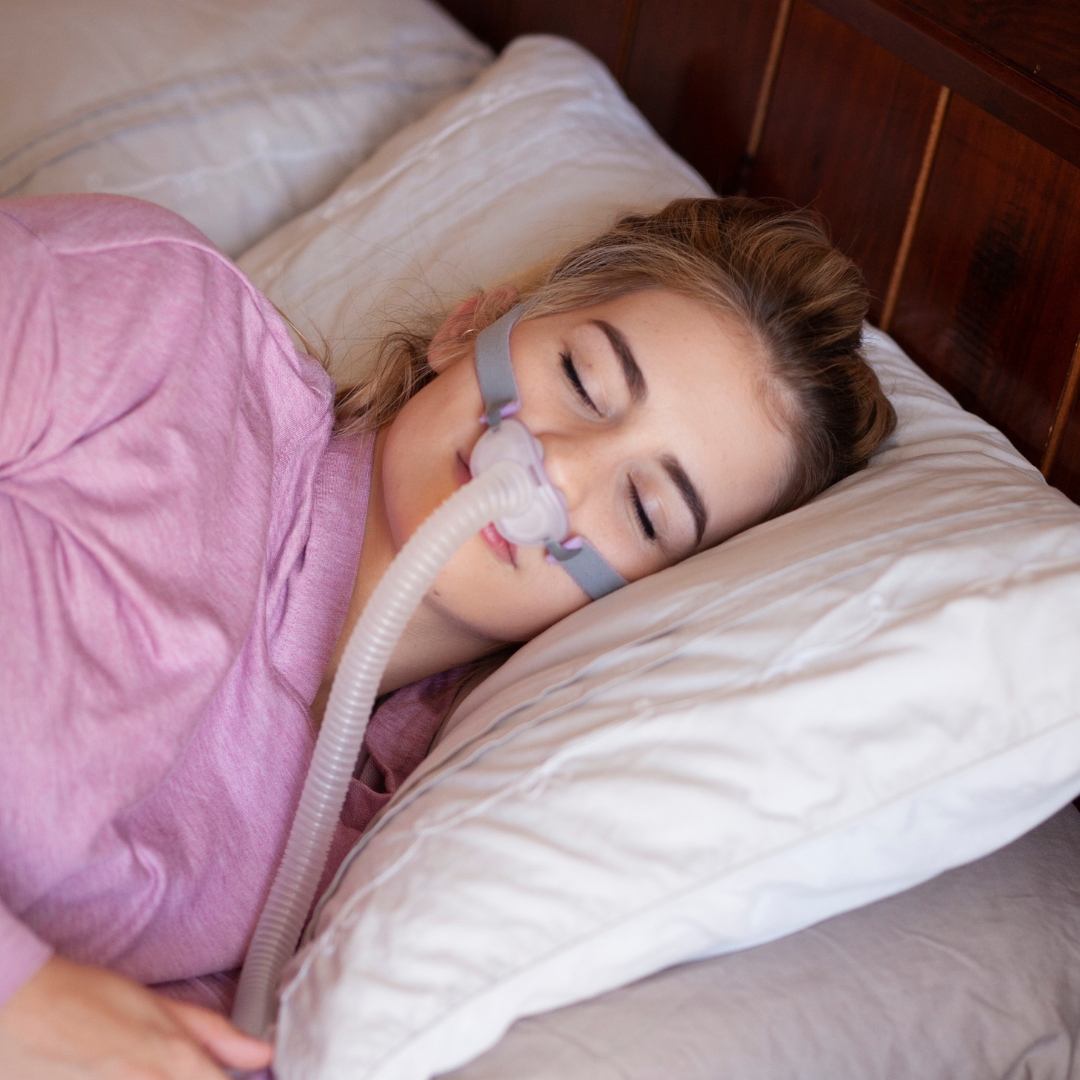
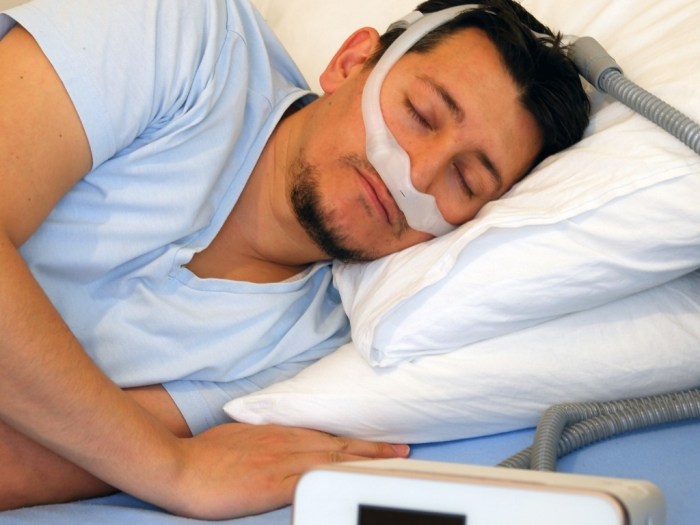
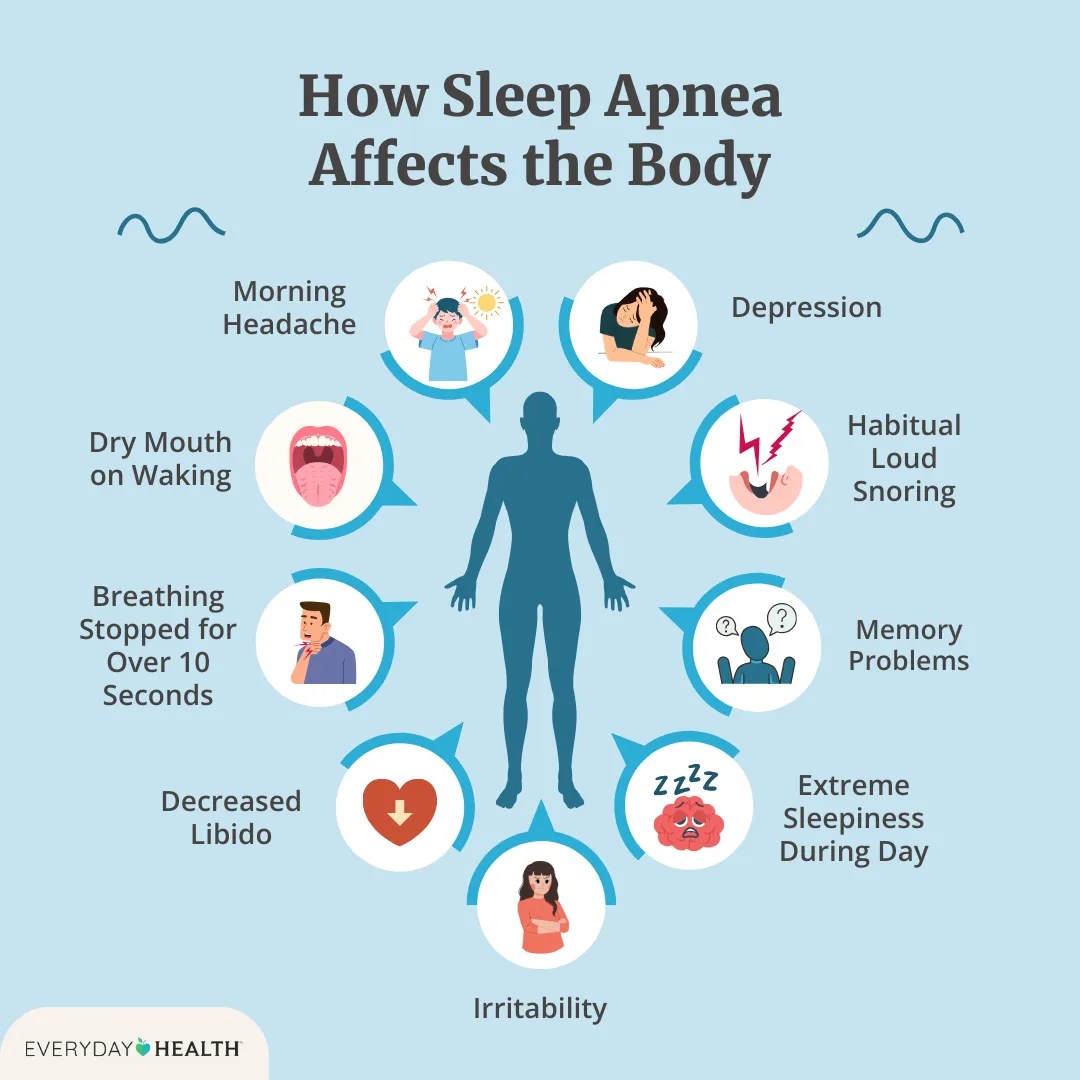
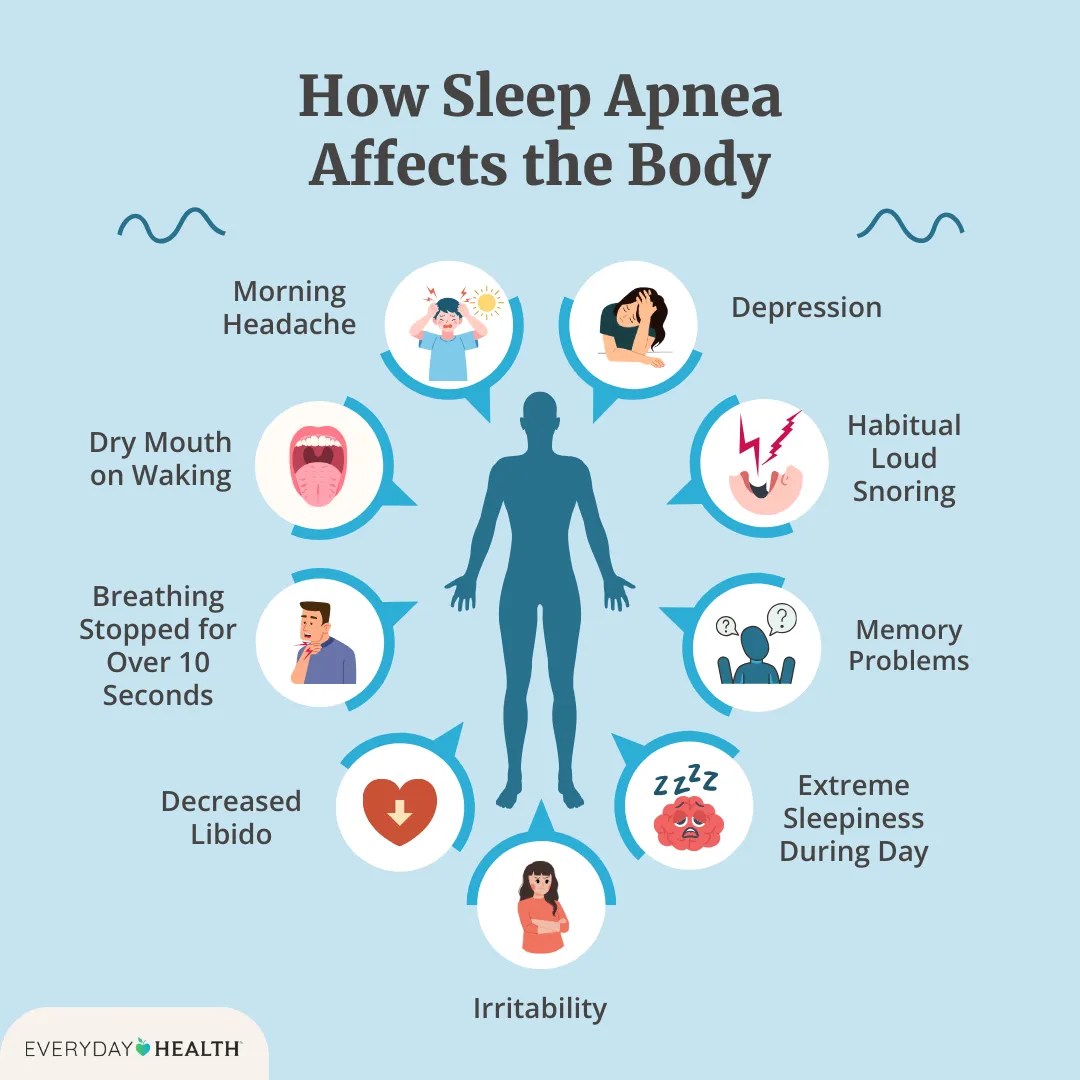
How long do you have to use CPAP? This crucial question impacts sleep apnea sufferers, impacting their overall health and quality of life. Understanding the factors that influence CPAP treatment duration is essential for informed decision-making. This exploration delves into the various aspects of CPAP therapy, from typical usage durations to the potential long-term benefits and drawbacks.
CPAP therapy aims to improve breathing during sleep, which can vary greatly in duration depending on factors like the severity of sleep apnea, individual response to treatment, and adherence to the prescribed regimen. Different phases of treatment, along with potential reasons for discontinuation, will be explored. This comprehensive guide helps users navigate the often complex world of CPAP therapy.
