Feeling of something stuck in throat can be incredibly uncomfortable and worrisome. This blog post dives deep into the possible causes, from everyday irritants to more serious medical conditions. We’ll explore potential triggers, diagnostic considerations, management strategies, and preventive measures to help you understand this common issue.
From anxiety to specific foods, a variety of factors can contribute to the sensation of a foreign object lodged in your throat. We’ll also cover the importance of accurate self-assessment and when to seek immediate medical attention. This comprehensive guide aims to provide clarity and practical advice to help navigate this often frustrating experience.
Possible Causes
A persistent feeling of something stuck in the throat, medically known as globus sensation, can be a distressing experience. While often benign, it can sometimes signal an underlying medical condition. Understanding the potential causes, both organic and non-organic, is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.This feeling is not just a bothersome sensation; it can significantly impact daily life, leading to anxiety and discomfort.
That feeling of something being stuck in your throat can be seriously uncomfortable, right? Sometimes, it’s just a minor irritation, but other times it could be a sign of something more. Learning about medications like Bentyl dicyclomine can be really helpful in understanding potential causes. For example, if you’re experiencing this and suspect it might be related to your gut, what you need to know about bentyl dicyclomine could provide valuable information about how this medication might help.
In the end, if this feeling persists, it’s always a good idea to chat with your doctor to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Careful consideration of the accompanying symptoms, frequency, and potential triggers can aid in determining the root cause and appropriate intervention.
Organic Causes
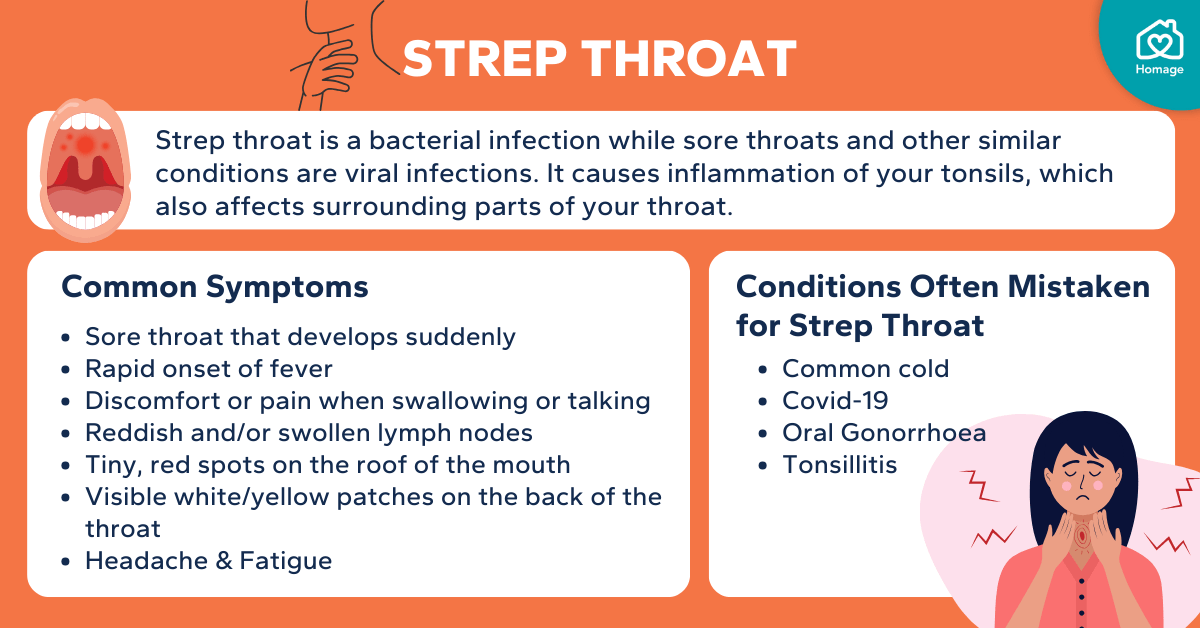
Various medical conditions can cause a feeling of something stuck in the throat. These conditions involve physical abnormalities or issues within the throat and esophagus. Examples include acid reflux, esophageal spasms, tumors (benign or malignant), thyroid problems, and even certain neurological disorders. Understanding the underlying pathology is essential for targeted treatment.
