can occur around the mouth, appearing as redness, scaling, and sometimes small bumps. This is more likely with potent topical steroids.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of hair follicles can be caused by topical steroids, especially in individuals with pre-existing skin conditions.
Risk Factors for Adverse Reactions
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing adverse reactions to topical steroids. Understanding these risk factors can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans and monitor patients more closely.
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: Individuals with sensitive skin or pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, may be more susceptible to side effects.
- Dosage and Duration of Treatment: Higher potency steroids used for longer durations increase the risk of side effects.
- Areas of Application: Applying topical steroids to large areas or delicate areas, such as the face or genitals, may increase the risk of certain side effects.
- Individual Patient Factors: Genetic predispositions or other underlying health conditions may influence an individual’s response to topical steroids.
Importance of Discontinuing Use
If any adverse reactions occur during topical steroid treatment, it’s essential to discontinue use immediately and seek medical advice. This is crucial to prevent worsening of the skin condition and potential long-term complications.
Frequency of Side Effects by Potency Level
The frequency of side effects varies depending on the potency of the topical steroid. Lower potency steroids generally cause fewer side effects compared to higher potency ones.
| Potency Level | Likelihood of Side Effects | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Generally Low | Hydrocortisone 1% |
| Medium | Moderate | Triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% |
| High | Higher | Fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% |
Precautions
Adhering to prescribed guidelines and taking precautions can significantly reduce the risk of side effects.
- Proper Application Technique: Applying the medication precisely as prescribed and avoiding overuse is critical.
- Duration of Treatment: Limiting the duration of treatment to the minimum effective period is essential to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Monitoring for Side Effects: Regularly monitoring the treated area for any signs of irritation or unusual reactions is crucial.
- Seeking Medical Advice: Consulting a healthcare professional if any side effects arise is essential.
Interactions with Other Medications
Topical steroids, while generally safe, can interact with other medications you might be taking. Understanding these interactions is crucial for preventing unexpected outcomes and ensuring the optimal effectiveness of your treatment. This section will detail potential interactions, emphasizing the importance of open communication with your healthcare provider.
Importance of Informing Healthcare Professionals
Thorough communication about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, is essential when using topical steroids. Your doctor or pharmacist needs this complete picture to assess potential interactions and adjust your treatment plan if necessary. Failing to disclose all medications could lead to unforeseen reactions or reduced effectiveness of the topical steroid. This comprehensive approach ensures personalized care and avoids potential complications.
Topical steroid strengths can be surprisingly helpful for various skin conditions, but it’s important to understand their potential side effects. One crucial aspect of overall health, often overlooked, is preventing osteoporosis, which can be greatly influenced by lifestyle choices. Learning how to prevent osteoporosis, like incorporating weight-bearing exercises and a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, can significantly improve your bone health.
Ultimately, choosing the right topical steroid strength requires careful consideration, weighing the benefits against potential risks, just as a proactive approach to bone health, like exploring how to prevent osteoporosis , is essential for a healthier life.
Interactions with Other Topical Treatments
Topical steroids can interact with other topical medications applied to the same area. For example, applying a topical steroid directly over a topical antibiotic cream could potentially alter the absorption rate of either medication. This can affect the effectiveness of both treatments. Careful consideration of the timing and sequence of topical applications is crucial. It is important to consult your healthcare provider about any potential interactions between topical treatments.
How Medications Might Alter Topical Steroid Effectiveness
Certain medications can influence the effectiveness of topical steroids. For instance, some medications may increase or decrease the absorption of the topical steroid, affecting its potency. Similarly, some medications may interfere with the steroid’s ability to reach its target cells, reducing its effectiveness. Therefore, it’s vital to discuss all medications you’re taking with your doctor. This information will help them tailor the topical steroid regimen for optimal results.
Table of Potential Interactions, Steroids topical steroid strengths
| Topical Steroid | Interacting Medication | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | Topical antifungal agents | Possible alteration in the effectiveness of either medication. |
| Betamethasone | Topical retinoids | May increase the risk of skin irritation or dryness. |
| Triamcinolone | Topical antibiotics | Possible interaction that could affect the absorption or effectiveness of both medications. |
| Fluticasone propionate | Oral corticosteroids | Potential for increased side effects or reduced effectiveness of either medication. |
| Any topical steroid | Sunscreen (containing certain ingredients) | Possible interaction that may affect the absorption of the steroid or the effectiveness of the sunscreen. |
Note: This table is not exhaustive and should not be used as a definitive guide. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Special Considerations for Specific Skin Conditions: Steroids Topical Steroid Strengths
Topical steroids are a valuable treatment option for a wide range of skin conditions, but the appropriate strength and application method can vary significantly depending on the specific issue. Choosing the right steroid for the job is crucial to maximize efficacy and minimize potential side effects. This section delves into the nuanced considerations for different skin conditions, including variations in treatment for children and the elderly.Understanding the unique characteristics of each skin condition is paramount to selecting the optimal topical steroid.