CPAP Usage Duration Overview
CPAP therapy, while often effective in managing sleep apnea, isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The duration of CPAP use varies significantly from person to person, influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors can help patients and healthcare providers better anticipate and manage the treatment process.CPAP treatment duration is not a fixed period. It’s a dynamic process tailored to individual needs and responses.
Factors like the severity of sleep apnea, patient adherence, and the effectiveness of the chosen CPAP settings all contribute to how long someone needs to use CPAP. Success often depends on a combination of consistent use, proper mask fitting, and adjustments to treatment parameters as needed.
Typical CPAP Usage Durations
CPAP therapy is often a long-term commitment. Many patients find that continuous use is necessary to maintain optimal health outcomes. While some might experience symptom improvement and transition to occasional use or discontinuation, others may need to continue using CPAP indefinitely. This is highly dependent on the individual and the severity of their condition. The typical duration is variable, but many studies indicate that long-term use, sometimes for years or even decades, is common for those with moderate to severe sleep apnea.
Factors Influencing CPAP Treatment Duration
Several factors play a role in determining the length of time someone needs CPAP therapy. These include:
- Severity of sleep apnea: Patients with more severe sleep apnea, characterized by lower oxygen saturation levels and higher apnea-hypopnea indices (AHI), often require longer-term CPAP use to maintain optimal health outcomes. Mild cases might resolve with lifestyle changes, while severe cases often necessitate continued use.