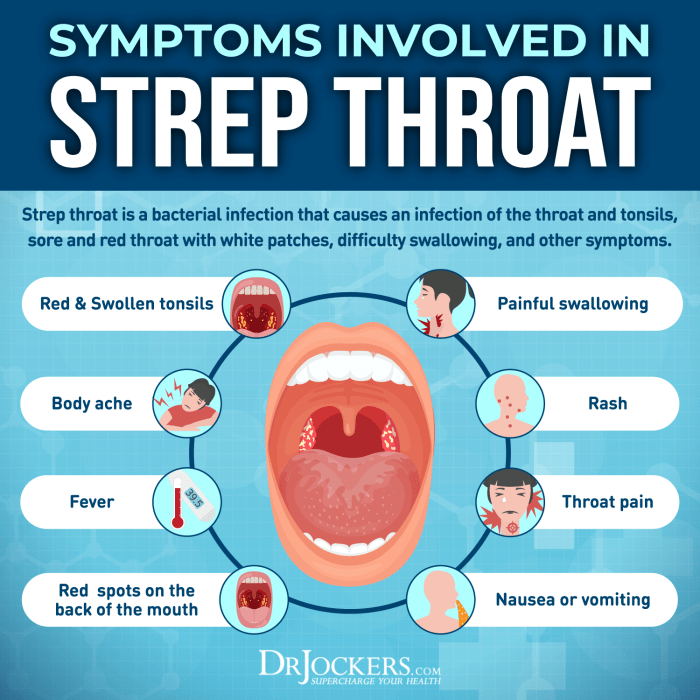
- Acid Reflux: Frequent backwash of stomach acid into the esophagus can irritate the lining, causing a feeling of fullness or a lump in the throat. This is often accompanied by heartburn and indigestion. Long-term acid reflux can lead to esophageal damage.
- Esophageal Spasms: Uncoordinated contractions of the esophageal muscles can cause intermittent, painful episodes of a stuck sensation. These spasms can be triggered by various factors and can mimic other esophageal conditions.
- Tumors: Benign or malignant growths within the throat or esophagus can create a feeling of obstruction. Symptoms often vary depending on the size and location of the tumor.
- Thyroid Problems: Enlarged thyroid glands, or thyroid disorders, can exert pressure on the esophagus, leading to a feeling of something caught in the throat.
- Neurological Disorders: Some neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, can affect the nerves controlling swallowing, leading to the sensation of something stuck in the throat.
Non-Organic Causes
Anxiety and stress are significant contributors to the globus sensation. Psychological factors can trigger or exacerbate the feeling of something stuck in the throat, even in the absence of a physical cause. Chronic stress, worry, and anxiety can induce muscle tension in the throat, which might manifest as a lump or a foreign body sensation. Furthermore, the mind-body connection is powerful, and psychological distress can lead to physical symptoms.
- Anxiety and Stress: Anxiety disorders, generalized stress, or stressful life events can lead to muscle tension in the throat and a feeling of a lump. This is a common psychosomatic response to emotional distress. In these cases, the sensation often correlates with emotional states.
- Specific Foods: Certain foods, such as spicy or acidic foods, can trigger a feeling of something stuck in the throat. Dehydration can also lead to similar symptoms.
- Environmental Factors: Dry air, irritants, and allergens can inflame the throat, causing irritation and the sensation of a lump.
- Medications: Some medications, such as those for high blood pressure or certain antihistamines, can cause side effects including a feeling of something stuck in the throat.
Symptom Comparison
| Symptom | Description (Mild) | Description (Severe) |
|---|---|---|
| Discomfort | Mild, occasional, temporary | Persistent, severe, and prolonged |
| Pain | Minor, occasional | Intense, sharp, or burning pain |
| Difficulty Swallowing | Slight or intermittent | Severe, frequent, and complete obstruction |
| Sensation of Lump | Occasional feeling | Persistent and noticeable feeling |
Comparison of Medical Causes
| Cause | Symptom 1 | Symptom 2 | Symptom 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Reflux | Heartburn | Indigestion | Burning sensation in chest |
| Esophageal Spasms | Intermittent globus sensation | Sharp, episodic pain | Difficulty swallowing |
| Tumors | Persistent globus sensation | Difficulty swallowing | Possible weight loss |
Diagnostic Considerations
A persistent feeling of something stuck in your throat can be unsettling, and proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Understanding the factors a doctor considers, the tests they might use, and how to effectively communicate your symptoms are key steps in getting the care you need. This section will delve into the diagnostic process, highlighting the importance of a thorough medical history and clear communication.The diagnostic approach to a sore throat or feeling of something stuck in the throat hinges on a careful evaluation of the patient’s complete medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings.