Factors like the severity, location, and type of inflammation need careful consideration. Furthermore, potential interactions with other medications and pre-existing medical conditions must be taken into account.
Varying Strengths Based on Skin Condition
Different skin conditions exhibit varying degrees of inflammation and require different levels of steroid potency. A mild skin condition might respond well to a weaker steroid, while a more severe condition may necessitate a stronger preparation. The selection process should always be guided by a healthcare professional.
- Contact Dermatitis: This common condition, often triggered by allergens or irritants, usually responds well to lower-strength topical steroids. Mild to moderate cases often see improvement with hydrocortisone 1% or 2.5%. More severe cases may require stronger steroids, like triamcinolone acetonide 0.1%, under medical supervision.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild dryness to severe inflammation. The selection of topical steroid strength depends on the severity of the eczema flare-up. Mild cases might benefit from low-potency hydrocortisone, while moderate to severe cases might need higher-potency steroids, but always under the guidance of a dermatologist.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is characterized by red, scaly patches. Topical steroids can help manage the inflammation and scaling associated with psoriasis. However, the choice of strength often depends on the severity and location of the affected areas. Mild to moderate psoriasis might respond well to lower-potency steroids, while more extensive or severe cases may require higher-potency options, but should be carefully monitored for potential side effects.
Topical Steroid Use in Children and the Elderly
Special considerations are needed when prescribing topical steroids to children and the elderly. Children’s skin is generally thinner and more sensitive, and the elderly may have decreased skin barrier function. Therefore, lower-potency steroids are often preferred for children and individuals with sensitive skin. The elderly may also require a shorter duration of treatment.
- Children: The skin of children is more delicate and prone to thinning. Consequently, lower-potency topical steroids are typically used to minimize potential side effects like skin atrophy or striae (stretch marks). The treatment duration should be as short as possible, and the application area limited.
- Elderly: Elderly individuals may have decreased skin barrier function, making them more susceptible to side effects from topical steroids. Low-potency steroids and shorter treatment durations are often preferred to mitigate these risks. Regular monitoring of the treated area is critical to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Specific Precautions for Certain Skin Conditions
Certain skin conditions may require specific precautions when using topical steroids. For example, conditions with a history of infection or those that are located in areas with potential for increased absorption need extra attention. Strict adherence to the prescribed application guidelines is crucial in these situations.
- Skin Infections: Topical steroids should not be used as a primary treatment for skin infections. If a skin infection is suspected, the appropriate antibiotic or antifungal medication should be used in conjunction with or instead of topical steroids.
- Facial Applications: Topical steroids applied to the face may be associated with a higher risk of skin thinning. Therefore, lower-potency steroids are generally preferred for facial applications.
- Intertriginous Areas: Areas of skin folds (intertriginous areas) can trap moisture, which may increase the risk of skin infections. Higher-potency steroids are generally avoided in these areas.
Examples of Skin Conditions Treated with Topical Steroids
Topical steroids are commonly used to treat various skin conditions. These include but are not limited to:
- Contact dermatitis
- Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Dermatitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Allergic reactions
Table of Topical Steroid Strengths for Different Skin Conditions
| Skin Condition | Typical Topical Steroid Strength | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Contact Dermatitis | Hydrocortisone 1% | Avoid higher-potency steroids unless advised by a doctor. |
| Moderate Eczema | Triamcinolone acetonide 0.1% | Consider other treatment options if symptoms persist. |
| Severe Psoriasis | Clobetasol propionate 0.05% | Use only under the guidance of a dermatologist. |
| Facial Dermatitis | Hydrocortisone 1% or lower | Use for a shorter duration to minimize skin thinning. |
Patient Education and Counseling
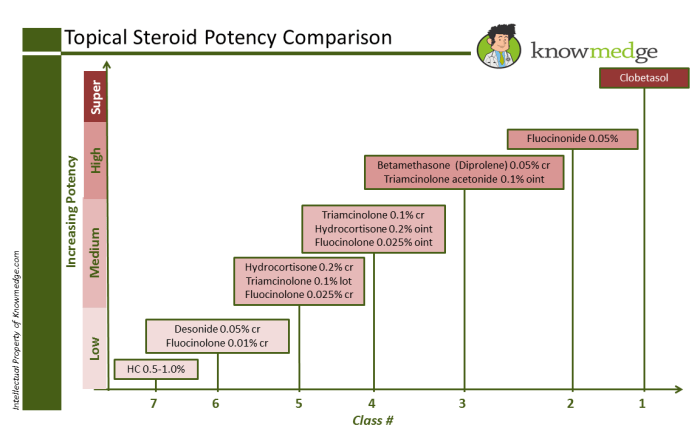
Topical steroids are powerful medications that, when used correctly, can effectively treat various skin conditions. However, improper use can lead to adverse effects. Thorough patient education is crucial to ensure safe and effective treatment. A well-informed patient is more likely to adhere to the prescribed regimen and achieve optimal outcomes.Clear and concise communication about the medication’s benefits, risks, and proper application techniques is paramount.