- Patient adherence: Consistent use of CPAP is crucial for effectiveness. Factors like mask comfort, noise levels, and overall patient motivation influence adherence. Poor adherence can lead to less effective treatment and potentially a longer treatment period.
- Response to treatment: Individual responses to CPAP vary. Some patients experience a significant improvement in symptoms after a relatively short period, while others may require a longer adjustment period. Factors such as underlying health conditions can also influence the response.
- Effectiveness of CPAP settings: Properly adjusted CPAP settings are essential. If the settings are not optimized, it may result in ineffective treatment, leading to a longer duration of use.
- Underlying health conditions: Coexisting health conditions can impact the duration and effectiveness of CPAP therapy. The presence of other medical issues might necessitate a longer treatment period.
Different Phases of CPAP Therapy
CPAP therapy can be broken down into several phases, each with its own considerations regarding duration:
- Initial Adjustment Phase: This phase focuses on establishing a comfortable routine with the CPAP machine. It typically lasts for several weeks to a few months as patients adapt to the device and associated lifestyle changes. During this time, adjustments to the mask, pressure settings, and overall comfort are crucial.
- Maintenance Phase: Once the initial adjustment phase is complete, the focus shifts to long-term maintenance. This phase emphasizes consistent use and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan. Monitoring symptoms and adjustments to settings, if needed, are essential.
- Possible Discontinuation/Adjustment Phase: Some patients might experience symptom improvement to the point where they can transition to occasional use or even discontinuation. This is dependent on the individual and the severity of their condition.
Reasons for Discontinuing CPAP Use
Discontinuation of CPAP therapy can stem from a variety of factors.
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Mask discomfort | Uncomfortable masks can lead to poor adherence, reducing treatment effectiveness and potentially leading to discontinuation. |
| Machine noise | Noisy CPAP machines can be disruptive, affecting sleep quality and motivation to use the device. |
| Pressure intolerance | High pressure settings can cause discomfort, leading to a reduction in CPAP use and effectiveness. |
| Lack of symptom improvement | Insufficient symptom relief can cause patients to discontinue treatment, believing it is ineffective. |
| Cost or access issues | Financial constraints or limited access to CPAP devices can affect adherence. |
| Lifestyle factors | Changes in daily schedules, travel, or other lifestyle factors might impact the ability to maintain consistent CPAP use. |
CPAP Treatment Goals and Duration

CPAP therapy, or continuous positive airway pressure therapy, aims to improve sleep quality and overall health for individuals with sleep apnea. Understanding the specific goals of this treatment is crucial to comprehend the expected duration of use. A personalized approach, considering the individual’s specific needs and severity of sleep apnea, is essential.CPAP therapy’s objectives are multifaceted, focusing on restoring normal breathing patterns during sleep.
This involves increasing the pressure in the airway, preventing airway collapse, and improving oxygen saturation levels. The primary goal is to alleviate the symptoms of sleep apnea, such as snoring, gasping, and daytime sleepiness. Achieving these goals often leads to significant improvements in daytime alertness, cognitive function, and overall well-being. Furthermore, CPAP therapy can help prevent or mitigate the long-term health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea, such as cardiovascular problems, stroke, and diabetes.
The duration of treatment is therefore highly dependent on the effectiveness of achieving these objectives.
CPAP Therapy Goals and Treatment Duration Relationship
CPAP therapy’s effectiveness in achieving its goals directly impacts the duration of treatment. If the therapy effectively restores normal breathing patterns and addresses the underlying causes of sleep apnea, the treatment duration may be shorter. Conversely, if the therapy doesn’t achieve its goals, the treatment duration may be prolonged or even require adjustments to the CPAP settings. The level of adherence to the therapy is also a significant factor.
Sleep Apnea Severity and Expected Treatment Duration
The severity of sleep apnea significantly influences the anticipated duration of CPAP treatment. Generally, individuals with milder cases of sleep apnea may find that CPAP therapy is needed only for a specific period, such as during certain life stages or periods of increased risk. More severe cases, however, may necessitate ongoing CPAP use for a substantial period or even for life.
- Mild Sleep Apnea: Individuals with mild sleep apnea might experience periods of improved sleep quality and reduced symptoms after a period of consistent CPAP use. The duration of use may be shorter and possibly intermittent, such as when experiencing specific life factors that increase the risk of sleep apnea. Treatment could be used as needed to mitigate sleep apnea symptoms.
- Moderate Sleep Apnea: In moderate sleep apnea, CPAP therapy is typically necessary for a longer duration, possibly for several months or even years, to effectively address the symptoms. The therapy’s goal is to maintain a consistent, stable airway pressure. Treatment goals include improving sleep quality and mitigating long-term health risks associated with untreated moderate sleep apnea.
- Severe Sleep Apnea: Individuals with severe sleep apnea often require lifelong CPAP therapy. The therapy’s goal is to address the underlying causes of severe airway obstruction and improve sleep quality, which may be significantly compromised without consistent CPAP use. The duration is often prolonged due to the severity and potential long-term complications. Treatment may be needed indefinitely.