This multi-faceted approach helps rule out various possible causes, from simple irritations to more serious conditions.
Crucial Factors in Diagnosis
A comprehensive medical history is paramount. This includes details about the duration, frequency, and characteristics of the sensation, any associated symptoms (like fever, difficulty swallowing, pain, or changes in voice), and any recent illnesses, medical conditions, or medications. Past medical history, particularly any prior episodes of similar sensations, allergies, or exposure to potential irritants, is also valuable.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
A variety of tests and procedures might be employed to determine the cause of the persistent feeling of something stuck in the throat. These can range from straightforward examinations to more complex investigations.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination is usually the first step. This involves checking the throat and surrounding areas for any visible abnormalities, such as inflammation, swelling, or lesions. The doctor will also assess the patient’s overall health and look for any signs of other conditions that could be contributing to the problem.
- Endoscopy: An endoscopy, which uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera, can visualize the throat, esophagus, and upper digestive tract. This procedure allows the doctor to identify any structural issues or abnormalities that might be causing the sensation. Examples include finding a tumor or foreign object lodged in the throat.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, may be necessary to rule out certain causes, like tumors or blockages. They provide detailed images of the affected areas, assisting in the diagnosis.
- Blood Tests: In some cases, blood tests may be conducted to detect underlying infections or other medical conditions that could be contributing to the symptoms. These tests can provide valuable insights into the patient’s overall health.
- Swallowing Studies: These studies, also known as videofluoroscopy, examine the way the patient swallows. This can help determine if there are any issues with the muscles involved in swallowing or any structural abnormalities in the esophagus.
Importance of a Thorough Medical History
A complete medical history is essential in guiding the diagnostic process. It provides context for the symptoms, helping to narrow down the possible causes and prioritize investigations. For instance, a history of recent surgery or a known esophageal stricture can significantly influence the diagnostic approach.
Effective Communication with Medical Professionals
Accurate description of the sensation is critical for effective diagnosis. Patients should describe the location, intensity, duration, and frequency of the feeling. Using descriptive language like “a persistent scratchy feeling” or “a lump in my throat” can help the doctor understand the nature of the problem. Important details to convey include the onset of the sensation, any triggers, and any associated symptoms.
Diagnostic Tools Table
| Diagnostic Tool | Purpose | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual inspection of the throat and surrounding areas. | The doctor examines the throat, mouth, and neck for any visible abnormalities. |
| Endoscopy | Visual examination of the throat, esophagus, and upper digestive tract. | A thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth or nose to visualize the relevant areas. |
| Imaging Tests (X-rays, CT scans) | Detailed visualization of the affected area. | X-rays or CT scans provide images of the throat, esophagus, and surrounding structures. |
| Blood Tests | Detection of underlying infections or medical conditions. | Blood samples are collected and analyzed in a laboratory. |
| Swallowing Studies (Videofluoroscopy) | Evaluation of swallowing function. | The patient swallows a liquid or food while being monitored by X-ray. |
Management and Treatment
The feeling of something stuck in the throat, while often distressing, is frequently manageable. Understanding the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment. Approaches range from simple lifestyle modifications to, in some cases, more involved medical interventions. The key is to address the root problem and alleviate the discomfort.
That feeling of something lodged in your throat can be seriously uncomfortable, right? Sometimes, it’s not just a bit of food or a weird sensation, but could be a symptom of something more. Myofascial pain syndrome, a condition where muscle pain and stiffness can cause a variety of symptoms, including those that mimic a foreign object in the throat, could be the culprit.
If you’re struggling with this persistent feeling, learning more about what is myofascial pain syndrome might help you understand the potential causes and explore treatment options. It’s definitely worth considering!
Common Management Approaches
Various strategies can help alleviate the feeling of something stuck in the throat. These range from simple home remedies to more involved medical interventions, depending on the suspected cause. A critical aspect of management is identifying and addressing the specific cause, as this dictates the most appropriate course of action.
