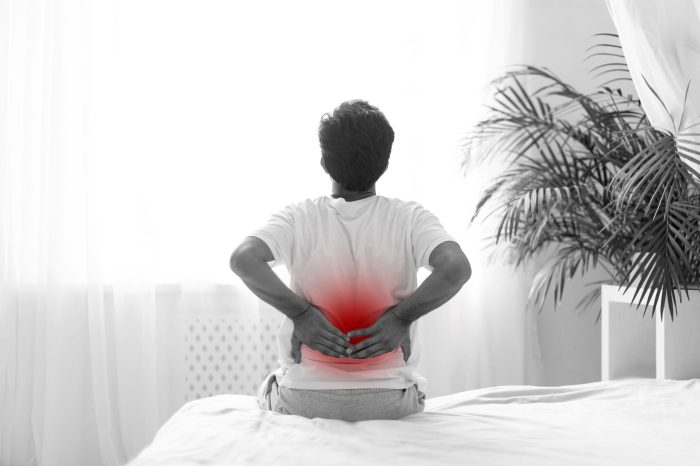
When back pain is serious, it’s crucial to understand the potential indicators and know when to seek immediate medical attention. This comprehensive guide delves into the various symptoms, underlying conditions, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options associated with serious back pain. We’ll explore the nuances between acute and chronic pain, red flag symptoms, and the importance of timely medical intervention.
Identifying the source of the pain is key, as different conditions can manifest in similar ways. From spinal stenosis and herniated discs to fractures and infections, this guide will help you navigate the complexities of serious back pain, empowering you to make informed decisions about your health.
Identifying Serious Back Pain

Knowing when back pain warrants immediate medical attention is crucial. Ignoring persistent or worsening symptoms can lead to delayed diagnosis and potentially more serious complications. This guide helps you recognize the warning signs of serious back pain, differentiating it from common, manageable discomfort.Understanding the nuances between acute and chronic back pain, along with the role of pain location and radiation, empowers you to make informed decisions about your health.
By examining potential causes and correlating symptoms with severity levels, you can better assess the urgency of your situation and seek appropriate medical care.
Symptoms Suggesting Serious Back Pain
Recognizing the symptoms that signal a need for immediate medical intervention is paramount for swift diagnosis and treatment. Severe or persistent back pain, accompanied by certain other symptoms, could indicate a more serious underlying condition.
- Sudden, intense pain that significantly limits movement or daily activities.
- Pain radiating down one or both legs, often accompanied by numbness or tingling.
- Pain that worsens with rest or at night, especially if it’s not relieved by over-the-counter pain medications.
- Unexplained fever or chills associated with back pain.
- Inability to control bowel or bladder function.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs, feet, or buttocks.
- Significant weight loss without explanation.
Acute vs. Chronic Back Pain
Differentiating between acute and chronic back pain is vital for determining the appropriate course of action. Acute pain typically develops suddenly and resolves within a few weeks, while chronic pain persists for longer than three months.
- Acute back pain often results from injuries like muscle strains or sprains. The pain is usually intense but temporary, typically subsiding within a few weeks with appropriate care. The severity of acute pain can vary significantly depending on the cause and the individual’s response.
- Chronic back pain is more persistent and may not have a clear, single cause. It can result from various conditions, including degenerative disc disease, arthritis, or spinal stenosis. The pain may fluctuate in intensity but often remains present for an extended period. Severity indicators in chronic pain often include a reduced quality of life and impact on daily functioning.
Pain Location and Radiation
The location of back pain and whether it radiates to other areas can provide valuable clues about the potential cause. Pain in specific regions may indicate involvement of particular structures or nerves.
- Pain localized to the lower back may suggest muscle strains, ligament sprains, or lumbar disc problems. Pain radiating down one leg might indicate a herniated disc or sciatica.
- Pain in the upper back might indicate issues with the thoracic spine, ribs, or muscles, potentially related to posture or trauma. Thoracic pain radiating to the arm might suggest nerve compression.