Adherence to CPAP Therapy and Treatment Duration
Consistent and correct use of CPAP therapy is crucial for achieving treatment goals and minimizing the duration of therapy. Adherence directly impacts how effectively CPAP therapy works and whether the desired outcomes are reached.
- High Adherence: High adherence to CPAP therapy generally leads to a faster reduction in sleep apnea symptoms and improved sleep quality. This often results in a more rapid achievement of the treatment goals and potentially a shorter duration of use. This may allow the treatment to be reduced or potentially discontinued depending on the severity and response to therapy.
- Low Adherence: Low adherence to CPAP therapy significantly hinders the achievement of treatment goals. This leads to a prolonged duration of therapy as the symptoms may not be effectively addressed, requiring adjustments to the treatment plan and potential strategies to improve adherence.
Factors Affecting CPAP Treatment Duration
CPAP therapy, while highly effective for managing sleep apnea, isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The length of time a patient needs to use CPAP can vary significantly. Understanding the factors that influence this duration is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This helps in setting realistic expectations and tailoring treatment strategies for optimal outcomes.Several factors interplay to determine how long someone needs to use CPAP.
Patient compliance, the severity of their sleep apnea, and even their age and overall health all play important roles in the duration of treatment. This comprehensive look at these factors will shed light on why some individuals may need CPAP for shorter periods, while others may require it long-term.
Patient Compliance
Patient adherence to CPAP therapy is paramount for its success. If a patient consistently uses the device as prescribed, the treatment is more likely to achieve its intended goals. Conversely, poor compliance can significantly impact the effectiveness of CPAP, potentially prolonging the treatment duration or even rendering it ineffective. This often necessitates a proactive approach from healthcare providers, involving adjustments to the device, educational sessions, and support systems to encourage consistent use.
For example, a patient who finds the CPAP mask uncomfortable or the device noisy may be less likely to use it regularly, thus requiring additional interventions to improve compliance.
Severity of Sleep Apnea
The severity of sleep apnea directly correlates with the expected duration of CPAP treatment. Individuals with mild sleep apnea might require CPAP therapy for a shorter period, perhaps just for a few months or even weeks. Conversely, those with moderate to severe sleep apnea may need CPAP therapy long-term, possibly for years or even throughout their lives. The severity is often measured by the number of apnea and hypopnea events per hour of sleep, as indicated by a sleep study.
Patients with more severe apnea events need consistent CPAP use to maintain adequate oxygen levels and respiratory function throughout their sleep.
Age
Age can influence the expected duration of CPAP therapy, although this isn’t always a definitive factor. Younger patients with sleep apnea might need CPAP for a specific period, such as during a growth spurt or a specific medical condition, and then it may no longer be required. Older individuals with chronic conditions or other health issues may require CPAP therapy for longer periods due to the increased likelihood of those conditions impacting the duration of sleep apnea treatment.
However, the duration isn’t strictly age-dependent; other factors, such as the severity of the apnea and overall health, still play a crucial role.
| Age Group | Typical Duration | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Children (ages 5-12) | Variable, often temporary | Treatment duration depends on the underlying cause of sleep apnea, such as adenoid or tonsil issues, which often resolve with age. |
| Adults (ages 18-65) | Variable, often long-term | Treatment duration depends on the severity of sleep apnea and overall health. Some may only require CPAP during certain life stages. |
| Seniors (ages 65+) | Variable, potentially long-term | Treatment duration depends on the severity of sleep apnea and co-occurring health conditions. |
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Long-Term CPAP
Living with sleep apnea can be challenging, but consistent CPAP therapy can significantly improve your quality of life. Understanding the potential long-term advantages and disadvantages of this treatment is crucial for making informed decisions. Long-term CPAP use can lead to substantial improvements in various aspects of your health, but also presents some potential drawbacks. It’s important to weigh these factors carefully, alongside other treatment options.Consistent CPAP therapy offers a powerful approach to managing sleep apnea, leading to a range of positive outcomes.
However, like any long-term treatment, it comes with potential drawbacks that need to be considered. Careful consideration of both benefits and drawbacks, along with regular follow-ups, is key to optimizing your CPAP experience.
Long-Term Benefits of Consistent CPAP Use
Consistent CPAP use can lead to a cascade of positive health improvements. Improved sleep quality is a cornerstone benefit. Reduced daytime sleepiness, a common symptom of untreated sleep apnea, is a significant advantage, leading to increased alertness and productivity. The benefits extend beyond sleep; consistent CPAP therapy often leads to improvements in cardiovascular health, lowering the risk of heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure.
Furthermore, improved cognitive function is a common outcome, attributed to better oxygenation and blood flow to the brain.