- Dietary Modifications: Adjusting the types and textures of food consumed can be a significant factor in reducing the sensation. Avoiding overly dry, hard, or rough foods can help prevent further irritation. Also, ensuring proper hydration by drinking plenty of fluids is often helpful.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises or mindfulness, can play a crucial role in reducing throat irritation. Smoking cessation and avoiding environmental irritants, if applicable, are also essential steps. Poor posture can also exacerbate throat issues; maintaining good posture throughout the day can make a positive difference.
- Over-the-counter Medications: For mild cases, over-the-counter pain relievers and throat lozenges can help reduce discomfort and inflammation. These can provide temporary relief and are often effective for conditions like minor throat irritation or inflammation.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, more extensive medical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the sensation of something stuck in the throat. The specific intervention will depend on the identified diagnosis.
- Medications: Depending on the diagnosis, prescription medications may be necessary. For example, if acid reflux is the culprit, proton pump inhibitors can help neutralize stomach acid. If a bacterial infection is the cause, antibiotics might be prescribed. These medications are typically prescribed by a physician based on the diagnosed condition.
- Therapy: In cases of chronic or recurring throat issues, therapy can be valuable. Speech therapy, for instance, may be recommended to address issues like dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) or vocal cord dysfunction. This is particularly relevant for patients with conditions that affect their ability to swallow properly.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgical interventions are typically reserved for more severe cases or when other treatments have proven ineffective. Conditions like tumors or structural abnormalities may require surgical intervention to correct the problem. The decision to pursue surgery is always made in consultation with a medical professional.
Comparison of Treatment Options
The most effective treatment approach varies significantly depending on the underlying cause of the sensation of something stuck in the throat. For example, dietary modifications are usually sufficient for mild irritation, while acid reflux may require medication. A thorough diagnosis is essential to determine the most appropriate and effective treatment strategy.
That feeling of something being stuck in my throat is so frustrating, isn’t it? It’s often a symptom of various things, and sometimes it can be linked to low levels of serotonin, which can manifest in a multitude of ways. For more information on what low serotonin feels like, check out this helpful resource: what does low serotonin feel like.
Even though it might not be the direct cause, it’s worth considering if you’re experiencing this persistent throat discomfort, as it can be a contributing factor to this uneasy sensation. And, yes, it’s still that annoying feeling of something stuck in my throat!
Treatment Summary Table
| Treatment | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary Modifications | Often effective for mild cases | Minimal, if any |
| Lifestyle Adjustments | Can significantly reduce symptoms | Usually minimal, if any |
| Over-the-counter Medications | Provides temporary relief | Possible mild side effects, such as stomach upset |
| Prescription Medications | Effective for specific conditions (e.g., acid reflux) | Potential side effects vary by medication |
| Surgical Procedures | Highly effective for structural issues | Potentially significant side effects |
Preventive Measures
The feeling of something stuck in your throat can be incredibly frustrating and uncomfortable. While sometimes unavoidable, taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the likelihood of experiencing this sensation. Understanding the potential triggers and adopting preventative measures can contribute to overall well-being.Preventive measures are crucial in managing the recurrence of a feeling of something stuck in the throat.
A proactive approach can minimize the risk of discomfort and potential complications. These strategies are designed to address dietary choices, oral hygiene, and environmental factors that may contribute to this issue.
Dietary Recommendations
Proper dietary habits play a pivotal role in preventing the sensation of something stuck in the throat. A balanced diet, rich in fiber and water, promotes healthy digestion and prevents the formation of food particles that can get lodged in the throat.
- Increase fiber intake:
- Fiber-rich foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, help maintain a healthy digestive tract. This aids in preventing food particles from becoming lodged in the throat during or after eating.
- Stay hydrated:
- Drinking plenty of water helps soften food and aids in its smooth passage through the digestive system. Water also helps lubricate the throat, further reducing the risk of food getting lodged.
- Avoid overly dry or hard foods:
- Dry, hard, or chewy foods can be more likely to get stuck in the throat. Opt for softer, more easily digestible foods.
- Consume smaller meals:
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals can improve digestion and reduce the chance of food getting lodged in the throat. This allows for better chewing and swallowing.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall health and can also play a role in preventing the feeling of something stuck in the throat.
- Regular brushing and flossing:
- Regular brushing and flossing removes food particles and plaque buildup that can contribute to irritation and inflammation in the throat.