Comparison of Back Pain Symptoms
This table helps to categorize common back pain symptoms based on potential severity. Severity is a subjective measure and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice.
| Symptom | Potential Severity Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sharp, stabbing pain | Potentially serious | Suggests nerve involvement or inflammation. |
| Dull, aching pain | May or may not be serious | Often associated with muscle strains or general discomfort. |
| Numbness | Potentially serious | Indicates nerve damage or compression. |
| Tingling | Potentially serious | Often accompanies nerve damage or compression. |
| Weakness | Potentially serious | Indicates nerve damage or muscle weakness. |
Potential Causes of Serious Back Pain
Various medical conditions and injuries can lead to serious back pain. Accurate diagnosis requires careful evaluation by a healthcare professional.
| Potential Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Herniated or ruptured disc | A condition where the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges or ruptures, pressing on nearby nerves. |
| Spinal stenosis | Narrowing of the spinal canal, potentially compressing nerves and causing pain. |
| Spondylolisthesis | A condition where one vertebra slips forward over another, potentially causing nerve impingement. |
| Cauda equina syndrome | A serious neurological emergency involving compression of the nerves at the end of the spinal cord. |
| Infections (e.g., spinal osteomyelitis) | Bacterial or fungal infections that can affect the vertebrae and surrounding tissues. |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Knowing when to seek immediate medical attention for back pain is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring prompt treatment. Ignoring serious symptoms can delay diagnosis and treatment, potentially leading to long-term problems. This section Artikels situations where immediate medical attention is vital and provides examples of red flag symptoms.While most back pain resolves on its own, certain symptoms necessitate urgent medical care.
These “red flags” often signal underlying conditions requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding these red flags empowers individuals to recognize when immediate medical attention is necessary.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Recognizing red flag symptoms is essential for prompt medical intervention. These symptoms often indicate serious underlying conditions that necessitate immediate medical evaluation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.
- Sudden, severe, or unrelenting back pain, particularly if accompanied by other symptoms.
- Pain that worsens at night or with rest.
- Pain radiating down one or both legs, often with numbness or weakness.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Pain accompanied by fever or chills.
- Recent injury or trauma to the back, especially if the pain is severe.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Pain associated with significant muscle weakness or numbness in the legs or buttocks.
- Recent infection or weakened immune system.
Detailed Explanation of Red Flags
Red flags associated with serious back pain often signal underlying conditions requiring immediate medical attention. Careful assessment of these red flags can help determine the severity of the situation and guide appropriate medical interventions.
- Neurological Deficits: Symptoms like numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of bowel or bladder control in the legs or feet often indicate nerve compression or damage. These require immediate evaluation to prevent permanent nerve damage.
- Fever and Chills: Fever and chills can accompany infections or inflammatory conditions affecting the spine or surrounding tissues. This warrants immediate medical attention to identify and treat the underlying cause.
- Recent Injury or Trauma: Severe back pain following a fall, accident, or other traumatic event demands immediate medical evaluation. Such injuries may involve fractures, dislocations, or other serious structural damage.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss associated with back pain may indicate underlying cancer or other serious medical conditions. This warrants prompt investigation to identify the cause.
Assessing the Severity of Back Pain
Assessing the severity of back pain involves a structured approach. This process helps determine whether immediate medical attention is necessary.
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
|---|---|
| Sudden, severe pain | Potential fracture, disc herniation, or other serious injury |
| Pain radiating down the leg | Possible nerve root impingement |
| Loss of bladder or bowel control | Urgent need for medical evaluation; possible cauda equina syndrome |
| Fever and chills | Possible infection or inflammatory condition |
| Unexplained weight loss | Potential for underlying cancer or other serious condition |
Flowchart for Decision-Making
A flowchart outlining the decision-making process for seeking immediate medical care for back pain is provided below. This visual guide aids in determining the appropriate course of action.
A flowchart depicting a decision-making process for back pain, including red flag symptoms, potential diagnoses, and recommendations for seeking immediate medical attention, is essential. This tool aids in guiding individuals through the process of evaluating the severity of their back pain and determining the appropriate course of action.