Potential Drawbacks of Long-Term CPAP Therapy
While CPAP offers numerous benefits, potential drawbacks exist. Discomfort is a common complaint, especially in the initial stages of treatment. Some individuals experience nasal dryness, congestion, or skin irritation from the mask. Mask leaks can also be a problem. The need for consistent adherence to the treatment plan can be a challenge.
This includes remembering to use the device every night and maintaining the mask and equipment. Psychological factors, such as the initial adjustment period or the perceived inconvenience, can also contribute to treatment non-adherence.
Comparison of Long-Term CPAP Effectiveness with Other Sleep Apnea Treatments
Different approaches exist for managing sleep apnea. While CPAP is often a highly effective treatment, its long-term effectiveness varies among individuals. Other treatments, such as oral appliances or surgery, might be more suitable for some patients. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the individual’s overall health, and personal preferences. The long-term effectiveness of each treatment must be assessed in conjunction with the individual’s specific needs.
Importance of Regular Follow-up Appointments for CPAP Users
Regular check-ups are crucial for CPAP users. These appointments provide an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of the therapy and address any emerging issues. Doctors can monitor sleep quality, adjust CPAP settings if needed, and identify any potential complications. This proactive approach helps ensure the long-term success and safety of CPAP therapy. Early detection of problems can prevent more serious health issues.
These check-ups can be crucial for maintaining optimal treatment and addressing potential concerns early on.
CPAP Adherence and Duration Strategies
Successfully managing CPAP therapy hinges on consistent use. Long-term adherence isn’t just about the initial purchase; it’s about ongoing comfort, support, and strategies to overcome challenges. This section details actionable steps to improve your CPAP experience and maximize treatment benefits.Effective CPAP therapy requires more than just the machine; it demands a proactive approach to ensure long-term use. This includes addressing potential discomfort, understanding available resources, and recognizing the importance of ongoing support.
Figuring out how long you need to use CPAP can be tricky, and it really depends on your individual needs. Sometimes, people with conditions like obsessive compulsive personality disorder obsessive compulsive personality disorder might find it challenging to adjust to the routine, but CPAP therapy is often a long-term commitment. Ultimately, your doctor will help you determine the best course of action and how long you need to use CPAP for optimal results.
Improving CPAP Comfort and Management
Consistent CPAP use often hinges on comfort and ease of use. Addressing discomfort proactively can significantly enhance adherence. Finding the right mask type, size, and fit is crucial. A proper mask seal prevents air leaks, which are a major source of discomfort and can lead to poor sleep quality. Experimentation with different mask types, sizes, and cushions is often necessary to find the most suitable option.
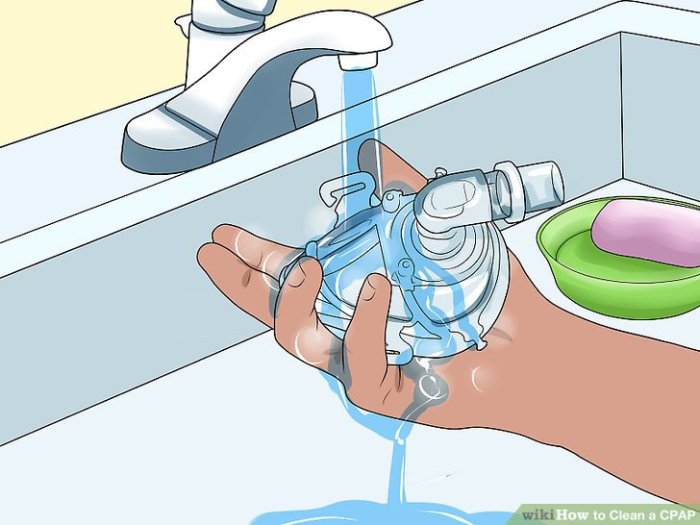
Regular mask cleaning and maintenance are essential to prevent mold growth and maintain hygiene.
Addressing Potential Side Effects
Some users experience side effects such as nasal dryness, pressure points, or headaches. These side effects, though common, can be mitigated with targeted strategies. Nasal dryness can be treated with saline nasal sprays or humidifiers. Proper mask fit and adjustments can minimize pressure points. Headaches might respond to different mask types or adjusting the pressure settings.
A healthcare professional can provide tailored recommendations based on individual needs.
CPAP Support Systems
Support groups and resources play a vital role in CPAP adherence. Connecting with others who understand the challenges of CPAP therapy can provide invaluable encouragement and practical advice. Support groups, both online and in-person, offer a platform for sharing experiences, asking questions, and receiving encouragement from peers. Dedicated CPAP clinics or sleep centers can provide personalized support, ongoing monitoring, and guidance.
Strategies for Enhancing Adherence
Sustained CPAP use relies on consistent motivation and support. Creating a routine and integrating CPAP into daily life is a critical step. Using a sleep diary can help track CPAP use, identify patterns, and address any issues that may be contributing to inconsistent use. Setting realistic goals and celebrating small victories along the way are important to maintain motivation.