- Proper tongue cleaning:
- Tongue cleaning helps remove bacteria and debris that can cause inflammation in the mouth and throat, potentially leading to discomfort.
- Visiting the dentist regularly:
- Regular dental checkups and cleanings can identify and address potential oral issues that might contribute to the feeling of something stuck in the throat.
Environmental Factors
Certain environmental factors can influence the likelihood of experiencing a feeling of something stuck in the throat. Recognizing and mitigating these factors can be helpful.
- Dry air:
- Dry air can lead to throat dryness, making it more susceptible to irritation and the sensation of something stuck. Using a humidifier can help maintain appropriate moisture levels.
- Exposure to irritants:
- Exposure to smoke, dust, or other irritants can irritate the throat, leading to discomfort and the sensation of something stuck. Minimizing exposure to these irritants can be helpful.
- Certain medications:
- Some medications can cause dryness in the mouth and throat, increasing the risk of discomfort. Discussing potential side effects with a healthcare professional can help mitigate this risk.
Preventive Actions
Taking specific actions can help avoid the feeling of something stuck in the throat.
- Chew food thoroughly:
- Thorough chewing breaks down food into smaller particles, making it easier to swallow and reducing the risk of it getting lodged.
- Avoid talking while eating:
- Focusing on eating and not talking can prevent food particles from being inhaled or swallowed improperly, potentially leading to the sensation of something stuck.
- Be mindful of posture:
- Maintaining proper posture while eating can facilitate smooth swallowing. Avoiding hunching or leaning can help.
Self-Care Strategies
Managing a persistent feeling of something stuck in your throat can be frustrating and uncomfortable. Beyond seeking medical advice, incorporating self-care techniques can significantly contribute to managing the discomfort and improving overall well-being. These strategies offer practical approaches to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.Self-care strategies complement medical interventions by providing additional avenues for symptom relief and promoting overall well-being.
They are not a substitute for professional medical advice, but rather a supportive component of a comprehensive approach to managing the issue. Implementing these techniques can provide a sense of agency and empower individuals to take proactive steps towards managing their discomfort.
Relaxation and Stress-Reduction Techniques, Feeling of something stuck in throat
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate various physical sensations, including the feeling of something stuck in the throat. Practicing relaxation and stress-reduction techniques can help alleviate these symptoms by calming the body and mind. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness meditation are examples of effective stress-reduction techniques. Regular practice of these methods can lead to a reduction in stress hormones and a sense of calm.Guided imagery, where individuals visualize calming scenes or experiences, can also be helpful.
Creating a relaxing environment at home with soft lighting and calming music can further enhance relaxation efforts.
Home Remedies for Temporary Relief
Several home remedies can provide temporary relief from the discomfort associated with a feeling of something stuck in the throat. Warm liquids, such as herbal teas, warm water with honey, or broth, can help soothe the throat and alleviate inflammation. Humidifiers can add moisture to the air, which can also help alleviate dryness and irritation. Gargle with warm salt water, a time-tested remedy for sore throats, can be helpful in reducing inflammation and soothing the affected area.
Avoid harsh or acidic foods that may further irritate the throat.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Over-the-counter medications can provide symptomatic relief from various conditions that can cause the feeling of something stuck in the throat. Analgesics, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and discomfort. Cough suppressants may be helpful if a cough is contributing to the sensation. Lozenges and throat sprays containing local anesthetics can provide temporary numbing and soothing effects.
Always follow the dosage instructions carefully, and consult with a pharmacist if you have any concerns.
Comparison of Self-Care and Medical Interventions
| Self-Care Method | Description | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep Breathing Exercises | Controlled breathing techniques to reduce stress and anxiety. | Can reduce anxiety, promote relaxation, and potentially alleviate discomfort. | May not be effective for all individuals or conditions. Requires practice and consistency. |
| Warm Liquids | Consuming warm beverages to soothe the throat. | Can provide temporary relief from irritation and inflammation. | May not address underlying causes. |
| Over-the-Counter Medications | Use of pain relievers or cough suppressants. | Can provide temporary pain relief and symptom reduction. | May have side effects, and may not address the underlying cause. Consult with a pharmacist. |
| Medical Intervention (e.g., antibiotics, steroids) | Prescription medications to address specific medical conditions. | Effective in treating infections or inflammation. | May have more significant side effects than over-the-counter remedies. Requires a doctor’s diagnosis and prescription. |
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Feeling Of Something Stuck In Throat
A persistent feeling of something stuck in your throat can be uncomfortable and concerning. While often manageable with self-care and home remedies, certain situations demand immediate medical attention. Recognizing the warning signs and understanding when to seek emergency care is crucial for ensuring prompt and effective treatment.