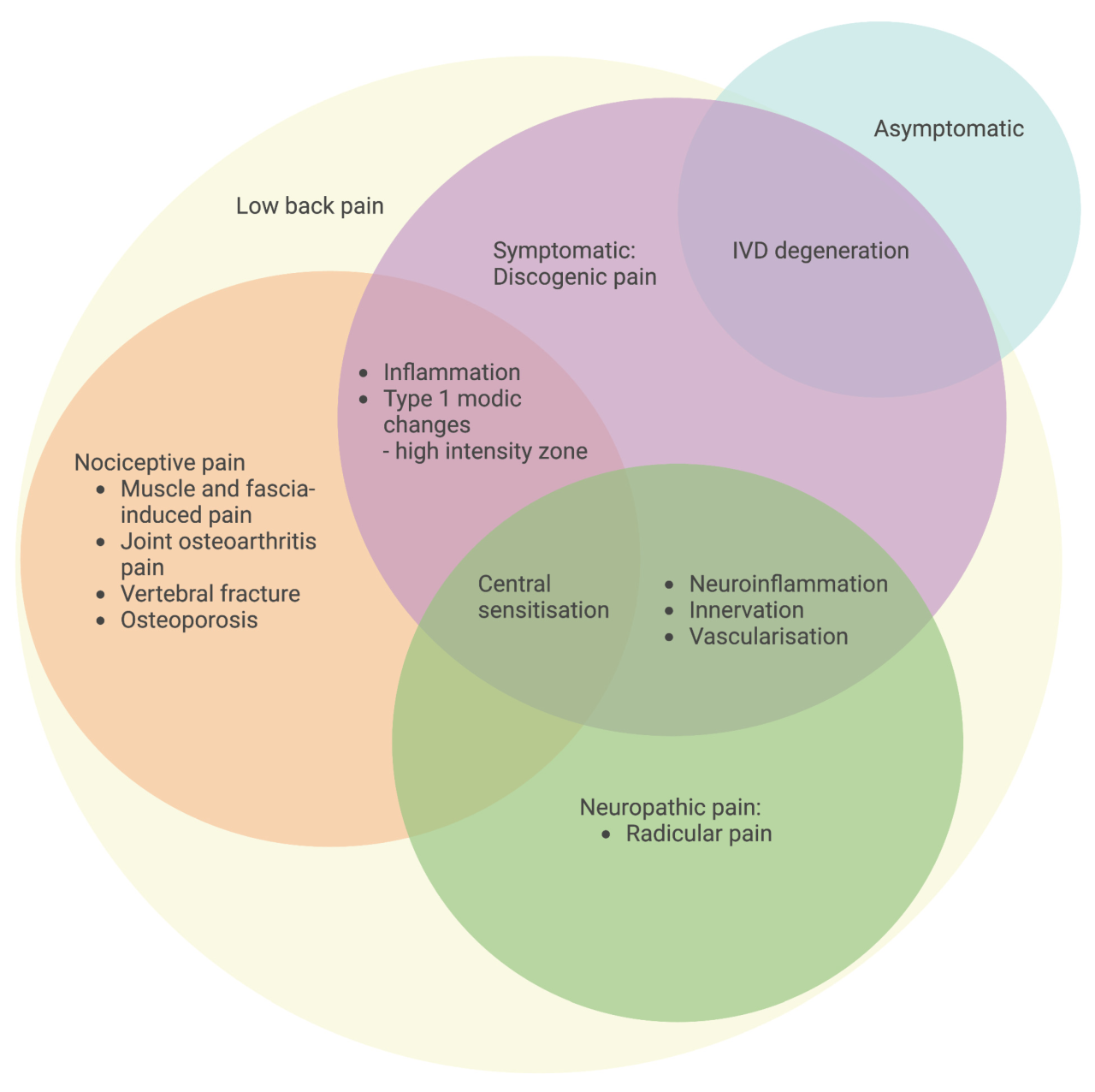
Understanding Underlying Conditions
Serious back pain can stem from various underlying medical conditions, requiring careful diagnosis and treatment. Pinpointing the specific cause is crucial for effective management and preventing potential complications. A thorough understanding of these conditions empowers individuals to seek appropriate medical attention promptly.Many conditions can mimic back pain, making accurate diagnosis challenging. A healthcare professional will consider a patient’s medical history, physical examination findings, and potentially diagnostic imaging to determine the root cause.