Consider making CPAP use a non-negotiable part of your nightly routine.
Personalized Strategies for Long-Term Success
The key to long-term CPAP success lies in developing a personalized approach. Open communication with your healthcare provider is essential to discuss any challenges, adjust settings as needed, and address any side effects. Regular check-ups and adjustments to your treatment plan ensure that CPAP therapy continues to meet your evolving needs.
Long-Term CPAP Treatment Success Stories
Embarking on a journey to manage sleep apnea with CPAP can be a significant commitment. Long-term success stories highlight the positive impact of consistent CPAP use on overall health and well-being, demonstrating that perseverance and the right support systems are key. These narratives often reveal invaluable insights into navigating the challenges and celebrating the triumphs of this journey.Sustained CPAP use is more than just a technical solution; it’s a lifestyle adjustment.
Successful patients often develop coping mechanisms and find strategies to maintain adherence, demonstrating the crucial role of personal adaptation and support. The stories shared below offer inspiration and understanding, showcasing how CPAP can be integrated into daily life.
Success Stories: Real-Life Examples
Numerous individuals have achieved remarkable improvements in their sleep quality and overall health by consistently using CPAP therapy. These positive experiences underscore the potential benefits of CPAP and inspire those considering this treatment.
-
Sarah, a 45-year-old office worker, initially struggled with CPAP adherence. Her sleep apnea was severely impacting her daytime alertness and energy levels. With the encouragement of her doctor and a dedicated support group, Sarah slowly adjusted to the therapy. She found that using a humidifier with her CPAP mask and establishing a consistent sleep schedule greatly improved her comfort and adherence.
Within months, she experienced noticeable improvements in her energy levels and mood. She reported feeling less irritable and more focused during the day, positively impacting her work performance and personal relationships.
-
Michael, a 62-year-old retired teacher, had been diagnosed with sleep apnea several years prior. He initially struggled with the discomfort of the mask and the noise of the machine. With the help of a skilled sleep specialist who guided him on various mask types and machine settings, Michael found a combination that worked best for him. By establishing a regular sleep routine and using a white noise machine to mask the CPAP sound, Michael achieved remarkable success.
He noted significant improvements in his memory and cognitive function, leading to increased enjoyment in his hobbies and a more fulfilling retirement.
The Role of Support Systems
Sustaining CPAP therapy requires more than just the equipment; it demands a supportive network. The involvement of family, friends, and healthcare professionals plays a crucial role in encouraging consistent use and managing potential challenges.
- Family members can provide emotional support and encouragement, helping to address any anxieties or concerns associated with the therapy. They can also assist in reminding the patient about the importance of adherence.
- Healthcare professionals, including doctors, sleep specialists, and therapists, offer guidance and support. They provide adjustments to the CPAP settings, educate on proper mask usage, and address any discomfort or issues.
- Support groups provide a valuable platform for sharing experiences and receiving encouragement from others facing similar challenges. They offer a sense of community and understanding, empowering individuals to continue their CPAP journey.
Fostering a Positive Outlook
Maintaining a positive attitude and a proactive approach are crucial for long-term success with CPAP therapy. Focusing on the potential benefits and actively seeking solutions to challenges can make a significant difference in the patient’s experience.
- Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential. This ensures that any adjustments or issues are addressed promptly. Openly discussing concerns and seeking feedback can foster a positive and supportive relationship.
- Setting realistic goals and celebrating small victories along the way can help maintain motivation. Tracking progress and recognizing personal achievements reinforces the positive impact of the therapy.
- Focusing on the long-term health benefits of CPAP, such as improved sleep, energy levels, and overall well-being, can help maintain a positive outlook. Remembering the importance of this therapy for long-term health can reinforce motivation.
CPAP Use in Specific Populations

CPAP therapy, while highly effective for many, isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. The duration and approach to CPAP use can vary significantly depending on the individual’s age, overall health, and specific medical conditions. Understanding these variations is crucial for optimizing treatment outcomes and ensuring patient comfort and adherence. This section delves into how CPAP usage duration can differ across various populations.
CPAP Use in Children
Children with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) often require careful management of CPAP therapy. The duration of CPAP use in children can be influenced by the severity of their OSA, their age, and their ability to tolerate the device. Younger children may need more support and encouragement to maintain CPAP usage. There may also be specific challenges with mask fitting and comfort.
The goal in pediatric CPAP therapy is to achieve consistent and effective treatment while minimizing potential adverse effects and promoting positive long-term outcomes. For example, a child with mild OSA might only need CPAP for a few nights a week or even intermittently as needed, while a child with severe OSA might require CPAP therapy on a nightly basis for several years, or even throughout their childhood.
CPAP Use in the Elderly
Older adults may experience unique challenges with CPAP therapy. Factors like reduced tolerance for discomfort, potential underlying health conditions, and cognitive impairment can affect adherence to the treatment plan. The duration of CPAP use in the elderly often depends on the severity of their sleep apnea and their overall health status. For example, an elderly patient with mild OSA might only need intermittent CPAP use, while someone with severe OSA might require ongoing CPAP therapy.