Critical Symptoms Requiring Immediate Medical Intervention
Knowing when to seek immediate medical help is vital for preventing potentially serious complications. A variety of symptoms, when present alongside the feeling of something stuck, necessitate urgent medical attention. These situations warrant immediate action.
Possible Emergency Situations
Certain circumstances warrant immediate medical intervention. These scenarios can be life-threatening and require swift action. The presence of these symptoms, combined with the feeling of something stuck, indicates a serious condition that needs immediate attention.
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath: If you experience significant difficulty breathing, or if you feel like you can’t get enough air, this is a serious emergency requiring immediate medical help. This could be due to swelling in the airway or a blockage that is rapidly compromising breathing. A sudden onset of severe breathing difficulties warrants immediate action.
- Severe or persistent pain in the throat or neck: Unbearable pain that radiates from the throat to the neck, or that is associated with difficulty swallowing, requires prompt medical evaluation. This could signal an infection, an abscess, or other serious conditions. Sudden, intense pain warrants urgent attention.
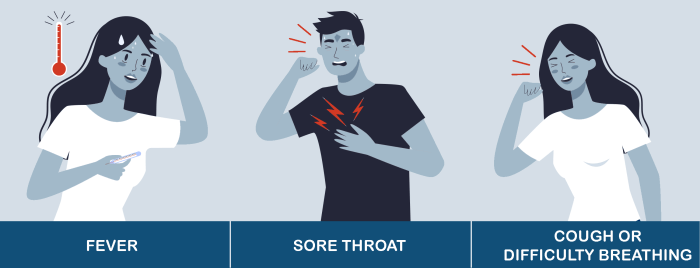
- High fever and difficulty swallowing: A high fever (above 101°F or 38.3°C) accompanied by difficulty swallowing could indicate a severe infection. The combination of these symptoms warrants immediate medical intervention to prevent complications and address the underlying cause.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus around the affected area: Significant inflammation or discharge around the throat area could signal a severe infection that requires immediate attention. These symptoms need prompt medical evaluation to prevent the spread of infection and address the underlying cause.
- Sudden onset of hoarseness or voice loss: If you experience sudden and significant hoarseness or complete loss of voice, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, immediate medical attention is needed. This could indicate a problem with the vocal cords or the airway, and requires rapid evaluation.
- Persistent drooling: If you experience excessive drooling, especially if accompanied by difficulty swallowing or other concerning symptoms, it warrants immediate medical evaluation. This could be a sign of a blockage or injury in the mouth or throat.
- Loss of consciousness or dizziness: If you experience loss of consciousness or sudden dizziness associated with the feeling of something stuck, seek immediate medical help. These symptoms could indicate a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Identifying warning signs for immediate medical intervention is essential for timely and effective treatment. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for prompt action and potentially preventing serious complications.
- Persistent or worsening symptoms: If the feeling of something stuck in your throat persists or worsens despite self-care measures, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Prolonged discomfort necessitates professional evaluation to identify and address the underlying cause.
- Symptoms that disrupt daily activities: If the symptoms significantly interfere with your daily activities or cause significant discomfort, consult a medical professional. Persistent discomfort warrants a medical evaluation.
- Symptoms accompanied by other concerning issues: If the feeling of something stuck in your throat is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as fever, pain, or difficulty breathing, immediate medical attention is crucial. These combined symptoms warrant urgent evaluation.
- Recent trauma to the throat or neck area: If you have recently experienced trauma to the throat or neck area, seek immediate medical evaluation, even if the symptoms seem mild. The presence of trauma necessitates immediate assessment to prevent further complications.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the feeling of something stuck in your throat can stem from a range of causes, some benign and others requiring medical intervention. Understanding the potential triggers, diagnostic process, and management strategies is crucial for effective self-care. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, seeking professional medical advice is essential. This blog post has provided a detailed overview of this often-misunderstood issue, empowering you to better manage and address this common discomfort.