This approach ensures a precise identification of the underlying issue and guides the most suitable course of action.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis involves narrowing of the spinal canal, which houses the spinal cord and nerves. This narrowing can put pressure on the nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs. Symptoms often worsen with activity and improve with rest. Patients may experience pain radiating down the legs, a feeling of heaviness or weakness in the legs, and numbness or tingling.
So, when is back pain truly serious? Beyond the usual aches and stiffness, it’s important to know when to seek medical attention. Sometimes, a combination of medications can be helpful in managing the pain. For example, exploring different types of combination pills, like those found on this site types of combination pills , could offer a tailored approach.
Ultimately, though, it’s crucial to remember that only a doctor can properly diagnose the cause and recommend the right course of action for severe back pain.
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans to visualize the spinal canal and identify the extent of the narrowing.
Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges or ruptures, pressing on nearby nerves. This can cause sharp, shooting pain that radiates down the leg or buttock. Other symptoms include numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness in the affected area. The pain is often exacerbated by movements like bending, twisting, or lifting.
Diagnostic imaging, such as MRI scans, is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and evaluating the extent of the herniation.
Fractures
Fractures, especially of the vertebrae, can cause severe back pain. The pain is often sudden and intense, especially after a fall or a traumatic injury. Associated symptoms may include bruising, swelling, and tenderness around the affected area. X-rays are often the initial diagnostic test to identify the fracture and its location. CT scans or MRIs may be needed for a more detailed assessment of the fracture and surrounding structures.
Other Potential Causes
- Infections: Infections of the spine (discitis, osteomyelitis) can cause severe, persistent back pain, often accompanied by fever, chills, and malaise. Blood tests and imaging studies, such as MRI, are used to diagnose infections.
- Tumors: Tumors, both benign and malignant, can develop in the spine or nearby structures, causing pain, especially if they are growing in size. Symptoms may vary, and they may be gradual. Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, along with blood tests, can help detect tumors.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Inflammatory conditions like ankylosing spondylitis can cause chronic back pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the spine. Diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, blood tests, and imaging studies like MRI, can aid in the diagnosis. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential to evaluate the severity and characteristics of the symptoms.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
Understanding the cause of serious back pain often requires specialized diagnostic tests. These procedures help healthcare providers pinpoint the underlying issue, whether it’s a muscle strain, a herniated disc, or a more serious condition. Accurate diagnosis allows for the most appropriate and effective treatment plan.Diagnostic tests provide crucial information about the structure and function of the spine and surrounding tissues.
They help rule out various possibilities and guide treatment decisions. The choice of test depends on the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the suspected cause of the pain.
X-rays
X-rays are a fundamental imaging technique for evaluating the skeletal structure of the spine. They reveal the alignment of the vertebrae, identifying potential fractures, dislocations, or other bony abnormalities.The procedure involves positioning the patient on a table while an X-ray machine takes images of the spine from different angles. Patients are usually asked to remain still during the procedure to ensure clear images.
Preparation for an X-ray typically involves removing any metal objects that might interfere with the images.Medical professionals interpret X-rays to assess the overall integrity of the spine’s structure. An example of an X-ray interpretation might involve identifying a compression fracture in a vertebra, which could be a result of osteoporosis or trauma.
CT Scans
Computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the spine and surrounding tissues. CT scans offer a more comprehensive view than X-rays, revealing soft tissue structures like ligaments and muscles, as well as bone detail.The procedure involves lying on a table that slides into a CT scanner. The machine rotates around the patient, taking multiple X-ray images.
The images are then processed by a computer to create detailed cross-sectional views. No special preparation is generally needed, except for removing any metal objects.Medical professionals interpret CT scans to assess for various abnormalities, such as tumors, herniated discs, or bone density loss. A CT scan may reveal a spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal that can compress nerves and cause pain.
MRIs, When back pain is serious
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides detailed images of the soft tissues within the spine, including the spinal cord, nerves, ligaments, and discs. MRIs are particularly useful for identifying soft tissue injuries, herniated discs, and other conditions that might not be visible on X-rays or CT scans.The procedure involves lying on a table that slides into a large, donut-shaped MRI machine.
The machine uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images. Patients are often asked to lie still for extended periods during the scan. Some patients might need to use earplugs or headphones to reduce noise.Medical professionals interpret MRI scans to assess the condition of the soft tissues in the spine. A herniated disc, a common cause of back pain, can be clearly visualized on an MRI.