Moreover, the mask fitting process might require adjustments to accommodate for changes in facial anatomy associated with aging.
Factors Influencing CPAP Therapy Duration for Specific Medical Conditions
The duration of CPAP therapy can vary significantly depending on the underlying medical condition. For example, individuals with chronic lung diseases, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may experience respiratory difficulties that necessitate a tailored approach to CPAP therapy. Likewise, individuals with cardiovascular conditions, such as congestive heart failure (CHF), might require careful monitoring and adjustments to CPAP settings to avoid exacerbating their existing conditions.
The severity of the sleep apnea itself also plays a critical role. Patients with more severe cases may need to use CPAP for a longer period of time to achieve and maintain symptom relief.
Impact of Comorbidities on CPAP Treatment Duration
Comorbidities, or co-occurring medical conditions, can significantly impact the duration of CPAP therapy. Conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders can influence both the effectiveness and the duration of CPAP treatment. For instance, a patient with diabetes and sleep apnea might need a longer duration of CPAP therapy to effectively manage their blood sugar levels and their sleep apnea symptoms.
The treatment plan will be adjusted to accommodate the needs of the comorbidities.
Wondering how long you’ll need to use CPAP? It really depends on your individual needs and the severity of your sleep apnea. Recent advancements in treatments like the ones detailed in what s new in mash are constantly improving outcomes. However, the duration of CPAP use often involves ongoing monitoring and adjustments by your doctor to ensure optimal results.
Comparison of CPAP Use Across Demographics, How long do you have to use cpap
The duration of CPAP use can vary across different demographics. While CPAP is effective for many, the individual’s response to the treatment may be influenced by factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. For example, research suggests that certain ethnic groups may be more susceptible to sleep apnea. In such cases, the duration of CPAP use may need to be tailored to address specific needs and challenges.
Figuring out how long you need to use CPAP can depend on a lot of factors, like the severity of your sleep apnea. Sometimes, it’s a temporary fix, and other times, it’s a long-term solution. For example, if you’re trying to figure out if you might be pregnant after missing a pill, you might find useful information on the potential consequences at can i get pregnant if i missed a pill.
Ultimately, talking to your doctor is key to determining the right course of action for your CPAP usage and your overall health.
Furthermore, access to healthcare resources and education about CPAP therapy can also affect treatment outcomes. These factors are essential to consider when developing personalized CPAP treatment plans for each individual.
Future Trends in CPAP Therapy and Duration: How Long Do You Have To Use Cpap
CPAP therapy has revolutionized the treatment of sleep apnea, significantly improving the quality of life for millions. However, ongoing research and technological advancements promise even more effective and personalized approaches in the future. This evolution is poised to impact the duration of CPAP treatment, potentially leading to shorter therapy periods and improved patient outcomes.The future of CPAP therapy is intertwined with the development of more sophisticated technologies and personalized treatment plans.
These advancements hold the potential to not only improve the efficacy of CPAP but also to enhance patient comfort and adherence, ultimately impacting the duration of therapy needed.
Potential Advancements in CPAP Technology
Ongoing research and development are focused on enhancing CPAP machines and masks. These improvements aim to address patient comfort, adherence, and the effectiveness of treatment. For instance, the development of lighter, quieter CPAP machines is expected to improve patient acceptance and long-term compliance. Similarly, more sophisticated mask designs, such as those incorporating advanced pressure adjustments or personalized fit, could increase patient comfort and reduce the incidence of leaks, both contributing factors in treatment duration.
Personalized CPAP Therapy Plans
The concept of tailoring CPAP therapy to individual needs is gaining traction. This personalized approach, leveraging data from home sleep studies and other patient-specific factors, could lead to optimized treatment plans. For example, a personalized pressure profile adjusted based on individual breathing patterns could improve treatment effectiveness and reduce the duration of therapy required.
The Impact of Home Sleep Testing
Home sleep testing (HST) has become more accessible and accurate. As a result, it plays a crucial role in diagnosing sleep apnea and guiding CPAP treatment. The increased accuracy and convenience of HST will allow for earlier and more precise diagnosis, leading to better-tailored CPAP therapy and potentially a reduced treatment duration. The availability of sophisticated data analysis tools, integrated with CPAP machines, could further refine the personalized pressure profiles and optimize the treatment plan, thereby potentially shortening the required treatment period.
Real-time feedback and adjustment options based on HST data could be a game-changer for personalized CPAP therapy.
Summary
In conclusion, the duration of CPAP use is a personalized journey, shaped by individual needs and responses. While typical durations and factors influencing treatment length are discussed, the ultimate success hinges on patient adherence and a proactive approach to ongoing management. Remember, consistent communication with your healthcare provider is key to navigating this aspect of sleep apnea care effectively.