This empowers patients to actively participate in their care and fosters a collaborative relationship with their healthcare provider.
Guidelines for Educating Patients
Effective patient education should cover all aspects of topical steroid use, from application methods to potential side effects. A comprehensive approach that anticipates potential questions and concerns is key to successful patient management. Patients should be informed about the medication’s purpose, how to use it, and what to expect during treatment.
- Understanding the Condition: Explain the specific skin condition being treated and how topical steroids work to alleviate symptoms. Highlight the importance of addressing the underlying cause, if possible, along with the topical steroid’s role in symptom management.
- Proper Application Techniques: Demonstrate the correct method of applying the medication, emphasizing the importance of precise dosage and consistent application. This includes avoiding overuse, which can lead to thinning of the skin. Visual aids, such as diagrams or videos, can be highly effective in reinforcing instructions.
- Frequency and Duration of Use: Clearly Artikel the recommended frequency and duration of treatment, emphasizing the importance of following the prescribed regimen and not exceeding the recommended duration. Patients should understand that discontinuation should be gradual under the supervision of a healthcare provider to avoid rebound effects.
- Potential Side Effects: Discuss common and rare potential side effects, such as skin irritation, redness, or thinning. Explain how to recognize these side effects and when to contact the healthcare provider. Emphasize the importance of reporting any unusual symptoms immediately.
- Avoiding Overuse and Areas to Avoid: Educate patients about the potential for skin thinning and other adverse effects from prolonged or excessive use. Explain which areas of the body should not be treated with topical steroids (e.g., eyes, mucous membranes) and why. Examples include the face, especially around the eyes, and the groin area.
Importance of Clear Communication
Providing clear and concise information is essential for patient comprehension and adherence. Patients should feel comfortable asking questions and expressing concerns without fear of judgment. Active listening and empathetic communication are crucial components of effective patient counseling. The goal is to foster a collaborative relationship where patients feel empowered to manage their skin condition effectively.
- Active Listening and Questioning: Encourage patients to ask questions and actively listen to their concerns. Create a safe space for open dialogue and address any misconceptions or anxieties they may have.
- Use of Plain Language: Avoid medical jargon and use simple, understandable language to explain complex information. Use analogies or examples to clarify concepts. Consider using visual aids to further enhance understanding.
- Follow-up Appointments: Schedule regular follow-up appointments to monitor treatment progress and address any emerging concerns. This allows for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed, based on individual responses.
Role of the Healthcare Provider
The healthcare provider plays a vital role in guiding patients through the complexities of topical steroid use. They are responsible for providing comprehensive information, addressing concerns, and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
| Responsibility | Action |
|---|---|
| Patient Education | Providing clear and concise instructions on application, frequency, and duration of use. |
| Monitoring for Adverse Effects | Encouraging patients to report any adverse reactions and adjusting treatment plans accordingly. |
| Addressing Concerns | Creating a supportive environment for open communication and addressing patient anxieties. |
| Ensuring Adherence | Providing clear instructions and reminders for medication adherence. |
Helping Patients Understand Risks and Benefits
Presenting the potential risks and benefits of topical steroid use in a balanced way is crucial for informed decision-making. A frank discussion about potential side effects, along with their likelihood and severity, is essential. This allows patients to weigh the benefits against the risks and make choices that align with their individual needs and preferences.
“A balanced discussion of risks and benefits empowers patients to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care.”
End of Discussion
In conclusion, choosing the correct topical steroid strength is paramount for effective and safe treatment. This detailed exploration of strengths, potencies, applications, and potential side effects equips you with the knowledge to navigate this complex area of dermatological care. Remember, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and optimal results.