Nerve Conduction Studies
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) evaluate the function of the nerves that control the muscles in the spine. These studies are helpful for identifying nerve damage or compression, which can contribute to pain.The procedure involves placing electrodes on the skin along the path of the nerves. Small electrical impulses are sent through the nerves, and the electrical activity is measured.
No special preparation is typically needed, except for avoiding lotions or creams that might affect the electrodes.Medical professionals interpret NCS results to evaluate the speed and strength of nerve impulses. A slowed or diminished response could indicate nerve damage or compression, potentially due to conditions like sciatica or nerve root impingement.
Diagnostic Tests for Serious Back Pain
| Diagnostic Test | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|
| X-rays | Assessing bone alignment, fractures, and dislocations |
| CT Scans | Detailed visualization of soft tissues and bones, identifying tumors, herniated discs, spinal stenosis |
| MRIs | Detailed visualization of soft tissues, identifying herniated discs, spinal cord compression, ligament tears |
| Nerve Conduction Studies | Evaluating nerve function, identifying nerve damage or compression |
Treatment Options for Serious Back Pain

Navigating serious back pain can feel overwhelming. The right treatment approach is crucial for managing pain, restoring function, and improving quality of life. Understanding the various options, their potential benefits and risks, and the role of conservative therapies is essential for making informed decisions.Effective management of serious back pain often involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining different treatment modalities.
This can include medications, physical therapy, and potentially, surgical intervention. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause of the pain, its severity, and the individual’s overall health.
Medications
Medications play a significant role in managing the pain and inflammation associated with serious back pain. They can be crucial for achieving pain relief and improving function, allowing for participation in other treatment modalities. However, it’s essential to remember that medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and naproxen are often used for pain relief and reducing inflammation. These can be effective for mild to moderate pain, but long-term use requires careful monitoring for potential side effects.
- Opioids, such as codeine and morphine, are sometimes prescribed for severe pain, but they carry a risk of addiction and other side effects. Their use is often limited to short-term management, and careful monitoring is critical.
- Muscle relaxants can help to alleviate muscle spasms, which can contribute to back pain. They are typically used in combination with other treatments and for a limited duration.
- Corticosteroids, like prednisone, can be injected directly into the affected area to reduce inflammation. This can provide significant relief, but long-term use should be avoided due to potential side effects.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a vital component of managing serious back pain. It focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected area. A tailored physical therapy program can help improve posture, reduce pain, and enhance overall function.
Back pain can be a real drag, but when it’s severe, it’s time to see a doctor. Sometimes, soothing remedies like an oatmeal bath for diaper rash, oatmeal bath for diaper rash , can offer surprising relief for various skin irritations. But when the back pain is persistent or accompanied by other symptoms, don’t hesitate to prioritize your health and seek professional medical advice.
- Exercises designed to strengthen core muscles, improve posture, and increase flexibility are crucial components of physical therapy.
- Manual therapy techniques, like massage and spinal manipulation, can help to alleviate muscle tension and improve joint mobility.
- Education on proper body mechanics and ergonomics is vital for preventing future episodes of back pain. This helps patients understand how to move and position themselves to avoid injury.
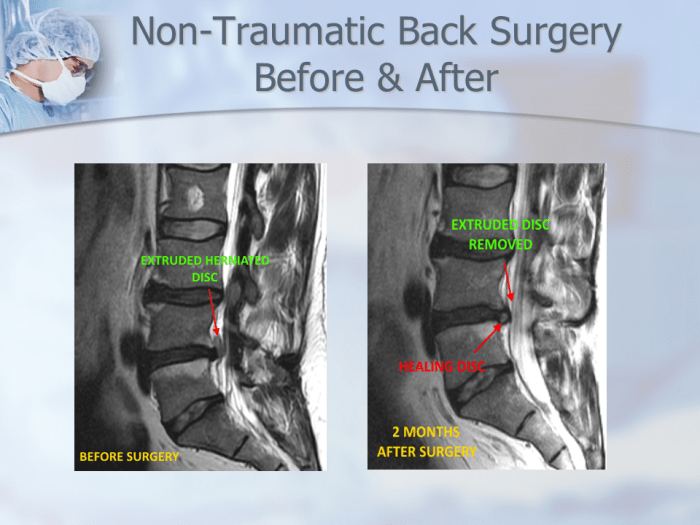
Surgery
Surgical intervention may be necessary in cases of serious back pain where conservative treatments have proven ineffective. Surgical procedures aim to address the underlying cause of the pain, such as spinal stenosis or herniated discs.
- Laminectomy: This procedure removes part of the lamina, the bony arch of the vertebra, to create more space for the spinal cord or nerves.
- Discectomy: This involves removing a damaged or herniated disc to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Spinal fusion: This procedure joins two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine and reduce pain.
Conservative Therapies
Conservative therapies, which avoid surgery, are often the initial approach to managing serious back pain. These therapies aim to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent further injury.
- Heat and cold therapy can provide temporary pain relief.
- Rest and activity modification can help reduce stress on the affected area.
- Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular exercise, are crucial for long-term pain management.
Specialists Involved
Several specialists may be involved in the treatment of serious back pain, depending on the specific condition.
- Orthopedic surgeons specialize in musculoskeletal conditions and may perform surgical procedures.
- Neurologists diagnose and treat conditions affecting the nervous system.
- Physical therapists focus on restoring function and mobility.
- Pain management specialists provide comprehensive pain relief strategies.
Treatment Approach Comparison
| Treatment Approach | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Medications | Fast pain relief, potentially effective for inflammation | Potential side effects, may not address the underlying cause |
| Physical Therapy | Improved function, restores strength and flexibility, addresses underlying issues | Can be time-consuming, requires patient commitment |
| Surgery | Potential for complete resolution of pain, fixes the underlying problem | Risk of complications, significant recovery time |
| Conservative Therapies | Less invasive, generally safer, often first-line approach | May not provide complete pain relief, effectiveness varies |
Managing and Preventing Recurrence
Taking proactive steps to manage and prevent serious back pain episodes is crucial for long-term well-being. A comprehensive approach that addresses lifestyle factors, physical conditioning, and mental well-being is essential to minimize the risk of future episodes. Understanding the triggers and contributing factors specific to your situation allows for tailored strategies to prevent future pain.Preventing serious back pain involves a multi-faceted approach that goes beyond just pain relief.
It necessitates understanding the root causes of your back pain and actively working to mitigate those factors. This proactive strategy fosters a healthier and more resilient spine, leading to improved quality of life.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting healthier habits significantly reduces the risk of back pain recurrence. These modifications encompass a wide range of lifestyle choices that contribute to overall well-being, including diet, exercise, posture, and stress management.
Experiencing persistent back pain that’s interfering with daily life? That’s a definite sign it’s time to seek professional help. While a handful of walnuts every day for health benefits like better blood flow and joint support handful of walnuts every day for health might seem like a good approach, it’s crucial to remember that this is just one piece of the puzzle.
Ignoring serious back pain can lead to long-term complications, so don’t hesitate to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Dietary Changes: Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the necessary nutrients for strong bones and healthy tissues. Limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive caffeine can further reduce the risk of inflammation and contribute to overall health. For example, individuals with a history of back pain might find that a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health and reduces the risk of fractures.
- Regular Exercise: Consistent physical activity strengthens core muscles, improves flexibility, and promotes better posture. Examples include swimming, walking, yoga, and Pilates. Building core strength is particularly important in preventing back pain, as it supports the spine and reduces stress on the lower back. A daily 30-minute walk can help strengthen the body, improving posture and flexibility, which can reduce the risk of future back pain.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts extra stress on the spine, increasing the risk of back pain. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is crucial in preventing and managing back pain. For instance, losing even a moderate amount of weight can significantly lessen the load on the spine, reducing pain and improving overall function.
Posture and Lifting Techniques
Correct posture and proper lifting techniques are vital in preventing back pain. Poor posture can strain the back muscles and lead to long-term issues.
- Maintaining Good Posture: Good posture involves keeping the spine aligned, shoulders back, and core engaged. This can be practiced throughout the day, from sitting at a desk to standing in line. For example, when sitting, ensuring that the back is supported against the chair and feet are flat on the floor can prevent unnecessary strain on the spine.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Lifting heavy objects incorrectly can cause severe back pain. Using proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees, keeping the back straight, and lifting with your legs, is crucial to prevent injury. For instance, when lifting a heavy box, one should bend at the knees, keeping the back straight and using the leg muscles for lifting.
Stress Management and Relaxation
Chronic stress can contribute to muscle tension and back pain. Implementing stress-reducing techniques can significantly improve overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of back pain episodes.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and promote relaxation. Stress reduction techniques help to relax muscles and improve circulation. For instance, mindfulness practices can calm the nervous system, reducing muscle tension and improving overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep allows the body to repair and recover, reducing muscle tension and pain. Adequate sleep helps to reduce inflammation and promote tissue repair, which can contribute to a healthier spine and lower back pain.
Illustrative Cases and Examples
Understanding serious back pain involves more than just symptoms; it’s crucial to grasp the diverse scenarios and how they manifest. Each case is unique, highlighting the complexities of spinal conditions. Learning from real-life examples helps us better appreciate the importance of prompt medical attention and tailored treatment plans.
Case Study 1: A Young Athlete with Acute Back Pain
A 22-year-old collegiate basketball player experienced sudden, severe back pain after a particularly forceful jump. The pain radiated down his left leg, accompanied by numbness and tingling. Initial physical examination revealed limited spinal mobility and muscle spasms. Diagnostic imaging (MRI) showed a herniated disc at L4-L5. Treatment included physical therapy focusing on core strengthening and pain management with medication.
A gradual return to sports activities, under strict medical supervision, was successfully achieved.
Case Study 2: A Middle-Aged Woman with Chronic Back Pain
A 45-year-old office worker experienced chronic back pain for over a year. The pain, described as a dull ache, worsened with prolonged sitting and stress. Her symptoms included stiffness, limited range of motion, and occasional sharp shooting pains. Extensive diagnostic testing, including X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests, ruled out fractures, tumors, and infections. Treatment focused on managing pain with medication, ergonomic adjustments at work, and mindfulness techniques.
The patient’s pain improved significantly, but periodic flare-ups continued, requiring ongoing management.
Case Study 3: An Elderly Patient with Spinal Stenosis
An 80-year-old woman presented with progressive back pain, worsened by walking. She also reported numbness and weakness in her legs. Her symptoms were consistent with spinal stenosis, a narrowing of the spinal canal. Diagnostic imaging confirmed the diagnosis, and she was prescribed physical therapy, medication, and in some cases, surgery. Treatment focused on alleviating symptoms and maintaining mobility.
Hypothetical Case: Mr. Johnson’s Experience
Mr. Johnson, a 50-year-old construction worker, woke up with a sudden, sharp pain in his lower back. The pain intensified with movement and was accompanied by a burning sensation radiating down his right leg. He found it difficult to stand straight and experienced numbness in his toes. He sought immediate medical attention.
Initial assessments revealed muscle spasms and limited range of motion. X-rays ruled out fractures. MRI confirmed a herniated disc at L5-S1. Treatment involved pain medication, physical therapy, and eventually, a minimally invasive surgical procedure to decompress the nerve. He recovered gradually, regaining full function within several months.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Case Study | Patient Profile | Symptoms | Diagnosis | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Young Athlete | Sudden, severe back pain, radiating leg pain, numbness | Herniated disc | Physical therapy, medication |
| Case 2 | Middle-Aged Woman | Chronic, dull back pain, worsened by sitting | Likely musculoskeletal issues | Medication, ergonomics, mindfulness |
| Case 3 | Elderly Woman | Progressive back pain, worsened by walking, leg numbness | Spinal stenosis | Physical therapy, medication, possible surgery |
Final Wrap-Up: When Back Pain Is Serious
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of serious back pain and understanding when immediate medical attention is necessary is vital for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment. This guide has provided a framework for understanding the various aspects of serious back pain, from identifying symptoms to navigating diagnostic procedures and treatment options. Remember, seeking professional medical advice is crucial in managing back pain effectively.
By arming yourself with knowledge, you can take proactive steps towards a healthier back.